Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
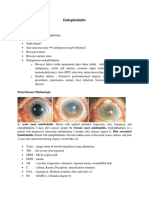
Acute Suppurative Parotitis: Related Summaries
Transféré par
Farida Dwi IrnawatiDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Acute Suppurative Parotitis: Related Summaries
Transféré par
Farida Dwi IrnawatiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
See www.DynamicMedical.
com for the latest version as DynaMed is updated daily
You are viewing a DynaMed summary. Use of DynaMed indicates acceptance of DynaMed Terms of Use.
Limitations of DynaMed are contained in the DynaMed Terms of Use. To search within this summary, click
Expand All, and then Edit - Find (Ctrl-F) in your browser.
Acute suppurative parotitis
Updated 2008 Jul 14 03:06 PM: guideline update
review of differential diagnosis of neck masses (Infect Dis Clin North Am 2007 Jun)
case report of acute suppurative parotitis due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis
Derg 2007)
Related Summaries:
Mumps
Chronic recurrent parotitis
General Information (including ICD-9/-10 Codes)
Description:
inflammatory and infectious process of parotid gland
(2 )
Also called:
acute parotitis
sialadenitis
sialoadenitis
surgical parotitis
postoperative parotitis
ICD-9 Codes:
527.2 sialoadenitis
527.3 abscess of salivary gland
ICD-10 Codes:
K11.2 sialoadenitis
K11.3 abscess of salivary gland
Organs involved:
parotid gland
(1 )
Who is most affected:
elderly
(2 )
case report and review of neonatal suppurative parotitis can be found in
Pediatr Infect Dis J 2004 Jan;23(1):76
Incidence/Prevalence:
estimated incidence
(2 )
reported to be 0.01% to 0.02% of all hospital admissions
reported to be 0.002% to 0.04% of postoperative patients
less common due to use of perioperative antibiotics
(2 )
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes:
Page 1of 7 Acute suppurative parotitis - DynaMed
20/10/2008 http://dynaweb.ebscohost.com/Detail.aspx?docid=/dynamed/aa8ab174b62316218525...
gram-positive bacteria most commonly involved
(1 )
Staphylococcus aureus has been cultured in 50-90% of cases
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (case report in South Med
J 2004 Nov;97(11):1139)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pyogenes
Haemophilus influenzae
other bacteria reported less frequently
Escherichia coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Salmonella
Pseudomonas pseudomallei
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (case report in Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis
Derg 2007;17(5):272)
Mycobacterium scrofulaceum (case report in patient with AIDS in Sex
Transm Infect 2005 Dec;81(6):517)
Treponema pallidum (syphilis)
anaerobes
Candida albicans (case report of parotid abscess in Acta Otolaryngol 2006
Mar;126(3):334)
Pathogenesis:
retrograde contamination by oral cavity bacteria
(1 )
salivary stasis
(1 )
parotid predilection may be due to different composition of secretions
(1 )
Likely risk factors:
dehydration
(1 )
postoperative state
(1 )
advanced age
(1 )
prematurity
(1 )
immunocompromise
(1 )
prior radiation therapy
(1 )
medical illnesses
(1 )
hepatic failure
renal failure
diabetes mellitus (type 1, type 2)
hypothyroidism
malnutrition
HIV
Sjogren's syndrome
hyperuricemia
hyperlipoproteinemia
cystic fibrosis (sialectasis)
lead intoxication
Cushing's disease
Page 2of 7 Acute suppurative parotitis - DynaMed
20/10/2008 http://dynaweb.ebscohost.com/Detail.aspx?docid=/dynamed/aa8ab174b62316218525...
psychiatric illness
(1 )
depression
anorexia
bulimia
prescription medications
(1 )
antihistamines
diuretics
tricyclic antidepressants
phenothiazines
beta blockers
barbiturates
anticholinergics
presence of tracheostomy
(1 )
foreign body obstruction or trauma to duct
(1 )
oral cavity neoplasm
(1 )
pneumoparotitis
(1 )
poor oral hygiene
(2 )
Complications and Associated Conditions
Complications:
abscess
(1 )
systemic infection
(1 )
osteomyelitis
(1 )
thrombophlebitis
(1 )
parapharyngeal extension of abscess
(1 )
facial nerve dysfunction
(1 )
extension of infection into deep neck space (case report in Am J Emerg Med
1999 Jan;17(1):46)
Associated conditions:
in parotitis of strict anaerobic etiology
(2 )
Sjogren's syndrome
rheumatoid arthritis
History
Chief Concern (CC):
sudden onset of severe pain
(1 )
pain exacerbated by meals and salivation
(1 )
swelling over affected gland
(1 )
Medication History:
ask about use of anticholinergic drugs or diuretics
(1 )
Past Medical History (PMH):
ask about other comorbid conditions (see Likely risk factors )
ask about recent surgery
(1 )
postoperative parotitis usually within 2 weeks after procedure
peak incidence between postoperative days 5-7
Page 3of 7 Acute suppurative parotitis - DynaMed
20/10/2008 http://dynaweb.ebscohost.com/Detail.aspx?docid=/dynamed/aa8ab174b62316218525...
has been reported up to 15 weeks postoperatively
Physical
General physical:
may appear toxic, with high fever, possibly delirium
(1 )
Skin:
general skin turgor may be decreased, indicating dehydration
(1 )
HEENT:
area of induration, erythema, edema and heat in cheek
(1 )
extreme tenderness over mandibular angle
(1 )
inflammation of Stensen's or Wharton's duct, purulent discharge may be
present
(1 )
dry or crusted oral mucous membranes
(1 )
redness and swelling accompany bacterial but not viral parotitis
(1 )
facial nerve dysfunction rare
(2 )
Diagnosis
Making the diagnosis:
diagnosis based on clinical exam and presentation
(1 )
Rule out:
differential diagnosis should include
(2 )
viral parotitis (mumps)
cystic fibrosis
collagen vascular diseases (connective tissue diseases)
alcoholism
sarcoidosis
sialolithiasis
chronic recurrent parotitis
if no response to medical therapy, consider
(1 )
lymphoma (see Hodgkin's disease or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma)
actinomycosis
cat-scratch disease
cervical lymphadenitis
Sjogren's syndrome
Wegener's granulomatosis
review of differential diagnosis of neck masses can be found in Infect Dis
Clin North Am 2007 Jun;21(2):523
Testing to consider:
white blood cell count
(1 )
needle aspiration and diagnostic culture if abscess present
(1
(1 )
)
CT, MRI or ultrasound to rule out abscess if no improvement after 48 hours
of medical therapy
(1 )
sialography (contraindicated in acute infection)
(1 )
Blood tests:
Page 4of 7 Acute suppurative parotitis - DynaMed
20/10/2008 http://dynaweb.ebscohost.com/Detail.aspx?docid=/dynamed/aa8ab174b62316218525...
white blood cell count - leukocytosis with predominance of neutrophils
(1 )
serum amylase usually normal
(1 )
(case series of 4 patients with acute
parotitis and asymptomatic hyperamylasemia after whole-brain radiation
therapy can be found in Ann Neurol 1980 Apr;7(4):385)
Imaging studies:
computed tomography (CT) with intravenous contrast medium
(2 )
first-choice radiologic evaluation
can differentiate soft tissue densities in gland
ultrasound to show abscess formation
(2 )
sialography contraindicated in acute infection due to risk of ectatic duct
rupture from pressure of injected dye
(2 )
Prognosis
Prognosis:
variable depending on underlying medical condition of patient
sepsis complication associated with poor prognosis
(1 )
resolution likely in healthy patients who receive early aggressive treatment
(1 )
may result in chronic recurrent parotitis due to ductal stenosis
(1 )
Treatment
Treatment overview:
treat underlying medical condition
(2 )
discontinue antisialagogic medications
(2 )
hydration
(2 )
stimulate salivary flow
(2 )
antibiotic therapy based on culture and sensitivity
(2 )
cannulate and dilate duct if complete obstruction of Stensen's duct
(2 )
surgery if medical therapy failure
(2 )
Activity:
methods to stimulate salivary flow
(1 )
warm compresses
mouth irrigations
administer sialagogues (e.g. citrus lozenges or beverages)
external and intraoral bimanual massage of gland if tolerated by
patient
Medications:
antibiotic therapy
(1,2 )
tailor antibiotic therapy to specific organisms based on culture and
sensitivity
10-14 day course
oral therapy if no systemic illness but intravenous therapy indicated if
no response within 48 hours
if due to S. aureus, drugs of choice include
anti-staphylococcal penicillin, such as nafcillin, oxacillin,
ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn), amoxicillin/clavulanate
(Augmentin)
Page 5of 7 Acute suppurative parotitis - DynaMed
20/10/2008 http://dynaweb.ebscohost.com/Detail.aspx?docid=/dynamed/aa8ab174b62316218525...
first-generation cephalosporin, such as cefazolin
clindamycin
consider vancomycin if due to methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
especially if nursing home or other nosocomial environment
for recalcitrant infection
consider addition of third-generation cephalosporin to enhance gram-
negative coverage
consider addition of aminoglycoside for critically ill patients
Surgery:
surgical drainage
(2 )
indications
no improvement after 3-5 days of antibiotics therapy
facial nerve involvement
involvement of adjacent structures (e.g. lateral pharyngeal
space, deep fascial spaces)
abscess formation within gland parenchyma
standard parotidectomy incision in direction of facial nerve should be
used
Other management:
radiation therapy not shown to be beneficial and no longer recommended
(historically used as adjuvant therapy)
(1 )
Follow-up:
after resolution
(2 )
consider imaging (CT scan or sialogram) to evaluate gland
parenchyma
consider surgical interventions if calculi, mucous plugs, or strictures
develop
evaluation for parotid tumor by routine clinical exam and imaging
when indicated
Prevention and Screening
Prevention:
perioperative hydration to avoid salivary stasis
(1 )
References including Reviews and Guidelines
General references used:
1. McQuone SJ. Acute viral and bacterial infections of the salivary glands.
Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1999 Oct;32(5):793-811.
2. Fattahi TT, Lyu PE, Van Sickels JE. Management of acute suppurative
parotitis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002 Apr;60(4):446-8.
Reviews:
review can be found in Pediatric Surgery Update 2003 Mar;20(3):3 full-text
review of management of acute suppurative parotitis can be found in J Oral
Maxillofac Surg 2002 Apr;60(4):446
Guidelines:
Page 6of 7 Acute suppurative parotitis - DynaMed
20/10/2008 http://dynaweb.ebscohost.com/Detail.aspx?docid=/dynamed/aa8ab174b62316218525...
no relevant guideline for "acute suppurative parotitis or sialadenitis" found
2008 May 1 on systematic search of MEDLINE (using guidelines limiter) and
National Guideline Clearinghouse
Patient Information
Patient information:
handout on parotitis from EBSCO Publishing Health Library PDF or in
Spanish PDF
Acknowledgements
DynaMed topics are created and maintained by the DynaMed Editorial Team.
Over 500 journals and evidence-based sources (DynaMed Content Sources) are
monitored directly or indirectly using a 7-step evidence-based method for
systematic literature surveillance. DynaMed topics are updated daily as newly
discovered best available evidence is identified.
Competing interests:
Each participating member of the DynaMed Editorial Team has declared no
competing interests (financial or otherwise) related to this topic.
Please give us your feedback by clicking on the link below to send an e-mail to DynaMed:
DynaMedEditor@ebscohost.com
Page 7of 7 Acute suppurative parotitis - DynaMed
20/10/2008 http://dynaweb.ebscohost.com/Detail.aspx?docid=/dynamed/aa8ab174b62316218525...
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Special Operations Forces Medical HandbookD'EverandSpecial Operations Forces Medical HandbookÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Tetanus. Gas Gangrene.Document8 pagesTetanus. Gas Gangrene.Hemanathan PraemPas encore d'évaluation
- Otogenic Complications of Otitis Media Experience at Tertiary Care HospitalDocument5 pagesOtogenic Complications of Otitis Media Experience at Tertiary Care HospitalAjeng Ratna HaryantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa InfectionsDocument22 pagesPseudomonas Aeruginosa InfectionsMiguel RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Malignant Otitis External-Our Experience: R. B. Sardesai, T. KrishnakumarDocument4 pagesMalignant Otitis External-Our Experience: R. B. Sardesai, T. KrishnakumarSuci PramadianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mucormycosis in Covid 19 - 2ND Wave: Clinical Profile in Central IndiaDocument5 pagesMucormycosis in Covid 19 - 2ND Wave: Clinical Profile in Central IndiaIJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Exudative TonsillitisDocument4 pagesAcute Exudative TonsillitisRiska PashaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Deep Neck Space InfectionsDocument6 pagesA Study On Deep Neck Space InfectionsbebetteryesyoucanPas encore d'évaluation
- Resistenze Batteriche e Terapia Delle Infezioni PostoperatorieDocument23 pagesResistenze Batteriche e Terapia Delle Infezioni PostoperatoriedantefuertePas encore d'évaluation
- Antifungal LectureDocument62 pagesAntifungal LectureVandana TayalPas encore d'évaluation
- SplitPDFFile 601 To 800Document200 pagesSplitPDFFile 601 To 800Shafan ShajahanPas encore d'évaluation
- G Eneral Surgery MB AnswersDocument56 pagesG Eneral Surgery MB AnswersChris Jardine LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Rhinosinusitis: Autors:Jana Kraķe MF3, 8.grupa Mentors: Gints TomiņšDocument26 pagesAcute Rhinosinusitis: Autors:Jana Kraķe MF3, 8.grupa Mentors: Gints TomiņšVenkatesh PaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ajayan 2013Document3 pagesAjayan 2013Dung TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Brugada Syndrome: CardiologyDocument12 pagesBrugada Syndrome: CardiologyMahmoud HussienPas encore d'évaluation
- 035 Quick Queries Acute RhinosinusitisDocument4 pages035 Quick Queries Acute RhinosinusitisRika FitriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Infective ENDOCARDITIS - FinalDocument81 pagesInfective ENDOCARDITIS - FinalMary Anne Cabalza ApinardoPas encore d'évaluation
- EpiglottitisDocument3 pagesEpiglottitisessamPas encore d'évaluation
- Airway Stenosis Endoscopic Management MGhadiali 11-19-08Document104 pagesAirway Stenosis Endoscopic Management MGhadiali 11-19-08Steffy GosalPas encore d'évaluation
- Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) & Sepsis: Dr.H.Asril Zahari SP.B.KBDDocument43 pagesSystemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) & Sepsis: Dr.H.Asril Zahari SP.B.KBDPark ji SangPas encore d'évaluation
- Rational Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Deep Neck Infections: Analysis of 233 Consecutive CasesDocument7 pagesRational Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Deep Neck Infections: Analysis of 233 Consecutive CasesIlman Fathony MartanegaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bab I Literature Review 1.1 Definition: (Pasternack and Marton, 2010)Document20 pagesBab I Literature Review 1.1 Definition: (Pasternack and Marton, 2010)Rosi Arly FadilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheumatic FeverDocument27 pagesRheumatic FeverMalueth AnguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By:-Dr. Saqib Majeed Salik Resident Maxillofacial Supervised By: - Dr. Suad A Ahmad Consultant Maxillofacial King Abdullah Hospital BishaDocument53 pagesPresented By:-Dr. Saqib Majeed Salik Resident Maxillofacial Supervised By: - Dr. Suad A Ahmad Consultant Maxillofacial King Abdullah Hospital BishaSaqib Majeed SalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Jced 9 E319Document6 pagesJced 9 E319sorayahyuraPas encore d'évaluation
- باطنية 3-6Document46 pagesباطنية 3-6Mariah WaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications of Suppurative Otitis Media: Still A Problem in The 21st CenturyDocument7 pagesComplications of Suppurative Otitis Media: Still A Problem in The 21st CenturyNisa SulistiaPas encore d'évaluation
- LP Bacteria ChartDocument21 pagesLP Bacteria ChartTaman HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Mimics: An Emergency Medicine-Focused Review of Streptococcal Pharyngitis MimicsDocument7 pagesClinical Mimics: An Emergency Medicine-Focused Review of Streptococcal Pharyngitis MimicsDestinea SilvanaputriPas encore d'évaluation
- Infective Endocarditis Today (Version 1 Peer Review: 1 Not Approved)Document9 pagesInfective Endocarditis Today (Version 1 Peer Review: 1 Not Approved)preetPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Factors Associated With Acute PharyngitisDocument4 pagesStudy of Factors Associated With Acute PharyngitisMarsya Yulinesia LoppiesPas encore d'évaluation
- DiphtheriaDocument49 pagesDiphtheriasultanPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Holmstrup Et Al-2018-Journal of Clinical PeriodontologyDocument16 pages4 Holmstrup Et Al-2018-Journal of Clinical PeriodontologyALEJANDRO CARDENAS BALCAZARPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Infection AgentsDocument18 pagesAnti Infection AgentsRawabi SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) : Pranee Sitaposa, MDDocument43 pagesSystemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) : Pranee Sitaposa, MDAli TawbePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Report: Hyperprolactinemia Secondary To Allergic Fungal Sinusitis Compressing The Pituitary GlandDocument4 pagesCase Report: Hyperprolactinemia Secondary To Allergic Fungal Sinusitis Compressing The Pituitary GlandfuadizzuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Oral Hemangiomas With 3 Sodium Tetradecyl Sulfate Study of 24 Cases - September - 2020 - 1598873161 - 7405760Document2 pagesTreatment of Oral Hemangiomas With 3 Sodium Tetradecyl Sulfate Study of 24 Cases - September - 2020 - 1598873161 - 7405760naveed gulPas encore d'évaluation
- SepsisDocument36 pagesSepsisWan FaizuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQSDocument258 pagesMCQSmuhannedPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengue Oral ManifestationDocument7 pagesDengue Oral ManifestationGowthamChandraSrungavarapuPas encore d'évaluation
- CellulitisDocument6 pagesCellulitisjadePas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical InfectionsDocument45 pagesSurgical InfectionsShabeel PnPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Medical Terminology (Hal 7-10 Belum)Document10 pagesJurnal Medical Terminology (Hal 7-10 Belum)Ajiss MahriPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapy CardiovascularDocument35 pagesTherapy CardiovascularCavinpal SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Gs 10 03 1135Document12 pagesGs 10 03 1135Ashu AberaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Fungal Sinusitis Natural History and The Role of Frozen SectionDocument8 pagesAcute Fungal Sinusitis Natural History and The Role of Frozen SectionwitariPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurding Mata EndophthalamitisDocument24 pagesJurding Mata EndophthalamitisBenk Setsuna F. SeieiPas encore d'évaluation
- Esquemas OclusalesDocument18 pagesEsquemas OclusalesKarla AlanisPas encore d'évaluation
- Scleritis and EpiscleritisDocument27 pagesScleritis and EpiscleritisJT RodierPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Otitis Media: by DR - Imran Qazi T.M.O Ent A Ward KTH MTI PeshawarDocument26 pagesAcute Otitis Media: by DR - Imran Qazi T.M.O Ent A Ward KTH MTI Peshawarimran qaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacaan UrosepsisDocument14 pagesBacaan Urosepsisizza rnPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Report: Vertigo As A Predominant Manifestation of NeurosarcoidosisDocument5 pagesCase Report: Vertigo As A Predominant Manifestation of NeurosarcoidosisDjumadi AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Urosepsis-Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment: Continuing Medical EducationDocument14 pagesUrosepsis-Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment: Continuing Medical EducationMuhammad Imam NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Gradenigo Syndrome in A ChildDocument4 pagesManagement of Gradenigo Syndrome in A ChildmitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Ulcerative Stomatitis.Document5 pagesAcute Ulcerative Stomatitis.Manar AlsoltanPas encore d'évaluation
- Endophtalmitis: AnamnesisDocument6 pagesEndophtalmitis: AnamnesisErlinda AgustinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Salivary Gland DiseaseDocument18 pagesSalivary Gland DiseaseEkky Rizky MaulanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Necrotizing Fasciitis: David Hough MSIII Penn State College of MedicineDocument33 pagesNecrotizing Fasciitis: David Hough MSIII Penn State College of Medicineaaz220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument14 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisAnonymous D976HVjqcgPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 IppDocument24 pagesChapter 5 IppRoseann EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Urban PlanningDocument33 pagesWhat Is Urban PlanningDivine Grace FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Corrosion Performance of Mild Steel and GalvanizedDocument18 pagesCorrosion Performance of Mild Steel and GalvanizedNarasimha DvlPas encore d'évaluation
- SANDWICH Elisa (Procedure) - Immunology Virtual Lab I - Biotechnology and Biomedical Engineering - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabDocument2 pagesSANDWICH Elisa (Procedure) - Immunology Virtual Lab I - Biotechnology and Biomedical Engineering - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabsantonuPas encore d'évaluation
- A Method For Prediction of Gas/Gas Ejector PerformanceDocument6 pagesA Method For Prediction of Gas/Gas Ejector PerformancedhavaleshPas encore d'évaluation
- Lord of The Flies - Chapter Comprehension QuestionsDocument19 pagesLord of The Flies - Chapter Comprehension Questionsjosh johnsyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1en 02 PDFDocument96 pages1en 02 PDFAndrey100% (2)
- Uniden PowerMax 5.8Ghz-DSS5865 - 5855 User Manual PDFDocument64 pagesUniden PowerMax 5.8Ghz-DSS5865 - 5855 User Manual PDFtradosevic4091Pas encore d'évaluation
- VERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesVERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperNezer Byl P. VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAditya ShanbhagPas encore d'évaluation
- Monster Hunter: World - Canteen IngredientsDocument5 pagesMonster Hunter: World - Canteen IngredientsSong HoePas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 1 Computer Science ASDocument194 pagesPaper 1 Computer Science ASLailaEl-BeheiryPas encore d'évaluation
- Cella Di Carico Sartorius MP77 eDocument3 pagesCella Di Carico Sartorius MP77 eNCPas encore d'évaluation
- Charles Zastrow, Karen K. Kirst-Ashman-Understanding Human Behavior and The Social Environment-Thomson Brooks - Cole (2007)Document441 pagesCharles Zastrow, Karen K. Kirst-Ashman-Understanding Human Behavior and The Social Environment-Thomson Brooks - Cole (2007)joan82% (17)
- KM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)Document4 pagesKM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)krzysiek1975Pas encore d'évaluation
- All Nobel Prizes in LiteratureDocument16 pagesAll Nobel Prizes in LiteratureMohsin IftikharPas encore d'évaluation
- WoundVite®, The #1 Most Comprehensive Wound, Scar and Post-Surgical Repair Formula Receives Amazon's Choice High RatingsDocument3 pagesWoundVite®, The #1 Most Comprehensive Wound, Scar and Post-Surgical Repair Formula Receives Amazon's Choice High RatingsPR.comPas encore d'évaluation
- (Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesDocument196 pages(Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesAmbrose66Pas encore d'évaluation
- Furniture AnnexDocument6 pagesFurniture AnnexAlaa HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Research Project Science ReportDocument8 pagesStudent Research Project Science Reportapi-617553177Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prometric Questions-1 AnswersDocument45 pagesPrometric Questions-1 AnswersNina Grace Joy Marayag-Alvarez100% (1)
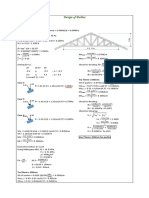
- Design of Purlins: Try 75mm X 100mm: Case 1Document12 pagesDesign of Purlins: Try 75mm X 100mm: Case 1Pamela Joanne Falo AndradePas encore d'évaluation
- 3E Hand Over NotesDocument3 pages3E Hand Over NotesAshutosh MaiidPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveKiara Fajardo matusPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 1 KeyDocument3 pagesClass 1 Keyshivamsingh.fscPas encore d'évaluation
- Action Plan in T.L.E Project Title Objectives Activities Person-In-Charge Time Frame Success IndicatorDocument1 pageAction Plan in T.L.E Project Title Objectives Activities Person-In-Charge Time Frame Success IndicatorEdelmar BenosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment - UK Forestry Data ICT THEORY For CAT1Document13 pagesAssessment - UK Forestry Data ICT THEORY For CAT1Joanna AchemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Baby DedicationDocument3 pagesBaby DedicationLouriel Nopal100% (3)
- Abdominal Migraine and HomoeopathyDocument17 pagesAbdominal Migraine and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Review - Part Time Job Among StudentDocument3 pagesLiterature Review - Part Time Job Among StudentMarria65% (20)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeD'EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsD'EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (42)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityD'EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (24)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedD'EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (9)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsD'EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningD'EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaD'EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDD'EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsD'EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessD'EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (328)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeD'EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (253)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerD'EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (392)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsD'EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (169)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.D'EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceD'EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (51)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyD'EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosD'Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (207)