Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Albumina 1
Transféré par
Vale FrancoDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Albumina 1
Transféré par
Vale FrancoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
TECO DIAGNOSTICS
1268 N. Lakeview Ave. Anaheim, CA 92807 1-800-222-9880
ALBUMIN BCG METHOD
TC MATRIX
INTENDED USE For the quantitative determination of albumin in serum or plasma on TC Matrix analyzers. SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST Albumin is the most abundant individual protein in serum. Normal health adult contains 35~50 g/l of serum and A/G ratio of 1.3~1.8. The liver is the site of synthesis of albumin and hence liver disease is one of the most common causes of decreased albumin level. Other conditions such as congestive heart failure, malnutrition, starvation, nephritis, gloemlonephritis, leukemia and severe burns also resulted in the decrease of albumin level. Albumin levels may be elevated in dehydration, shock, hemoconcent ration, or upon administration of large quantities of concentrated albumin intravenously. Bromcresol green (BCG), an ionic dyes, binds tightly to albumin when serum is added. The albumin- BCG complex absorbs light at 600 nm more intensively than BCG alone. The TC Matrix System automatically proportions the appropriate sample and reagent volumes into the cuvette. The system monitors the change in absorbance at 600 nanometers. This change in absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of albumin in the sample and is used by the TC Matrix System to calculate and express albumin concentration. Albumin + BCG ------� Albumin-BCG complex. REAGENT CONTENTS: Each kit contains: Six Albumin reagent 1 (6 x 40 ml) Instruction Insert . REAGENT PREPARATION No preparation is required.
3. For plasma, add whole blood directly into a tube containing anticoagulant. Acceptable anticoagulants are listed in the LIMITATIONS section.
CALIBRATION
1. Calibrator required: TECO MULTI Calibrator. 2. The system must have a valid calibration in memory before controls or patient samples can be run. 3. The TC Matrix system will automatically perform checks on the calibration and produce data at the end of calibration.
MATERIALS NEEDED BUT NOT SUPPLIED WITH REAGENT KIT
TECO MULTI Calibrator. At least two levels of control material.
LIMITATIONS
1. The anticoagulants Potassium Oxalate, Sodium Fluoride and Sodium Citrate were found to be incompatible with this method. 2. The anticoagulants EDTA, Lithium Heparin, Sodium Heparin, Ammonium Heparin were found to be compatible with this method. INTERFERENCE 1. Hemoglobin may interfere with this methodology. 2. Lipemic samples >3+ should be ultra-centrifuged and the analysis performed on the infranate. 3. On this method, refer to the work of Young for a review of drug and comprehensive list of substances effect on Albumin level. EXPECTED VALUE 3.5-5.0g/dL or 35~50 g/L PRECAUTIONS: 1. For in vitro diagnostic use only. 2. Since all specimens are potentially infectious, they should be handled with appropriate precautions and practices in accordance with Biosafety level 2 as recommended by USA NIH manual Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories, and in accordance with National or local regulations related to the safety precautions of such materials. 3. Each laboratory has to perform the quality control test to assure the results being reliable before running the specimen tests. PROCEDURES
TEST NAME: TEST NO. FULL NAME: REFERENCE NO.: ANALY.TYPE: PRI. WAVE : SECON. WAVE: TREND: REACT. TIME: Endpoint 630 nm / Ascending 0 18 Albumin ALB R1: R2: SAMPLE VOLUME: R1 BLANK: MIX REAG. BLANK: CONCENTRATION: LINEARITY LIMIT: SUBSTRATE LIMIT: FACTOR: / 450 0 3 / 0.1 - 1.5 / 1-7 /
REAGENT COMPOSITION
Bromcresol green: 0.28 mmol/L Also non-reactive chemicals for optimal system performance. REAGENT STORAGE AND STABILITY Albumin Reagent stored unopened at room temperature is stable until the expiration date showed on the bottle label. Once opened, Albumin Reagent is stable for 30 days, unless the expiration date is exceeded. DO NOT FREEZE. SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND HANDLING 1. The test can be performed on serum, plasma. For serum, blood is drawn into a tube which does not contain anticoagulant and allow clotting. The serum is them separated from the clot. A maximum limit of two hours from the time of collection is recommended. 2. Separated serum or plasma should not remain at room temperature longer than 8 hours. If assays are not completed within 8 hours, serum and plasma should be stored at 2C to 8C. If assays are not completed within 48 hours, or the separated sample is to be stored beyond 48 hours, samples should be frozen at -15C to -20C. Frozen samples should be thawed only once. Analyte deterioration may occur in samples that are repeatedly frozen and thawed.
INCUBATE TIME: UNIT: PRECISION:
/ g/dl 0.1
PROZONE CHECK: Q1: / PC: / Q2: / Q3: / ABS.: /
/ Q4: /
10. Young, D.S., Effects of Drugs on Clinical Laboratory Tests, 3rd. Ed., AACC Press, Washington DC, 1990, 3-104 thru 3-106. A502 510TM: 02/08
Calibration Type: Calibrate+Reag.Blank
Calibration Rule: Two-point linear
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Analytical Range: 1.0-7.0 g/dl
For Albumin analyte by Albumin Reagent on TC Matrix System, this method has been demonstrated to be linear from 1.0-7.0 g/dl.
Accuracy: Comparison study was performed on TC Matrix System from 40 samples. Beckman Coulter Albumin reagent was used to compare with Albumin Reagent. The results of this study in yield a correlation coefficient of 0.991 with a regression equation of y=0.991X + 0.200. Precision: Within Run precision for Albumin Reagent Set was determined following a modification of NCCLS EP5-A.Two commercial human serum, TECO MULTI Calibrators were assayed on TC Matrix System for 25 times.
Sample N Mean (mg/dl) Standard Deviation (mg/dl) Coefficient of Variation (%) Sample 1 25 4.0 0.09 2.1 Sample 2 25 2.8 0.07 2.0
Run-Day precision for Albumin Reagent was determined following a modification of NCCLS EP5-A.Two commercial human serums, TECO MULTI Calibrators were assayed on TC Matrix Systems five times per day for five days for the total of 25 values.
Sample N Mean (mg/dl) Standard Deviation (mg/dl) Coefficient of Variation (%) Sample 1 25 4.0 0.08 2.1 Sample 2 25 2.8 0.08 2.2
REFERENCES: 1. Doumas, B.T.et.a. clinn, chem. Acta 31:87, 1971. 2. Doumas, B.T.and Biggs, H.G. In standard Methods of clinical chemistry 7,175,1972. 3. Tiez, N.W., Speciman Collection and Processing; Sources of Biological Variation, Textbook of Clinical Chemistry, 2nd Edition, W.B. Saunders, Philadephia, PA (1994) 4. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Approved Guidline, NCCLS publication C28-A, Villanova, PA (1994). 5. Henry, J. B., ed., Clinical Diagnostics and Management by Laboratory Methods, 18th Edition, W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia. 6. Tietz,N.W., ed., Clinical Guide to Laboratory Tests, 2 nd Edition, W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA (1990) 7. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Method Comparison and Bias Estimation Using Patient Samples; Tentative Guideline, NCCLS Publication EP9-T, Villanova, PA (1993) 8. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Precision Performance of Clinical Chemistry Devices; Tentative Guideline, 2nd Edition, NCCLS publication EP5-T2, Villanova, PA (1992) 9. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, National Evaluation Protocols for Interference Testing, Evaluation Protocol Number 7, Vol. 4, No, June 1984.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A524 780TM1Document2 pagesA524 780TM1clinical_pathologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Albumin: OSR6102 4 X 29 ML R1 OSR6202 4 X 54 ML R1 OSR6602 4 X 173 ML R1Document2 pagesAlbumin: OSR6102 4 X 29 ML R1 OSR6202 4 X 54 ML R1 OSR6602 4 X 173 ML R1irwoons70Pas encore d'évaluation
- C-Peptide: Diagnostic Automation, IncDocument6 pagesC-Peptide: Diagnostic Automation, IncmusiboyinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 AlbuminDocument6 pages4 AlbuminAzhar Clinical Laboratory TubePas encore d'évaluation
- En AlbuminDocument2 pagesEn AlbuminCướpBiểnChộtPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Report August 2012 Edited - V2 - 2Document26 pagesSummary Report August 2012 Edited - V2 - 2CARLOSPas encore d'évaluation
- ALBUMIN BLOSR6x02 ENDocument2 pagesALBUMIN BLOSR6x02 ENMeethuanPas encore d'évaluation
- AAGP2 enDocument3 pagesAAGP2 enLince WijoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bsis13-I Creatinina 2014Document1 pageBsis13-I Creatinina 2014Alejandra MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- A93a01225cen Glucose Pap CPDocument6 pagesA93a01225cen Glucose Pap CPimrecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mixing StudyDocument3 pagesMixing StudyKholifah LintangPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Policies C Reactive Protein CRP - Cobas c501 Lab 4232Document4 pagesLab Policies C Reactive Protein CRP - Cobas c501 Lab 4232Wisnu Dwi PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Potassium (K)Document3 pagesPotassium (K)ZINEB DAHMANIPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Policies Triglycerides - Cobas c501 Lab 4455Document4 pagesLab Policies Triglycerides - Cobas c501 Lab 4455Marj MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- AAT2 enDocument3 pagesAAT2 enSyahdie FahlediePas encore d'évaluation
- Clonatest Amylase MRDocument4 pagesClonatest Amylase MRSuprovet LabotatorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Policies Free Thyroxine FT4 Cobas E601 Lab 4045Document4 pagesLab Policies Free Thyroxine FT4 Cobas E601 Lab 4045TohăneanR.RomeliaPas encore d'évaluation
- c311 AAGP2 enDocument3 pagesc311 AAGP2 endr. SheryarOrakzaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Glucose c111 RocheDocument3 pagesGlucose c111 RocheHarditya FirdhausPas encore d'évaluation
- AlbuminaDocument4 pagesAlbuminaSuprovet LabotatorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Insert C3C-2 0003001938322c501 V8 enDocument4 pagesInsert C3C-2 0003001938322c501 V8 enBayaniCmPas encore d'évaluation
- A46221DDocument15 pagesA46221DQuoctytranPas encore d'évaluation
- C-Reactive Protein Test for Beckman AnalyzersDocument3 pagesC-Reactive Protein Test for Beckman AnalyzersYến Minh NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOPRO J MET Albumin 508Document15 pagesBIOPRO J MET Albumin 508Official NutkopPas encore d'évaluation
- ALB2Document4 pagesALB2Jonalyn SalandoPas encore d'évaluation
- CORTIZOLDocument24 pagesCORTIZOLFlorea RodicaPas encore d'évaluation
- ALTL enDocument3 pagesALTL enyolanda0811Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Policies TSH - Cobas E411 Lab 1598Document5 pagesLab Policies TSH - Cobas E411 Lab 1598Bassam Alharazi100% (1)
- CRP LX High Sensitive enDocument4 pagesCRP LX High Sensitive enLince WijoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Total PSADocument4 pagesTotal PSAYeni Valderrama CcahuanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Can-Fte-260 - Free TestosteroneDocument2 pagesCan-Fte-260 - Free TestosteronevijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- AST/GOT 4+1 SL Analyzer TestDocument2 pagesAST/GOT 4+1 SL Analyzer TestMatthew KingPas encore d'évaluation
- APTT MispaClogDocument1 pageAPTT MispaClogDharmesh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Glucose KitDocument2 pagesGlucose KitJuan Enrique Ramón OrellanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transferrin Reagent PerformanceDocument2 pagesTransferrin Reagent PerformanceTanveerPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Procedure Manual: Triglycerides Serum Cobas 6000 Chemistry AnalyzerDocument18 pagesLaboratory Procedure Manual: Triglycerides Serum Cobas 6000 Chemistry AnalyzerGuneyden GuneydenPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP For ABO GroupingDocument5 pagesSOP For ABO GroupingDUKEPas encore d'évaluation
- CreaDocument5 pagesCreaKouame Francis0% (1)
- 04 FS Package InsertDocument6 pages04 FS Package InsertImas NurhayatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Apobt: Nacl Diluent 9%Document3 pagesApobt: Nacl Diluent 9%Yunita RapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Principle Principle PrincipleDocument12 pagesPrinciple Principle PrincipleDarshana JuvekarPas encore d'évaluation
- A93a01239ben Magnesium RtuDocument4 pagesA93a01239ben Magnesium RtuimrecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cortez Diagnostics, IncDocument5 pagesCortez Diagnostics, IncShazib MunshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct LDL-C Assay KitDocument2 pagesDirect LDL-C Assay KitNanda Nabilah UbayPas encore d'évaluation
- CreatinineDocument1 pageCreatinineDesiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Policies Hemoglobin A1C - Cobas c501 Lab 4004Document6 pagesLab Policies Hemoglobin A1C - Cobas c501 Lab 4004yosefinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Policies Complete Blood Count of Whole Blood On The Sysmex KX 21N - RB Lab 1535Document20 pagesLab Policies Complete Blood Count of Whole Blood On The Sysmex KX 21N - RB Lab 1535tomPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.3.1 BasesDocument8 pages3.3.1 BasesMark ReinhardtPas encore d'évaluation
- T4Document26 pagesT4Florea RodicaPas encore d'évaluation
- CREATININE-JDocument2 pagesCREATININE-JIng BiomédicoPas encore d'évaluation
- EN - TOTAL PROTEIN - BAOSR6x32 - USDocument3 pagesEN - TOTAL PROTEIN - BAOSR6x32 - USDharmesh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- AmylaseDocument1 pageAmylasetuan vănPas encore d'évaluation
- PI e CYSC 2Document2 pagesPI e CYSC 2sitirahmawatiningsih25Pas encore d'évaluation
- AB362 IfuDocument2 pagesAB362 IfuRahmatPas encore d'évaluation
- SYNCHRON System(s) Chemistry Information Sheet HDL CholesterolDocument11 pagesSYNCHRON System(s) Chemistry Information Sheet HDL CholesterolanggaririnPas encore d'évaluation
- SGPT Serum Glutamic Pyruvic TransaminaseDocument2 pagesSGPT Serum Glutamic Pyruvic TransaminaseNaveed WarraichPas encore d'évaluation
- 罗氏 Crpl3 (免疫比浊法)英文说明书Document4 pages罗氏 Crpl3 (免疫比浊法)英文说明书hua jiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory SOPsDocument286 pagesLaboratory SOPsMohamed Annavi100% (1)
- A-00 IndexDocument10 pagesA-00 IndexNizarHamrouniPas encore d'évaluation
- Uvas CaractDocument10 pagesUvas CaractgondeluPas encore d'évaluation
- EMC Design Guide For PCBDocument78 pagesEMC Design Guide For PCBFaruq AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Smartrac - Iolineug - r5Document66 pagesSmartrac - Iolineug - r5Darwin Elvis Giron HurtadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Zero Moment of Truth On Consumer Behavior For FMCGDocument14 pagesEffects of Zero Moment of Truth On Consumer Behavior For FMCGBoogii EnkhboldPas encore d'évaluation
- V Ships Appln FormDocument6 pagesV Ships Appln Formkaushikbasu2010Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Meaning of Solar CookerDocument4 pagesThe Meaning of Solar CookerJaridah Mat YakobPas encore d'évaluation
- Axis Bank Placement Paper Interview Questions 48072Document3 pagesAxis Bank Placement Paper Interview Questions 48072Ravi RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vox Latina The Pronunciation of Classical LatinDocument145 pagesVox Latina The Pronunciation of Classical Latinyanmaes100% (4)
- All Paramedical CoursesDocument23 pagesAll Paramedical CoursesdeepikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bond Strength of Normal-to-Lightweight Concrete InterfacesDocument9 pagesBond Strength of Normal-to-Lightweight Concrete InterfacesStefania RinaldiPas encore d'évaluation
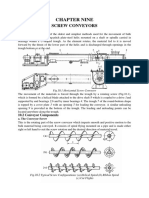
- Chapter 9 Screw ConveyorsDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Screw ConveyorsMarew Getie100% (1)
- ACCA P1 Governance, Risk, and Ethics - Revision QuestionsDocument2 pagesACCA P1 Governance, Risk, and Ethics - Revision QuestionsChan Tsu ChongPas encore d'évaluation
- Tchaikovsky Piano Concerto 1Document2 pagesTchaikovsky Piano Concerto 1arno9bear100% (2)
- Primary Checkpoint - Science (0846) October 2016 Paper 2 MSDocument12 pagesPrimary Checkpoint - Science (0846) October 2016 Paper 2 MSdinakarc78% (9)
- Keb Combivis 6 enDocument232 pagesKeb Combivis 6 enhaithamPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 2 Solarcon Catalogue Final RevisedDocument8 pages2017 2 Solarcon Catalogue Final RevisedNavarshi VishnubhotlaPas encore d'évaluation
- JVW 110Document2 pagesJVW 110Miguel Leon BustosPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Salicylic Acid'S Level in Acne Cream Which Sold in Kemiling Using Spektrofotmetry Uv VisDocument7 pagesDetermination of Salicylic Acid'S Level in Acne Cream Which Sold in Kemiling Using Spektrofotmetry Uv VisJuan LambeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Term Business Economy - Ayustina GiustiDocument9 pagesMid Term Business Economy - Ayustina GiustiAyustina Giusti100% (1)
- 6th GATEDocument33 pages6th GATESamejiel Aseviel LajesielPas encore d'évaluation
- PHCDocument1 pagePHCsinh24X7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Declarative and Procedural Knowledge (Lêda's Final Paper) 2010 01Document13 pagesDeclarative and Procedural Knowledge (Lêda's Final Paper) 2010 01Jair Luiz S. FilhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study OrthoDocument21 pagesCase Study Orthojoshua_santiago_5Pas encore d'évaluation
- CuegisDocument2 pagesCuegisTrishaPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Data Sheet: Eas Configurator: Easy Online Configuration Ekv1+1 120 Vg4Gxhq (Vg4Gxhq)Document1 pageProduct Data Sheet: Eas Configurator: Easy Online Configuration Ekv1+1 120 Vg4Gxhq (Vg4Gxhq)Attila HorvathPas encore d'évaluation
- Dice Resume CV Narendhar ReddyDocument5 pagesDice Resume CV Narendhar ReddyjaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/12Rodolph Smith100% (2)
- Borang JPK CA 01 Tahap 2Document2 pagesBorang JPK CA 01 Tahap 2ajai1010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eladio Dieste's Free-Standing Barrel VaultsDocument18 pagesEladio Dieste's Free-Standing Barrel Vaultssoniamoise100% (1)