Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Energy Efficiency PPT Notes
Transféré par
api-235634024Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Energy Efficiency PPT Notes
Transféré par
api-235634024Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Energy Efficiency PPT Notes
Energy efficiency- measure of useful energy An energy efficient appliance would convert energy with minimal amount of heat returned as energy 2nd law of Thermodynamics- Quality of energy deteriorates gradually over time. During a chemical reaction, energy is converted. Chemical> Mechanical (+heat) heat is a form of energy that isn't usable Input- all the components entering the system Throughput-flow of all components Output- components leaving system % efficiency= (output/input)x 100. Cannot exceed 100% because of Law of Conservation of Energy Feedback loop- how output becomes input and affects system. Negative: reverses direction of flow, Positive: changes rate of throughput but no direction Four devices that waste large amount of energy- Incandescent light bulb (95%), internal combustion engine (94%), nuclear power plant (92%) and coal-burning power plant (66%) Solutions to reducing energy waste: prolongs fossil fuel supplies, reduces oil imports, high net energy, low cost, reduces pollution Ways to improve energy efficiency: increase fuel efficiency, make vehicles lighter and stronger We can save energy in building by getting heat from the sun, superinsulating them and using plant covered green roofs We can save energy in an existing building by insulating them, plugging leaks and using energy-efficient heating and cooling systems Renewable energy: direct solar, moving water, wind and geothermal Ways to cool houses: super insulation, taking advantages of breezes, shading them, light covered or green roofs, geothermal cooling Biomass: plant materials and animal waste can be burned to provide heat or electricity or converted into gaseous or liquid biofuels Ethanol: crops such as sugarcane and corn can be converted into ethanol Passive/Active solar heating PRO-energy is free, net energy is moderate, quick installation, no co2 emissions CON-Need access to sun 60% of time, sun blocked by other structures Solar cells PRO- Fairly high net energy, No CO2 emissions, last 20-40 years CON-Need access to sun, low efficiency, high land use and costs Hydropower PRO-Moderate to high net energy, high efficiency, large untapped potential CON-High construction costs, environmental impact from flooding, high CO2 emissions Wind power PRO-Moderate to high net energy, high efficiency, moderate capital cost CON- Steady winds needed, high land use, visual pollution Biomass PRO-Large supply in some areas, moderate costs, no net CO2 increase
CON- Nonrenewable if harvested unsustainably, moderate to high environmental impact, low photosynthetic efficiency Ethanol PRO- High octane, some reduction in CO2 emissions, high net energy CON- Large fuel tank needed, lower driving range, low net energy Biodiesel PRO- Reduced CO2 emissions, reduced hydrocarbon emissions, high yield for oil palm crops CON- Increased emission of nitrogen oxides, high cost than regular diesel, low yield for soybean crops Methanol PRO-High octane, reduction in CO2, lower total air pollution CON- Large fuel tank needed, half the driving range, corrodes metal, plastic and rubber Geothermal PRO- High efficiency, moderate net energy, lower CO2 emissions CON- Scarcity, depleted if used too rapidly, CO2 emissions Hydrogen PRO- Can be produced from water, low environmental impact, renewable if from renewable resources, no CO2 emissions if produced from water CON- Not found in nature, energy is needed to produce fuel, negative net energy What can you do? Energy use and waste Get energy audit, use mass transit, walking and biking, turn off electronics when not in use, use passive solar heating
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- SMChap 018Document32 pagesSMChap 018testbank100% (8)
- The Omnivores Dilemma Chapter 4Document2 pagesThe Omnivores Dilemma Chapter 4api-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Asm Master Oral Notes - As Per New SyllabusDocument262 pagesAsm Master Oral Notes - As Per New Syllabusshanti prakhar100% (1)
- Cut Energy Waste & Transition to RenewablesDocument40 pagesCut Energy Waste & Transition to RenewablesMyrna M. Mesionna0% (1)
- PWS 150 - 2024 - Chapter 13 - Energy Resources_SVDocument43 pagesPWS 150 - 2024 - Chapter 13 - Energy Resources_SVnicksorenson20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apes in A Box Energy Type NotesDocument2 pagesApes in A Box Energy Type Notesapi-247723417Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages & Benefits of Hydrogen and Fuel Cell TechnologiesDocument4 pagesAdvantages & Benefits of Hydrogen and Fuel Cell TechnologiesTri YuniartoPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Conservation: Presentation by ROLL NO. - 25,26,27,28. Div. - H Branch - CivilDocument43 pagesEnergy Conservation: Presentation by ROLL NO. - 25,26,27,28. Div. - H Branch - CivilsurajsinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Green HydrogenDocument32 pagesGreen HydrogenMohammad AsadPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity Generation ProcessDocument26 pagesElectricity Generation ProcessSNEHA DEVARAJUPas encore d'évaluation
- Sustainability PresentationDocument12 pagesSustainability PresentationgeoffmanePas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument27 pagesRenewable Energy ResourcesEng Bile LastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Conventional and Non-conventional Energy SourcesDocument14 pagesConventional and Non-conventional Energy SourcesVizag ChandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy ConservationDocument32 pagesEnergy ConservationRam Krishna SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecotech EsportsDocument4 pagesEcotech EsportsJerzy Mae GloriosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Realization of Exhaust Air Recovery and Waste Heat Recovery Systems For Energy Conservation and Sustainable DevelopmentDocument5 pagesRealization of Exhaust Air Recovery and Waste Heat Recovery Systems For Energy Conservation and Sustainable DevelopmentRahmatullah Jami'inPas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid Solar Air Conditioning Saves up to 90Document2 pagesHybrid Solar Air Conditioning Saves up to 90mkhongPas encore d'évaluation
- Green Building: S8 Civil Thejus Engineering CollegeDocument23 pagesGreen Building: S8 Civil Thejus Engineering CollegeAnoop CkPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste To EnergyDocument24 pagesWaste To EnergySantosh Kumar BuyyaPas encore d'évaluation
- SOWMYAKUKATLADocument17 pagesSOWMYAKUKATLANOOB GAMINGPas encore d'évaluation
- ESSE SheetDocument3 pagesESSE SheetNicolas MaggioPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2 Renewable Energy in Buildings RevDocument23 pages3.2 Renewable Energy in Buildings RevOlusegun OyebanjiPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-IIIDocument48 pagesUNIT-IIIVD King BrothersPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Sources JustificationDocument13 pagesEnergy Sources Justificationapi-272862164Pas encore d'évaluation
- Convert Waste Plastics to Oil with ECP-101 MachineDocument12 pagesConvert Waste Plastics to Oil with ECP-101 Machineonejako12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cleaner Tech. AssignmentDocument6 pagesCleaner Tech. AssignmentShameel ZeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Efficiency and Renewable Resources Test ReviewDocument39 pagesEnergy Efficiency and Renewable Resources Test ReviewEUNAH LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Source How Does It Work? Pros ConsDocument12 pagesEnergy Source How Does It Work? Pros Consapi-272560904Pas encore d'évaluation
- Green Building Concept ExplainedDocument34 pagesGreen Building Concept ExplainedAnand EP100% (1)
- Brief Overview of Alternative Energy SourcesDocument2 pagesBrief Overview of Alternative Energy SourcesDUTY BOUNDPas encore d'évaluation
- Sustainable Energy Future: Efficiency and RenewablesDocument15 pagesSustainable Energy Future: Efficiency and Renewableszs28844Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell TechnologyDocument107 pagesHydrogen Fuel Cell TechnologyShriniketh Chandrashekhar67% (3)
- Group A: Mitigation AssignmentsDocument3 pagesGroup A: Mitigation Assignmentsrichiness madzudzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Greenhouse Energy Conservation and Alternatives by Rorabaugh Et AlDocument5 pagesGreenhouse Energy Conservation and Alternatives by Rorabaugh Et AlmarkovitPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermoelectric GeneratorDocument2 pagesThermoelectric GeneratorMuhammad Raza RafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- BLOOM ENERGY Final PresentationDocument6 pagesBLOOM ENERGY Final PresentationechoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is CogenerationDocument3 pagesWhat Is CogenerationmuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Es-Solar Energy (g16)Document8 pagesEs-Solar Energy (g16)Thuỳ DungPas encore d'évaluation
- AN INNOVATIVE SOLAR-BIOMASS HYBRID AIR HEATING SYSTEMDocument32 pagesAN INNOVATIVE SOLAR-BIOMASS HYBRID AIR HEATING SYSTEMHeri RustamajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Eco-Friendly Products: Nirav Kheni 19SE02CE035Document15 pagesEco-Friendly Products: Nirav Kheni 19SE02CE035Leo MessiPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy Sources By: P.V.P.Neppo AnandDocument17 pagesRenewable Energy Sources By: P.V.P.Neppo AnandneppoanandPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Heat Recovery Power Plant - Cement PlantDocument7 pagesWaste Heat Recovery Power Plant - Cement PlantknsaravanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploring Top 9 Alt Energy SourcesDocument2 pagesExploring Top 9 Alt Energy SourcesDUTY BOUNDPas encore d'évaluation
- BLOOM ENERGY Final PresentationDocument6 pagesBLOOM ENERGY Final PresentationAlagappan AngamuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Answers To Learning ActivitiesDocument2 pagesModel Answers To Learning ActivitiesAniket KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Capture and Green TechDocument10 pagesCarbon Capture and Green TechSk SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy ResourcesDocument69 pagesEnergy Resourcesluisa bautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- G. Tyler Miller's Living in The Environment 14 EditionDocument92 pagesG. Tyler Miller's Living in The Environment 14 EditionjyotiangelPas encore d'évaluation
- CeramicsDocument31 pagesCeramicsMuhammad FakhruddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Led PresentationDocument28 pagesLed PresentationhemadribabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Young Innovators Program 2022: Greenhouse Gas Artificial PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesYoung Innovators Program 2022: Greenhouse Gas Artificial Photosynthesisneetus creationPas encore d'évaluation
- The Way China Generates Electricity: Frank WangDocument6 pagesThe Way China Generates Electricity: Frank Wangqtkxbk8s56Pas encore d'évaluation
- Combine Heat & Powerplant.Document3 pagesCombine Heat & Powerplant.UsmanKhanPas encore d'évaluation
- EEE NotesDocument7 pagesEEE Notesrayyanop2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module - 1 NotesDocument20 pagesModule - 1 NotesSpoorthiPas encore d'évaluation
- OverviewDocument17 pagesOverviewbillPas encore d'évaluation
- Anshul Gour 19210132 Group C M.Tech 1 Year (Mechanical Engineering)Document1 pageAnshul Gour 19210132 Group C M.Tech 1 Year (Mechanical Engineering)Anshul GourPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Hydrogen Energy StationDocument2 pagesRenewable Hydrogen Energy StationRadu Victor TapuPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Conventional Source of EnergyDocument36 pagesNon-Conventional Source of EnergyaslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Suited Energy Source For The Current or Future Society by Engr. Majid AliDocument22 pagesSuited Energy Source For The Current or Future Society by Engr. Majid AliEngr Majid Ali BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementD'EverandClean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementPas encore d'évaluation
- Clean Energy Catalyst: Green Hydrogen Revolutionizing RefiningD'EverandClean Energy Catalyst: Green Hydrogen Revolutionizing RefiningPas encore d'évaluation
- Ozone AssignmentDocument3 pagesOzone Assignmentapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apes in A Box - Soil Profile and Soil TriangleDocument1 pageApes in A Box - Soil Profile and Soil Triangleapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Rise of Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Rise of Renewable Energyapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Oceans and WeatherDocument2 pagesThe Oceans and Weatherapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apes in A Box - Fossil FuelsDocument2 pagesApes in A Box - Fossil Fuelsapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phosphorus ArticleDocument2 pagesPhosphorus Articleapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cafo Contamination Case StudyDocument2 pagesCafo Contamination Case Studyapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Should We Grow GM CropsDocument1 pageShould We Grow GM Cropsapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apes in A Box - Fossil FuelsDocument2 pagesApes in A Box - Fossil Fuelsapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Harvest of Fear Guided ViewingDocument4 pagesHarvest of Fear Guided Viewingapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water SampleDocument1 pageWater Sampleapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apes in A Box - Ipm and BPCDocument2 pagesApes in A Box - Ipm and BPCapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- AnwrDocument2 pagesAnwrapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14-15Document5 pagesChapter 14-15api-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Melissa - ApesDocument3 pagesMelissa - Apesapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bubbles Data TableDocument1 pageBubbles Data Tableapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- TemperatureDocument1 pageTemperatureapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Easter Island Vs LoraxDocument2 pagesEaster Island Vs Loraxapi-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Epson 006Document4 pagesEpson 006api-235634024Pas encore d'évaluation
- VISCOSITY CLASSIFICATION GUIDE FOR INDUSTRIAL LUBRICANTSDocument8 pagesVISCOSITY CLASSIFICATION GUIDE FOR INDUSTRIAL LUBRICANTSFrancisco TipanPas encore d'évaluation
- Homer Christensen ResumeDocument4 pagesHomer Christensen ResumeR. N. Homer Christensen - Inish Icaro KiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ds 3805Document4 pagesDs 3805sparky2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate GovernanceDocument35 pagesCorporate GovernanceshrikirajPas encore d'évaluation
- Country Profile - NigerDocument1 pageCountry Profile - Nigernana kayPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniotic Membrane in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument13 pagesAmniotic Membrane in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgerySooraj SPas encore d'évaluation
- 114 ArDocument254 pages114 ArJothishPas encore d'évaluation
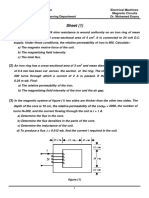
- Sheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMDocument2 pagesSheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMKhalifa MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan 12 Climate ChangeDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 12 Climate ChangeRey Bello MalicayPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Validation and Verification - BBC BitsizeDocument56 pagesData Validation and Verification - BBC BitsizeluciferothegoatPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Theory - BASICS - : By: Mr. Vinod SalunkheDocument17 pagesNetwork Theory - BASICS - : By: Mr. Vinod Salunkhevinod SALUNKHEPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Tools Cutting FluidsDocument133 pagesMachine Tools Cutting FluidsDamodara MadhukarPas encore d'évaluation
- BL3B User Manual PDFDocument142 pagesBL3B User Manual PDFRandy VanegasPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Beyond PDFDocument5 pagesEarth and Beyond PDFNithyananda Prabhu100% (1)
- SRC400C Rough-Terrain Crane 40 Ton Lifting CapacityDocument1 pageSRC400C Rough-Terrain Crane 40 Ton Lifting CapacityStephen LowPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment Vit CDocument4 pagesExperiment Vit CinadirahPas encore d'évaluation
- List of StateDocument5 pagesList of StatedrpauliPas encore d'évaluation
- Relation of Jurisprudence With Other Social Sciences - LLB NotesDocument4 pagesRelation of Jurisprudence With Other Social Sciences - LLB NotesPranjaliBawanePas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Steel Structures Handout 2012-2013Document3 pagesDesign of Steel Structures Handout 2012-2013Tushar Gupta100% (1)
- Beyond B2 English CourseDocument1 pageBeyond B2 English Coursecarlitos_coolPas encore d'évaluation
- WCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Document211 pagesWCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Antonio VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity2 Mba 302Document2 pagesActivity2 Mba 302Juan PasyalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ace3 1122.03 GB PDFDocument16 pagesAce3 1122.03 GB PDFArpit VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Indications, Treatment and Current PracticeDocument14 pagesClinical Indications, Treatment and Current PracticefadmayulianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bikini - USA - 03.2017Document68 pagesBikini - USA - 03.2017OvidiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Where Are The Women in The Water Pipeline? Wading Out of The Shallows - Women and Water Leadership in GeorgiaDocument7 pagesWhere Are The Women in The Water Pipeline? Wading Out of The Shallows - Women and Water Leadership in GeorgiaADBGADPas encore d'évaluation
- Women Safety AppDocument18 pagesWomen Safety AppVinod BawanePas encore d'évaluation
- Contract To Sell LansanganDocument2 pagesContract To Sell LansanganTet BuanPas encore d'évaluation