Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
HT Assgnmnt 2
Transféré par
Tamoor TariqDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HT Assgnmnt 2
Transféré par
Tamoor TariqDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Enlist at least six REASONS FOR INSULATING AN OBJECT with brief description.
1. Cothing:
Clothing is a thermal insulator which is chosen to maintain the temperature of the human
body.
2. Home Insulation:
Maintaining acceptable temperatures in buildings (by heating and cooling) uses a large
proportion of global energy consumption therefore A home insulated with fiber glass, rock
wool, and slag wool insulation is one of the most cost-effective ways of saving energy and
reducing heating and cooling bills
3. Reducing Noise in Buildings:
Many forms of thermal insulation also reduce noise and vibration, both coming from the
outside and from other rooms inside a building, thus producing a more comfortable
environment.
4. Internal Combustion Engines:
Internal combustion engines produce a lot of heat during their combustion cycle. This can
have a negative effect when it reaches various heat-sensitive components such as sensors,
batteries and starter motors. That is why thermal insulation is used to prevent the heat
from the exhaust reaching these components. Insulation is also used to increase the
performance of an engine.
5. Piping and Equipment Insulation:
Insulating piping and equipment in commercial, institutional, and industrial facilities with fiber
glass, rock wool, and slag wool insulation systems is the easiest and most cost-effective way to
conserve energy, save money, and preserve the environment.
6.HVAC Insulation:
Fiber glass has been used as thermal and acoustical insulation in forced air heating, ventilating,
and air-conditioning systems
6. Electrical Wires:
Materials such as plastics do not allow electrons to flow through them. That is why they are
use as insulators on electrical wires which provide protection between electrical current and
you.
Heat transfer is the movement of heat from a hotter object to a colder object. Heat itself is
how we experience molecular vibrations. Faster vibrations feel hotter to the touch. There
are three kinds of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is
transfer by contact. Convection involves the flowing of a fluid that carries the heat.
Radiation refers to electromagnetic radiation, such as visible light and infrared.
1. Conduction
o Conduction is heat transfer by touch. Examples include heating a pot on an electric stove
and cooling red-hot metal by dipping it in liquid water. A subtler example is the use of a fan
to cool off. Specifically, a layer of warmed air builds on our skin due to our body
temperature. A fan pushes that layer away to be replaced with a lower temperature of air,
making us feel cooler.
Convection
o Convection involves the movement of a fluid to transfer its heat energy content. Examples
include blowing on your hands in winter to warm them and warming something by fire.
Since fire is hot gas, it carries heat with it, then transfers the heat by conduction to objects
with which it makes contact. Convection prevention is the basis of wearing multiple layers of
clothes in the winter to keep warm.
Another interesting example is to leave chocolate in a bag in the sun. The inside heats up
because the heated air cannot escape, and will soften and even melt the chocolate. This can
be problematic if the chocolate is left in a handbag on a sunny day!
o Sponsored Links
Heating Processes
Single-Purpose Fluids to +650F Cooling-Heating Fluids to -127F
www.paratherm.com/fluids
Radiation
o Most terrestrial objects radiate in the infrared range. Cooler stars radiate in a fairly even
mix of infrared and visible light. The Sun radiates largely in the visible range, with a surface
temperature of about 6,000 K. Heated objects, such as in a light bulb or oven or forge
(where metal is melted), also glow in the visible range from heat radiation.
When sunlight comes in through a window, the glass is transparent to the visible light. The
light hits the objects inside, warming them. The objects then re-reradiate heat energy, but at
a much lower energy of wavelength, i.e. infrared. The infrared doesn't escape through the
glass, which is opaque to infrared.
Difference in Rates of Transfer
o The greater the difference in temperature between two objects in contact, the faster the rate
of heat transfer by conduction. In the fan example above, running the fan in a room where
the ambient temperature is close to body temperature will not feel very cool. The rate of
heat transfer between the skin and the fan-blown air is too low to feel relief. Only by blowing
away sweat does a fan give benefit at temperatures above 98.6C.
Because hot gases rise (because the faster gas molecules are the ones with enough energy to
reach higher altitudes), conduction happens more quickly vertically than horizontally.
Therefore, horizontal convection, such as air conditioning, sometimes benefits from
assistance from forced convection, such as use of a fan.
The rate of heat transfer by radiation depends on the radiating object's temperature. At high
temperatures, the rate of transfer is high, and not just because the radiated photons have
greater energy. Therefore, at terrestrial temperatures, radiation is generally the slowest heat
transfer method.
Read more: http://www.ehow.com/about_5314809_example-heat-transfer.html#ixzz2zMxCH49i
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter Nine Class 9thDocument10 pagesChapter Nine Class 9thShahbaz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental Questions:: Heat, The Ultimate Form of EnergyDocument12 pagesFundamental Questions:: Heat, The Ultimate Form of EnergyMohd HaniffPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 2: 1. Read Baka Makatulong Lang Kaso Hindi Ito Ung SagotDocument15 pagesExperiment 2: 1. Read Baka Makatulong Lang Kaso Hindi Ito Ung SagotPrincess Diane PalisocPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics EssayDocument1 pagePhysics EssayJLLOW GtPas encore d'évaluation
- ACTIVIDAD DE CIENCIA DE LOS MATERIALES - Ingles y Español - Jose Daniel BallestasDocument15 pagesACTIVIDAD DE CIENCIA DE LOS MATERIALES - Ingles y Español - Jose Daniel BallestasJose Daniel BallestasPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.this Is Due To Conduction.Document2 pages4.this Is Due To Conduction.shaymoon tanmoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer in The AtmosphereDocument21 pagesHeat Transfer in The Atmosphereesthy angeliaPas encore d'évaluation
- تقرير مادة الفيزياء التطبيقيةDocument15 pagesتقرير مادة الفيزياء التطبيقيةHayder AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Temperature Control & VentilationDocument30 pagesTemperature Control & VentilationAssasia HydePas encore d'évaluation
- SampleDocument14 pagesSampleShaashiniPas encore d'évaluation
- RadiationDocument45 pagesRadiationLinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 14-Revision Heat TransferDocument23 pages14-Revision Heat TransferYuichi AkasakaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.3 - Transfer of Thermal Energy - Physics With MR Shone 2Document6 pages10.3 - Transfer of Thermal Energy - Physics With MR Shone 2xinyi chanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kavita - Int Sci Heat TransferDocument10 pagesKavita - Int Sci Heat Transfer27h4fbvsy8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Audit: Unit - 2Document61 pagesEnergy Audit: Unit - 2Nikhil TiruvaipatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics About InsulationDocument17 pagesBasics About InsulationBalakumar100% (1)
- Flow of Heat Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesFlow of Heat Question and AnswersKunal SumukPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP 9 Science EssayDocument4 pagesCHP 9 Science EssayDiya VaswaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Selection of Insulation Material: What Is Thermal Insulation?Document14 pagesSelection of Insulation Material: What Is Thermal Insulation?VenkatThiruvengadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer ApplicationsDocument68 pagesHeat Transfer Applicationssangeet khulePas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis and Design of Cooling Load With and Without Installation of Insulating MaterialDocument15 pagesAnalysis and Design of Cooling Load With and Without Installation of Insulating MaterialFaizan NazeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat and TemperatureDocument53 pagesHeat and Temperaturegeorgy shibuPas encore d'évaluation
- Copy and Fill in The Missing WordsDocument4 pagesCopy and Fill in The Missing WordsSydney LezamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation ProcessesDocument20 pagesRadiation ProcessesAnmol MalgotraPas encore d'évaluation
- S5 Physics Revision NotesDocument40 pagesS5 Physics Revision NotesLibertyTong100% (1)
- 5054 Handouts Topic-9 Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument8 pages5054 Handouts Topic-9 Transfer of Thermal EnergyShehzad EhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Petit Seminaire Higher Sec School-Puducherry: Lesson-6 Heat and TemperatureDocument3 pagesPetit Seminaire Higher Sec School-Puducherry: Lesson-6 Heat and TemperaturemfvibhinjoshuahPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Joules Pound Fahrenheit SI: What Do You Understand by Insulation ?Document5 pagesWork Joules Pound Fahrenheit SI: What Do You Understand by Insulation ?Tanvi RanePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Heat TransferDocument3 pages1 Heat TransferAdam HartmannPas encore d'évaluation
- Father Agnel School, Noida Assignment Class Vii Ch-HeatDocument13 pagesFather Agnel School, Noida Assignment Class Vii Ch-HeatDeepak KansalPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.2 Heat TransferDocument5 pages11.2 Heat TransferCoolman PoonPas encore d'évaluation
- How Heat Is Produced: 4 Grade ScienceDocument20 pagesHow Heat Is Produced: 4 Grade Sciencenoman turkPas encore d'évaluation
- Crammer Powerpoint p1Document35 pagesCrammer Powerpoint p1Mrs S Baker100% (1)
- 07-08 S5 Physics Revision NotesDocument42 pages07-08 S5 Physics Revision NotesChan Yam PangPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation PDFDocument4 pagesRadiation PDFTahmeed AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat: - : Types of ThermometersDocument3 pagesHeat: - : Types of ThermometersSweet HomePas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Human ComfortDocument8 pagesReport On Human ComfortBrijesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Thermal Effects in BuildingsDocument46 pages1 - Thermal Effects in BuildingsNazim UddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter #12: Air ConditionDocument31 pagesChapter #12: Air ConditionM.IDREES KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Infrared RadiatorDocument13 pagesResearch Infrared Radiatormonther alsharifPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 7 - Heat NotesDocument3 pagesClass 7 - Heat NotesAditya TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-15 Thermal EnergyDocument8 pagesChapter-15 Thermal Energyananafra861Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermoregulation: How The Body Loses HeatDocument10 pagesThermoregulation: How The Body Loses Heatvishal pundirPas encore d'évaluation
- Igcse 42 ThermalenergyDocument43 pagesIgcse 42 ThermalenergyHany ElGezawy75% (4)
- Basics of Building Heating and CoolingDocument4 pagesBasics of Building Heating and CoolingVgie QuanicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Class VII I.I.T.foundation, N.T.S.E.& Science Olympiad Curriculum & Chapter NotesDocument107 pagesClass VII I.I.T.foundation, N.T.S.E.& Science Olympiad Curriculum & Chapter Notesspatel197250% (2)
- Ch-13 (Limit and Derivatives FINAL 02.01.06)Document9 pagesCh-13 (Limit and Derivatives FINAL 02.01.06)AnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Jsunil: Jsunil Tutorial, Samastipur PH: 9835859669Document6 pagesJsunil: Jsunil Tutorial, Samastipur PH: 9835859669ravilullaPas encore d'évaluation
- How Things Work: What Is Heat?Document7 pagesHow Things Work: What Is Heat?ChyNaluri89Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3 Thermal ProcessesDocument6 pages2.3 Thermal ProcesseshaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- David Physics s3Document12 pagesDavid Physics s3RUKUNDO OlivePas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledCABALIDA, FELICITY H.Pas encore d'évaluation
- AbsorberDocument9 pagesAbsorbermPas encore d'évaluation
- P2 Energy Transfer by HeatingDocument1 pageP2 Energy Transfer by HeatingArun DontePas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Chapter-10: Answer To The Short QuestionsDocument18 pagesHeat Chapter-10: Answer To The Short QuestionsG M Ali KawsarPas encore d'évaluation
- Temperature and HeatDocument25 pagesTemperature and HeatAlessandro YumangPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer ANTONIO VIDA VDocument40 pagesHeat Transfer ANTONIO VIDA Vshahanajmunni178Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advancement in Thermal Energy in Convention Devices: Submitted byDocument16 pagesAdvancement in Thermal Energy in Convention Devices: Submitted byhanuanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningD'EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Biofuel GasificationDocument60 pagesBiofuel GasificationTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Acre MSC Part 8 13 Mar 2014Document2 pagesAcre MSC Part 8 13 Mar 2014Tamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Acre MSC Part 9 12 Mar 2014Document17 pagesAcre MSC Part 9 12 Mar 2014Tamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- PC 2009 Powder Coating GlossaryDocument2 pagesPC 2009 Powder Coating GlossaryTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Acre MSC Part 7 06 Mar 2014Document25 pagesAcre MSC Part 7 06 Mar 2014Tamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Acre MSC Part 5 27 Feb 2014Document16 pagesAcre MSC Part 5 27 Feb 2014Tamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Usman 2011Document9 pagesUsman 2011Tamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Coreconceptsofbiochemicalengineering1 150509053327 Lva1 App6891Document120 pagesCoreconceptsofbiochemicalengineering1 150509053327 Lva1 App6891Tamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Acre MSC Part 6 05 Mar 2014Document17 pagesAcre MSC Part 6 05 Mar 2014Tamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact Factor: Formula For CalculationDocument4 pagesImpact Factor: Formula For CalculationTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Methodology: MajidDocument17 pagesResearch Methodology: MajidTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Experiments by Dr. Majid Majeed Akbar: Institute of Chemical Engineering & Technology University of The PunjabDocument19 pagesDesign of Experiments by Dr. Majid Majeed Akbar: Institute of Chemical Engineering & Technology University of The PunjabTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Methdology: Dr. Majid Majeed AkbarDocument11 pagesResearch Methdology: Dr. Majid Majeed AkbarTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Methodology: Dr. Majid Majeed AkbarDocument17 pagesResearch Methodology: Dr. Majid Majeed AkbarTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of BiochemistryDocument37 pagesFundamentals of BiochemistryTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Interdisciplinary Approach To BioprocessingDocument9 pagesInterdisciplinary Approach To BioprocessingTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Generalized View of BioprocessDocument20 pagesGeneralized View of BioprocessTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology, Bio-Processing Engineering and Biochemical EngineeringDocument6 pagesBiotechnology, Bio-Processing Engineering and Biochemical EngineeringTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
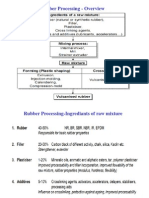
- Rubber Processing - OverviewDocument11 pagesRubber Processing - OverviewTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- API-The Nature of HeatDocument123 pagesAPI-The Nature of HeatTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture-4 Risk Assessment and SafetyDocument49 pagesLecture-4 Risk Assessment and SafetyTamoor TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum Testing Lab ManualDocument59 pagesPetroleum Testing Lab ManualHari_Kumar_143494% (33)
- Report - Fostering The Railway Sector Through The European Green Deal PDFDocument43 pagesReport - Fostering The Railway Sector Through The European Green Deal PDFÁdámHegyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence and Parametric Construction Cost Estimate Modeling State-of-The-Art ReviewDocument31 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Parametric Construction Cost Estimate Modeling State-of-The-Art ReviewmrvictormrrrPas encore d'évaluation
- Ferrovial / BAA - A Transforming Acquisition: 3rd July 2006Document38 pagesFerrovial / BAA - A Transforming Acquisition: 3rd July 2006Andrew YangPas encore d'évaluation
- General Director AdDocument1 pageGeneral Director Adapi-690640369Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rules and Regulations of Asian Parliamentary Debating FormatDocument2 pagesRules and Regulations of Asian Parliamentary Debating FormatmahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Slope Stability Analysis Using FlacDocument17 pagesSlope Stability Analysis Using FlacSudarshan Barole100% (1)
- Serious Game Overview PDFDocument28 pagesSerious Game Overview PDFjuanan.peterPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex-Capt. Harish Uppal Vs Union of India & Anr On 17 December, 2002Document20 pagesEx-Capt. Harish Uppal Vs Union of India & Anr On 17 December, 2002vivek6593Pas encore d'évaluation
- GDN-206 - Guidelines On Safety Management System in Petroleum IndustryDocument49 pagesGDN-206 - Guidelines On Safety Management System in Petroleum IndustrykarpanaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Python BarchartDocument34 pagesPython BarchartSeow Khaiwen KhaiwenPas encore d'évaluation
- Moeller Vol07 - Tab02 Signal Tower PDFDocument46 pagesMoeller Vol07 - Tab02 Signal Tower PDFArga WahyumiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- TCO & TCU Series Container Lifting Lugs - Intercon EnterprisesDocument4 pagesTCO & TCU Series Container Lifting Lugs - Intercon EnterprisesReda ElawadyPas encore d'évaluation
- Taiwan Petroleum Facilities (1945)Document85 pagesTaiwan Petroleum Facilities (1945)CAP History LibraryPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling Gas Compressor: Cable ListDocument4 pagesCooling Gas Compressor: Cable ListHaitham YoussefPas encore d'évaluation
- The Application of A Continuous Strip of Woven Material To A Body PartDocument15 pagesThe Application of A Continuous Strip of Woven Material To A Body Partczeremar chanPas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota Auris Corolla 2007 2013 Electrical Wiring DiagramDocument22 pagesToyota Auris Corolla 2007 2013 Electrical Wiring Diagrampriscillasalas040195ori100% (125)
- Electric Baseboard StelproDocument4 pagesElectric Baseboard StelprojrodPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To AccountingDocument36 pagesIntroduction To AccountingRajnikant PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Arab Open University B326: Advanced Financial Accounting TMA - Spring 2022-2023 V2Document7 pagesArab Open University B326: Advanced Financial Accounting TMA - Spring 2022-2023 V2samiaPas encore d'évaluation
- DefinitionDocument6 pagesDefinitionRatul HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Shubham Devnani DM21A61 FintechDocument7 pagesShubham Devnani DM21A61 FintechShubham DevnaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Flow ProfileDocument5 pagesWind Flow ProfileAhamed HussanPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions For Comprehensive Exams NovemberDocument2 pagesInstructions For Comprehensive Exams Novembermanoj reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- DOL, Rotor Resistance and Star To Delta StarterDocument8 pagesDOL, Rotor Resistance and Star To Delta StarterRAMAKRISHNA PRABU GPas encore d'évaluation
- Borang Pengesahan PembetulanDocument7 pagesBorang Pengesahan PembetulanARMIZAWANI BINTI MOHAMED BUANG (KMPH)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pace 349 ScheduleDocument3 pagesPace 349 Schedulesaxman011100% (1)
- X25Document10 pagesX25RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Autonics KRN1000 DatasheetDocument14 pagesAutonics KRN1000 DatasheetAditia Dwi SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- 1178-Addendum-Change in Sponsor - HDFC LTD To HDFC Bank - July 1, 2023Document3 pages1178-Addendum-Change in Sponsor - HDFC LTD To HDFC Bank - July 1, 2023Jai Shree Ambe EnterprisesPas encore d'évaluation
- Muster List: Vessel: M/T "Stena President" Call Sign: ZCDR6 Master: YURIY YASHINDocument9 pagesMuster List: Vessel: M/T "Stena President" Call Sign: ZCDR6 Master: YURIY YASHINwwaallPas encore d'évaluation