Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment #8 Polarization and Stability of Point Q
Transféré par
Crespi1200 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
13 vues6 pages1) The document describes an experiment to verify the stability of point Q in different transistor polarization circuits. It involves measuring current and voltage values for various circuit configurations with different resistor combinations.
2) Key parts of the experiment include measuring values for circuits with two different transistor polarizations, varying the base resistance and emitter resistance, and comparing measured to theoretical values.
3) Graphs are included to compare the linear relationships between measured and theoretical values for collector current and collector-emitter voltage under varying conditions.
Description originale:
Titre original
Assignment 8posta
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce document1) The document describes an experiment to verify the stability of point Q in different transistor polarization circuits. It involves measuring current and voltage values for various circuit configurations with different resistor combinations.
2) Key parts of the experiment include measuring values for circuits with two different transistor polarizations, varying the base resistance and emitter resistance, and comparing measured to theoretical values.
3) Graphs are included to compare the linear relationships between measured and theoretical values for collector current and collector-emitter voltage under varying conditions.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
13 vues6 pagesAssignment #8 Polarization and Stability of Point Q
Transféré par
Crespi1201) The document describes an experiment to verify the stability of point Q in different transistor polarization circuits. It involves measuring current and voltage values for various circuit configurations with different resistor combinations.
2) Key parts of the experiment include measuring values for circuits with two different transistor polarizations, varying the base resistance and emitter resistance, and comparing measured to theoretical values.
3) Graphs are included to compare the linear relationships between measured and theoretical values for collector current and collector-emitter voltage under varying conditions.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 6
LABORATORY OF ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
Students: Asato, Crespi y Genovese
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1
ASSIGNMENT N 8
POLARIZATION AND STABILITY OF POINT Q
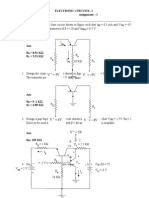
AIM: To verify the stability of point Q in different polarization circuits.
PART A:
CIRCUITS TO BE USED:
R
C
= 4,7K. R
C
= 4,7K.
R
B
= 1,8M. R
E
= 1K.
V
CC
= 12V. R1 = 100K
T = BC548B. R
2
= 22K.
V
CC
= 12V
T = BC548B.
MATERIALS TO BE USED:
_ Resistors of 4,7K,1K, 1,8M,100K 22K.
_ Three BC548B transistors
_ A power supply
_ A multimeter
_ A protoboard.
PROCEDURE:
1) Assemble circuit (a).
2) Measure I
CQ
, V
CEQ
and V
BE
for three transistors and write the values in the
corresponding table.
3) Assemble circuit (b).
4) Measure I
CQ
, V
CEQ,
V
BE
and V
BB
for three transistors and write the values
in the corresponding table.
MEASUREMENTS:
LABORATORY OF ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
Students: Asato, Crespi y Genovese
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2
Circuit (a) V
CC
(V) V
CE
(V) V
BE
(V) I
CQ
(mA) I
BQ
(A)
T
1
12,01 4,29 0,78 1,67 6,03
T
2
12,00 0,800 0,63 2,45 6,60
T
3
12,04 7,85 0,62 0,93 6,60
-
Circuit (b) V
CC
(V) V
CE
(V) V
BE
(V) V
BB
(V) I
CQ
(mA)
T
1
12,00 4,01 0,69 2,04 1,42
T
2
12,01 4,08 0,65 2,03 1,41
T
3
11,99 4,11 0,64 2,02 1,40
PART B:
VARYING THE BASE RESISTANCE
CIRCUIT TO BE USED:
R
C
= 1K.
R
E
= 3,3K.
R1 = 56K
R
2
= 47K.
V
CC
= 10V
T = BC548B.
PROCEDURE:
1) Assemble the circuit.
2) Measure I
CQ
and V
CEQ
. Complete the first row of the table.
3) Replace R
2
by the values shown in the table and complete the second and third
lines of the same.
4) Change again R
2
by 47K.
5) Change R
1
to the values shown in the table and complete the fourth and fifth
rows of the same
6) Disconnect R
1
. Complete the sixth row of the table.
7) Reconnect the 56K resistor as R
1
. Disconnect the 47K resistor (R
2
).
8) Complete the table with the corresponding theoretical values.
LABORATORY OF ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
Students: Asato, Crespi y Genovese
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3
R
E
= 3.3K and R
C
= 1K
Measured Values Theoretical Values
R
1
K
R
2
K
I
CQ
mA
V
CEQ
V
I
CQ
mA
VCEQ
V
Working
Zone
56 47 1,17 4,97 1,14 5,11 Linear
56 68 1,45 3,87 1,40 3,97 Linear
56 33 0,91 6,28 0,89 6,18 Linear
68 47 1,03 5,59 0,99 5,74 Linear
33 47 1,57 3,26 1,54 3,40 Linear
47 0,02 10,00 0,00 10,00 Cut
56 2,82 0,10 2,67 0,00 Saturation
QUIZ:
a) Does I
CQ
vary if R
1
and R
2
vary? Why?
Yes, it does because varying these resistors varies the base current, and that means that collector
current varies to.
b) If I
CQ
increases, V
CEQ
increases too? Justify your answer.
No, for more I
CQ
V
CEQ
decreases because there is more voltage drop in the collector and emitter
resistances.
c) Can V
CEQ
take a negative value? Why?
V
CEQ
can`t take a negative value, because it depends on I
CQ
and I
CQ
can`t be negative because the
semi-conductive behaviour of the transistor only let`s the current go in only one way, and being I
CQ
negative
will mean that the current is going in the wrong direction.
VARYING THE EMITTER RESISTANCE
PROCEDURE:
1) Reconnect the 47K resistor as R
2
.
2) Replace R
E
by the values shown in the next table.
3) Complete the table
R
1
= 56K, R
2
= 47K and R
C
= 1K
Measured Values Theoretical Values
R
E
K
I
CQ
mA
V
CEQ
V
I
CQ
mA
V
CEQ
V
1 3,66 2,27 3,57 2,86
3,3 1,17 4,57 1,14 5,11
4,7 0,82 5,11 0,80 5,41
VARYING THE COLLECTOR RESISTANCE
PROCEDURE:
1) Replace R
E
by the 3,3K resistor.
2) Replace R
C
by the values shown in the table.
3) Complete the next table.
R
1
= 56K , R
2
= 47K and R
E
= 3,3K
Measured Values Theoretical Values
R
C
K
I
CQ
mA
V
CEQ
V
I
CQ
mA
V
CEQ
V
1 1,17 4,97 1,14 5,11
LABORATORY OF ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
Students: Asato, Crespi y Genovese
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4
3,3 1,17 2,41 1,14 2,50
4,7 1,17 0,60 1,14 0,91
QUIZ:
Does I
CQ
vary if we change R
C
value? What about V
CEQ
?
I
CQ
does not vary because it does not depend on R
C
, it depends on the base current and R
E
. On the
other hand, V
CEQ
varies because the voltage drop changes in R
C
.
GRAPHS:
a) Represent the straight line corresponding to the measured values and the straight line
corresponding to the theoretical values in the same pair of axes with the appropriate scales.
Use the first table of PART B.
b) Represent the straight lines corresponding to each R
E
value in the same pair of axes with the
appropriate scales. Use the second table of PART B.
a)
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
I
C
Q
VCEQ
Measured Values
Theoretical Values
LABORATORY OF ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
Students: Asato, Crespi y Genovese
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5
b)
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
I
C
Q
VCEQ
Measured Values
Theoretical Values
LABORATORY OF ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
Students: Asato, Crespi y Genovese
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6
THEORICAL VALUES DETERMINATION:
In order to obtain H
FE,
we calculate de value of Ic solving the previous I
CQ
equation but despising R
E
/H
FE
.
With Ic, we enter in the trasistors graph and we determine the possible I
CQ
. If this I
CQ
is not less than ninety
percent of I
C
, this value is the true I
CQ
, but if it is less than ninety percert of I
C
we have to re-enter in the
transistors graph with this current value (the possible I
CQ)
to determine the true value of I
CQ.
R
E
Rc
R
BB
V
BB
Th
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Exp 8Document12 pagesExp 8esumshunPas encore d'évaluation
- ECI AssignmentIDocument9 pagesECI AssignmentIR Sathish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering Lab IV (ECEG-3207) EXAMDocument2 pagesElectrical Engineering Lab IV (ECEG-3207) EXAMmigadPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsDocument75 pagesLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsArnulfo LavaresPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.DC Biasing - BJTsDocument77 pages4.DC Biasing - BJTsNimra AftabPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 4 Bridge Measurement CircuitsDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 4 Bridge Measurement CircuitsRoseanne Camille SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment - 1 Study of Movement of Q-PointDocument4 pagesExperiment - 1 Study of Movement of Q-Pointyasir0% (1)
- Experiment Name-Study of Phase Shift OscillatorDocument2 pagesExperiment Name-Study of Phase Shift Oscillatormrana_56100% (2)
- SuuperhetDocument5 pagesSuuperhetnahj.fernandez69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsDocument78 pagesLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsTammanurRaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCDocument5 pagesLab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCAbdul QudoosPas encore d'évaluation
- LaboratoryManualforACElectricalCircuits PDFDocument78 pagesLaboratoryManualforACElectricalCircuits PDFAnonymous 8sqB76HcPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Transistors BJT Part IIDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Transistors BJT Part IIdoubleagent93Pas encore d'évaluation
- C2 Pspice ExperimentDocument5 pagesC2 Pspice ExperimentGulbanu KarimovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Electrical Engineering: First Year E.T. Lab Exp. No. - 3Document2 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: First Year E.T. Lab Exp. No. - 3Akshat GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 1: SCR SwitchDocument4 pagesExp 1: SCR Switchprop_kcpPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1.3: R-L Circuit Analysis and Power Factor DeterminationDocument5 pagesExperiment 1.3: R-L Circuit Analysis and Power Factor DeterminationDemoin GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis Vienna RectifierDocument8 pagesAnalysis Vienna RectifierJose Luis RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Qiang - 2017 - IOP - Conf. - Ser. - Mater. - Sci. - Eng. - 199 - 012148Document8 pagesQiang - 2017 - IOP - Conf. - Ser. - Mater. - Sci. - Eng. - 199 - 012148DRIS IDRISPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 8Document5 pagesLab 8tahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of E Ectrical Electronic Engineering Bangladesh Unive Sity of Engineering TechnologyDocument3 pagesDepartment of E Ectrical Electronic Engineering Bangladesh Unive Sity of Engineering TechnologyMeowPas encore d'évaluation
- RC Circuits: J H U, P ADocument6 pagesRC Circuits: J H U, P APavan PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab E1 RLC CircuitDocument11 pagesLab E1 RLC CircuitChing Wai Yong100% (1)
- Potential Divider Student Worksheet: TheoryDocument4 pagesPotential Divider Student Worksheet: TheoryJeremy HillPas encore d'évaluation
- 18EC42 First IA Test Q-PaperDocument2 pages18EC42 First IA Test Q-PapersharanbasappaPas encore d'évaluation
- 44 223 1 PBDocument7 pages44 223 1 PBThiru TrishPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.7 Biasing in BJT Amplifier Circuits: R A R A G G R R G R R R R R R R RDocument7 pages6.7 Biasing in BJT Amplifier Circuits: R A R A G G R R G R R R R R R R RJulian BuitragoPas encore d'évaluation
- EE 302 - Lab 6 RC and RL CircuitsDocument2 pagesEE 302 - Lab 6 RC and RL CircuitsduckebePas encore d'évaluation
- Research PaperDocument7 pagesResearch PaperAjmal FarooqPas encore d'évaluation
- Professor Modisette What Are Oscilloscopes?: ECE 206LDocument13 pagesProfessor Modisette What Are Oscilloscopes?: ECE 206Lapi-437430069Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 7.4.2016Document7 pagesExam 7.4.2016malathynarayaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Kirchhoff's RulesDocument18 pagesKirchhoff's Rulesthonah12100% (2)
- DC CircuitsDocument7 pagesDC CircuitsAmeer Bakry ZulkiffliPas encore d'évaluation
- EE315 Exp4 BJTssAmpDocument3 pagesEE315 Exp4 BJTssAmpserhatPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessors Lab 02Document17 pagesMicroprocessors Lab 02HuzafaPas encore d'évaluation
- PHY 122L Experiment 8Document6 pagesPHY 122L Experiment 8roden fabregasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportRacheal ShaktiPas encore d'évaluation
- Eecs100 Eecs43 Lab7-StrainGaugeDocument5 pagesEecs100 Eecs43 Lab7-StrainGaugegilmeanualexmihai100% (1)
- A Switched Capacitor Waveform GeneratorDocument3 pagesA Switched Capacitor Waveform GeneratorSaujal VaishnavPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering 2015 Set 2Document15 pagesElectrical Engineering 2015 Set 2Narendran KumaravelPas encore d'évaluation
- ItlogDocument11 pagesItlogkrazyyy chanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.transient Analysis of Series RL, RC CircuitsDocument11 pages3.transient Analysis of Series RL, RC CircuitsshubhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Softlab 1Document9 pagesSoftlab 1Mission DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 5Document16 pagesExp 5neelu marturuPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 BJTDiffPairLabDocument11 pages1 BJTDiffPairLaburim11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ec II Lab Manual (2013 2014)Document85 pagesEc II Lab Manual (2013 2014)surendhar1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- PK Aec Lab ManualDocument26 pagesPK Aec Lab ManualkrishnagdeshpandePas encore d'évaluation
- Pw2 - Ac RC Series Circuit - v1Document6 pagesPw2 - Ac RC Series Circuit - v1Hairul Anuar MasrolPas encore d'évaluation
- The Twelfth-Pulse Rectifier For Traction SubstatioDocument6 pagesThe Twelfth-Pulse Rectifier For Traction Substatiorishabh shahPas encore d'évaluation
- Identification of Parameters For Coupling CapacitoDocument7 pagesIdentification of Parameters For Coupling CapacitoPedro OcantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan LAB ELDEV 10Document8 pagesLaporan LAB ELDEV 10Oniel TirtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitive Reactance-Rc Trans, Series/Parallel Cir Examination Module/SubcourseDocument11 pagesCapacitive Reactance-Rc Trans, Series/Parallel Cir Examination Module/Subcourses69kingplaya69sPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of An RC Phase Shifter Circuit:: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAnalysis of An RC Phase Shifter Circuit:: Objectiveayesha amjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits 2-1 N-D-12Document15 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits 2-1 N-D-12nbprPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Question Paper - 2011 Class - X Subject - Science (PHYSICS / CHEMISTRY)Document5 pagesSample Question Paper - 2011 Class - X Subject - Science (PHYSICS / CHEMISTRY)sohial133Pas encore d'évaluation
- PH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexDocument28 pagesPH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexReddyvari VenugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsD'EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8D'EverandElectronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bihar SI Mains Syllabus-024b287317594Document3 pagesBihar SI Mains Syllabus-024b287317594Aryan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Determinants of MoralityDocument10 pagesThe Determinants of MoralityKaimi Ardee BorjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inquiries, Investigations and Immersion: Quarter 3 - Module 1Document8 pagesInquiries, Investigations and Immersion: Quarter 3 - Module 1Kenneth BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionI Am SmilingPas encore d'évaluation
- YDH FEED VerificationDocument10 pagesYDH FEED VerificationbillPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2: Java SocketsDocument5 pagesChapter 2: Java Socketsom18sahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Nishant Srivastav IPR Full PaperDocument16 pagesNishant Srivastav IPR Full PaperDIVYANSHI PHOTO STATEPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue Paper Hot Air Balloon: Andrea Badua Period 2 Physics Ms. BuenconsejoDocument14 pagesTissue Paper Hot Air Balloon: Andrea Badua Period 2 Physics Ms. BuenconsejoAndrea BaduaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Genes Evolution and BehaviourDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Genes Evolution and BehaviourAlex LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume of Tahmina Hossain BitheeDocument3 pagesResume of Tahmina Hossain BitheeJahid HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantitative Analysis For Management Ch06Document119 pagesQuantitative Analysis For Management Ch06Qonita NazhifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics PDFDocument17 pagesStatistics PDFSauravPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cultural Backdrop To Prospection: Exploring The Relevance of Time-Space DistanciationDocument16 pagesThe Cultural Backdrop To Prospection: Exploring The Relevance of Time-Space DistanciationJogy GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Median10.05 Qu25Z MidtermDocument3 pagesMedian10.05 Qu25Z MidtermLuwalhati TomilasPas encore d'évaluation
- Layout Strategies: © 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. 9 - 1Document17 pagesLayout Strategies: © 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. 9 - 1jeams vidalPas encore d'évaluation
- AD Admin Pack User GuideDocument34 pagesAD Admin Pack User GuideasreetoPas encore d'évaluation
- ACCT561 Quiz Week 3Document2 pagesACCT561 Quiz Week 3alparktuckerPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 16 CRM Project On Airtel 16Document15 pagesGroup 16 CRM Project On Airtel 16Ravi DahiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine DesignDocument376 pagesMachine Designssierro100% (5)
- EpdmDocument2 pagesEpdmhappale2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- LittleProfessor ManualDocument48 pagesLittleProfessor ManualÜMineiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Prometheus 2.0 - New Storage Layer Dramatically Increases Monitoring Scalability For Kubernetes and Other Distributed Systems - CoreOSDocument10 pagesPrometheus 2.0 - New Storage Layer Dramatically Increases Monitoring Scalability For Kubernetes and Other Distributed Systems - CoreOSFrankie LiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Baykon Tx13 Transmitter CatalogueDocument2 pagesBaykon Tx13 Transmitter CatalogueIvailo ZapryanovPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.occlusal Risk Factors Associated With Temporomandibular Disorders in Young Adults With Normal OcclusionsDocument5 pages5.occlusal Risk Factors Associated With Temporomandibular Disorders in Young Adults With Normal Occlusionsthiên lữPas encore d'évaluation
- Solman PDFDocument71 pagesSolman PDFdav00034Pas encore d'évaluation
- Srs TemplateDocument8 pagesSrs Templateferrys37Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rman Command DocumentDocument22 pagesRman Command DocumentanandPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual Molecular BiologyDocument19 pagesLab Manual Molecular BiologyLockerLingPas encore d'évaluation
- SFIDocument64 pagesSFIashwin71184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Itil Intermediate Capability Stream:: Operational Support and Analysis (Osa) CertificateDocument33 pagesItil Intermediate Capability Stream:: Operational Support and Analysis (Osa) CertificateNitinPas encore d'évaluation