Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Synthesis of Mechanisms
Transféré par
Prince SethiCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Synthesis of Mechanisms
Transféré par
Prince SethiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Synthesis of mechanisms
Freudensteins equation:
This equation is used to compute the length of links of a four bar mechanism.
The equation can be written as
1 4 2 2 3 2 4
cos cos cos( ......( K K K i + =
2 2 2 2
1 2 3
... ! .. ..
2
d d a b c d
where K K and K
a c ac
+ +
= = =
where a!b!c!d are lengths of links of the four bar mechanism with "
2
and "
4
as the input
and output link angles.
The equation (i can be written as for three pairs of #alues ("
21
! "
41
! ("
22
! "
42
and ("
23
!
"
43
as$
1 41 2 21 3 21 41
cos cos cos( ......( K K K ii + =
1 42 2 22 3 22 42
cos cos cos( ......( K K K iii + =
1 43 2 23 3 23 43
cos cos cos( ......( K K K iv + =
Subtracting equation (iii and (i# from (ii! we get
1 41 42 2 21 22 21 41 22 42
(cos cos (cos cos (cos cos (cos cos K K =
1 41 43 2 21 23 21 41 23 43
(cos cos (cos cos (cos cos (cos cos K K =
Sol#ing these two equations for %
1
and %
2
! we get
1 & 2 2
1
1 & ' 2
. .
. .
z x z x
K
x x x x
1 ' 2 1
2
& 1 2 '
. .
. .
z x z x
K
x x x x
(here
1 21 41 22 42
cos( cos( z =
2 21 41 23 43
cos( cos( z =
1 41 42
(cos cos x =
2 21 22
(cos cos x =
' 41 43
(cos cos x =
& 21 23
(cos cos x =
Substituting the #alues of %
1
and %
2
in equation (ii! we get the #alue of %
3.
)*ample$ + four bar mechanism is required such that the input and out angles are
coordinated as gi#en in the table.
Synthesi,e the 4-bar mechanism$
.nput crank angle ("
2
3/
/
'/
/
0/
/
1utput follower angle ("
4
/
/
3/
/
&/
/
Solution$
The displacement equation gi#en by 2reudenstein is written as$
1 4 2 2 3 2 4
cos cos cos( K K K + =
Substituting the #alues of input ("
2
and ("
4
in abo#e equation! we get
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos / cos3/ cos(3/ / ........( K K K i + =
1 2 3
/.0&& /.0&& K K K + =
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos3/ cos'/ cos('/ 3/ ........( K K K ii + =
/ /
1 2 3
/.0&& cos'/ cos 2/ K K K + =
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos &/ cos0/ cos(0/ &/ ........( K K K iii + =
/ /
1 2 3
/.' cos0/ cos(2/ K K K + =
Sol#ing equation (i! (ii and (iii! %
1
31.0321! %
2
31.4244! %
3
3/.2510
+ssuming the length of one link as unity i.e. a 3 1
(e know that
1
1
6
. 1 1.0321 1.0321
K d a
d a K x
=
= = =
2
2
1.0321
6 1.2015
1.4244
d
K d c c
k
= = = =
2 2 2 2
3
2
a b c d
K
ac
+ +
=
2 2 2
3
2 b acK a c d = + + +
2 2 2
27171.20157/.2510 1 (1.2015 (1.0321 = + + +
b3 2.3/34
The length of #arious links are$
a 3 1./
b3 2.3/34
c3 1.2015
d 3 1.0321
Function generation:
.n function generation! the motion of input link is correlated to motion of output link.
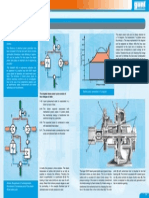
2igure shows a four bar mechanism
The input link +8 rotates through an angle "
2
and represents independent #ariable *.
The output link 9: rotates through angle "
4
and indicates independent #ariable y
.
;ere! < is dependent on *.
=et us assume
>
1
and >
2
are initial and final positions of independent #ariable >.
<
1
and <
2
are initial and final positions of dependent #ariable <.
There is linear relationship between "
2
and >
There is linear relationship between "
4
and <
?athematically!
2 2
1
2 1
tan
f i
r cons t
x x
= =
and
4 4
2
2 1
tan
f i
r cons t
y y
= =
where
"
2f
and "
2i
3 final and initial angular positions of input link
"
4f
and "
4i
3 final and initial angular positions of output link
The constants r
1
and r
2
are called scale factors.
.f link ratios are known i.e. a6b! a6c! a6d. ! the mechanism can be designed.
Precision points and structural error
=et us draw a graph between input #ariables and output #ariables as shown in figure$
2igure 4.11
The motion of input is represented by >
/
! >
/
! >
/
@@..>
n
! >
nA1
The motion of input is represented by <
/
! <
/
! <
/
@@..<
n
! <
nA1
:esired function and generated function meet at certain points. These are called
precision points.
The difference between generated function and desire function is called structural
error.
Chebyshev spacing of precision points
9hebyshe# spacing of precision points is useful to minimi,e the structural error.
2or n points in range
/ 1 n
x x x
+
! the precision points *
B
according to chebyshe#
spacing are gi#en as$
cos .
j j
x a b =
where
( )
/ 1
1 /
1
(
2
2 1
2
1
2
1! 2! 3!......!
n
j
n
a x x
j
n
b x x
j n
+
+
= +
=
=
=
)*ample$ Synthesi,e a four bar linkage using 2reudensteinCs equation to generate the
function < 3 >
1.'
for the inter#al 1 4 x . The input crank is to start form "
2
33/
/
and is
to ha#e range of 4/
/
. Take three accuracy points. Take output crank angle from / to 4/
/
.
Solution$
Step1$ 2ind out three accuracy points(n33$
cos .
j j
x a b =
where
/ 1
1 1
( (1 4 2.'
2 2
n
a x x
+
= + = + = ;ere >
/
31 and >
nA1
3 4 (Di#en
( ) ( )
1 /
1 1
4 1 1.'
2 2
n
b x x
+
= = =
1
1
2 1 271 1 1
2 273 &
j
j
j
n
=
= = =
2
2
2 1 272 1 3
2 273 &
j
j
j
n
=
= = =
3
3
2 1 273 1 '
2 273 &
j
j
j
n
=
= = =
Eut the #alue of a! b! "
B
in abo#e equation
1 1
1
cos . 2.' 1.'cos 7 1.2/
&
x a b = = =
2 2
3
cos . 2.' 1.'cos 7 2.'
&
x a b = = =
3 3
'
cos . 2.' 1.'cos 7 3.544
&
x a b = = =
>
S
31
1.' 1.'
(1 y x = =
<
S
31 "
2s
3 3/
/
"
4s
3 /
/
>
1
31.2/
1.'
(1.2/ =
<
1
31.314 "
21
3 3&
/
"
41
3 4./3
/
>
2
3 2.'
1.'
(2.' =
<
2
3 3.4'3 "
22
3F "
42
3F
>
3
33.544
1.'
(3.544 =
<
3
35.4/4 "
23
3F "
43
3F
>
f
3 4
1.'
(4 =
<
f
3 0 "
2f
312/
/
(Di#en "
4f
34/
/
(Di#en
G>34-133 ----- G<30-135 G"
2
34/
/
(Di#en G"
4
3 4/
/
(Di#en
=et the input crank angles corresponding to three accuracy points >
1
! >
2
and >
3
be "
21
!
"
22
! "23 respecti#ely. =et corresponding output crank angles be "
41
! "
42
! and "
43.
(e know that
2 2
2
.......(
s s
x x
i
x
=
and
4 4
4
..........(
s s
y y
ii
y
=
2rom equation (i and (ii
/
/ 21 2 1 21
21
/
2
3/ 1.2 1
3&
3 4/
s s
x x
x
= = =
/
/ 41 4 1 41
41
/
4
/ 1.314 1
4./3
5 4/
s s
y y
y
= = =
/
/ 22 21 2 1 22
22
/
2
3& 2.' 1.2
5'
3 4/
x x
x
= = =
/
/ 42 41 2 1 42
42
/
4
4./3 3.4'3 1.314
35.4&
5 4/
y y
y
= = =
/
/ 23 21 3 1 23
23
/
2
3& 3.544 1.2
113.45
3 4/
x x
x
= = =
/
/ 43 41 3 1 43
43
/
4
4./3 5.4/4 1.314
02.3
5 4/
y y
y
= = =
"
2s
3 3/
/
"
4s
3 /
/
"
21
3 3&
/
"
41
3 4./3
/
"
22
35'
/
"
42
335.4&
/
"
23
3113.45
/
"
43
302.33
/
"
2f
3 12/
/
"
4f
3 4/
/
The displacement equation gi#en by 2reudenstein is written as$
1 4 2 2 3 2 4
cos cos cos( K K K + =
(hen "
2
33&
/
and "
4
3 4./3
/
Substituting the #alues of input ("
2
and ("
4
in abo#e equation! we get
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos 4./3 cos3& cos(3& 4./3 K K K + =
1 2 3
/.445 /.0/4 /.'1'........( K K K i + =
(hen "
2
35'
/
and "
4
3 35.4&
/
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos35.4& cos 5' cos(5' 35.4& K K K + =
1 2 3
/.500 /.2'0 /.540........( K K K ii + =
(hen "
2
3113.45
/
and "
4
3 02.3
/
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos02.33 cos113.45 cos(113.45 02.33 K K K + =
1 2 3
/.133 /.4/& /.0'1........( K K K iii + =
Sol#ing the abo#e equations
%
1
3 /./04&
%
2
3 /.1254
%
3
3 /.52&'
=et us assume d 3 1./
1
1
1./
11.1&
/./04&
11.1&
d
d
K a
K
a
a
= = = =
=
2
2
1./
5.02
/.1254
5.02
d
d
K c
c
K
c
= = = =
=
2 2 2 2
3
2
a b c d
K
ac
+ +
=
2 2 2
3
2 5.5& b acK a c d = + + + =
Thus!
a3 11.1&! b3 5.5&! c3 5.02! d31./
)*ample 2$ + four bar function generator is used to generate the function < 3 (16> for
1 3 x between the input angle of a crank and angle of follower makes with the frame.
2ind the three precision points from 9hebyshe#Cs spacing if the initial #alue of input i.e.
crank angle and output i.e. the follower angle are 3/
/
and 2//
/
respecti#ely. The
difference between the final and initial #alues of the crank and follower angles are each
equal to 4/
/
.
Solution$ Di#en$ >
/
3 1! >
nA1
33! n33(Three precision points
Step1$ 2ind out three accuracy points$
cos .
j j
x a b =
where
/ 1
1 1
( (1 3 2
2 2
n
a x x
+
= + = + = ;ere >
/
31 and >
nA1
3 3 (Di#en
( ) ( )
1 /
1 1
3 1 1./
2 2
n
b x x
+
= = =
1
1
2 1 271 1 1
2 273 &
j
j
j
n
=
= = =
2
2
2 1 272 1 3
2 273 &
j
j
j
n
=
= = =
3
3
2 1 273 1 '
2 273 &
j
j
j
n
=
= = =
Eut the #alue of a! b! "
B
in abo#e equation
/
/
1 1
1 10/
cos . 2 1cos 7 2 1.cos 2 cos3/ 1.134
& &
x a b = = = = =
2 2
3
cos . 2 1.cos 7 2./
&
x a b = = =
3 3
'
cos . 2 1.cos 2.0&&
&
x a b
= = =
=et the input crank angles corresponding to three accuracy points >
1
! >
2
and >
3
be "
21
!
"
22
! "23 respecti#ely. =et corresponding output crank angles be "
41
! "
42
! and "
43.
(e know that
2 2
2
.......(
s s
x x
i
x
=
and
4 4
4
..........(
s s
y y
ii
y
=
2rom equation (i and (ii
/
/ 21 2 1 21
21
/
2
3/ 1.134 1./
3&./3
2 4/
s s
x x
x
= = =
/
/ 41 4 1 41
41
/
4
2// /.001 1
103.42
/.&&& 4/
s s
y y
y
= = =
/
/ 22 21 2 1 22
22
/
2
3&./3 2./ 1.134
5'
2 4/
x x
x
= = =
/
/ 42 41 2 1 42
42
/
4
103.42 /.'/ /.001
132.30
/.&&& 4/
y y
y
= = =
/
/ 23 21 3 1 23
23
/
2
3&./3 2.0&& 1.134
113.45
2 4/
x x
x
= = =
>
S
31 (16 (161 y x = = <
S
31 "
2s
3 3/
/
"
4s
32//
/
>
1
31.134 3161.134 <
1
3/./001 "
21
3 F "
41
3 F
>
2
3 2./ 3162./ <
2
3 /.' "
22
3F "
42
3F
>
3
32.0&& 3162.0&& <
3
3/.344 "
23
3F "
43
3F
>
f
3 3 3163 <
f
3 /.333 "
2f
312/
/
(Di#en "
4f
311/
/
(Di#en
G>33-
132./
---- G<3/.333-13
- /.&&&
G"
2
34/
/
(Di#en G"
4
3 4/
/
(Di#en
<
s
is reducing so angle "
4
will also reduce
/
/ 43 41 3 1 43
43
/
4
103.42 /.344 /.001
112./1
/.&&& 4/
y y
y
= = =
"
2s
3 3/
/
"
4s
3 2//
/
"
21
3 3&./3
/
"
41
3 103.42
/
"
22
35'
/
"
42
3132.30
/
"
23
3113.45
/
"
43
3112./1
/
"
2f
312/
/
"
43
311/
/
The displacement equation gi#en by 2reudenstein is written as$
1 4 2 2 3 2 4
cos cos cos( K K K + =
(hen "
2
33&./3
/
and "
4
3 103.42
/
Substituting the #alues of input ("
2
and ("
4
in abo#e equation! we get
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos103.42 cos3&./3 cos(3&./3 103.42 ....( K K K i + =
(hen "
2
35'
/
and "
4
3 132.30
/
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos132.30 cos 5' cos(5' 132.30 .....( K K K ii + =
(hen "
2
3113.45
/
and "
4
3 112./1
/
/
/ / /
1 2 3
cos112./1 cos113.45 cos(113.45 112./1 ...( K K K iii + =
Sol#ing the abo#e equations
%
1
3 '.351
%
2
3 -13.'
%
3
3 0.252
=et us assume d 3 1./
1
1
1./
/.10&
'.351
/.10&
d
d
K a
K
a
a
= = = =
=
2
2
1./
/./54
13.'
/./54
d
d
K c
c
K
c
= = = =
=
(Hegati#e sign indicates that the direction of 9 has re#ersed itself.
2 2 2 2
3
2
a b c d
K
ac
+ +
=
2 2 2
3
2 1./33 b acK a c d = + + + =
Thus!
a3 /.10&! b3 1./33! c3 -/./54! d31./
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- SSC Junior Engineers (JE)Document19 pagesSSC Junior Engineers (JE)Prince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Question Paper2Document6 pagesSample Question Paper2Phanendra Singam SettiPas encore d'évaluation
- SSC JE Mechanical SyllabusDocument6 pagesSSC JE Mechanical SyllabusPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Productivity Improvement TechniquesDocument30 pagesProductivity Improvement TechniquesMansoor KhanaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To IE 3Document2 pagesIntro To IE 3Prince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document15 pages1Prince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- 300gk QuestionsDocument20 pages300gk QuestionsPraveen SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Current 2010Document213 pagesCurrent 2010Prince Sethi0% (1)
- Automobile Engineering Unit 2: ClutchesDocument9 pagesAutomobile Engineering Unit 2: ClutchesPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- True ReligionDocument42 pagesTrue ReligionPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Btech Reappear 2k12 May13Document11 pagesBtech Reappear 2k12 May13Prince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Correct Steering Angle and Perfect RollingDocument8 pagesCorrect Steering Angle and Perfect RollingPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Suspension SetupDocument5 pagesSuspension SetupAshutosh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Wheel Alignment AnglesDocument33 pagesUnderstanding Wheel Alignment AnglesahiremanojPas encore d'évaluation
- E ChallanSyndicateDocument1 pageE ChallanSyndicatePrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTER PROGRAMMING TECHNIQUESDocument1 pageNUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTER PROGRAMMING TECHNIQUESPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- E ChallanCanaraDocument1 pageE ChallanCanaraPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacity Utilization ProjectDocument23 pagesCapacity Utilization ProjectPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 04Document57 pagesCH 04robinho086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Automobile Enginering: Unit:-Front Axle and SteeringDocument9 pagesAutomobile Enginering: Unit:-Front Axle and SteeringPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Power Plants EnglishDocument1 pageSteam Power Plants EnglishMirza Zubair RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Samsung House, 1000 Hill Swood Drive, Chertsey, Surrey, KT16 0PSDocument1 pageSamsung House, 1000 Hill Swood Drive, Chertsey, Surrey, KT16 0PSPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine DesignDocument2 pagesMachine DesignPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- IC EngineDocument2 pagesIC EnginePrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Me TrologyDocument2 pagesMe TrologyPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine DesignDocument2 pagesMachine DesignPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Mat - Sc.Document15 pagesAssignment Mat - Sc.Prince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Siemens Jobs VacancyDocument3 pagesSiemens Jobs VacancyPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- WinnerDocument1 pageWinnerPrince SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Paulson 2007 Year End Report Earns Nearly 600Document16 pagesPaulson 2007 Year End Report Earns Nearly 600Tunaljit ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- An - APX18 206516L CT0Document2 pagesAn - APX18 206516L CT0Maria MartinsPas encore d'évaluation
- PartlowControllerCatalog PDFDocument98 pagesPartlowControllerCatalog PDFvinh nguyen thePas encore d'évaluation
- Imantanout LLGDDocument4 pagesImantanout LLGDNABILPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Cover Letter Oil and GasDocument1 pageSample Cover Letter Oil and GasNadira Aqilah67% (3)
- Fiber Optics Splicing Procedures: Your Source To Fiber Optics, Industrial Datacomm & Fieldbus Products-Solutions-ServicesDocument7 pagesFiber Optics Splicing Procedures: Your Source To Fiber Optics, Industrial Datacomm & Fieldbus Products-Solutions-ServicesHafis Aikal AmranPas encore d'évaluation
- TROOP - of - District 2013 Scouting's Journey To ExcellenceDocument2 pagesTROOP - of - District 2013 Scouting's Journey To ExcellenceAReliableSourcePas encore d'évaluation
- Hutchinson - Le Joint Francais - National O-RingDocument25 pagesHutchinson - Le Joint Francais - National O-RingkikorrasPas encore d'évaluation
- Priceliost Ecatalog 2021 Div. DiagnosticDocument2 pagesPriceliost Ecatalog 2021 Div. Diagnosticwawan1010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis Statement About Plastic BagsDocument7 pagesThesis Statement About Plastic Bagslyjtpnxff100% (2)
- Depreciation Methods ExplainedDocument2 pagesDepreciation Methods ExplainedAnsha Twilight14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sharp MX2310U Technical Handy ManualDocument64 pagesSharp MX2310U Technical Handy ManualUserPas encore d'évaluation
- Office of The Controller of Examinations Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025Document4 pagesOffice of The Controller of Examinations Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025M.KARTHIKEYANPas encore d'évaluation
- Reinforced and Filled Poly (Phenylene Sulfide) (PPS) Injection Molding and Extrusion Materials Using ASTM MethodsDocument6 pagesReinforced and Filled Poly (Phenylene Sulfide) (PPS) Injection Molding and Extrusion Materials Using ASTM MethodsJosé Miguel Palomino GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochures Volvo Engines d11 CanadaDocument4 pagesBrochures Volvo Engines d11 CanadaDIONYBLINK100% (2)
- Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesMarking Schememohamed sajithPas encore d'évaluation
- Ap22 FRQ World History ModernDocument13 pagesAp22 FRQ World History ModernDylan DanovPas encore d'évaluation
- NURKSE's Balanced GrowthDocument7 pagesNURKSE's Balanced GrowthArnab MutsuddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Barcelona Traction Case DigestDocument3 pagesBarcelona Traction Case DigestCheChePas encore d'évaluation
- Bode PlotDocument6 pagesBode PlotChandan S KPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpretation 1Document17 pagesInterpretation 1ysunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Routine E-Mail Messages and Memos-Ch 8Document43 pagesRoutine E-Mail Messages and Memos-Ch 8Faryal ArifPas encore d'évaluation
- Create Email Alerts For Mulitple People or Group - XpoDocument79 pagesCreate Email Alerts For Mulitple People or Group - XponiravmodyPas encore d'évaluation
- Destruction FormDocument2 pagesDestruction FormHanabishi RekkaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISB - PM - Week 4 - Required Assignment 4.2 - TemplateDocument2 pagesISB - PM - Week 4 - Required Assignment 4.2 - Templatesriram marinPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel Pumps Left in Off PositionDocument7 pagesFuel Pumps Left in Off PositionherbuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Tool Catalog Ei18e-11020Document370 pagesTool Catalog Ei18e-11020Marcelo Diesel85% (13)
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportapi-463513182Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cough: by Dr. Meghana Patil (Intern Batch 2016)Document24 pagesCough: by Dr. Meghana Patil (Intern Batch 2016)Meghana PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Martillo Komac KB1500 Parts ManualDocument12 pagesMartillo Komac KB1500 Parts ManualJOHN FRADER ARRUBLA LOPEZ100% (1)