Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Modul Bio SBP 2011 Ans
Transféré par
Alan WangCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Modul Bio SBP 2011 Ans
Transféré par
Alan WangDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
1
BAHAGIAN SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH DAN
SEKOLAH KLUSTER
KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA
PERFECT
SCORE
BIOLOGY
2011
Teachers Module
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
2
Paper 2 Section A:
Structural Questions Marks Student
notes
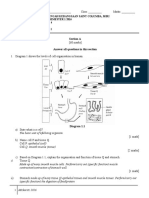
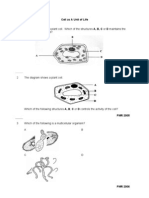
1. Diagram 1.1 shows a somatic cell of an insect undergoing meiosis.
Diagram 1.1
(a) Label Q, R and S in Diagram 1.1.
[3 marks]
3m
(b) In the space below draw chromosome behaviour during metaphase I
and metaphase II.
[2 marks]
2m
Metaphase I
Metaphase II
Q: Chromosome/
chromatid
R: Centromere
S: Nuclear
membrane
Process X
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
3
(c) Explain how the process X involves in producing variation in organisms.
P1 - During prophase Meiosis 1, crossing over occurs between
homologous chromosomes
P2 - resulting a new genetic combination.
P3- It is also producing the exchange of genetic material between
paternal chromosome and maternal chromosome // between
homologous chromosomes.
[3 marks]
Any
3=3m
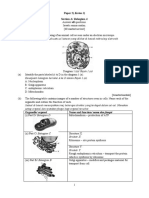
(d) Diagram 1.2 shows the formation of an ovum.
(i) What are process M and N?
M : Meiosis I
N : meiosis II
[2 marks]
2m
(ii) Describe the process that occurs if a sperm present at process N.
P1: meiosis II completed // ovum form
P2: (nucleus) ovum is fertilized by sperm nucleus
P3 : zygote is form
[2 marks]
2m
M
N
M
N
Primary oocyte (2n)
Oogonium (2n)
First polar body
(n)
Secondary oocyte
(n)
Second polar body
(n)
Diagram 1.2
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
4
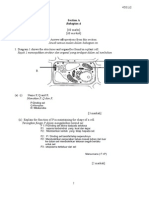
2.
Diagram 2 shows the digested food is being carried from small intestine
to the liver and body cell.
(a)(i) Name process X at the villus.
Absorption
[1 mark]
1m
(ii) Explain ONE adaptation of the villus for the process in (a)(i).
F : Has thin wall//one cell thick wall
E : Diffusion of nutrient occurs rapidly //
F: Has network of blood capillary
E : transport nutrient to body tissue
1F=1m
1E=1m
Diagram 2
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
5
F : has lacteal //
E : to absorb/ transport fatty acid/glycerol to body tissue
F : numerous
E : increase total surface area
[2 marks]
(b) Vessel P and Q transport digested food from the villi to the liver and body
cells respectively.
Name vessel P and vessel Q.
P :Hepatic portal vein
Q: Lymphatic vessel
[2 marks]
1m
1m
(c) Explain what happens to the excessive amino acids in the liver?
P1 : Excess amino acid is converted into urea
P2 : process is called deamination
[2 marks]
1m
1m
(d) Digested food are used by the body cells for growth, to form complex
compounds or structural components.
State how lipids, amino acid and glucose are used in the cell.
Lipids:
L1: is used to build up plasma membrane/phospolipid
L2 : excess lipid is stored in adipose tissue
L3 : is used as energy reserve in the body
Amino acids:
A1: Amino acids are used in protein synthesis
A2 : to repair damage tissue
A3: used in synthesis of enzyme/hormones/antibody
Glucose:
G1 : is used in cellular respiration/ is oxidized to release energy
G2 : Glucose is stored as adipose tissue.
[3 marks]
L=1m
A=1m
G=1m
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
6
(e) Explain what will happen to a person if his liver receives insufficient insulin
from the pancreas.
P1 : Blood sugar level increases// Diabetes mellitus
P2 : Excess glucose cannot be converted to glycogen
[2 marks]
1m
1m
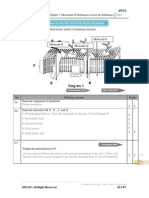
3. Diagram 3 shows the structure of respiratory system in human.
Diagram 3
(a) Based on Diagram 3, explain one adaptation of alveolus for efficient
gases exchange.
F1 : one cell thick
P1 : gas doesnt have far to diffuse //diffuse easily
F2 : supply with network of blood capillary.
P2 : to increase the diffusion // transportation of respiratory gases to
/from all the body cells.
F3 : large surface area // numerous number of alveoli
P3 : increase the diffusion of respiratory gases
F4 : inner surface of alveoli are moist
P4 : oxygen dissolve in the film of water
1F=1m
1P=1m
Bronchus
P
Blood
capillary
Cells
Alveolus
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
7
Any F with correspond P
(b)(i) Name P
Trachea
1m
(b)(ii)
Explain the role of P to prevent dirt and bacteria from entering the
alveolus.
F1 : secrete sticky fluid/mucus
P1 : traps dirt / bacteria that are breathed in.
F2 : cells in P have cilia / tiny hair-like structures
P2 : sweeping the mucus out towards the mouth.
Any F with correspond P
1F=1m
1P=1m
(c)(i)
On Diagram 3, draw labeled arrow ( ) to show the direction of
Blood flow (P1)
Oxygen diffusion (P2)
Carbon dioxide diffusion (P3)
[3 marks]
Blood flow= arrow from blood capillary to other side of blood
capillary
Oxygen diffusion = arrow from alveolus to blood capillary
// arrow from blood capillary to cells
Carbon dioxide diffusion = arrow from blood capillary to alveolus
// from cells to blood capillary
P1=1m
P2 =1m
P3 = 1m
(c)(ii) Explain why the diffusion of oxygen occur at the alveolus.
F: the partial pressure of oxygen in the air of the alveoli is higher
compared to the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood capillary
P: ( therefore,) oxygen diffuses across the surface of the alveolus to
the blood.
1m
1m
(d) A hard mass of food passing down the oesophagus might indirectly
interrupt the air supply to lung by pressing on P.
Explain how P overcome this problem.
F : P/trachea is protected (against closure by a series of closely
packed C-shaped) ring of cartilage
P : cartilage keep the trachea open// prevent from collapse
1m
1m
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
8
Structural Questions Marks Student
notes
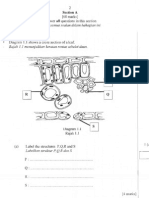
4. Diagram 4.1 shows a cross section of a leaf.
.
Diagram 4.1
(a)(i) On Diagram 4.1 label the structures P and Q.
P : Xylem
Q : Phloem
[2 marks]
1m
1m
(a)(ii) Explain the stage of cell organization of the leaf .
F : Organ
E: made up of ground tissue, epidermal tissue, mesophyll tissue
and vascular tissue // consists of various types of tissues
combined together to perform spesific functions.
[2 marks]
1m
1m
(b)(i) Q are important structure in plant transport system.
Explain how structure Q in the leaf help in plant transportation.
P1: Q / Phloem tissue composed of sieved tubes
P2: with the end walls of each cell are perforated by pores to form
sieves plates
P3:which allow substances to pass from one cell to another.
[2 marks]
1m
1m
1m
(b)(ii) Name the process occurs in (b)(i).
Translocation
[1 marks]
1m
P: ________________
Q: _______________
__________________
____
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
9
Diagram 4.2 shows a longitudinal section of structure Q.
(b)(iii)
On Diagram 4.2 label the structures R and S.
[2 marks]
1m
1m
(c) R plays an important role in helping S in the plant transportation.
Predict what happen to the plant if structure R is not presence ?
P1: The plant will be dye
P2: (without R / companion cell) no energy will be provided to the
sieve tube
P3:hence dissolve organic substances/sucrose/ cannot be
transported (from leaves to the storage organ/other part of
plant)
[2 marks]
Any 2
= 2m
Diagram 4.3 (a) and 4.3 (b) shows a student removed the ring bark from
the branch of a woody plant.
S: Sieve tube cell
_____________
R: Companion
ccecell
____________
Diagram 4.2
Diagram 4.3(a) Diagram 4.3(b)
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
10
(d)
Predict the effect of removing the ring bark from the branch.
Explain your answer.
P1: The branch will be die
P2: owing to a lack of organic substances in the parts below the
ring.
[2 marks]
1m
1m
5. Diagram 5 shows three types of neurones in the human body.
(a) Name neurone P and neurone Q.
Neurone P : Afferent neurone / sensory neurone.
Neurone Q: Interneurone
[2 marks]
1m
1m
(b)(i) Name structure X.
Synapse
[1 mark]
1m
(b)(ii) Explain how the transmission of nerve impulse across the X.
P1 - When an impulses / electrical signals reaches in the axon
terminal
P2 - Stimulates (synaptic) vesicles to move towards (and
bind with the presynaptic membrane)
P3 - The vesicles fuse / release the neurotransmitter/ acetylcoline /
example of neurotransmitter into the synapse / X.
P4 - The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse / X
P5 - This leads to the generation of new impulse/ electrical signals
in which travels along the Q / neurone
[3 marks]
Any 3=
3m
Diagram 5
P
Q
R
X
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
11
(c) Describe the pathway in the reflex action involved the three neurons
above.
P1 - Receptor detect the stimulus and triggers the nerve impulses
P2 (The nerve impulses) are transmitted along neurone P to
neurone Q (in the spinal cord) through/ via synapse.
P3 (The nerve impulses) are then transmitted from neurone Q to
neurone R through synapse
[3 marks]
Any3 =
3m
(d)
Based on the above statement describe how endocrine system is
involved in the fight and flight situation.
P0 adrenaline is secreted by adrenal gland
P1 (adrenaline) cause the heartbeat / breathing rate increase
P2 more oxygen and glucose are sent/ transported to the tissues
P3 metabolic rate / cellular respiration increases
P4 - more energy is produced to contraction and relaxation of
muscle (to run away)
[3 marks]
Any 3=
3m
A dog suddenly barks and chases you. Your heartbeat increases
and your palms become sweaty. You feel so scared and run away.
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
12
6. Diagram 6 .1 shows a part of human brain, kidney and a nephron which
involve in the process of osmoregulation.
(a) What is the function of kidney in osmoregulation ?
P1: Kidney regulates salts/solutes and water levels in the blood
P2: to maintain a constant water potential in the body /
regulates the osmotic pressure of the blood
[1 mark]
1m
(b)(i) Individual Y drinks excessive water.
What happen to the blood osmotic pressure in his body?
Osmotic pressure in plasma decreases // water potential increases
[ 1 mark ]
1m
(b)(ii) Explain how hypothalamus and gland M response to the condition in
(b)(i) ?
Hypothalamus:
P1: Osmoreceptor (in hypothalamus) detect the changes /
less stimulated.
Gland M :
P2:Pituitary gland / gland M is less/ not stimulated/trigger
P3:Hence less hormone P / ADH secreted
P4:Less water reabsorbed
[ 2 marks]
P1 =1m
Any P2-
P4 = 2m
Diagram 6.1
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
13
(c) If individual Y eating a very salty food, the adrenal gland will release less
hormone Q .
What is hormone Q and explain how hormone Q involved in the
mechanism to restore the osmotic pressure of the blood back to normal
levels.
P1: Hormon Q is aldosterone hormone
E1:(Adrenal gland less stimulated) ,
E2; less aldosterone produced,
E3: less salt is reabsorbed
E4:most of it will be secreted through urine
[ 3 marks ]
3 any =
3m
(d) Explain what happen to the filtrate that flows from glomerulus to
collecting duct?
P 1 : Water /glucose/amino acid is reabsorbed into blood capillary
P2 : urea is secreted into distal convoluted tubule
P3 : salt is reabsorb/ secreted depends on osmotic pressure
[ 2 marks ]
2 m
(e) Kidney function may be impaired by excessive blood loss, certain poisons
or infectious diseases which can lead to kidney failure.
Diagram 6.2 shows a haemodialysis machine which can save a kidney
patients life.
(e) Explain how the machine operates.
P1: blood is pump into semi permeable membrane in the dialysis
machine
P2: contains (dialysate) solution
P3: waste substances /urea diffuse out (from the blood)
P4: useful substances are not.
P5: cleaned blood returns to the patient
[ 3 marks ]
Any 3
=3 m
Diagram 6.2
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
14
7. Diagram 7 shows the changes of four type of hormone which control the
menstrual cycle and follicle development in the ovaries
(a) Based on Diagram 7, name the hormone labelled P and R.
P : Luteinising hormone
R : Oestrogen hormone
[2 marks]
2m
(b) Complete the follicle development in boxes L and N in Diagram 7.
L : ovum release from graafian follicle/ovulation (diagram)
N : size of corpus luteum is smaller than M.(diagram)
[2 mark]
2m
(c) Based on Diagram 7, explain the relationship between structure M and
the level of hormone S.
P1 : Structure M /corpus luteum develop after ovulation
P2 : Structure M secretes Hormone S /progesterone
P3 : concentration/level of hormone S increase
P4: when the structure M degenerate, level of hormone S decrease
[3 marks]
Any
3=3m
Diagram 7
L
M
N
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
15
3(d) If fertilisation occurred, the level of hormones S is maintained and the
pregnancy is proceed. Explain the importance of hormone S.
P1 : to thicken the endometrium wall
P2 : with epithelium tissue/ network of blood capillary//highly
vascular
P3 : prepare for implantation of foetus
[3 marks]
3m
(e) If the sperm counts of a husband is too low, artificial insemination can be
carried out to overcome this in fertility problem. Discuss the appropriate
technique should be used.
P1 : sperm are collected
P2 : (over a period of time) until the count of sperm will be high
enough
P3 : the sperm are injected directly into Fallopian tube
[2 marks]
2m
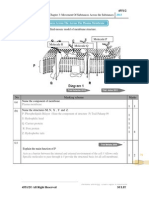
8. Diagram 8 shows a longitudinal section of the reproductive parts of a
flower during fertilization.
(a). On Diagram 8, name the structure P, Q, R and S.
[4 marks]
4m
Diagram 8
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
16
(b)(i) In the space below, draw a section through the ovule, showing all the
cells in R.
Label the cell involved in the fertilization.
D= 1m
L= 2m
(b)(ii) What is the significance of having two Q structure in the fertilization.
P1: one cell Q/ male gamete fertilizes an egg cell to form the diploid
zygotes
P2: one cell Q/ male gamete fertilizes 2 polar nuclei to form the
triploid zygote to form endosperm
[2 marks]
2m
(c)(i) A farmer spraying hormone X on the tomatos flower to produce mature
tomato.
What is hormone X?
Auxin.
[1 mark]
1m
(c)(ii) Explain the role of hormone X in the production of mature tomato fruits.
P1: Auxin stimulates the ovaries of the tomato flowers to develop
into fleshy fruits
P2: without pollination and fertilization
P3: the process is called partenocarpy
P4: where the tomato fruits are seedless
Any 2=
2 m
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
17
9. Diagram 9.1 shows the relationship between a cell, chromosome, DNA,
genes and bases.
(a) On Diagram 9.1 , mark and label of the following terms :
i) DNA
ii) Bases
iii) Chromosomes
[3 marks]
3m
(b) State the chromosome number of the cell shown in Diagram 9.1.
Answer : 12
[1 mark]
1m
(c)
What can you deduce about genes based on Diagram 9.1?
gene consists of a (short) segment of DNA molecule //
genes carried genetic information in form of sequence of
nitrogenous base / A, G, T.
[1 mark]
1m
genes
Diagram 9.1
Chromosome
DNA
Base
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
18
Diagram 9.2 shows parts of a molecule of DNA.
(d)(i)
Name the basic unit of DNA.
Answer: Nucleotide
[ 1 mark ]
1m
(d)(ii) What is K ?
answer: (Pentose) sugar // Deoxyribose
[ 1 mark ]
1m
(d)(iii)
Complete the Diagram 9.2, to show that DNA molecule consist of two
strands that joined together by hydrogen bond.
Criteria Correctly
C1. paired base
C2. position of polynucleotide ( opposite direction )
C3. Connection between molecules in polynucleotide
[ 3 marks]
C1=1m
C2=1m
C3=1m
Diagram 9.2
A
T
G
Unit of
DNA
K
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
19
Diagram 9.3 shows chromosomes with the alleles for crosses between
two varieties of pea plants: yellow and smooth seed variety, with a green
and wrinkled seed variety. Yellow seed (Y) is dominant over green seed
(y) while smooth seed (S) is dominant over wrinkled seed (s).
(e)(i)
Based on Diagram 9.3, indicate the pair of alleles found in the F
1
generation.
[1 mark]
1m
(e)(ii)
Determine the phenotype of the offspring in the F
1
generation.
Answer: Yellow and smooth seed.
[1 mark]
1m
Diagram 9.3
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
20
10. Diagram 10 show the pedigree inheritance of the characteristics,
haemophilia in a family. The characteristics, haemophilia is controlled by
a pair of alleles hh that are linked to the sex chromosomes. H is dominant
to h.
Key :
Normal male Haemophiliac male
Normal female Haemophiliac female
(a) Explain briefly the characteristics haemophilia.
(A phenomenon which is) blood fail to clot due to lack of blood
clotting factor.
[1 marks]
1m
(b)(i) What is the genotype of K?
Answer: X
H
X
h
[1 mark]
1m
(b)(ii) Explain how to determine the genotype in (b)(i)?
P1 :K has a male haemophiliac offspring, X
h
Y.
P2 :K is a normal female, hence she has a pair of
heterozygous alleles X
H
X
h
(to produce a male haemophiliac offspring with genotype X
h
Y)
[2 marks]
2m
L
K
Q
S
R
Diagram 10
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
21
(c)(i) State the genotypes and gametes for the parent in the third generation.
Female x Male
Phenotype : Normal Normal
Genotype : X
H
X
h
X
H
Y
Gamete : X
H
X
h
X
H
Y
[2 marks]
2m
(c)(ii) Q and R are sisters and are normal. They are found to have different
genotypes. Explain why?
P1 :One of them inherits X
H
from her father and X
H
from her mother
P2:The other one inherits X
H
from her father and X
h
from her
P3 :mother. Both are normal but genotypically, one of them is a
carrier
[2marks]
2m
(c)(iii) If a haemophilic female marries the child S in the third generation, what is
the probability of obtaining children that are haemophiliac?. Explain
your answer by constructing a genetic diagram for this inheritance.
Parental generation :
Phenotype Haemophiliac female x normal male
Genotype X
h
X
h
X
H
Y
meiosis
Gametes X
h
X
H
Y
Fertilisation
Offspring :
Genotype X
H
X
h
X
h
Y
Phenotype: Normal (female) Haemophiliac (male)
Probability : 50% normal and 50% haemophiliac //
Phenotypic ratio : 1 normal female : 1 haemohilia male
[4 marks]
1m
1m
1m
1m
1m
Max 4m
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
22
(d) Sex-linked trait such as haemophilia and colour-blindness are usually
associated with males. Explain why?
P1 :Males are determined by the presence of the X and Y
chromosomes // male only has one X chromosome
P2: Sex-linked genes are absent in the Y chromosomes//only
presence in X chromosome.
P3 : Therefore, the presence of one sex-linked gene in the X
chromosome will affect the male as compared to the
female who needs recessive genes to be present in both
X chromosomes for her to be affected.
[2 marks]
Any2 =
2m
PERFECT SCORE BIOLOGY 2011
23
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Module SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyDocument102 pagesModule SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyKen Yew PiongPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Document0 pageAnswer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Thuran NathanPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Kertas 2Document9 pagesSkema Kertas 2Sitinorsyahidah Jantan100% (1)
- Confidential: ATP SynthetaseDocument5 pagesConfidential: ATP SynthetaseazszahPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise PDFDocument12 pagesExercise PDFAmsyidi Asmida100% (1)
- Reactive Oxygen Species: Signaling Between Hierarchical Levels in PlantsD'EverandReactive Oxygen Species: Signaling Between Hierarchical Levels in PlantsFranz-Josef SchmittPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNDocument15 pagesBiology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNMiz KarstzPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument4 pagesGaseous ExchangeArvin DiNozzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleft Lip and Palate Management: A Comprehensive AtlasD'EverandCleft Lip and Palate Management: A Comprehensive AtlasRicardo D. BennunPas encore d'évaluation
- Jawab Semua Soalan Dalam Bahagian Ini: Section ADocument34 pagesJawab Semua Soalan Dalam Bahagian Ini: Section AArleenaAmnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Jawapan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2012 BioDocument9 pagesSkema Jawapan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2012 Biogomathi24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsD'EverandPhysical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsMitsuru NagasawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeDocument283 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeCikgu Faizal87% (15)
- Current Topics in Bioenergetics: Volume 12D'EverandCurrent Topics in Bioenergetics: Volume 12D. Rao SanadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K2 SkemaDocument12 pagesTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K2 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Biology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2Document9 pagesBiology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2Athirah Maestro100% (1)
- Sulit 4551/2: Reject: Provide Reject: AbsorbDocument17 pagesSulit 4551/2: Reject: Provide Reject: AbsorbYatihanna MrodiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument15 pagesCell Structure and Organisationzulkarnain100% (4)
- 4551 BIO - Skema Kertas 1 & 2 & 3Document19 pages4551 BIO - Skema Kertas 1 & 2 & 3Yeow Pow ChooPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Sac PDFDocument24 pagesSkema Sac PDFNoridaAnisPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 BerjawapanDocument15 pagesSPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 Berjawapanpss smk selandarPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Biology Paper 123 Trial SPM 2013 MRSM Del JsuDocument43 pagesSkema Biology Paper 123 Trial SPM 2013 MRSM Del JsuAhmad Imran Idzqandar100% (2)
- Bioskema k2-phg2010Document15 pagesBioskema k2-phg2010Syam SimpsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme Bio Paper 2 2011Document12 pagesScheme Bio Paper 2 2011Hafiq IkhwanPas encore d'évaluation
- 0610 w11 QP 22Document20 pages0610 w11 QP 22If HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 SBP Bio SkemaDocument33 pages2011 SBP Bio SkemaChe ShazuandyPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial Spm-Bio k2 SkemaDocument14 pagesTrial Spm-Bio k2 SkemaFarah Shafiqah AmiruddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Key Science PRE BOARD II 2018 19Document21 pagesAnswer Key Science PRE BOARD II 2018 19AdtPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahan Seminar Biology (Soalan)Document21 pagesBahan Seminar Biology (Soalan)Siti Nor AishahPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul Biologi 2016 t5 Skema PDFDocument43 pagesModul Biologi 2016 t5 Skema PDFIsmaliza IshakPas encore d'évaluation
- GRADE 9 Q1 W1 Respiratory System and Diseases GRADE 9 Q1 W1 Respiratory System and DiseasesDocument9 pagesGRADE 9 Q1 W1 Respiratory System and Diseases GRADE 9 Q1 W1 Respiratory System and DiseasesRheaPas encore d'évaluation
- KERTAS 2 Ting 5Document23 pagesKERTAS 2 Ting 5Ismaliza IshakPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaDocument65 pagesModul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaIsmaliza IshakPas encore d'évaluation
- Perfect Score Biology: Module Form 5Document15 pagesPerfect Score Biology: Module Form 5Farhanah AlawdeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 5 TransportationDocument3 pagesBiology Form 5 TransportationM I K R A MPas encore d'évaluation
- Bab 2 Kertas 2Document8 pagesBab 2 Kertas 2Wan RoziahPas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Secondary Model Examination February 2012 ZoologyDocument4 pagesHigher Secondary Model Examination February 2012 ZoologyAkhil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Jnwuh Semua Socilan Ckilam H Zhugiun Ini: (60 Marks) Answer Questions in This SectionDocument5 pagesJnwuh Semua Socilan Ckilam H Zhugiun Ini: (60 Marks) Answer Questions in This SectionazszahPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology: James Ruse Agricultural High SchoolDocument17 pagesBiology: James Ruse Agricultural High SchoolAlexCuiPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM 4551 2005 Biology k2Document24 pagesSPM 4551 2005 Biology k2pss smk selandarPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 3Document23 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 3Shephard Png92% (26)
- Sains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 2)Document12 pagesSains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 2)JeyShida73% (11)
- XAPlus 2016 Answer MiauDocument24 pagesXAPlus 2016 Answer MiauzulkarnainPas encore d'évaluation
- T1 BAB 2 LinDocument12 pagesT1 BAB 2 LinNorhamizah Megat AzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 2 (Kertas 2) Section A/ Bahagian ADocument22 pagesPaper 2 (Kertas 2) Section A/ Bahagian ANgu Toh OnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and IonDocument14 pagesCell Structure and IonNur NaNa100% (1)
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 3Document23 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 3wenwen160499Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse - X - Biology - PT-1 - April 2023 Key)Document9 pagesCbse - X - Biology - PT-1 - April 2023 Key)LAZED YT GAMINGPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Bio Prelim P2 2009Document16 pagesH2 Bio Prelim P2 2009Tan Eng BoonPas encore d'évaluation
- F4 BIO2 Year End 2022 AnswersDocument9 pagesF4 BIO2 Year End 2022 AnswersArsyad DanishPas encore d'évaluation
- Solaf 1 4551/1Document21 pagesSolaf 1 4551/1kabil86Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 (John H. Mathews) PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 1 (John H. Mathews) PDFpja752Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 (John H. Mathews)Document43 pagesChapter 2 (John H. Mathews)Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Structured Programming Week1Document8 pagesStructured Programming Week1Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 (John H. Mathews)Document39 pagesChapter 5 (John H. Mathews)Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 (John H. Mathews)Document29 pagesChapter 3 (John H. Mathews)Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 (John H. Mathews)Document58 pagesChapter 6 (John H. Mathews)Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- The Structure of The Absolute Central of Certain Groups: Wang Kah Lun Sei130031Document62 pagesThe Structure of The Absolute Central of Certain Groups: Wang Kah Lun Sei130031Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Structured Programming Slide Week5Document10 pagesStructured Programming Slide Week5Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Structured Programming Slide Week4Document8 pagesStructured Programming Slide Week4Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract AlgebraDocument9 pagesAbstract AlgebraAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Structured Programming Slide Week6Document10 pagesStructured Programming Slide Week6Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Structured Programming Slide Week2Document8 pagesStructured Programming Slide Week2Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Structured Programming Slide Week3Document9 pagesStructured Programming Slide Week3Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract AlgebraDocument5 pagesAbstract AlgebraAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Matrix TheoryDocument14 pagesMatrix TheoryAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Gtokifandonlyif: Sjem 2213/sjes2216 Algebra I Chapter 4 Homomorphism 4.1. Definition. Let G, K Be Two Groups. A FunctionDocument8 pagesGtokifandonlyif: Sjem 2213/sjes2216 Algebra I Chapter 4 Homomorphism 4.1. Definition. Let G, K Be Two Groups. A FunctionAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Sjem 2213 Algebra I Chapter 1 Groups 1.1 Definition. A SetDocument9 pagesSjem 2213 Algebra I Chapter 1 Groups 1.1 Definition. A SetAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract AlgebraDocument12 pagesAbstract AlgebraAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 8Document10 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 8Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract AlgebraDocument6 pagesAbstract AlgebraAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract AlgebraDocument5 pagesAbstract AlgebraAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 10Document14 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 10Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 9Document26 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 9Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 5Document11 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 5Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 3Document20 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 3Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 6Document24 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 6Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 7Document30 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 7Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 4Document25 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 4Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics Lecture Note 2Document23 pagesThermal Physics Lecture Note 2Alan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Article: An Approach To The Child With Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesReview Article: An Approach To The Child With Acute GlomerulonephritisLu Jordy LuhurPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal MCQ 1Document2 pagesRenal MCQ 1AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapeutic DietDocument8 pagesTherapeutic Dietannie100% (1)
- Poster Combur10Document1 pagePoster Combur10Lory LanePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study HyperkalemiaDocument10 pagesCase Study HyperkalemiaJamaica Cerrero100% (1)
- The Excretory System-Biology-Unit 7 The Excretory SystemDocument6 pagesThe Excretory System-Biology-Unit 7 The Excretory SystemCamille ComasPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - FMGE Dec GH VersionDocument14 pages1 - FMGE Dec GH VersionHarshit SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinalysis 1: Mr. Arian Ray E. MalintadDocument55 pagesUrinalysis 1: Mr. Arian Ray E. MalintadAbraham DemeterioPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Blood ChemDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Blood ChemMary Gold EleveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Campbell's Urology, 7th Edition. (3 Volume Set)Document2 pagesCampbell's Urology, 7th Edition. (3 Volume Set)Eka0% (1)
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 2021Document42 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 2021Letlhogonolo RaotsilePas encore d'évaluation
- Kdigo 2021 BP GLDocument92 pagesKdigo 2021 BP GLAndres BermudezPas encore d'évaluation
- N Engl J Med 2022 386 964 - AppendixDocument5 pagesN Engl J Med 2022 386 964 - AppendixEvelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Excretion in Humans 3 QP-merged PDFDocument43 pagesExcretion in Humans 3 QP-merged PDFrachit100% (1)
- Kidney Nephron Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesKidney Nephron Structure and Functionxanxan4321Pas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Tumors in AdultsDocument23 pagesRenal Tumors in AdultsmadhuPas encore d'évaluation
- (PharChem Lab) Post Lab Finals For Students 2015Document4 pages(PharChem Lab) Post Lab Finals For Students 2015JeannePas encore d'évaluation
- Renal StonesDocument12 pagesRenal StonesDamandeep KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- OedemaDocument23 pagesOedemaTavleen KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Intellicare - ACCREDITED SPECIALTYCLINICS As of June 2010Document3 pagesIntellicare - ACCREDITED SPECIALTYCLINICS As of June 2010Dey Ferrer OliveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic and Microbiological Tools in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument36 pagesDiagnostic and Microbiological Tools in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryrajtanniruPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7.8.9 - Glomerulopathies (Including Nephritic, Nephrotic, Minimal Change, Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and Membrane Nephropathy)Document92 pagesLecture 7.8.9 - Glomerulopathies (Including Nephritic, Nephrotic, Minimal Change, Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and Membrane Nephropathy)mihalachemirelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Urea UvDocument1 pageUrea Uvpsychejane100% (1)
- Change in Measured GFR Vs EGFR CKD OutcomeDocument9 pagesChange in Measured GFR Vs EGFR CKD OutcomeAlizaPinkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Glomerular Diseases: DR Rashmi NazarethDocument49 pagesGlomerular Diseases: DR Rashmi NazarethRohit RajeevanPas encore d'évaluation
- CAPE Biology Unit 2 - Module 2 TestDocument1 pageCAPE Biology Unit 2 - Module 2 TestLorenzini GrantPas encore d'évaluation
- Life Processes XDocument124 pagesLife Processes XAyush SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Failure and PancytopeniaDocument3 pagesRenal Failure and PancytopeniaIvan VeriswanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Kidney Injury For NAUTHDocument39 pagesAcute Kidney Injury For NAUTHfranklin ifioraPas encore d'évaluation
- Abbot, Diabetes ManagementDocument1 pageAbbot, Diabetes ManagementMelissa Grace DizonPas encore d'évaluation