Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
RPT - Add Math F5
Transféré par
supbarTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RPT - Add Math F5
Transféré par
supbarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
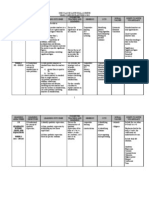
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
YEARLY PLAN 2011
SEKOLAH
SUBJECT
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
FORM
WEEK/DATE
TOPIC
1
03/01 07/01
Progressions
SUB TOPIC
1)
Understand and use
the concept of
arithmetic
progression.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
(i) Identify characteristics of
arithmetic progressions
(ii) Determine whether a given
sequence is an arithmetic
progression
(iii) Determine by using formula:
a) specific terms in arithmetic
progressions,
b) the number of terms in
arithmetic progressions
(iv) Find:
a) the sum of the first n terms of
arithmetic progressions,
b) the sum of a specific number
of consecutive terms of
arithmetic progressions,
c) the value of n, given the sum
of the first n terms of
arithmetic progressions
(v) Solve problems involving
arithmetic progressions
COMPLETED DATE
(REASON IF CANT
ACHIEVE)
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
2
10/01 14/01
3
17/01 21/01
.
Progressions
2)
Understand and use
the concept of
geometric
progression
(i)
Progressions
2.
Understand and use
the concept of
geometric
progression
(v) Find:
a) the sum to infinity of
geometric progressions,
b) the first term or common
ratio, given the sum to infinity
of geometric progressions.
(vi) Solve problems involving
geometric progressions
Identify characteristics of
geometric progressions.
(ii) Determine whether a given
sequence is a geometric
progression.
(iii) Determine by using formula:
a) specific terms in
geometric progressions,
b) the number of terms in
geometric progressions.
(iv) Find:
a) the sum of the first n terms
of geometric progressions,
b) the sum of a specific number
of consecutive terms of
geometric progressions,
c) the value of n, given the sum
of the first n terms of
geometric progressions,
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
4
24/01 28/01
Linear Law
1) Understand and use
the concept of lines of
best fit.
5
31/01 04/02
(i)
Draw lines of best fit by
inspection of given data
(ii) Write equations for lines of
best fit
(iii) Determine values of
variables from:
a) Lines of best fit,
b) Equations of lines of best fit
CHINESE NEW YEAR
6
07/02 11/02
Linear Law
2) Apply linear law to
non-linear relations
(i)
Reduce non-linear relations to
linear form.
(ii) Determine values of constants
of non-linear relations given
a) lines of best fit
b) data
(iii) Obtain information from
a) lines of best fit
b) equations of lines of best fit
7
14/02 18/02
Integration.
1) Understand and use
the concept of
integration indefinite
integral.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
Determine integrals by reversing
differentiation.
Determine integrals of ax n
where a is a constant and n is
an integer,n 1.
Determine integrals of algebraic
expressions.
Find constants of integration, c,
in indefinite integrals
Determine equations of curves
from functions of gradients
Determine by substitution the
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
integrals of expressions of the
form (ax + b) n , where a and b
are constants, n is an integer
and n -1
8
21/02 25/02
Integration
2) Understand and use
the concept of
definite integrals
i)
Find definite integrals of
algebraic expressions
(ii) Find areas under curves as the
limit of a sum of areas.
(iii) Determine areas under curves
using formula.
9
28/02 04/03
10
07/03 11/03
PK 1
2011
Integration
2) Understand and use
the concept of
definite integrals
(iv) Find volumes of revolutions
when region bounded by a curve
is rotated completely about the
a) x-axis,
b) y-axis
as the limit of a sum of
volumes.
(iii) Determine volumes of
revolutions using formula.
MID SEMESTER
HOLIDAYS
12/03 20/03
11
21/03 25/03
Vector
1) U nderstand and use
the concept of
vector .
(i)
Differentiate between vector
and scalar quantities.
(ii) Draw and label directed line
segments to represent vectors
(iii) Determine the magnitude and
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
direction of vectors represented
by directed segments
segments.
(iv) Determine whether two vectors
are equal.
(v) Multiply vectors by scalars.
(vi) Determine wether two vectors
are parallel.
12
28/03 01/04
Vector
2)
Understand and use
the concept of
addition and
subtraction of vectors
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
13
04/04 08/04
Vector
3. Understand and use
the vectors in
Cartesian Plane
(i)
Determine the resultant vector of
two parallel vectors
Determine the resultant vector of
two non-parallel vectors using:
a) triangle law,
b) parallelogram law.
Determine the resultant vector of
three or more vectors using the
polygon law
Subtract two vectors which are:
a) Parallel,
b) non-parallel.
Represent a vector as a
combination of other vectors.
Solve problems involving
addition and subtraction of
vector
Express vectors in the form:
a) xi + yj
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
b)
x
y
(ii) Determine magnitudes of vectors
(iii) Determine unit vectors in given
directions
(iv) Add two or more vectors
(v) Subtract two vectors
(vi) Multiply vectors by scalars
(vii) Perform combined operations on
vectors
(viii) Solve problems involving vectors
14
11/04 15/04
Trigonome- tric
Functions
1) Understand the
concept of positive
and negative angles
measured in degrees
and radians.
(i)
(ii)
2) Understand and use
the six trigonometric
functions of any
angle.
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
Represent in a Cartesian plane,
angles greater than 360 0 or 2
radians for:
a) positive angles,
b) negative angles
Define sine, cosine and tangent
of any angle in a Cartesian plane
Define cotangent, secant and
cosecant of any angle in a
Cartesian plane
Find values of the six
trigonometric functions of any
angle
Solve trigonometric equations
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
15
18/04 22/04
Trigonome- tric
Functions
3) Understand and use
graphs of sine,
cosine, and tangent
functions..
(i)
Draw and sketch graphs of
trigonometric functions:
a) y = c + a sin bx,
b) y = c + a cos bx,
c) y = c + a tan bx
where a, b and c are constants
and b > 0
(ii) Determine the number of
solutions to a trigonometric
equation using sketched graphs.
(iii) Solve trigonometric equations
using drawn graphs.
16
25/04 29/04
Trigonome- tric
Functions
4) Understand and use
basic identities
(i) Prove basic identities:
a) sinA + cosA = 1,
b) 1 + tanA = secA,
c) 1 + cotA = cosecA
(ii) Prove trigonometric identities
using basic identities
(iii) Solve trigonometric equations
using basic identities
17
02/05 06/05
Trigonome- tric
Functions
5) Understand and use
addition formula and
double-angle formula.
(i)
Prove trigonometric identities
using addition formula for
sin (A B), cos (A B) and
tan (A B).
(ii) Derive double-angle formula for
sin 2A, cos 2A and tan 2A.
(iii) Prove trigonometric identities
using addition formula and/or
double-angle formula.
(iv) Solve trigonometric equations
18
Permutations and
1) Understand and use
(i)
Determine the total number of
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
09/05 13/05
Combinations
the concept of
permutation.
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
19
16/05 20/05
20
23/05 27/05
Permutations and
Combinations
Probability
2) Understand and use
the concept of
combination
(i)
1) Understand and use
the concept of
probability
(i)
ways to perform successive
events using multiplication rule
Determine the number of
permutations of n different
objects
Determine the number of
permutations of n different
objects taken r at a time
Determine the number of
permutations of n different
objects for given conditions.
Determine the number of
permutations of n different
objects taken r at a time for
given conditions
Determine the number of
combinations of r objects
chosen from n different objects.
(ii) Determine the number of
combinations r objects chosen
from n different objects for given
conditions
Describe the sample space of
an experiment.
(ii) Determine the number of
outcomes of an event.
(iii) Determine the probability of an
event
(iv) Determine the probability of two
events:
a) A or B occurring,
b) A and B occurring
MID YEAR
HOLIDAYS
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
28/05 12/06
21
13/06 17/06
Probability
2) Understand and use
the concept of
probability of
mutually exclusive
events
(i)
Determine whether two events
are mutually exclusive
(ii) Determine the probability of two
or more events that are mutually
exclusive.
3) Understand and use
the concept of
probability of
independent events
(i)
Determine whether two events
are independent
(ii) Determine the probability of two
independent events.
(iii) Determine the probability of
three independent events.
22
20/06 24/06
Probabilty
Distributions
1) Understand and use
the concept of
binomial distribution
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
23
27/06 01/07
Probabilty
Distributions
2) Understand and use
the concept of
normal distribution
(i)
List all possible values of a
discrete random variable.
Determine the probability of an
event in a binomial distribution
Plot binomial distribution graphs.
Determine mean, variance and
standard deviation of a binomial
distribution
Solve problems involving
binomial distributions.
Describe continuous random
variables using set notations
(ii) Find probability of z-values for
standard normal distribution.
(iii) Convert random variable of
normal distributions, X, to
standardised variable, Z.
(iv) Represent probability of an
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
event using set notation.
(v) Determine probability of an
event
(vi) Solve problems involving
normal distributions
24
04/07 08/07
Motion Along A
Straight Line
1) Understand and use
the concept of
displacement
(i)
(ii)
2) Understand and use
the concept of
velocity.
(iii)
i)
(ii)
(iii)
25
11/07 15/07
26
18/07 22/07
Identify direction of
displacement of a particle from a
fixed point
Determine displacement of a
particle from a fixed point.
Determine the total distance
travelled by a particle over a
time interval using graphical
method.
Determine velocity function of a
particle by differentiation.
Determine instantaneous
velocity of a particle
Determine displacement of a
particle from velocity function by
integtration
PK2
2011
Motion Along A
Straight Line
3) Understand and use
the concept of
acceleration
(i)
Determine acceleration function
of a particle by differentiation
(ii) Determine instantaneous
acceleration of a particle
(iii) Determine instantaneous
velocity of a particle from
acceleration function by
integration
(iv) Determine displacement of a
particle from acceleration
function by integration
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
(v) Solve problems involving motion
along a straight line.
27
25/07 29/07
28
01/08 05/08
29 31
08/08 26/08
Linear Programming 1) Understand and use
the concept of graphs
of linear inequalities
(i)
Identify and shade the region on
the graph that satisfies a linear
inequalities
(ii) Find the linear inequality that
defines a shaded region.
(iii) Shade region on the graph that
satisfies several linear
inequalities.
(iv) Find linear inequalities that
define a shaded region.
Linear Programming 2) Understand and use
the concept of linear
Programming
(i)
Solve problems related to linear
programming by:
a) writing linear inequalities
andequations describing a
situation,
b) shading the region of feasible
solutions,
c) determining and drawing the
objective function ax + by = k
where a, b and k are constants,
d) determining graphically the
optimum value of the
objective function.
INTENSIVE REVISION OF
PAST YEAR QUESTION
RPT : ADD MATH FORM 5
32
29/08 02/09
33 35
05/09 23/09
36 43
26/09 18/11
HARI RAYA PUASA &
MID SEM
HOLIDAYS
SPM TRIALS
2011
INTENSIVE REVISION OF
TRIAL PAPERS FROM OTHER STATES
PAST YEAR QUESTIONS
SPM EXAMINATIONS
2011
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Advanced Numerical Methods with Matlab 2: Resolution of Nonlinear, Differential and Partial Differential EquationsD'EverandAdvanced Numerical Methods with Matlab 2: Resolution of Nonlinear, Differential and Partial Differential EquationsPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Annual Scheme of Work: SMK Penangah Telupid Form 5 Additional MathematicsDocument9 pages2014 Annual Scheme of Work: SMK Penangah Telupid Form 5 Additional Mathematicsjosnih bin murniPas encore d'évaluation
- Interactions on Digital Tablets in the Context of 3D Geometry LearningD'EverandInteractions on Digital Tablets in the Context of 3D Geometry LearningPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT - Add Math F4 - 2015Document12 pagesRPT - Add Math F4 - 2015supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan P&P Mathematics Form 4Document25 pagesRancangan Tahunan P&P Mathematics Form 4Mohd Sani Abd HamidPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT ADD MATH FRM 4Document12 pagesRPT ADD MATH FRM 4Arfa Suhaida ZainPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Maths F 5 2011Document20 pagesYearly Plan Maths F 5 2011ysheng98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan f5 2007Document10 pagesYearly Lesson Plan f5 2007hazwani_sPas encore d'évaluation
- YLP Form 5 MathematicsDocument18 pagesYLP Form 5 MathematicsRisma RobinPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Addmathsf413Document10 pagesYearly Lesson Addmathsf413SasiKalaRamayahPas encore d'évaluation
- PLANNING MATHEMATICS LESSONS FORM 4Document10 pagesPLANNING MATHEMATICS LESSONS FORM 4hazwani_sPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Maths f4 2013Document16 pagesRPT Maths f4 2013Kang CkPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT : MATHEMATICS FORM 5 YEARLY PLAN 2010Document14 pagesRPT : MATHEMATICS FORM 5 YEARLY PLAN 2010Madiah JaafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 5Document10 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 5ryePas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Cs Form 5Document6 pagesMaths Cs Form 5juriah binti ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Form 5,2013 (Terkini)Document18 pagesYearly Plan Form 5,2013 (Terkini)Chen ChiuwenPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Teaching Plan 2011-Mathsf4Document13 pagesYearly Teaching Plan 2011-Mathsf4Nor SyahidatulnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Math Lesson Plan (2012) Form 5Document19 pagesYearly Math Lesson Plan (2012) Form 5Nie Anthon100% (1)
- RPT Math Form 2Document16 pagesRPT Math Form 2Hartini KosnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Matematik Tambahan Tingkatan 5 2015 Yearly PlanDocument9 pagesMatematik Tambahan Tingkatan 5 2015 Yearly PlanSuziana MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional Math Form 5Document8 pagesAdditional Math Form 5Jeyaletchumi JeyaPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Add Math Form 4Document9 pagesRPT Add Math Form 4Norhapidah Mohd SaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Akademik Sekolah-Sekolah Negeri Kelantan: Catatan: Masukkan Tarikh Seperti Di Dalam Takwim SekolahDocument14 pagesStandard Akademik Sekolah-Sekolah Negeri Kelantan: Catatan: Masukkan Tarikh Seperti Di Dalam Takwim SekolahFarid YusofPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics or Mathematics (Core)Document17 pagesGeneral Mathematics or Mathematics (Core)Akpevweoghene Kelvin IdogunPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics or Mathematics (Core)Document16 pagesGeneral Mathematics or Mathematics (Core)Anonymous qaI31HPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Number Bases in Different Numeral SystemsDocument17 pagesUnderstanding Number Bases in Different Numeral Systemsriesya1206Pas encore d'évaluation
- SMJK HENG EE MATHEMATICS SCHEME OF WORK 2015Document19 pagesSMJK HENG EE MATHEMATICS SCHEME OF WORK 2015Tiviya Tarini ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- F4 Maths YPDocument10 pagesF4 Maths YPKelvinYongPas encore d'évaluation
- RPH m3 f3Document19 pagesRPH m3 f3Lynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Area: 1) Number Bases Mathematics: Form 5 Week/Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Generics Ccts Moral Value NotesDocument17 pagesLearning Area: 1) Number Bases Mathematics: Form 5 Week/Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Generics Ccts Moral Value NotesNur BainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Yearly Plan f4 2012Document14 pagesMath Yearly Plan f4 2012Soh Tyan JiinPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheme of Work Mat F5Document17 pagesSheme of Work Mat F5mpuziahPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusDocument9 pagesForm 4 Modern Mathematics Syllabusjuriah binti ibrahim100% (2)
- Mastering Mathematics Concepts and ApplicationsDocument11 pagesMastering Mathematics Concepts and ApplicationsscorpionketanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acet - Syllabus 1 - FacDocument8 pagesAcet - Syllabus 1 - FacYogesh AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- f5 Add Maths Annual Scheme (2008)Document6 pagesf5 Add Maths Annual Scheme (2008)Abdul ManafPas encore d'évaluation
- Add Maths Form 4Document10 pagesAdd Maths Form 4Azrul AkmarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Scheme of Work Add Maths F5Document9 pages2015 Scheme of Work Add Maths F5nurizwahrazakPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan 2012 Mathematics Form 2Document14 pagesYearly Plan 2012 Mathematics Form 2FikriSalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam AFF700 211210 - SolutionsDocument11 pagesExam AFF700 211210 - Solutionsnnajichinedu20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Plan for Additional Mathematics Form 5Document20 pagesTeaching Plan for Additional Mathematics Form 5Haswa ShazwatiPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Form4 MateDocument15 pagesRPT Form4 MateNurazniza MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- ICSE Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus 2017 - 2018Document7 pagesICSE Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus 2017 - 2018Udit Kumar NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics: Section I: Number and Numeration. 1. Number BasesDocument7 pagesMathematics: Section I: Number and Numeration. 1. Number BasesAisha ShuaibuPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional Maths Scheme of Work for Form 5Document15 pagesAdditional Maths Scheme of Work for Form 5Green QingPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics SyllabusDocument13 pagesMathematics SyllabusForla MiPas encore d'évaluation
- Jamb Mathematics SyllabusDocument13 pagesJamb Mathematics SyllabusOlusesi ToluwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- No. of PagesDocument3 pagesNo. of PagesDonaldPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.0 Standard Form Week 1 4/1 - 6/1/12 1.1 UnderstandDocument31 pages1.0 Standard Form Week 1 4/1 - 6/1/12 1.1 UnderstandNur BainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 2Document16 pagesScheme of Work Mathematics Form 2Stephanie Kimi100% (2)
- PQT111 and EQT101 Past Year QuestionsDocument6 pagesPQT111 and EQT101 Past Year QuestionsNURHADI ALHAKIM BIN ISMAIL STUDENTPas encore d'évaluation
- UTME Math Syllabus BreakdownDocument7 pagesUTME Math Syllabus BreakdownAdeola MojeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Maths Form 4Document24 pagesYearly Plan Maths Form 4JiaJia LauPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 MathsDocument5 pagesClass 10 MathsAndrea BatesPas encore d'évaluation
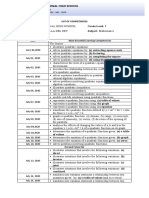
- List of CompetenciewsDocument3 pagesList of CompetenciewsJaninne Villa del Rey0% (1)
- Actuarial Common Entrance Test ACETDocument8 pagesActuarial Common Entrance Test ACETPushkar NarayanPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Math F4 2013Document34 pagesRPT Math F4 2013ummuinsyirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Title Marine Engineering MathematicsDocument10 pagesTitle Marine Engineering MathematicsgunapalshettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Jamb MathematicsDocument6 pagesJamb Mathematicsnwogbodavid7Pas encore d'évaluation
- MSJ Convent Bukit Nanas Mathematics Lesson Plan Form 4 2009Document26 pagesMSJ Convent Bukit Nanas Mathematics Lesson Plan Form 4 2009Elfysia FredolinPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 3-No 10Document2 pages5 3-No 10supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Equally y Gradient Y: 2erte'sDocument1 pageEqually y Gradient Y: 2erte'ssupbarPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.3 - No.8Document1 page5.3 - No.8supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 2-No 12Document3 pages5 2-No 12supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.3-No.9 - (One More Way)Document3 pages5.3-No.9 - (One More Way)supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Name List For 1D and 1JDocument2 pagesName List For 1D and 1JsupbarPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 3-No 9Document2 pages5 3-No 9supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Note 9 Nov 2020Document2 pagesNote 9 Nov 2020supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Selangor - Soalan Set 1Document29 pagesSelangor - Soalan Set 1qaisaraPas encore d'évaluation
- T1Document20 pagesT1supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Automated Circulation System Using Visual Basic: NN L F Libr R S I N D Um NT Ti n47 I 0Document18 pagesAutomated Circulation System Using Visual Basic: NN L F Libr R S I N D Um NT Ti n47 I 0supbarPas encore d'évaluation
- De Thi Toan Apmops 2001-2017Document168 pagesDe Thi Toan Apmops 2001-2017Tho Nguyen TruongPas encore d'évaluation
- Form Five MathematicsDocument10 pagesForm Five MathematicsronreshPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 PPPPDocument1 page1 PPPPMohamed Abdalla Mohamed AlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential CalculusDocument386 pagesDifferential CalculusSalim Mohd RazPas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring the Value of Pi Through Sphere VolumesDocument33 pagesMeasuring the Value of Pi Through Sphere VolumesFrankieNgPas encore d'évaluation
- School Leader ResumeDocument2 pagesSchool Leader Resumeapi-280917953Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grade Five Capstone ProjectDocument5 pagesGrade Five Capstone Projectapi-79455357Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math 1 6Document45 pagesMath 1 6Dhamar Hanania Ashari100% (1)
- 1st Practice Test 2 Levels 6-8 - With Calculator (439kB)Document24 pages1st Practice Test 2 Levels 6-8 - With Calculator (439kB)Nguyen Thi Anh TrangPas encore d'évaluation
- Mtap 6 ReviewerDocument17 pagesMtap 6 ReviewerDonna Fe Quilana100% (1)
- Mcqueeny Aam ResumeDocument1 pageMcqueeny Aam Resumeapi-335069538Pas encore d'évaluation
- Divide Decimals Clue A TESDocument2 pagesDivide Decimals Clue A TEScikgurazifPas encore d'évaluation
- StatDocument3 pagesStatgracePas encore d'évaluation
- CHERRYFIELD MONTESSORI END OF TERM EXAM REVIEWDocument12 pagesCHERRYFIELD MONTESSORI END OF TERM EXAM REVIEWEmmanuel AgbavorPas encore d'évaluation
- 1MA0 2H Que 20130614Document28 pages1MA0 2H Que 20130614examman123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) : Unit - IDocument22 pagesSample Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) : Unit - IDaveed stark100% (1)
- 10.1 Tangents To CirclesDocument32 pages10.1 Tangents To CirclesArnab Biswas100% (1)
- Click On 4 Plan LectieDocument2 pagesClick On 4 Plan LectieMirela Baciu100% (1)
- Circles and Conic Sections GuideDocument13 pagesCircles and Conic Sections Guidenoli m. nogaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vygotsky and Piaget on Child DevelopmentDocument6 pagesVygotsky and Piaget on Child Developmentjoshua VillamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument21 pagesRoles and ResponsibilitiesQifaysVg67% (3)
- Grade 8 Square and Square Roots inDocument12 pagesGrade 8 Square and Square Roots inSanjay AdakPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Class VIII MOCK EXAMDocument3 pagesMaths Class VIII MOCK EXAMANSH PORWAL 007261-16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11Document4 pagesChapter 11Preetham RaajPas encore d'évaluation
- Gad Accomplishment Report NWMCDocument2 pagesGad Accomplishment Report NWMCAnnick Winsyl Nillosguin100% (2)
- MATHEMATICS QUESTION BANKDocument15 pagesMATHEMATICS QUESTION BANKSangaPas encore d'évaluation
- m2 CH 10 Application of Differentiation Supp ExDocument3 pagesm2 CH 10 Application of Differentiation Supp Exapi-303501215Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pascal's Triangle WorksheetDocument11 pagesPascal's Triangle WorksheetIndraneel GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Cheat-Sheet - Boas Mathematical Methods in The Physical SciencesDocument4 pagesCheat-Sheet - Boas Mathematical Methods in The Physical Sciencesakkarbakkarbambepor67% (3)
- Bertonicolleen Professional Resume For WeeblyDocument3 pagesBertonicolleen Professional Resume For Weeblyapi-396517404Pas encore d'évaluation