Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
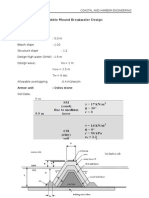
Riprap Sizing
Transféré par
zulkifli1220Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Riprap Sizing
Transféré par
zulkifli1220Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
d
50
(m) d
50
(ft) d
50
(in)
Maynord 0.03 0.09 1.12
USACOE (1) 0.05 0.18 2.12
Simons & Senturk 0.07 0.23 2.76
ASCE 0.04 0.13 1.55 Slope < 2%
USBR 0.06 0.20 2.38 for downstream of stilling basin
USGS 0.08 0.27 3.24 Usually higher then other methods
Ibash 0.07 0.22 2.70
CA DOT 0.11 0.35 4.24 dept of transportation
HEC-11 0.02 0.08 0.97 Q>1.4 cms 50cfs
0.00
Average Value 0.06 0.20 2.34
4.5 average water depth in channel (ft)
depth (m) 1.37 average water depth in channel (m)
3.87 average channel velocity (fps)
Vel (m/s) 1.18 average channel velocity (m/s)
q = 26.6 angle of side slope to horizontal q = 26.6 for 2:1 side slopes
S = 0.005 channel bed slope q = 21.8 for 2.5:1 side slopes
d
50
=
0.07 Trial riprap size (m) that which 50% of the riprap material is finer q = 18.4 for 3:1 side slopes
V = 1.18 local depth averaged velocity (m/s)
l =
0.005 angle of streamlines to horizontal (approx. angle of bed to horizontal)
d
50
(m) % Difference
0.3 91%
0.48 89%
0.38 82%
0.43 91%
0.43 86%
0.83 90%
0.46 85%
0.66 84%
0.09 73%
Method
Calculated Values
from Prakash, 2000
Estimated Riprap Size
for 2:1 side slopes
for 2.5:1 side slopes
for 3:1 side slopes
Maynards Method (Maynord, et. al., 1989)
d
30
/D = SF*0.30 [{g/(g
s
-g)}
0.5
*V/(g*D)
0.5
]
2.5
Where:
d
30
=
0.02 riprap size (m) than which 30% of the riprap material is finer
D = 1.3716 average water depth in channel (m)
SF = 1.2 factor of safety (1.2 suggested for this method)
V = 1.179576 local depth averaged velocity (m/s)
g = 9.81 acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s
2
)
g = 1000 unit weight of water (1000 kg/m
3
)
g
s
=
2404
unit weight of stone (kg/m
3
)
d
50
=
0.03
d
50
(m) is approximately equal to 1.5*d
30
US Army Corps of Engineers Method 1 (West Consultants, Inc., 1996)
d
30
/D = SF*C
s
*C
v
*C
t
[{g/(g
s
-g)}
0.5
*V/(g*D*K)
0.5
]
2.5
Where:
d
30
=
0.04 riprap size (m) than which 30% of the riprap material is finer
D = 1.4 average water depth in channel (m)
SF = 1.5 factor of safety (1.5 suggested for this method)
V = 1.179576 local depth averaged velocity (m/s)
g = 9.81 acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s
2
)
g = 1000 unit weight of water (1000 kg/m
3
)
g
s
=
2404
unit weight of stone (kg/m
3
)
C
s
=
0.3 stability coefficient = 0.30 for angular stones
C
v
=
1 vertical velocity distribution coefficient = 1.0 for straight channels
C
t
=
1
thickness coefficient = 1.0 for riprap thickness equal to d
100
K = 0.71747 side slope correction factor = [1-sin
2
q/sin
2
j)]
0.5
q = 26.6 angle of side slope to horizontal q = 26.6 for 2:1 side slopes
j = 40 angle of repose for stone q = 21.8 for 2.5:1 side slopes
q = 18.4 for 3:1 side slopes
d
50
=
0.05
d
50
(m) is approximately equal to 1.5*d
30
Simons and Senturk Method (Barfield, et al, 1981; Nelson, et al, 1986; Simons and Senturk, 1977)
(1)
t
max
=
10.42
maximum shear stress = 0.76 gDS
(2)
h =
2.23
= 21t
max
/[(g
s
-g)d
50
]
(3) b = 70.84 = arctan [cosl / {(2 sin q / h tan j)+sinl}]
(4) h ' = 2.17 = h [1+ sin (l + b)] / 2
(5) SF = 0.38 = cos q tan j / [h' tan j + sin q cos b]
Where:
d
50
=
0.07 riprap size (m) that which 50% of the riprap material is finer
D = 1.3716 average water depth in channel (m)
SF = 1.5 factor of safety (1.5 suggested for this method)
g = 1000 unit weight of water (1000 kg/m
3
) q = 26.6 for 2:1 side slopes
g
s
=
2404
unit weight of stone (kg/m
3
)
q = 21.8 for 2.5:1 side slopes
q = 26.6 angle of side slope to horizontal q = 18.4 for 3:1 side slopes
j = 40 angle of repose for stone
l = 0.572939 angle of streamlines to horizontal (approx. angle of bed to horizontal)
S = 0.01 channel bed slope
This method computes SF corresponding to a trial value of d
50
,
using equation 5. If the computed SF is not acceptable, then the
trial value of d
50
is modified until an acceptable SF is obtained.
American Society of Civil Engineers Method (Vanoni, 1977)
(1)
d
50
= [6 W
50
/ (p g
s
)]
0.333
(2) W
50
= 0.0232 G
s
V
6
/ [(G
s
- 1)
3
cos
3
q]
Where:
W
50
=
0.08
weight of stone (kg) of diameter d
50
G
s
=
2.4 specific gravity of stone
V = 1.179576 local depth averaged velocity (m/s)
g
s
=
2404
unit weight of stone (kg/m
3
)
q = 26.6 for 2:1 side slopes
q = 26.6 angle of side slope to horizontal q = 21.8 for 2.5:1 side slopes
q = 18.4 for 3:1 side slopes
d
50
=
0.04 riprap size (m) that which 50% of the riprap material is finer
USBR Method (Peterka, 1958)
(1)
d
50
= .043 V
a
2.06
Where:
V
a
=
1.179576 average channel velocity (m/s)
d
50
=
0.06 riprap size (m) that which 50% of the riprap material is finer
USGS Method (West Consultants, 1996)
(1)
d
50
= .055 V
a
2.44
Where:
V
a
=
1.179576 average channel velocity (m/s)
d
50
=
0.08 riprap size (m) that which 50% of the riprap material is finer
Ibash Method (Maynard, et al, 1989; West Consultants, 1996)
(1)
d
50
= V
a
2
/[2 g C
2
(G
s
- 1)]
Where: C = 0.86 0.86 for high and 1.2 for low turbulence zones
G
s
=
2.4 specific gravity of stone
V
a
=
1.179576 average channel velocity (m/s)
g = 9.81 acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s
2
)
d
50
=
0.07 riprap size (m) that which 50% of the riprap material is finer
California Department of Transporation Method (West Consultants, 1996)
(1)
W
33
= 0.0113 G
s
V
x
6
/ [(G
s
- 1)
3
sin
3
(r - q)]
(2) d
33
= [6 W
33
/ (p g
s
)]
.333
Where:
W
33
=
0.46
weight of stone (kg) of diameter d
33
G
s
=
2.4 specific gravity of stone
V
x
=
1.57
4/3 V
a
for impinging flows and 2/3 V
a
for tangential flows
V
a
=
1.179576 average channel velocity (m/s)
g
s
=
2404
unit weight of stone (kg/m
3
)
q = 26.6 for 2:1 side slopes
q = 26.6 angle of side slope to horizontal q = 21.8 for 2.5:1 side slopes
r = 70 70
0
for randomly placed rubble stone q = 18.4 for 3:1 side slopes
d
33
=
0.07 riprap size (m) than which 33% of the riprap material is finer
d
50
=
0.11
d
50
(m) is approximately equal to 1.5*d
33
y 62.4
d 4.5
S 0.007
T 1.9656
HEC-11 Method (West Consultants, 1996)
Rip-Rap Sizing
(1) d
50
= d
50
' C
f
C
s
(2) d
50
' = .005943 V
a
3
/ [K
1.5
(D)
.5
]
(3) C
f
= [SF / 1.2]
1.5
(4) C
s
= 2.12 / [G
s
- 1]
1.5
Where: SF = 1.5 factor of safety (1.5 suggested for this method)
V
a
=
1.18 average channel velocity (m/s)
G
s
=
2.4 specific gravity of stone
D = 1.37 average water depth in channel (m)
K = 0.71747 side slope correction factor = [1-sin
2
q/sin
2
j)]
0.5
q = 26.6 for 2:1 side slopes
q = 26.6 angle of side slope to horizontal q = 21.8 for 2.5:1 side slopes
j = 40 angle of repose for stone q = 18.4 for 3:1 side slopes
d
50
' =
0.01
C
f
=
1.40
C
s
=
1.28
d
50
=
0.02 riprap size (m) that which 50% of the riprap material is finer
d
50
=
0.08 riprap size (m) that which 50% of the riprap material is finer
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Year 5 Science Test PaperDocument13 pagesYear 5 Science Test Paperemelliaghalli75% (52)
- Rubble Mound Breakwater DesignDocument27 pagesRubble Mound Breakwater DesigntsuakPas encore d'évaluation
- Rubble Mound Breakwater Design - ExampleDocument14 pagesRubble Mound Breakwater Design - Examplehhshiyam100% (2)
- Solution Manual HydraulicsDocument14 pagesSolution Manual HydraulicsVivekka Olivia John75% (4)
- CL420 Water Engineering 2 H41 GVF LabDocument17 pagesCL420 Water Engineering 2 H41 GVF LabDavid Thomson0% (1)
- AENG 1 - Fundamentals of Agricultural Engineering Problem Set No. 4Document2 pagesAENG 1 - Fundamentals of Agricultural Engineering Problem Set No. 4gigoongPas encore d'évaluation
- SEWERAGE - Analysis & CalculationDocument185 pagesSEWERAGE - Analysis & CalculationMohd RafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1 Design of Sanitary Wastewater Manholes - 1456Document4 pages5.1 Design of Sanitary Wastewater Manholes - 1456sitehab100% (2)
- Water Supply Problems and SolutionsDocument13 pagesWater Supply Problems and SolutionsNobody100% (2)
- Tutorial and AssignmentsDocument8 pagesTutorial and Assignmentstedy yidegPas encore d'évaluation
- Chilled Water Pump Head CalculationDocument6 pagesChilled Water Pump Head CalculationMohammed Hassan Mohiuddin Khan67% (3)
- Canal Hydraulics DesignDocument1 541 pagesCanal Hydraulics DesignSamarakoon Banda100% (2)
- Hydr-Design of Settling Basin NewDocument36 pagesHydr-Design of Settling Basin NewHendarmin Lubis100% (1)
- Design of Stable Open ChannelsDocument12 pagesDesign of Stable Open ChannelsUribe AldoPas encore d'évaluation
- BW Design ExampleDocument17 pagesBW Design ExampleHaryo ArmonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Depth For A Discharge Through A Trapezoidal ChannelDocument4 pagesNormal Depth For A Discharge Through A Trapezoidal ChannelRichard Tandi PranataPas encore d'évaluation
- Friction IntroDocument13 pagesFriction IntroblozzerPas encore d'évaluation
- Open Channel Hunt: BFC 21103 Hydraulics S4 DR Siti Nazahiyah Binti RahmatDocument17 pagesOpen Channel Hunt: BFC 21103 Hydraulics S4 DR Siti Nazahiyah Binti RahmatNur AzreenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Force Exerted On An Immersed BodyDocument37 pagesForce Exerted On An Immersed BodyNyi NyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathcad - Tugas 5Document19 pagesMathcad - Tugas 5Faridah ZahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Upgradation and Relocation of Karakorum Highway For Basha Diamer Dam ProjectDocument14 pagesUpgradation and Relocation of Karakorum Highway For Basha Diamer Dam ProjectkuttakhaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 LectureDocument78 pagesChapter 4 LectureAmit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical 2Document5 pagesNumerical 2Utsav PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- Preliminiary TreatmentDocument22 pagesPreliminiary TreatmentIsmail toro100% (1)
- Full Project HydraulicDocument13 pagesFull Project HydraulicAfzal RazaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Desander Underground Type1Document8 pagesDesander Underground Type1Sambhav PoddarPas encore d'évaluation
- Headworks DesignDocument6 pagesHeadworks Designrajeshsapkota123100% (2)
- Project Hydraulics and HydrologyDocument17 pagesProject Hydraulics and HydrologyEiyra NadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Dermaga BBMDocument31 pagesLoad Dermaga BBMFaridah ZahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Concrete DamDocument31 pagesDesign of Concrete DamShankar KhanalPas encore d'évaluation
- BSC (Hons) in Civil EngineeringDocument33 pagesBSC (Hons) in Civil EngineeringFaisal NazeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Jump Example PDFDocument30 pagesHydraulic Jump Example PDFkhonjan1000100% (1)
- Design of Vertical Drop Weir Calculafion Complete Design The FollowingDocument9 pagesDesign of Vertical Drop Weir Calculafion Complete Design The Followinginam.emadi2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Parameters in Uniform Flow For Open ChannelsDocument3 pagesHydraulic Parameters in Uniform Flow For Open ChannelsHala HalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary TreatmentDocument22 pagesPrimary TreatmentEmil AbdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimension of Structure (Calculation Sheet)Document16 pagesDimension of Structure (Calculation Sheet)Budi Mulyono NtomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline CalculationsDocument10 pagesPipeline Calculationsaulia13110% (1)
- Bottle Rocket Calculations: Example Using 70 Psi and 350 ML of WaterDocument11 pagesBottle Rocket Calculations: Example Using 70 Psi and 350 ML of WaterMasha MusthafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Design of Check DamDocument2 pagesHydraulic Design of Check DamSooraj Kannan, P.V.100% (1)
- APPENDIX C Worked ExampleDocument20 pagesAPPENDIX C Worked Examplenorsam1511Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Design of TroughDocument18 pagesSample Design of TroughAsela UdayangaPas encore d'évaluation
- HYDRAULIC DESIGN OF DELIVERY CISTERN (Designing Cistern As A Vertical Drop)Document14 pagesHYDRAULIC DESIGN OF DELIVERY CISTERN (Designing Cistern As A Vertical Drop)p_ignatiusPas encore d'évaluation
- Solucionario Capitulo 13 Física Serway and FaughnDocument13 pagesSolucionario Capitulo 13 Física Serway and FaughnRafael Colindres100% (1)
- Annex 30 Tool - Design - Waste Stabilization PondsDocument8 pagesAnnex 30 Tool - Design - Waste Stabilization Pondsmurkeking100% (1)
- CEB707 - 5 - Water Treatment Plant DesignDocument18 pagesCEB707 - 5 - Water Treatment Plant Designalex100% (2)
- Assignment 1 Prob 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1 Prob 1wajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Influencing Hydraulic RoughnessDocument5 pagesFactors Influencing Hydraulic RoughnessFaruk AtalarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cive1400 200405 SolutionsDocument10 pagesCive1400 200405 SolutionsnaefmubarakPas encore d'évaluation
- Canal DesignDocument34 pagesCanal Designniranjan100% (2)
- Flow, Slope &pipe Dia. Calculation Using Manning's FormulaDocument18 pagesFlow, Slope &pipe Dia. Calculation Using Manning's FormulaMohammad Risky NaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fs References 1013Document12 pagesFs References 1013Mohamed Abd El DayemPas encore d'évaluation
- Sewerage and Sewage Treatment - 2014 - Solutions For End Semester ExaminationDocument16 pagesSewerage and Sewage Treatment - 2014 - Solutions For End Semester ExaminationDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow in Pipes and Channels - Solved ExamplesDocument6 pagesFlow in Pipes and Channels - Solved ExamplesEngr Ghulam MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesD'Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportD'EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportPas encore d'évaluation
- Tables of the Velocity of Sound in Sea Water: Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTables of the Velocity of Sound in Sea Water: Mathematical Tables SeriesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Hydrogeochemistry Fundamentals and Advances, Environmental Analysis of GroundwaterD'EverandHydrogeochemistry Fundamentals and Advances, Environmental Analysis of GroundwaterPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationD'EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationPas encore d'évaluation
- Kon Ver Siu Kuran Sip IlDocument4 pagesKon Ver Siu Kuran Sip Ilzulkifli1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rating Curve - RevDocument17 pagesRating Curve - Revzulkifli1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tyrolean IntakeDocument9 pagesTyrolean Intakezulkifli1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vetiver System For Slope StabilizationDocument51 pagesVetiver System For Slope Stabilizationzulkifli1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Erection Manual Hydro-1Document63 pagesErection Manual Hydro-1rajfab100% (1)
- Time Schedule (Jadwal Pelaksanaan) PekerjaanDocument2 pagesTime Schedule (Jadwal Pelaksanaan) Pekerjaanzulkifli1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Calculation of Pipe Culvert: WLD Wlo Wli WluDocument1 pageHydraulic Calculation of Pipe Culvert: WLD Wlo Wli Wluzulkifli1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Form HID CH QADocument2 pagesStandard Form HID CH QAzulkifli1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- List of Accepted PaperDocument54 pagesList of Accepted Paperzulkifli1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sika Viscocrete - 20heDocument2 pagesSika Viscocrete - 20heTARGET TRADE LINKSPas encore d'évaluation
- QC Chart - Graphite AAS - DRAFTDocument13 pagesQC Chart - Graphite AAS - DRAFTConsultant JerocasPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano MaterialsDocument38 pagesNano Materialsaedi0611100% (3)
- Buoyancy and StabilityDocument56 pagesBuoyancy and StabilityJuan Sebastian Varela SanabriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Compatibility Of: Aluminium and SteelDocument3 pagesCompatibility Of: Aluminium and SteelNasaii AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Ecosystem CyclesDocument18 pages03 Ecosystem CyclesAngelo Miguel GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Large Scale Industrial Ammonia Cracking PlantDocument4 pagesLarge Scale Industrial Ammonia Cracking PlantZ APas encore d'évaluation
- Material Engineeringg CeramicsDocument36 pagesMaterial Engineeringg CeramicsAndy WidyasayogoPas encore d'évaluation
- Options For High Temperature Well StimulationDocument11 pagesOptions For High Temperature Well StimulationFra FraPas encore d'évaluation
- CP 201: Material and Energy Balances Chapter 3: Energy and Energy BalancesDocument20 pagesCP 201: Material and Energy Balances Chapter 3: Energy and Energy BalancesEvelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Vessel Design by Biruk Solomon BadeDocument76 pagesPressure Vessel Design by Biruk Solomon BadebrookPas encore d'évaluation
- AV-231 - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL & RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN E AND V - Lecture - 17Document18 pagesAV-231 - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL & RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN E AND V - Lecture - 17Hamza Salah-Ud-DinPas encore d'évaluation
- Field Test of Construction MaterialsDocument25 pagesField Test of Construction MaterialsAntarjyami PradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Application TA 018e 2Document2 pagesApplication TA 018e 2Goni GoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Layers-Of-The-Earth-Webquest-Worksheet1-6 1Document4 pagesLayers-Of-The-Earth-Webquest-Worksheet1-6 1api-268569185Pas encore d'évaluation
- 030 Intro To Secondary Metabolism and BiosynthesisDocument64 pages030 Intro To Secondary Metabolism and BiosynthesisRadi TyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Corn Starch Biopolymer: November 2020Document5 pagesReview of Corn Starch Biopolymer: November 2020Zinabu Tunu JilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Gulnur KenzheevaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4CzIPN T Bu-Catalyzed Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer For Photosynthesis of Phosphorylated N HeteroaromaticsDocument9 pages4CzIPN T Bu-Catalyzed Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer For Photosynthesis of Phosphorylated N HeteroaromaticsLalchan MiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer 589Document3 pagesAnswer 589Sasa LiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Data Sheet TERMINATOR! Antibacterial CleanerDocument7 pagesSafety Data Sheet TERMINATOR! Antibacterial CleanerIPKL RSBHAYANGKARA KEDIRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 11 - Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesExperiment 11 - Types of Chemical ReactionsUpekkha Phm100% (1)
- L. M. Chart: Products & SolutionDocument2 pagesL. M. Chart: Products & SolutionMallesh MunjePas encore d'évaluation
- CSM Technical SpecDocument1 pageCSM Technical SpecabasakPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Markers of Varietal Unifloral HoneysDocument3 pagesChemical Markers of Varietal Unifloral HoneysBrian DGPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 1111 SygsuDocument4 pagesPhys 1111 SygsuLeporePas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Drinking Water Quality of Navsari District Gujarat 47-53Document7 pagesEvaluation of Drinking Water Quality of Navsari District Gujarat 47-53ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionPas encore d'évaluation
- Momentum 1 QPDocument18 pagesMomentum 1 QPtechnical videosPas encore d'évaluation
- L7 - Properties of MetalsDocument22 pagesL7 - Properties of Metalsمحمد المطيريPas encore d'évaluation