Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ajc h2 Math p2 Solutions
Transféré par
jimmytanlimlongCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ajc h2 Math p2 Solutions
Transféré par
jimmytanlimlongDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Anderson Junior College
Preliminary Examination 2011
H2 Mathematics Paper 2 (Solutions)
Section A: Pure Mathematics [40 marks]
1
(i)
d
100 3
d
97 , 0
u
ku
t
ku k
=
= >
( )
1
du 1 d
97
1
ln97
ln97
97 e where
1
97 e (shown)
kt kc
kt
t
ku
ku t c
k
ku kt kc
ku A A e
u A
k
= +
=
= =
=
} }
(ii) For the processing tank, when t =0, u =0.
Hence,
( )
1
97 0 97 A A
k
= = .
Therefore,
( )
1
97 97e
kt
u
k
= .
Since u =70 when t =1, we have
( )
1
70 97 97e 0.69220 (5 s.f. from GC)
k
k
k
= =
Amount of water in the processing container when t =2
=
( )
2(0.6922)
1
97 97e
0.6922
=105.03 litres
Amount of water pumped in when t =2 =200 litres
Hence, amount of water processed =200 105.03 - 6 litres
=89.0 litres (3 s.f.)
(iii)
As
( )
0.6922
1 97
, 97 97e 140.13 litres
0.6922 0.6922
t
t u
+ = ~
The minimum volume of the tank is 141 litres.
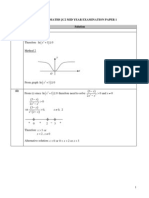
2
(a)
(i) Method 1 (using differentiation)
1
2
1
f '( ) ( 1) sin
1
x x x
x
| |
= + +
|
\ .
For
1
0
2
x s s , f '( ) 0 f ( ) x x > is a strictly increasing function and therefore f is a 1 to
1 function.
Since f is 1-1, the inverse function f
-1
exist.
Method 2 (using graphical test):
Any horizontal line y =k intersects the graph of f at at most one point f is a one-one
function the inverse function f
-1
exist.
( Or : any horizontal line y =k, 0 1
4
k
t
s s + , intersects the graph of f at exactly one point
f is a one-one function the inverse function f
-1
exist)
To find the value of f
-1
(1), solve f(x) =1
1
( 1)sin 1 1
1 (rejected since 0) or 0
x x
x x x
+ + =
= > =
1
f (1) 0
=
(ii) At 0, f '(0) 1 and 1 x y = = =
Equation of tangent to the curve y =f(x) at x =0: y =x +1
(iii) At x =1, we will use the symmetry properties of the curve of f and f
-1
along y =x
Equation of tangent to the curve y =f
-1
(x) at x =1: x =y +1 y =x 1
2
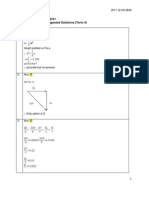
(b)
(b) (i) Range of g =[-11,5]
(ii) Different values of a will translate the curve
1
=1+ y
x
along the x-axis by a units to
give
1
=1+ y
x a
Domain of g
g
[-11, 5]
h
Range of hg
Since domain of h =[-11, 5] and we need range of hg to be subset of (1, ), therefore [-11,
5] must fall in the interval (a, )
From the diagram, it can be observed that the greatest value of a is -12.
3
(i)
2 2 2 2 2 1
2
3
3 0 2 ( 3) 1 2 cos cos
70
1 2
| | | |
| | | |
| |
= + + +
| |
| |
\ . \ .
| |
\ . \ .
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
2 2
2
2 2
2 2 2
2
3
2 2 14 2
70
5 2 2 9 2
20 2 1 9 2
11 40 16 0
(11 4)( 4) 0
4
4 as = (rejected as <0)
11
+ = +
+ = +
+ + = +
+ =
+ =
=
y
y
x =a
x
5 -11
y=1
x
-11
5 y=g(x)
(ii) Using ratio theorem,
4 2 10
3 1 1
3 0 3 3
4 4 4
2 1 7
OB OA
OM
| | | | | | | |
+ | | | |
= = + =
| | | |
| | | |
\ . \ . \ . \ .
10 10
4 4 1 1
3 3
3 3 4 3
7 7
OC OM
| | | | | |
| | |
= = =
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
(iii) p represents the perpendicular distance of C from the line AB (or p is the height of the
triangle ABC with AB as its base).
10 2 16
1 1
3 3 6
3 3
7 1 4
AC
| | | | | |
| | |
= =
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
,
4 2 6
0 3 3
2 1 1
AB
| | | | | |
| | |
= =
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
16 6 6
1
6 3 8
3
4 1 12
1 1 122
3 3 23 36 9 1 46
AC AB
p
AB
| | | | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
= = = =
+ +
3
1
122
3
23
q OM
p MC
q p
= =
= =
4
(i)
9
4 3
3 4
iz i
z i
+ + =
+
9
4 3
3 4
i z i
z i
+ =
+
( )
2
3 4 9 z i + =
( ) 3 4 3 z i + =
A
B
M
C
O
p
q
(ii) max arg (z +i)
1
2 2
3
2sin
2
3 5
t
| |
= +
|
+
\ .
2.65 =
( ) arg 2.65
2
z i
t
s + s
(iii) * 4 w w = 4 w w = - locus is the line x =2 [1]
( ) z iw z iw + = =distance between locus of z (circle) and the locus of points representing
iw .
Locus of iw is the line y =-2
Therefore least value of 3 z iw AB + = =
5
(i) c =0 as the line l is on t
2
. [B1]
(ii) Since the line l is on t
2
, l is perpendicular to the normal of t
2
.
1
5 0
1 1
5 1 0
5 1 (shown)
b
a
b a
b a
| | | |
| |
=
| |
| |
\ . \ .
+ + =
+ =
(iii)
Method1:
1 1 2
2 1
0 1 2
a
a
| | | | | |
| | |
=
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
isavector to
1
t
2
1 5 0 2 5 2 0 2 7
2 1
b
b a a b
a
| | | |
| |
- = + + = + =
| |
| |
\ . \ .
Method2:
1 5
5 1
1 1 5
b a
a b
ab
| | | | | |
| | |
=
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
isavector to
1
t
5 1
1 2 0 5 2 2 0 2 7
5 0
a
b a b a b
ab
| | | |
| |
- = + = + =
| |
| |
\ . \ .
Method3:
1 2
2 5 1
0 1 5 2
b
b
| | | | | |
| | |
=
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
isavector to
1
t
2 1
1 0 2 5 2 0 2 7
5 2 1
a a b a b
b
| | | |
| |
- = + + = + =
| |
| |
\ . \ .
Method4:
1 1 2
2 1
0 1 2
a
a
| | | | | |
| | |
=
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
isavector to
1
t
1 2
2 5 1
0 1 5 2
b
b
| | | | | |
| | |
=
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
isavector to
1
t
2 2
1 1
2 5 2
k
a b
| | | |
| |
=
| |
| |
\ . \ .
1 and 2 5 2 k a b = =
2 7 a b + =
Using 5 1 b a = from part (ii) and solving simultaneous equation,
we get a =-1 and b =4.
(iv) Possible answers are:
4 4
5 4 42 or 5 4 42
1 1
| | | |
| |
= =
| |
| |
\ . \ .
r r
Section B (Statistics) [60 marks]
6 There are 9 distinct letters: C, O (2), R (2), E, L, A, T, I, N
(i) Treat all the letters as distinct then arrange them according to the restriction. This will be
followed by taking the repeated letters into account.
Number of arrangements
5 9! 6
2721600
2!2!
= =
(ii) Case 1: All distinct
No. of ways =
9
6
60480 P =
Case 2: 1 pair of repeated letters
No. of ways =
2 8
1 4
6!
50400
2!
C C =
Case 3: 2 pairs of repeated letters
No. of ways =
7
2
6!
3780
2!2!
C =
Total no. of ways 60480 50400 3780 114660 = + + =
7 (i) Let X be the number of lemon candies in a randomly selected packet of 20.
(20,0.24) X B
( ) 20 0.24 4.8 E X = =
( ) 20 0.24 0.76 3.648 Var X = =
Since 60 ( 50) n = > , by Central Limit Theorem,
3.648
4.8,
60
X N
| |
|
\ .
.
( 5) 0.20865208 P X > = =0.209 (3sf)
(ii) The sample is biased, as only students are surveyed. Not everyone in the population has an
equal chance of being surveyed.
It will be difficult to get an exhaustive list of people of all age groups to do a proper
stratification. (no sampling frame)
Use Quota Sampling
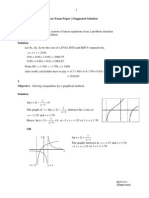
8 (i)
(ii) From GC, the product moment correlation coefficient =0.940 (3 sig fig)
(iii) The points in the scatter plot fits closely to the curve
Bt
x Ae = (left) and the r value is close to 1. Thus this
model is suitable.
Transformation of
Bt
x Ae = into a linear model: ln ln x A Bt = +
From GC, ln 1.71086 5.53, 0.0476 A A B = = =
(iv) If t is increased by 5, the increase in x is as follows:
( ) ( )
( 5) 5 5(0.0476)
1
(1.269)
Bt
o
B t B
o o o
x Ae
x Ae e x e x x
+
=
= = = =
The rate of chirps is estimated to increase by 26.9% from the rate before the
temperature is increased.
The estimate is not reliable because we are extrapolating beyond the region where the
data is collected and analyzed.
(v) The value of r remains the same since it is not affected by any translation or scaling.
9
2
~ (45000,2000 ) A N
2
~ (30000,1850 ) B N
(i) ( )
1 2
2 ~ (30000,22845000) A B B N +
( ) ( )
1 2
2 25000 0.85224 0.852 P A B B + > = = (3 sig fig)
Assumption: The distributions of the lifespans of all televisions are independent of each
other.
(ii) Let W denotes the number of plasma televisions out of 50 with a life span of more than
30000 hours.
~ (50,0.5) W B
(14 22) (15 21) P W P W < < = s s
( 21) ( 14) P W P W = s s
0.16112 0.0013011 =
0.15982 =
0.160 =
(iii)
2
2000
~ 45000, X N
n
| |
|
\ .
( 46500) 0.99 P X s >
46500 45000
0.99
2000
P Z
n
| |
|
s > |
|
|
\ .
3
0.99
4
n
P Z
| |
s >
|
|
\ .
3
2.32635
4
n
>
9.6212 n >
Least 10 n =
(iv) (I) will be greater as A >25000 and B >25000 is a subset of A+B >50000.
10
~ ( )
o
X P
(i)
2 3
10
( 2) 10 ( 3) 0
2! 3!
e e
P X P X
= = = =
2
10
1 0
2! 3
e
| |
=
|
\ .
3
E( ) 0.3
10
X = = = (shown)
(ii) Let U denotes the total number of errors in a randomly selected textbook.
~ (15)
o
U P
( 10) 0.04861075 P U = =
(iii) Let A and B denotes the total number of errors in the pages 1 to 10 plus 41 to 50 and 11
to 40 respectively.
~ (6)
o
A P and ~ (9)
o
B P ,
Probability
( 1) ( 9) ( 0) ( 10)
( 10)
P A P B P A P B
P U
= = + = =
=
=
(0.01487251)(0.13175564) (0.0024788)(0.11858007)
0.04861075
+
=
=0.046357=0.0464 (3 sig fig)
(iv) ( 18) 1 ( 18) P U P U > = s 0.18053 =
Let x be the minimum selling price, in order to make a profit,
1.15(12 12 ( 18))
16.291
x P U
x
> + >
>
Minimum selling price is $16.30.
(v) Let V be the r.v denoting the number of textbooks that has more than 18 errors out of 50
books.
(50,0.18053) V B
Since n is large and np >5 and nq >5, (9.0265,7.3969) V N approximately
( ) P 6 P( 5) P( 5.5) 0.0974 V V V < = s = < =
11 (i) For the die, letx =P(1) =P(3) =P(5).
2 2 2 1
1 1
P(1) (shown)
9 9
x x x x x x
x
+ + + + + =
= =
P(1) = P(3) = P(5) =
1
9
and P(2) = P(4) = P(6) =
2
9
(ii) For the coin, P(tail) =
1
3
and P(head) =
2
3
P(the coin to show tail and the die to show a number that is at most 4)
=P(tail,1) +P(tail,2) +P(tail,3) +P(tail,4)
1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2
. . . .
3 9 3 9 3 9 3 9
= + + +
2
9
= or independence P(tail) [P(1)+P(2)+P(3)+P(4)]
(iii)
P(coin shows a tail or the die shows a number that is at most 4, or both)
=P(coin shows a tail)+P(die shows a number that is at most 4) P(tail and at most 4)
1 6 2
3 9 9
= +
7
9
=
(iv) P(coin shows a head if the score is at most 4)
( 'tail' most 4)
( 'tail' and most 4)
most 4
P coin is score is at
P coin is score is at
score is at
=
=
2
9
('tail',1 or 'tail',2 or 'tail',3 or 'tail',4
or 'head',1 or 'head',2)
2
9
2 2 1 2 2
. .
9 3 9 3 9
1
2
P
=
=
+ +
=
(v) For each throw, Mary is expected to gain $
4 5
1. 0.5
9 9
( | | | |
+
| | (
\ . \ .
1
$
6
=
Therefore, Mary is not expected to make a profit as she is expected to lose $10.00 in the game.
12 (i)
Unbiased estimate of the population mean
44.8
3.7333333
12
x = = = =3.73 (3sf)
Unbiased estimate of the population variance
( )
2
1.9467
0.1769727273
11 11
x x
= = =
=0.177
(3sf)
(ii) Let X be the time, in hours, that a randomly chosen customer spends shopping at Takayama
Shopping Complex, and be the mean time.
Test : 4
o
H = (managers claim)
vs
1
: 4 H = (superiors suspicion)
Assume that X is normally distributed.
Since 12 n = is small, and population variance is unknown, we use a T Test.
Test Statistic:
4
(11)
X
T t
s n
=
Use a two-tailed test at 6%, and reject
o
H if 0.06 p < .
Using GC, with
56
15
x = , 0.1769727273 s = , n=12
0.0504 0.06 p = <
We reject
o
H . There is sufficient evidence at 6% significance level to confirm the company
superiors suspicion.
(iii) Since the value of p in part (ii) is less than 6%, the new value of p would be half of the
value in (ii), therefore it would still be less than 6%. Thus, the conclusion would remain the
same.
OR
Since Tcalc <Tcritical in part (ii), and now Tcritical (new) >Tcrictical, this implies that Tcalc
<Tcritical (new). Thus conclusion will remain the same.
(iv) Test
0
:
o
H = (managers claim)
vs
1 0
: H < (manager overstated the average time)
Test Statistic:
Since X is normally distributed, and population variance is known, we use a Z Test.
0
X
Z
n
o
=
Use a one-tailed test at 6%, and reject
o
H if 0.06 p < .
For manager to justify that he has not overstated the average time,
i.e. do not reject
0
H at 6% (z calc does not lie in critical region)
0
4.2375
1.5547736
0.466 8
calc
z
= >
0
0.466
4.2375 1.5547736
8
| |
>
|
\ .
0
4.493658 < hrs
0
4 < hrs 29.62 mins
Largest possible value of
0
is 4 hours 29 mins
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Nyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionDocument10 pagesNyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesRI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695100% (1)
- 2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsDocument11 pages2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsLionel Torres LeePas encore d'évaluation
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Ri h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument11 pagesRi h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument10 pagesNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument13 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 RJC Math PrelimDocument32 pages2007 RJC Math PrelimDaniel Oon Wei RhenPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Paper 2 Solutions PDFDocument10 pagesMJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Paper 2 Solutions PDFRyan LeePas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnDocument8 pages2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim Solnfocuscharade_8247490Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 RI Prelims Chem H2 P3 AnsDocument7 pages2009 RI Prelims Chem H2 P3 AnsJasonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 NJC H2 Maths PromoDocument18 pages2016 NJC H2 Maths Promomadhih123Pas encore d'évaluation
- AJC H2Maths 2008 Prelim P2Document5 pagesAJC H2Maths 2008 Prelim P2junkgamePas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Physic 2009 A Level SolutionsDocument28 pagesH2 Physic 2009 A Level Solutionsonnoez0% (2)
- 2010 AJC H2 Math Promo With AnswersDocument8 pages2010 AJC H2 Math Promo With AnswersCindy KrisnadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Jae InfoDocument158 pagesJae InfoTHAN HANPas encore d'évaluation
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document12 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - HCI P2 Solution PDFDocument14 pages2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - HCI P2 Solution PDFcherylhzy100% (1)
- H2 Physic 2010 A Level SolutionsDocument32 pagesH2 Physic 2010 A Level Solutionsonnoez50% (4)
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1Document18 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 JC2 H2 Maths Victoria Junior College PDFDocument33 pages2015 JC2 H2 Maths Victoria Junior College PDFVu Quang MinhPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 SAJC H2 Maths Promo Exam (Solution)Document7 pages2016 SAJC H2 Maths Promo Exam (Solution)Vincent See100% (2)
- 2019 Y5 Promo Revision (Sem1 Topics)Document10 pages2019 Y5 Promo Revision (Sem1 Topics)Sarah RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- DHS 2015 H2 Y5 Math Promos QuestionsDocument7 pagesDHS 2015 H2 Y5 Math Promos QuestionsAlxPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsDocument21 pages2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsNicholas ChoyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 SolutionDocument13 pages2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 Solutioncherylhzy0% (4)
- 2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim1Document3 pages2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim1focuscharade_8247490Pas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- h2 Mathematics Practice Paper 1 For Prelim Exam 2011Document4 pagesh2 Mathematics Practice Paper 1 For Prelim Exam 2011Augustine NgPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC 2015 H2 J1 Math Promos QuestionsDocument7 pagesMJC 2015 H2 J1 Math Promos QuestionsAlxPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 h2 Math Prelim p1 (Solns)Document19 pages2008 h2 Math Prelim p1 (Solns)Utsav NiroulaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 A Level H2 Chem Paper 2 Suggested Solutions and Comments PDFDocument8 pages2013 A Level H2 Chem Paper 2 Suggested Solutions and Comments PDFImagreenbucklegirl SGPas encore d'évaluation
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2Document15 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesPJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 TPJC Prelim Paper 1Document6 pages2010 TPJC Prelim Paper 1cjcsucksPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 DHS Paper 1solDocument10 pages2010 DHS Paper 1solnothingtodo1992Pas encore d'évaluation
- RI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 TPJC Prelim p11Document5 pages2014 TPJC Prelim p11Ngo Duy VuPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 H2 Chemistry Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsDocument5 pages2017 H2 Chemistry Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsLee Jun HuiPas encore d'évaluation
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument6 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1Document8 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 TJC SolDocument12 pages2010 TJC SolPooja KapurPas encore d'évaluation
- Acjc h2 Maths p1 QN PaperDocument6 pagesAcjc h2 Maths p1 QN Papervincesee85Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 jc1 Math Promo PDFDocument225 pages2013 jc1 Math Promo PDFGeorge ChooPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 HCI C1 Block Test H2 Mathematics Revision Package SolutionsDocument80 pages2013 HCI C1 Block Test H2 Mathematics Revision Package SolutionsGabriel Francis ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- TJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesTJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Challenging Problems in Binomial Theorem - Special HL Level SumsDocument11 pagesChallenging Problems in Binomial Theorem - Special HL Level Sumssriramaniyer85% (13)
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Math PracticeDocument7 pagesH2 Math PracticePhoebe Heng100% (2)
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Yjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesYjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse 2014 DelhiDocument17 pagesCbse 2014 DelhiharshdalalPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 YJC Paper 1solDocument12 pages2007 YJC Paper 1solYudi KhoPas encore d'évaluation
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesRI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P2 Solutionsnej200695Pas encore d'évaluation
- AJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesAJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAcjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- J1 Lecture - Human Rights LectureDocument20 pagesJ1 Lecture - Human Rights LecturejimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Which of The Following Equations Is Correct? (A) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/s (B) 8 J 2 KG × (2 M/S) (C) 8 J 2 KG × 2 (M/S) (D) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/sDocument1 pageWhich of The Following Equations Is Correct? (A) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/s (B) 8 J 2 KG × (2 M/S) (C) 8 J 2 KG × 2 (M/S) (D) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/sjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- J1 Lecture - Technology Part 1 - 2aDocument8 pagesJ1 Lecture - Technology Part 1 - 2ajimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 NJC H2 Econs Paper 2 (Answers)Document34 pages2013 NJC H2 Econs Paper 2 (Answers)jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- J1 Lecture - Technology Lecture 1 Student NotesDocument8 pagesJ1 Lecture - Technology Lecture 1 Student NotesjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Section B AnsDocument7 pagesSection B AnsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesTJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- J2 Lecture - HealthDocument8 pagesJ2 Lecture - HealthjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument13 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document10 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- TJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesTJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document14 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1Document18 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2Document15 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesRI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document6 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document7 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document7 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlong0% (1)
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document10 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument10 pagesNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Vishal (Performance Appraisal)Document58 pagesVishal (Performance Appraisal)Abhijeet Gheware100% (1)
- The Role of Probability - BostonDocument39 pagesThe Role of Probability - BostonThai ChePas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On " Employee Satisfaction in Modern Hyundai": 1. Name of The Student: Simran MaheshwariDocument4 pagesA Study On " Employee Satisfaction in Modern Hyundai": 1. Name of The Student: Simran MaheshwariAnkita PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Major and Minor Research Project Application FormDocument10 pagesMajor and Minor Research Project Application FormAmal MechanicPas encore d'évaluation
- 9686 21424 1 PBDocument8 pages9686 21424 1 PBOscar Kweku AhinampongPas encore d'évaluation
- dc09 - West - SAMPLE STATADocument35 pagesdc09 - West - SAMPLE STATARahat Syful HoquePas encore d'évaluation
- G7 U5m10 Te PDFDocument34 pagesG7 U5m10 Te PDFAhmed SalemPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaspard PR ProposalDocument22 pagesGaspard PR ProposalGaspardus MFASHIJWENIMANAPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissertation - Elijah DePalmaDocument266 pagesDissertation - Elijah DePalmaedepalma173Pas encore d'évaluation
- Market/demand Analysis: Meaning & PurposesDocument33 pagesMarket/demand Analysis: Meaning & PurposesmesfinPas encore d'évaluation
- SamplingDocument74 pagesSamplingGita MentariPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Statistical Design of ExperimentsDocument11 pagesBasic Statistical Design of ExperimentsKean CardenasPas encore d'évaluation
- IJHSS - A Study On - Md. Afzalur RahmanDocument10 pagesIJHSS - A Study On - Md. Afzalur Rahmaniaset123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Effectiveness of Bacopa Herb For Solving Dementia in The ElderlyDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of Bacopa Herb For Solving Dementia in The ElderlyMark ManzanasPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPCR - Safe and Secure School EnvironmentDocument44 pagesNCPCR - Safe and Secure School EnvironmentRishab ManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 English Learning PlanDocument5 pagesGrade 10 English Learning Plangladen shelley billonesPas encore d'évaluation
- ABSTRACTS The Ecological Society of America 88thannual MeetingDocument398 pagesABSTRACTS The Ecological Society of America 88thannual MeetingYendra PratamaTerrificninetyninefoldPas encore d'évaluation
- Probability SamplingDocument5 pagesProbability SamplingAra RoqueroPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are The Different Sources of Data?Document5 pagesWhat Are The Different Sources of Data?Jesien MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Rec 2A - Experiments-1Document4 pagesRec 2A - Experiments-1Skylar HsuPas encore d'évaluation
- Measure of Central TendencyDocument37 pagesMeasure of Central Tendencyদিব্যজয় পালPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample IIMJRATDocument5 pagesSample IIMJRATswapneel06Pas encore d'évaluation
- TVS MOTORS - Customer Perception-46Document53 pagesTVS MOTORS - Customer Perception-46Chaturvedi Divyanshu50% (6)
- Research1 Sessions 1 6.docx-1Document6 pagesResearch1 Sessions 1 6.docx-1Sabrina MascardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Arpit's SIP Project On "Retailer's Satisfaction"Document63 pagesArpit's SIP Project On "Retailer's Satisfaction"Arpit GargPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 PDFDocument8 pages1 PDFChristine DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- PROJECT Mba PDFDocument60 pagesPROJECT Mba PDFPawan rathorePas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report: A Study of Employee Satisfaction at Cremica Food LimitedDocument57 pagesProject Report: A Study of Employee Satisfaction at Cremica Food LimitedSurender Dhuran PrajapatPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Process & Scientific MethodDocument21 pagesResearch Process & Scientific Methodanis2323100% (1)
- Nasty Project Proposal FFDocument9 pagesNasty Project Proposal FFADEBAYO TAIWOPas encore d'évaluation