Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Anterior Compartment of The Thigh
Transféré par
pedropedro19540 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues9 pagesThe thigh is completely surrounded by a dense layer of deep fascia called the fascia lata. The femoral triangle is an anatomic region of the upper thigh that has the following boundaries: inguinal ligament sartorius adductor longus the floor of the triangle is made up of the: iliopsoas muscle pectineus muscle. The superficial inguinal lymph nodes receive lymph drainage from the entire lower limb and the superficial structures of the per
Description originale:
Titre original
Anterior Compartment of the Thigh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe thigh is completely surrounded by a dense layer of deep fascia called the fascia lata. The femoral triangle is an anatomic region of the upper thigh that has the following boundaries: inguinal ligament sartorius adductor longus the floor of the triangle is made up of the: iliopsoas muscle pectineus muscle. The superficial inguinal lymph nodes receive lymph drainage from the entire lower limb and the superficial structures of the per
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues9 pagesAnterior Compartment of The Thigh
Transféré par
pedropedro1954The thigh is completely surrounded by a dense layer of deep fascia called the fascia lata. The femoral triangle is an anatomic region of the upper thigh that has the following boundaries: inguinal ligament sartorius adductor longus the floor of the triangle is made up of the: iliopsoas muscle pectineus muscle. The superficial inguinal lymph nodes receive lymph drainage from the entire lower limb and the superficial structures of the per
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 9
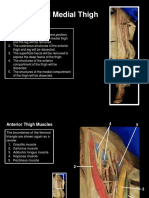
Anterior Compartment of the Thigh
After removing the skin from the anterior
thigh, you can identify the cutaneous
nerves and veins of the thigh and the
fascia lata. The fascia lata is a dense layer
of deep fascia surrounding the large
muscles of the thigh. The great saphenous
vein reaches the femoral vein by passing
through a weakened part of this fascia
called the fossa ovalis which has a sharp
margin called the falciform margin.
Located high in the thigh, just below the
inguinal ligament, are the superficial
inguinal lymph nodes, usually arranged in
a T-shape. These nodes receive lymph
drainage from the entire lower limb and
the superficial structures of the perineum.
The cutaneous nerves found piercing the
deep fascia are the:
lateral femoral cutaneous
intermediate cutaneous, branches
of the femoral nerve
medial cutaneous, branches of the
femoral nerve
The anterior compartment of the thigh
contains a large muscle, consisting of
four heads, the uadriceps femoris
muscle. This is a strong e!tensor of
the knee. The four heads of the
uadriceps femoris muscle are the:
rectus femoris
vastus lateralis
vastus medialis
vastus intermedius
"ne other muscle of the anterior
compartment is the sartorius.
The thigh is completely surrounded by
a dense layer of deep fascia called the
fascia lata. This fascia is particularly
thickened on the lateral aspect of the
thigh and is named the iliotibial tract.
This tract e!tends from the iliac crest
to the lateral condyle of the tibia.
Femoral Triangle
The femoral triangle is an anatomical
region of the upper thigh that has the
following boundaries:
inguinal ligament
sartorius
adductor longus
The floor of the triangle is made up of
the:
iliopsoas muscle
pectineus muscle
The contents of the femoral triangle
from lateral to medial are:
femoral nerve
femoral artery
femoral vein
femoral ring #usually contains a
lymph node$
The last three structures are found in a
sheath of deep fascia that has
e!tended down from the abdominal
wall, the femoral sheath. The sheath
contains the following items, from
lateral to medial:
femoral artery
femoral vein
femoral canal #usually
containing a lymph node$. The
femoral canal is also the site of
a femoral hernia.
The femoral nerve is not
considered to be in the sheath.
Nerve of the Anterior Compartment of the Thigh
The femoral nerve #L%,L&,L'$ supplies the muscles of the anterior compartment of
the thigh, including the pectineus muscle. The psoas muscles receives its nerve
supply from the lumbar ple!us.
Artery of the Anterior Compartment of the Thigh
The femoral artery #($ is the principal supply to the anterior
compartment of the thigh, as well as the rest of the lower
limb.
)ts branches are:
superficial iliac circumfle! #&$. This branch travels
along the lower border of the inguinal ligament and
supplies lower abdomen and upper thigh.
e!ternal pudendal #%$. This branch supplies superficial
perineal structures.
lateral femoral circumfle! #*$. The lateral circumfle!
travels around the anterior surface of the surgical
neck of the femur and anastomoses with the medial
circumfle!.
medial femoral circumfle! #'$. The medial circumfle!
travels around the posterior surface of the surgical
neck of the femur.
profunda femoris #+$ . The deep #profunda$ femoris
artery descends along the attached margin of the
adductor magnus muscle, giving rise to
o & perforating branches #+a-+c$
superior #highest$ genicular #,$
The femoral artery changes its name to become the popliteal
artery after it passes through the adductor hiatus.
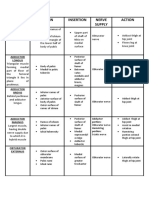
Table of Muscles
Muscle Origin Insertion Action
Nerve
Supply
sartorius anterior superior iliac
spine
upper medial
surface of tibial
shaft
fle!es,
abducts,
laterally
rotates
thigh- fle!es
and medially
rotates leg at
knee
femoral nerve
iliacus iliac fossa with psoas into
lesser
trochanter
fle!es thigh- if
thigh is fi!ed,
it fle!es the
trunk on the
thigh
as in sitting up
femoral nerve
psoas major (%th thoracic
vertebral body
transverse process,
bodies and
intervertebral
disks of lumbar
vertebrae
lesser
trochanter
same as
iliacus
segmental
branches from
lumbar ple!us
pectineus superior ramus of
pubis
upper end shaft
of femur
fle!es and
adducts thigh
femoral nerve
rectus
femoris
straight head:
anterior inferior iliac
spine
reflected head: ilium
just above the
acetabulum
patella e!tension of
leg
femoral nerve
vastus
lateralis
upper end shaft of
femur
uadriceps
tendon into
patella
e!tension of
leg
femoral nerve
vastus
medialis
upper end shaft of
femur
uadriceps
tendon to
patella
e!tension of
leg
femoral nerve
vastus
intermedius
shaft of femur uadriceps
tendon to
patella
e!tension of
leg
femoral nerve
Cross Section Through the Thigh
)t helps sometimes
to be able to
e!amine a section of
the body, in order to
gain a third
dimension to the
region. Again, when
e!amining a cross
section through the
body, you are
looking up into the
the section. This is
the left leg so medial
should be to your
left as you e!amine
it.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Sclerotherapy: Treatment of Varicose Telangiectatic Leg VeinsDocument439 pagesSclerotherapy: Treatment of Varicose Telangiectatic Leg VeinsjesussalvadorsuazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Muscles of The BodyDocument86 pagesMuscles of The BodyFadhli Quzwain100% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Femorals PDFDocument145 pagesFemorals PDFnoronisa talusobPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Sistema Venoso ProfundoDocument12 pagesSistema Venoso ProfundoEngie VersabethPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- 16-Front of ThighDocument31 pages16-Front of Thighgospel munkondya100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- 2013 - Lower Limb-Fascial Compartments of Thigh - Student VersionDocument28 pages2013 - Lower Limb-Fascial Compartments of Thigh - Student Versionmarina_shawkyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Understanding "Sports Hernia" Athletic PubelgiaDocument13 pagesUnderstanding "Sports Hernia" Athletic PubelgiaVijay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Gross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighDocument20 pagesGross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighOnah ArinzePas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Anterolateral Thigh FlapDocument6 pages14 Anterolateral Thigh FlapAngga Putra100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Casting and Restraining of AnimalsDocument5 pagesCasting and Restraining of Animalsmuzammilhussain512786Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- SCLEROTHERAPYDocument439 pagesSCLEROTHERAPYVishal Gaikwad100% (2)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Venous Disease: Chronic Venous Insufficiency Anatomical BackgroundDocument16 pagesVenous Disease: Chronic Venous Insufficiency Anatomical BackgroundSteve ColbertPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Medial Compartment of MuscleDocument1 pageMedial Compartment of MuscleFiza TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Contribution of Muscle MRI For Diagnosis of MyopathyDocument20 pagesContribution of Muscle MRI For Diagnosis of MyopathyJose EdgarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Syllabus of BMRIT-1Document19 pagesSyllabus of BMRIT-1Megha NaithaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Lab 1 - Frog DissectionDocument12 pagesLab 1 - Frog DissectionCherry Ann MacalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyDocument7 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyMavic VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular System of Frog Autofit To ContentsDocument3 pagesMuscular System of Frog Autofit To ContentsBanana LattePas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Vein Anatomy and FunctionDocument4 pagesVein Anatomy and FunctionAn'umillah Arini ZidnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lower Limb McqsDocument55 pagesLower Limb McqsKeshav NagpalPas encore d'évaluation
- Block II Review Winter 2023 Abdomen, Pelvis, & Lower Limb: DR Douglas A CotancheDocument112 pagesBlock II Review Winter 2023 Abdomen, Pelvis, & Lower Limb: DR Douglas A CotancheLester Cintron-PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide 1Document12 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide 1api-637418753Pas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer DescriptorDocument243 pagesConsumer DescriptorMfazlyadam MzalPas encore d'évaluation
- Toaz - Info Imaginefx Presents How To Draw and Paint Anatomy Uk PR 55f8581af53dc57Document95 pagesToaz - Info Imaginefx Presents How To Draw and Paint Anatomy Uk PR 55f8581af53dc57numero 5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Traumatic Disorders: Compartment SyndromeDocument57 pagesTraumatic Disorders: Compartment SyndromeMayahati NazayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Anterior Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Anterior Muscular SystemcbmorgansmomPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Ceu - School of Medicine Subject - Gross Anatomy Learning Objectives in Gross Anatomy Introduction To Gross AnatomyDocument26 pagesCeu - School of Medicine Subject - Gross Anatomy Learning Objectives in Gross Anatomy Introduction To Gross AnatomyDylan WhitePas encore d'évaluation
- 14-Anterior and Medial Thigh PDFDocument18 pages14-Anterior and Medial Thigh PDFANSHU PATELPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy & Physiology Muscles Flashcards - QuizletDocument10 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Muscles Flashcards - Quizletmalenya1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topographical Anatomy of The Lower Limb - Listed AlphabeticallyDocument3 pagesTopographical Anatomy of The Lower Limb - Listed AlphabeticallySaba Adde Duhera-HamidovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)