Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
VJC H2 Math P2
Transféré par
jimmytanlimlongTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
VJC H2 Math P2
Transféré par
jimmytanlimlongDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2
Section A: Pure Mathematics [40 marks]
1 The equations of 3 planes p
1
, p
2
and p
3
are given by
2x 2y 3z = 5,
5x 5y 4z = 2,
x + 2y +5z =
respectively.
(i) Find a vector equation of the line of intersection between p
1
and p
2
. [2]
(ii) Given that the 3 planes intersect in a line, find the values of and . [3]
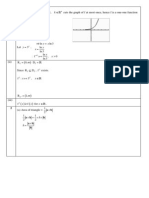
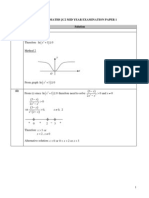
2 The equation of a curve C is
2
2
( )
, 0 1.
4
x a
y a
x
+
= < <
(i) Write down the equations of any asymptotes of C. [2]
(ii) Find, in terms of a, the coordinates of any stationary points of C. [4]
(iii) Sketch C. [2]
3 A Global Positioning System (GPS) tracks the movement of a bullet train from point A to
point B using a Cartesian graph with A as the origin. The point (x, y) represents the
position of the train t hours after leaving A, where x hundred km is the distance travelled
in the east direction and y hundred km is the distance travelled in the north direction.
It is found that
2
2
d
sec tan
d
x
t t
t
= and
4
t
hours after the train has left A, ln(1 2). x = +
Solve the differential equation. [3]
Given further that
1
d 1
d tan
y
t y
= and B is 2 hundred km north of A, find the coordinates of
the point in the Cartesian graph that represents B. [5]
4 A graphic calculator is not to be used in answering this question.
Verify that
( )( )
( )
2 2 i i
e e 2 cos
-
z r z r z r z r
u u
u = + . [1]
Solve the equation
6
1
64
z = , expressing the solutions in the form
i
e r
u
, where 0 r > and
t u t < , giving u in exact form. [4]
Hence, or otherwise, express
6
64 1 z + as the product of three quadratic factors with real
coefficients, giving each factor in exact and non-trigonometrical form. [4]
3
5 The functions f and g are defined as follows.
2 1
f : e , 0,
2
x
x x s
1
g : ln(2 ), .
2
x x x >
(i) State, giving a reason, why
1
f
exists and find
1
f ( ). x
[4]
(ii) Determine the domain of
1
g
. [1]
(iii) Show that composite function gf exists, and find the values of such that
2
gf ( ) . = [5]
Section B: Probability and Statistics [60 marks]
6 The events A and B are such that
2
P( )
3
A = ,
4
P( | )
7
A B = and
1
P( | ' ) .
3
B A =
Find
(i) P( ), A B
[3]
(ii) P( ). A B [3]
7 Research shows that children are less likely to develop myopia if they spend at least 14
hours a week outdoors.
See Bak suspects the mean time that children in Singapore spend outdoors is less than 14
hours a week. To verify this, he randomly selected 36 children and found out how much
time they spent outdoors the previous week. The results are summarized as follows.
2
( 14) 3.9 and ( 14) 2.7, x x = =
where x hours is the amount of time each child spent outdoors the previous week.
Assuming that the time spent outdoors each week by children in Singapore is normally
distributed,
(i) test See Baks suspicion at the 5% level of significance, stating clearly the
hypotheses used, [5]
(ii) find the range of values of the sample mean of 36 children such that See Baks
suspicion will be supported, at the 5% significance level, if the standard deviation of
the time spent outdoors each week for children in Singapore is known to be 0.3 hours.
[3]
[Turn over
4
8 Men and children staying in a particular hotel have masses, in kg, that are normally
distributed with means and standard deviations as shown in the following table. Their
masses are independent of each other.
Mean mass (kg) Standard deviation (kg)
Men 68 10
Children 20 5
(i) A man and a child are randomly chosen from the hotel. Find the probability that the
mass of the man is less than three times the mass of the child. [2]
(ii) Two men and three children are randomly chosen from the hotel. Find the
probability that their average mass will lie within 60 kg from 100 kg. [3]
The safety limit of a hotel lift is 600 kg.
(iii) Nine men are chosen at random from the hotel. Find the probability that their total
mass exceeds the safety limit. [2]
(iv) Nine men from the hotel enter the lift, at a time when a large number of sumo
wrestlers are staying at the hotel. Give one reason why the probability that their total
mass exceeds the safety limit may be different from the value calculated in part (iii).
[1]
9 The Art Club of a certain school consists of 10 members, of whom 2 are from the IP 1
level, 2 are from the IP 2 level, 3 are from the JC 1 level and 3 are from the JC 2 level.
They have to take a group photo for the school magazine.
Find the number of ways of taking the photograph if all the members are to stand
(i) in a row such that the 2 IP 1 members are together and no JC 2 members are
together, [2]
(ii) in 2 equal rows, 1 row in front of the other, such that the 4 IP members are at the 4
corners. [2]
After the photo shoot, all the members went to the Art Room and sat at a round table.
Find the probability that the 2 IP 1 members are seated together. [2]
5
10 Nine healthy male recruits from an army camp were selected at random. The ratio x of the
length of the ring finger to that of the index finger was measured. A blood test was
conducted to determine their testosterone level, y ng/dl. The results are shown in the
following table.
x 0.97 0.98 0.99 1.01 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.07 1.08
y 260 321 456 599 630 696 787 881 1000
(i) Explain what is meant by at random within the context of the question. [1]
(ii) Calculate the product moment correlation coefficient between x and y and sketch a
scatter diagram for the data. Hence explain, with supporting reasons, how the ratio
of the length of the ring finger to that of the index finger and the testosterone level
are correlated. [4]
(iii) Estimate the testosterone level when the ratio is 0.95 and explain, with a reason, if
this estimate is valid. [2]
(iv) State the equation of the least squares regression line used in estimating the ratio
when the testosterone level is given. [1]
(v) Explain why it is not valid to conclude that a higher ratio of the length of the ring
finger to that of the index finger will cause the testosterone level in the blood to be
higher. [1]
11 In a certain factory, it is known that 100p% of all articles produced are defective.
(i) 10 articles are randomly selected. Find, in terms of p, the probability that there are
not more than 1 defective article, leaving your answer in factorised form. [2]
(ii) Assuming now that p = 0.1, 60 random samples, each of size 10, are drawn.
(a) Using a suitable approximation, find the probability that less than 53 samples
will each contain not more than 2 defective articles. [5]
(b) Find the probability that the sum of the defective articles in these samples
exceeds 80. [3]
[Turn over
6
12 The number of customers arriving at a service counter of bank A and the number of
customers arriving at a service counter of bank B are recorded separately. It is found that,
on average, 4 customers arrived at the service counter of bank A in an hour and 2
customers arrived at the service counter of bank B in an hour. The number of customers
arriving at the service counter of bank A is independent of the number of customers
arriving at the service counter of bank B.
(i) Find the probability that there are at least 8 customers arriving at the service
counters of both banks in one hour. [2]
(ii) Using a normal approximation, find the maximum value of n, correct to 1 decimal
place, such that the probability that there are at least 45 customers arriving at the
service counter of bank A is less than 0.01 over a period of 2n hours. [7]
(iii) Suppose that there are 7 service counters in Bank A and the numbers of customers
arriving at these service counters are independent of each other. Find the probability
that there are more than 2 but not more than 6 service counters with at least 4
customers arriving at each counter in an hour. [4]
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- AJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P2Document6 pagesAJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P2nej200695Pas encore d'évaluation
- TPJC Prelim H2 Paper2Document7 pagesTPJC Prelim H2 Paper2Wei Qin Ashleigh Lim0% (1)
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Hci Prelim p2Document6 pages2014 Hci Prelim p2Chia Pei XianPas encore d'évaluation
- Section A: Pure Mathematics (40 Marks) 1 Given: y y y X y y yDocument4 pagesSection A: Pure Mathematics (40 Marks) 1 Given: y y y X y y yjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 Mathematics HCI Prelim Paper 2Document5 pages2011 Mathematics HCI Prelim Paper 2ShaphynaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nanyang Junior College 2008 Jc2 Preliminary ExaminationDocument5 pagesNanyang Junior College 2008 Jc2 Preliminary ExaminationkarpeoPas encore d'évaluation
- AJC H2Maths 2008 Prelim P2Document5 pagesAJC H2Maths 2008 Prelim P2junkgamePas encore d'évaluation
- Nyjc H2 Math P2Document6 pagesNyjc H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Hci H2 Math P2Document6 pagesHci H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Ajc H2 Math P2Document8 pagesAjc H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 AJC Paper 2Document5 pages2010 AJC Paper 2Fang Wen LimPas encore d'évaluation
- 15XD25Document3 pages15XD2520PW02 - AKASH APas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 VJC H1 Math PrelimDocument4 pages2010 VJC H1 Math PrelimPxtri FarainPas encore d'évaluation
- Ijc H2 Math P2Document5 pagesIjc H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Year End Exam Question Paper 2Document6 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Year End Exam Question Paper 2DKFBPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 A LevelsDocument8 pages2007 A LevelsKok Chee KeanPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC/2011 JC2 Preliminary Exam Paper 2/9740Document4 pagesMJC/2011 JC2 Preliminary Exam Paper 2/9740jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Y A X B: 2 Section A: Pure Mathematics (40 Marks)Document5 pagesY A X B: 2 Section A: Pure Mathematics (40 Marks)jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Catholic Junior College: MathematicsDocument4 pagesCatholic Junior College: MathematicskarpeoPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 2 (PCGHS)Document4 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 2 (PCGHS)HaRry ChgPas encore d'évaluation
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Question Paper 2Document6 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Question Paper 2ofji4oPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 7 Means 27 MPH 6 2 7 9 9 8 8 7 4 3 2 3 3 5 5 7 8 9 7 6 6 4 0 4 1 1 3 4 5 5 6 7 8 9 9 8 6 4 1 1 5 0 2 4 5 9 7 4 1 0 0 6 1 11 A.M. 4 3 7 8 A.MDocument4 pages2 7 Means 27 MPH 6 2 7 9 9 8 8 7 4 3 2 3 3 5 5 7 8 9 7 6 6 4 0 4 1 1 3 4 5 5 6 7 8 9 9 8 6 4 1 1 5 0 2 4 5 9 7 4 1 0 0 6 1 11 A.M. 4 3 7 8 A.MHANSPas encore d'évaluation
- IJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document8 pagesIJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Math PracticeDocument7 pagesH2 Math PracticePhoebe Heng100% (2)
- 6046 Q 1 SpecimenDocument8 pages6046 Q 1 SpecimenEmmanuel ChipemberePas encore d'évaluation
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- MATHEMATICS 9740/02: Catholic Junior College General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Higher 2Document6 pagesMATHEMATICS 9740/02: Catholic Junior College General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Higher 2nothingtodo1992Pas encore d'évaluation
- CJC - Maths 2008 JC2 H1 Prelim ExamDocument4 pagesCJC - Maths 2008 JC2 H1 Prelim Exam09S43 ASHLEY CHUA YI HENGPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC 2008 H1 PrelimsDocument14 pagesPJC 2008 H1 PrelimsChia Pei XianPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Business Mathematics For CmaDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Business Mathematics For CmaSujay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- HCI H1 2009 QuestionDocument8 pagesHCI H1 2009 QuestionpappadutPas encore d'évaluation
- 9ABS304 Probability & StatisticsDocument4 pages9ABS304 Probability & StatisticssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Yjc H2 Math P1Document6 pagesYjc H2 Math P1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - I Em4Document3 pagesAssignment - I Em4Chaitanya KapilaPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document10 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 3 Joh MuarDocument2 pages2020 3 Joh MuarQuah En YaoPas encore d'évaluation
- HKDSE Practice Paper 2012 Mathematics - Module 1Document18 pagesHKDSE Practice Paper 2012 Mathematics - Module 1LPlasticPas encore d'évaluation
- Institute of Actuaries of India: ExaminationsDocument7 pagesInstitute of Actuaries of India: Examinationspallab2110Pas encore d'évaluation
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document6 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Pan African University: Institute For Basic Sciences, Technology and InnovationDocument9 pagesPan African University: Institute For Basic Sciences, Technology and InnovationMarc MarinPas encore d'évaluation
- MTech QROR PQB 2018Document13 pagesMTech QROR PQB 2018Vikas PotluriPas encore d'évaluation
- RI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P1Document4 pagesRI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P1nej200695Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pahang STPM Trial Mathematics t2 EditedDocument4 pagesPahang STPM Trial Mathematics t2 Editedorchid3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Penang Chinese Girls 2013 M2 (Q)Document4 pagesPenang Chinese Girls 2013 M2 (Q)STPMmathsPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Worksheet Mathematics Class: VIII: Q Answer The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesRevision Worksheet Mathematics Class: VIII: Q Answer The Following Questionshiren30101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Statistic and PRO. B. E. (Civil IV - Computer - E&C VI)Document0 pageStatistic and PRO. B. E. (Civil IV - Computer - E&C VI)www.bhawesh.com.npPas encore d'évaluation
- P2 SMK Ampuan Durah SerembanDocument5 pagesP2 SMK Ampuan Durah SerembanmasyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 JC2 H1 Maths Yishun Junior CollegeDocument15 pages2015 JC2 H1 Maths Yishun Junior CollegeHANSPas encore d'évaluation
- Probability and Statistics Question BankDocument9 pagesProbability and Statistics Question BankMadhavRaoPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Common To ME, CSE, IT, MCT, AME, MIE)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Common To ME, CSE, IT, MCT, AME, MIE)Abishek GoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion BankDiya SananPas encore d'évaluation
- MTC2 Seminar Questions 2022-1Document6 pagesMTC2 Seminar Questions 2022-1Majanga JohnnyPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 2 (SMJK Sam Tet Ipoh)Document4 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 2 (SMJK Sam Tet Ipoh)Jessica JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Section B AnsDocument7 pagesSection B AnsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- J1 Lecture - Technology Part 1 - 2aDocument8 pagesJ1 Lecture - Technology Part 1 - 2ajimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Which of The Following Equations Is Correct? (A) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/s (B) 8 J 2 KG × (2 M/S) (C) 8 J 2 KG × 2 (M/S) (D) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/sDocument1 pageWhich of The Following Equations Is Correct? (A) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/s (B) 8 J 2 KG × (2 M/S) (C) 8 J 2 KG × 2 (M/S) (D) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/sjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 NJC H2 Econs Paper 2 (Answers)Document34 pages2013 NJC H2 Econs Paper 2 (Answers)jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesTJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2Document15 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument13 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1Document18 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document11 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document10 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document10 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document7 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document6 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document7 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlong0% (1)
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument10 pagesNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- IJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document8 pagesIJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1Document8 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document10 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- How Is Extra-Musical Meaning Possible - Music As A Place and Space For Work - T. DeNora (1986)Document12 pagesHow Is Extra-Musical Meaning Possible - Music As A Place and Space For Work - T. DeNora (1986)vladvaidean100% (1)
- Mathematics Trial SPM 2015 P2 Bahagian BDocument2 pagesMathematics Trial SPM 2015 P2 Bahagian BPauling ChiaPas encore d'évaluation
- WHAT - IS - SOCIOLOGY (1) (Repaired)Document23 pagesWHAT - IS - SOCIOLOGY (1) (Repaired)Sarthika Singhal Sarthika SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 12 NotesIvanTh3Great100% (6)
- EIS Summary NotsDocument62 pagesEIS Summary NotsKESHAV DroliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stockholm KammarbrassDocument20 pagesStockholm KammarbrassManuel CoitoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1027 12Document3 pages1027 12RuthAnayaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Biofloc Technology (BFT) Water Quality, Biofloc Composition, and GrowthDocument8 pagesThe Biofloc Technology (BFT) Water Quality, Biofloc Composition, and GrowthHafez MabroukPas encore d'évaluation
- From Jest To Earnest by Roe, Edward Payson, 1838-1888Document277 pagesFrom Jest To Earnest by Roe, Edward Payson, 1838-1888Gutenberg.org100% (1)
- Level 5 - LFH 6-10 SepDocument14 pagesLevel 5 - LFH 6-10 SepJanna GunioPas encore d'évaluation
- Pagan and Wiccan Quotes and GuidanceDocument8 pagesPagan and Wiccan Quotes and GuidanceStinkyBooPas encore d'évaluation
- Contract of PledgeDocument4 pagesContract of Pledgeshreya patilPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus For B.A. (Philosophy) Semester-Wise Titles of The Papers in BA (Philosophy)Document26 pagesSyllabus For B.A. (Philosophy) Semester-Wise Titles of The Papers in BA (Philosophy)Ayan AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Right Hand Man LyricsDocument11 pagesRight Hand Man LyricsSteph CollierPas encore d'évaluation
- Jake Atlas Extract 2Document25 pagesJake Atlas Extract 2Walker BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor Banks in Power System Part FourDocument4 pagesCapacitor Banks in Power System Part FourTigrillo100% (1)
- Introduction To Public HealthDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Public HealthKristelle Marie Enanoria Bardon50% (2)
- The Cognitive Enterprise For HCM in Retail Powered by Ibm and Oracle - 46027146USENDocument29 pagesThe Cognitive Enterprise For HCM in Retail Powered by Ibm and Oracle - 46027146USENByte MePas encore d'évaluation
- The Gower Handbook of Project Management: Part 1: ProjectsDocument2 pagesThe Gower Handbook of Project Management: Part 1: ProjectschineduPas encore d'évaluation
- MPCDocument193 pagesMPCpbaculimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Past TenselDocument3 pagesSimple Past TenselPutra ViskellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Faith-Based Organisational Development (OD) With Churches in MalawiDocument10 pagesFaith-Based Organisational Development (OD) With Churches in MalawiTransbugoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Easter in RomaniaDocument5 pagesEaster in RomaniaDragos IonutPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathfinder CharacterSheet.1.8InterActiveDocument3 pagesPathfinder CharacterSheet.1.8InterActiveJessica AlvisPas encore d'évaluation
- D5 PROF. ED in Mastery Learning The DefinitionDocument12 pagesD5 PROF. ED in Mastery Learning The DefinitionMarrah TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Awareness CompetencyDocument30 pagesSocial Awareness CompetencyudaykumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Claribel Ria MaeDocument19 pagesClaribel Ria MaeGLENN MENDOZAPas encore d'évaluation
- A New Cloud Computing Governance Framework PDFDocument8 pagesA New Cloud Computing Governance Framework PDFMustafa Al HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Far Eastern University-Institute of Nursing In-House NursingDocument25 pagesFar Eastern University-Institute of Nursing In-House Nursingjonasdelacruz1111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Los Documentos de La Dictadura Que Entregó Estados Unidos (Parte 2)Document375 pagesLos Documentos de La Dictadura Que Entregó Estados Unidos (Parte 2)Todo NoticiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)D'EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsD'EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryD'EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeD'EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.D'EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormD'EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeD'EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersD'EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingD'EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathD'EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)