Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Scabies: Signs and Symptoms
Transféré par
Ibrahim Abdullah0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
70 vues4 pagesScabies
Titre original
Scabies
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentScabies
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
70 vues4 pagesScabies: Signs and Symptoms
Transféré par
Ibrahim AbdullahScabies
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Pharmacy Practice IV
Prepared by Ibrahim Abdullah, BPharm (Hons) Nottingham, UK.
Scabies // Page 1 of 4
Scabies
1. Latin word scabere means scratch
2. Scabies is not the same as lice, although the treatment
may be the same
3. Infestation of the skin with the microscopic mite Sarcoptes
scabiei:
a. Eight-legged parasites
b. Tiny, just 1/3 millimeter long
c. Not visible with the naked eye, although sometimes they are
visible as a pinpoint of white
d. Visible with a magnifying glass or microscope
e. If not on human skin does not live long (few days)
f. On human skin live up to one month
4. Common worldwide, affects people of all races, social classes and personal hygiene
Signs and Symptoms
1. Symptoms may take 4 - 6 weeks to show
2. Intense, severe and continuous itchy
a. Because mites move within and on the skin. Female burrow into
the top layer of human skin to lay their eggs. Burrow is short S-
shaped track that indicates the mite's movement under the skin.
The presence of the eggs and waste produces a massive allergic
response which produces more itching. The eggs mature in 21
days, and the new mites work their way to the surface of your
skin, where they mature and can spread to other areas of your
skin or to the skin of other people
b. Clue, especially if several members of the same family have same signs
c. First weeks, the itch is subtle, gradually becomes more intense. After a month or two, sleep becomes
almost impossible
d. Worse at night, at least in part because there is not much going on to distract people from thinking
about it
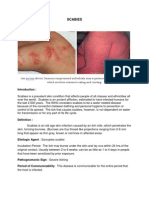
3. Small insect-type bites. Lesions may look like pimples. It may also be red and crusty due
to scratching of the area
a. Over most part of body mostly webs between fingers or toes, the buttocks, the elbows, the genital
area, under the breasts in women, armpits, around the waist, along wrists, back elbows, groin, around
the male genital, knees, shoulder blades
4. Burrow may be visible
5. The face usually does not become involved in adults
Pharmacy Practice IV
Prepared by Ibrahim Abdullah, BPharm (Hons) Nottingham, UK.
Scabies // Page 2 of 4
How Infestation Occurs / Who At risk
1. Highly contagious. Transmitted readily if there is close skin-to-skin contact household
members, sexual contact, hugging
2. Prolonged contact. Quick handshake or hug will usually not spread infestation
3. Spreads rapidly under crowded conditions such as in hospitals, institutions, child-care
facilities, and nursing homes
4. Elderly and weakened people in nursing homes and similar institutional settings may
have scabies without significant itching or visible signs. Thus can lead to widespread
epidemics among patients and health workers. [Furthermore, in normal conditions, it
takes approximately 4-6 weeks to develop symptoms after initial infestation]
5. Spread by clothing, bedding, or towels is a less significant risk, though possible
6. Pets. Pets become infested with a different kind of scabies mite (mange). Can transiently
affect human. Mite dies in a couple of days and does not reproduce. Do not need to be
treated. Until your pet is successfully treated, mites can continue to burrow into your
skin and cause you to have symptoms
Diagnosis
1. Scabies is frequently misdiagnosed as intense pruritus before papular eruptions form.
Distinctive its relentless quality, at least after several weeks. Other itchy conditions like
eczema tend to wane
2. Most can be diagnosed by describing the symptoms and on examination of the skin
3. Finding the burrows. Burrows sometimes appear as short, wavy, reddish, or darkened
lines on the skin's surface, especially around the
wrists and between the fingers. Difficult because
they are scarce, because they are obscured by
scratch marks, or by secondary dermatitis
4. Skin scraped and placed under microscope and
looked for presence of mite or its eggs. Typically,
there are fewer than 10 mites on the entire body of
an infested person infestation can be missed
5. The suspicious area can be rubbed with ink from a
fountain pen or alternately a topical tetracycline solution which will glow under a special
light. The surface is then wiped off with an alcohol pad; if the person is infected with
scabies, the characteristic zigzag or S pattern of the burrow across the skin will appear
Pharmacy Practice IV
Prepared by Ibrahim Abdullah, BPharm (Hons) Nottingham, UK.
Scabies // Page 3 of 4
Treatment - Medicines
1. Scabies will not go away on its own
2. Anyone with scabies, sexual partners and persons who have close, prolonged contact to
the infested person should also be treated at the same time
3. Best solution - cream or lotion to kill the mites
a. Applied to the skin all over the body (neck down), not just the affected area
b. Must remain on the skin for 8 to 12 hours before it can be washed off
c. Do not apply to eyes, face, or mucous membranes
d. After applying it, don't wash your hands scabies mites love the area between the fingers
e. Repeat 7 10 days later
f. Permethrin (A-scabs): not carcinogenic and teratogenic (animals). This is safe for use in children as
young as two months
g. Malathion applied for 24 hours effective in killing adult mites and eggs
h. Crotamiton (Eurax)
i. Lindane. When others have failed or contraindicated
can cause seizures if absorbed through the skin. Lindane should be washed off with warm,
and not hot, water to avoid absorption through the skin
not very safe in children and may cause neurotoxicity (dizziness, seizures)
not be used in pregnant or nursing women
should not be used if skin is significantly irritated or wet, such as with extensive skin
disease, rash, or after a bath
4. A single dose of ivermectin (broad spectrum anti-parasites, not yet available in Malaysia)
has been reported to cure scabies
a. Study found no statistically-significant differences in effectiveness between lindane and ivermectin
b. Has not been shown to be superior to permethrin in eradicating scabies
c. Although more convenient than cream, ivermectin has a greater risk of toxic side effects than
permethrin
5. Antihistamine relieve the itching. Itching may continue for days or weeks, and does
not mean that you are still infested. If the treatment is effective there should be no new
rashes or burrows after 24 to 48 hours
6. Cream hydrocortisone, etc to relieve itching and help the rash go away faster
7. Lotion calamine lotion relieve mild itchiness
8. Pregnant women and children use milder scabies medications. 10% sulfur can be used
in pregnant women and infants under two months of age. (Effectiveness?)
Pharmacy Practice IV
Prepared by Ibrahim Abdullah, BPharm (Hons) Nottingham, UK.
Scabies // Page 4 of 4
Treatment Nonpharmacological / Prevention
1. Difficult to prevent or avoid scabies once someone close to you has scabies. Once a close
contact or family member has been diagnosed with scabies, everyone should be treated
at the same time
2. Mites surface at times, especially at night. They can be washed or scratched off (should
be done with a washcloth to avoid cutting the skin, therefore infection). Not a cure but
helps to keep the total population low
3. Cleaning should be done simultaneously. Should include:
a. Vacuuming floors, carpets, and rugs
b. Disinfecting floor and bathroom surfaces by mopping
c. Without a host, scabies mites can on average survive up to 48-72 hours away from human skin.
Therefore it is recommended to wash in hot water all material (such as clothes, bedding, and towels)
that has been in contact with all infested persons in the last three days
d. Overnight freezing, in a plastic bag: stuffed animals, brushes, combs, shoes, coats, gloves, hats,
robes, wetsuits, etc.
e. Dry cleaning: things that cannot be washed, hot dried or frozen or quarantined
f. Starve the mites by quarantining in a plastic bag for two weeks: things that cannot be washed, hot
dried, frozen or dry-cleaned
g. Cut your nails and clean under them thoroughly to remove any mites or eggs that may be present
When to seek medical advice
1. Vigorous scratching can break your skin and allow a secondary bacterial infection such as
impetigo - usually staph (staphylococci) bacteria or occasionally by strep (streptococci)
bacteria. Needs antibiotic:
a. Cream non-prescription
b. Oral - prescription
2. In persons with severely reduced immunity, such as those with HIV infection, or people
being treated with immunosuppressive drugs like steroids, a widespread rash with thick
scaling may result. This variety of scabies is called Norwegian scabies
This article is for educational purpose only. The writer welcomes any feedback, which may be sent to
ibrahim.lecturer@gmail.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Best Home Remedies for Scabies, No More Complicated MedicationsD'EverandThe Best Home Remedies for Scabies, No More Complicated MedicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies GuidelineJanuary 2013Document13 pagesScabies GuidelineJanuary 2013anisarahma718Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies Diagnosis and ManagementDocument5 pagesScabies Diagnosis and ManagementAbdul Rauf ZakariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies Guideline Sept 07 PDFDocument10 pagesScabies Guideline Sept 07 PDFMira ApriliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Warts (Verruca) : Local Growth SurfaceDocument4 pagesWarts (Verruca) : Local Growth SurfaceIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument2 pagesScabiesPRINTDESK by DanPas encore d'évaluation
- General Information About ScabiesDocument16 pagesGeneral Information About ScabiesPramesti DarojahPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies Guideline 2015Document13 pagesScabies Guideline 2015Brenda KristiPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies - NarraDocument2 pagesScabies - NarraBryan De HopePas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies NotesDocument9 pagesScabies NotesAvi ePas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Scabies PDFDocument5 pagesManagement of Scabies PDFAfnindyas AtikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin ConditionsDocument43 pagesSkin ConditionspdladvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies Cont.: How Can The Spread of This Disease Be Prevented?Document2 pagesScabies Cont.: How Can The Spread of This Disease Be Prevented?Austine OsawePas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument14 pagesScabiesRohini SelvarajahPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Management of Skin and Parasitic DiseasesDocument14 pagesNursing Management of Skin and Parasitic Diseasesyer tagalajPas encore d'évaluation
- Background of The StudyDocument4 pagesBackground of The StudyFerreze AnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies.: Vanessa ChelimoDocument19 pagesScabies.: Vanessa ChelimoAlvin OmondiPas encore d'évaluation
- SCABIESDocument5 pagesSCABIESMenna GomaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin and Parasitic DiseasesDocument14 pagesSkin and Parasitic DiseasesduapajPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument4 pagesScabiesGenita Savitri EkandariPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument5 pagesScabiesSashi MehPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies: Signs and SymptomsDocument8 pagesScabies: Signs and Symptomspragna novaPas encore d'évaluation
- 336 ScabiesDocument2 pages336 ScabiesrozanfikriPas encore d'évaluation
- Vorwick ScabiesDocument3 pagesVorwick ScabiesTio Norman WicaksonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Document From BenjaminfjodDocument21 pagesDocument From BenjaminfjodBenjamin VanlaltlansangaPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductionfarmasi_hmPas encore d'évaluation
- ImpetigoDocument2 pagesImpetigoAMOS MELIPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument5 pagesScabiespakemainmainPas encore d'évaluation
- Kerry-Ann Williams, Tahirah Williams & David WilliamsDocument10 pagesKerry-Ann Williams, Tahirah Williams & David WilliamsKerry-Ann WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies SRU Rev 06Document31 pagesScabies SRU Rev 06Dwika HerdykiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument4 pagesScabiesNuradin JemalPas encore d'évaluation
- Reatment of Scabies Infestations: Mumcuoglu K.Y. & Gilead L.Document4 pagesReatment of Scabies Infestations: Mumcuoglu K.Y. & Gilead L.putrinurulapriliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies Management: Community Control of ScabiesDocument3 pagesScabies Management: Community Control of Scabiespet_trinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson: Lagonoy High School Quarter 3 Module 3Document3 pagesLesson: Lagonoy High School Quarter 3 Module 3John Mark PrestozaPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument14 pagesScabiessyemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies - Topic Overview: Mites Skin Scabies ScabiesDocument6 pagesScabies - Topic Overview: Mites Skin Scabies ScabiesKathy SuazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ntagious-Skin-Diseases/scabies ScabiesDocument10 pagesNtagious-Skin-Diseases/scabies ScabiespmPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies 160908065024Document12 pagesScabies 160908065024Syed NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument8 pagesScabiesJessica Dumayas Dela RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies: Check If It's ScabiesDocument3 pagesScabies: Check If It's ScabiesRicherson YovannlimPas encore d'évaluation
- SCABIESDocument14 pagesSCABIESNom Kumar Naik Rathod100% (1)
- ArthropodsDocument42 pagesArthropodsKatePas encore d'évaluation
- Fox Scabies EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesFox Scabies EncyclopediaNimfa Christina R WibowoPas encore d'évaluation
- TB and Scabies Ni NikkaDocument5 pagesTB and Scabies Ni NikkaLouise OpinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies 1Document25 pagesScabies 1pmPas encore d'évaluation
- HC-256-Warts Problem SolutionDocument2 pagesHC-256-Warts Problem SolutionAdmin workPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Lice (Singular Louse) : Pediculus Humanus Capitis Parasitic Wingless InsectsDocument4 pagesHead Lice (Singular Louse) : Pediculus Humanus Capitis Parasitic Wingless InsectsIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesfactsheetDocument2 pagesScabiesfactsheetpepe perezPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabie S: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument19 pagesScabie S: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleFrances Anne Nollido SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT III (Health)Document47 pagesUNIT III (Health)Lyn MontebonPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification and Epidemiology of Communicable DiseasesDocument40 pagesClassification and Epidemiology of Communicable DiseasesRwapembe StephenPas encore d'évaluation
- Makita Ra Ang Slide??????????????Document19 pagesMakita Ra Ang Slide??????????????Renato AbellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies: Signs and SymptomsDocument2 pagesScabies: Signs and SymptomsRiri KumalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jock ItchDocument4 pagesJock ItchFranzelle Estrella ÜPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Therapy Letter PDFDocument8 pagesSkin Therapy Letter PDFSherlocknovPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissertation ScabiesDocument8 pagesDissertation ScabiesPayPeopleToWritePapersWestValleyCity100% (2)
- Scabies Treatment ProphylaxisDocument4 pagesScabies Treatment Prophylaxisduch2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Scabies: Newer Perspectives: ReviewDocument6 pagesTreatment of Scabies: Newer Perspectives: ReviewRizkia MulyasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Acne to a Clear Skin: Saying Goodbye to all Skin Blemishes in 7 DaysD'EverandAcne to a Clear Skin: Saying Goodbye to all Skin Blemishes in 7 DaysPas encore d'évaluation
- Thrush / Vaginitis / Candidiasis / Yeast Infection: Contributing FactorsDocument6 pagesThrush / Vaginitis / Candidiasis / Yeast Infection: Contributing FactorsIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- MS Word Paging TipDocument3 pagesMS Word Paging TipIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Creating Great Powerpoint PresentationDocument25 pagesCreating Great Powerpoint PresentationIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Constipation: Constipation Fewer Than Three Bowel Movements Per WeekDocument8 pagesConstipation: Constipation Fewer Than Three Bowel Movements Per WeekIbrahim Abdullah100% (1)
- Helminthes Infestation: Threadworm / Pinworm: Diagnosis and SymptomsDocument3 pagesHelminthes Infestation: Threadworm / Pinworm: Diagnosis and SymptomsIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- DiarrhoeaDocument3 pagesDiarrhoeaIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- DermatitisDocument9 pagesDermatitisIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- CystitisDocument3 pagesCystitisIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Acne Vulgaris / Pimples / Spots / Zits: CommonDocument14 pagesAcne Vulgaris / Pimples / Spots / Zits: CommonIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Lice (Singular Louse) : Pediculus Humanus Capitis Parasitic Wingless InsectsDocument4 pagesHead Lice (Singular Louse) : Pediculus Humanus Capitis Parasitic Wingless InsectsIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Medicines ListDocument163 pagesMedicines ListIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion SicknessDocument5 pagesMotion SicknessIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- English - Simple Present Tense PDFDocument6 pagesEnglish - Simple Present Tense PDFIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Compliance and ConcordanceDocument17 pagesCompliance and ConcordanceIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Topical Therapy: Presented By: DR .Anjali Singh Junior Resident Department of DermatologyDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Topical Therapy: Presented By: DR .Anjali Singh Junior Resident Department of DermatologyRiyaSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- EagleBurgmann MG1 enDocument4 pagesEagleBurgmann MG1 ensanjeevvangePas encore d'évaluation
- Inherited Overflow Metabolic Overflow RenalDocument11 pagesInherited Overflow Metabolic Overflow RenalChrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure Based Drug DesignDocument91 pagesStructure Based Drug DesignMariamPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials and Design: Ehab A. El-Danaf, Magdy M. El-Rayes, Mahmoud S. SolimanDocument6 pagesMaterials and Design: Ehab A. El-Danaf, Magdy M. El-Rayes, Mahmoud S. Solimankamal touilebPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohols (The Production Of)Document15 pagesAlcohols (The Production Of)verity glenPas encore d'évaluation
- Fibc Type A B C D Classification SafetyDocument2 pagesFibc Type A B C D Classification Safetydhineshbabu rPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisher EZ Sliding - Stem Control Valve: The Easy - Et Valve FamilyDocument20 pagesFisher EZ Sliding - Stem Control Valve: The Easy - Et Valve FamilyAlberto GuillenPas encore d'évaluation
- Activated Sludge Combined With Powdered Activated Carbon (PACT Process) For The Petroleum Industry Wastewater Treatment: A ReviewDocument10 pagesActivated Sludge Combined With Powdered Activated Carbon (PACT Process) For The Petroleum Industry Wastewater Treatment: A ReviewAmmr MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- General Purpose ValvesDocument46 pagesGeneral Purpose ValvesbataPas encore d'évaluation
- Regents Homeostasis and EnzymesDocument5 pagesRegents Homeostasis and Enzymesapi-3031203990% (1)
- Feasibility Study of Isononanol ProductionDocument3 pagesFeasibility Study of Isononanol ProductionIntratec SolutionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Publication PDFDocument80 pagesPublication PDFakshatjain3001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chlorine and Water-A Table ResearchDocument5 pagesChlorine and Water-A Table ResearchrajaratnaPas encore d'évaluation
- SemDocument1 pageSemjakelowPas encore d'évaluation
- (T. R. Chouhan) Bhopal, The Inside Story - Carbide Workers Speak Out On The World's Worst Industrial DisasterDocument214 pages(T. R. Chouhan) Bhopal, The Inside Story - Carbide Workers Speak Out On The World's Worst Industrial DisasterANTENOR JOSE ESCUDERO GÓMEZPas encore d'évaluation
- SANDVIK - Steel Designation and Markings - STA-02-030EDocument4 pagesSANDVIK - Steel Designation and Markings - STA-02-030EPetr HavelPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulse GerminationDocument21 pagesPulse GerminationChetan KambojPas encore d'évaluation
- IB-DU1000 Metal-Enclosed Bus PDFDocument12 pagesIB-DU1000 Metal-Enclosed Bus PDFdestro57Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 6 12 Microbial Enumeration Tests PDFDocument5 pages2 6 12 Microbial Enumeration Tests PDFThao TrangPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument70 pagesBasic Mechanical EngineeringHemachandran100% (6)
- Structure of Atoms-11th Cbse Text AnswersDocument33 pagesStructure of Atoms-11th Cbse Text AnswersKalai VananPas encore d'évaluation
- Metaxil DANDocument1 pageMetaxil DANgurinder pal singhPas encore d'évaluation
- G10 - Handout - Organic - Makeup Handout - First WeekDocument4 pagesG10 - Handout - Organic - Makeup Handout - First WeekSheela BatterywalaPas encore d'évaluation
- DS335 - E - Earthing ImprovementDocument2 pagesDS335 - E - Earthing ImprovementCarlos PintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrozincados en 10152 (2009)Document18 pagesElectrozincados en 10152 (2009)joaopedrosousaPas encore d'évaluation
- HINO Cableado ElectricoDocument11 pagesHINO Cableado ElectricoWalter Eduard100% (1)
- Chemical Changes LabDocument5 pagesChemical Changes LabGildardo SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- ETT Seminar - Isotopes in MedicineDocument71 pagesETT Seminar - Isotopes in MedicineisocenterPas encore d'évaluation
- UO-II Chapter 4 (Adsorption)Document27 pagesUO-II Chapter 4 (Adsorption)Ghaydah Hamed Rashid Al-AbriPas encore d'évaluation