Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Helminthes Infestation: Threadworm / Pinworm: Diagnosis and Symptoms
Transféré par
Ibrahim AbdullahTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Helminthes Infestation: Threadworm / Pinworm: Diagnosis and Symptoms
Transféré par
Ibrahim AbdullahDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Prepared by Ibrahim Abdullah, BPharm (Hons) Nottingham, UK.
Threadworms // Page 1 of 3
Helminthes Infestation: Threadworm / Pinworm
1. Most common worm infestation (strongyloidiasis) is by Enterobius
vermicularis or threadworm.
2. These threadworms:
a. Resemble fine pieces of white cotton. They are about 2-13 mm long. The adult
female threadworms are larger (up to 15mm)
b. Are nematodes - unsegmented cylindrical bodies with a complete digestive
system that taper at both ends. These parasites live in the rectum and are generally harmless
c. Human host specific - will not survive in the intestine of household pets. However, it is still possible to
contract threadworms from eggs stuck to the fur of cats and dogs
Diagnosis and Symptoms
1. 90% without symptoms
2. Intense itchy feeling around the anus, usually at night or early in the morning
3. Restless sleep, grinding your teeth in your sleep and enuresis
4. Irritability
5. Loss of appetite
6. More definitive proof - look for them
a. See if any worms are visible on the surface of faeces after a bowel motion
(20% success rate), or
b. Best done in the morning as soon as the child wakes up. The worms themselves
will be visible to the naked eye. They will "glow" under the torchlight
7. Look for the eggs. A female threadworm can lay up to 16,000 eggs
before dying
a. Deposited around the anus on the perianal skin
b. Best detected at night and look like small white specks
c. Alternatively, Use the "adhesive tape test". In the morning before bathing or going to the toilet, apply a
piece of double-sided cellophane tape to a wooden stick. Press the tape against the anus and remove it.
Any threadworm eggs will appear as tiny white marks on the tape
Infestation
1. There are two main ways you can catch threadworms:
a. DIRECTLY - through contact with an infected person
b. INDIRECTLY - through touching a surface such as a tap, door handle, toilet seat, bedding, toys, pencil,
kitchen bench, clothing, door handles, food or furniture that have been contaminated by an infected person
Prepared by Ibrahim Abdullah, BPharm (Hons) Nottingham, UK.
Threadworms // Page 2 of 3
2. Very contagious. Both children and adults can be infected, although it is mostly found in
children.
a. Irritation around the anus (caused by the mucus, or "glue", that the female threadworm secretes in order
to attach the eggs to the skin) sufferer will scratch the itching area, collect eggs on the fingers and under
the nails. They easily get transferred to the mouth and some will be swallowed. Thumb sucking and sucking
other fingers is strongly associated with the prevalence of threadworms. Once ingested, the eggs hatch out
as threadworm larvae in the small intestine. After they have swallowed the eggs they hatch inside the small
intestine. The shells of the eggs are dissolved by stomach juices. The juvenile threadworm larvae then
move to the large intestine to grow and mate. It takes about a month, the incubation period taking
anywhere between 2 to 6 weeks, for the swallowed egg to turn into a sexually mature adult worm. An adult
worm lives for approximately two months, although the male threadworm dies after copulation
a. Can also spread rapidly to clothes. They survive for up to three weeks on clothing, bedding, in carpets and
within household dust. Eggs can even survive in swimming pools
b. Children in childcare institutions are easily infected by each other
3. If eggs remain on the perianal skin long enough to hatch then the juveniles will crawl back
into the anus to the intestines to mature into adults. This process is known as retroinfection
Treatment and Prevention of reinfestation
1. In untreated patients, the disease has a high rate of reinfestation caused by worms already
present in the body. This type of disease recurrence is called autoinfection. Because of
autoinfection, threadworms can remain inside humans for as long as 45 years after the initial
infestation
2. Drug treatment
a. Should be combined with hygiene measures
b. Treat whole family at the same time
c. Not intended to be used by pregnant women or children under two years-of-age
d. Albendazole (Zentel) and Mebendazole (Vermox). Inhibits the threadworms' ability to absorb glucose
(sugars) which depletes them of the energy that they need to survive. As a result the threadworm dies
within several days. Avoid food and drinks containing a lot of sugar because treatments containing
mebendazole are trying to starve the worms of glucose
e. Pyrantel (Combantrin) - a "neuro-muscular blocking agent", causes paralysis of the threadworm's nervous
system. The paralysed worms are then expelled in the faeces by the normal actions of the bowel. Eating
high-fibre food will help to prevent constipation and will assist expelling the worms
f. These medicines will not treat the eggs or immature worms and will not protect you or your children from
contracting threadworm if exposed to it again. So it's advisable to check roughly two weeks after the initial
dose
3. Good hygiene is essential to stop the infection being spread
a. Hygiene controls for 6 weeks, breaking the cycle of infection by removing all eggs and allowing the adult
worms to die
Prepared by Ibrahim Abdullah, BPharm (Hons) Nottingham, UK.
Threadworms // Page 3 of 3
b. Whilst poor hygiene habits can contribute to the spread of threadworms once you have contracted it,
catching threadworms can be as simple as touching an infected surface - it doesn't matter how clean you
are
c. Wash hands and scrub under the nails before eating and after visiting the toilet
d. Finger nails should be short and kept scrubbed clean
e. Until children are toilet trained, take special care when handling their excreta
f. Discourage children from sharing food and from placing objects into their mouths
4. Other measures:
a. Threadworm eggs may be left on common household surfaces, so give your home a thorough clean.
Vacuum carpets and wash floors, clothes and bedding with hot water, to kill any remaining eggs. Don't
forget the favourite teddy or security blanket, and take care not to shake linen when removing bedclothes -
you could be spreading infectious eggs into the air
b. Make sure that everyone in the household using their own towel and facecloth
c. Snug underpants fitted to children at night may make it harder to scratch, therefore reducing the risk of
eggs transferring to fingers
d. Underwear should be changed daily
e. Bed sheets should be changed frequently, especially 7 to 10 days after the treatment
f. Use hot laundry wash cycles for a while in order to kill the remaining eggs
g. Shower rather than bathe for several days after treatment, to dislodge any remaining eggs from the anal
region
Refer
1. Anyone who is pregnant or planning a pregnancy or who is breast feeding a child
2. Children under two years of age
3. Patients who persistently relapse should be seen by the GP and possibly referred to a
parasitologist
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- LESSON 10 Intestinal ParasitesDocument17 pagesLESSON 10 Intestinal Parasitesgimel tenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Pinworm Fact Sheet: Maryland Department of Health & Mental Hygiene Epidemiology & Disease Control Programs April 2008Document1 pagePinworm Fact Sheet: Maryland Department of Health & Mental Hygiene Epidemiology & Disease Control Programs April 2008Nosa MnPas encore d'évaluation
- Worm SummaryDocument3 pagesWorm SummaryAdebisi Jeleel AdekunlePas encore d'évaluation
- WormsDocument20 pagesWormsAdebisi Jeleel AdekunlePas encore d'évaluation
- Roundworm Infections, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandRoundworm Infections, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitic Zoonoses and Diagnostics For Dogs Dr.Document3 pagesParasitic Zoonoses and Diagnostics For Dogs Dr.pundaipundaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Worm InfestationDocument8 pagesWorm Infestationshavonprince97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study: MicrobiologyDocument13 pagesCase Study: MicrobiologywellYONGPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Importance of CoralsDocument3 pagesEconomic Importance of CoralsjaleelkabdulPas encore d'évaluation
- MICROPARA LAB G6 Enterobius VermicularisDocument3 pagesMICROPARA LAB G6 Enterobius VermicularisMary Jane TiangsonPas encore d'évaluation
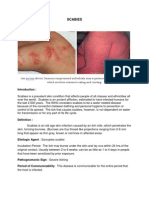
- Scabies: Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesScabies: Signs and SymptomsIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Rabbit ParasitesDocument14 pagesRabbit Parasiteseidjad222Pas encore d'évaluation
- Enterobius VermicularisDocument3 pagesEnterobius Vermicularisshahidkhan 654321654321Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies Prevention and Control ManualDocument57 pagesScabies Prevention and Control Manualvlada_cokoladaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hymenolepis DiminutDocument10 pagesHymenolepis DiminutLois RazonPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 10Document6 pagesLesson 10daryl jan komowangPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasiticfood Born 151110194810 Lva1 App6891Document119 pagesParasiticfood Born 151110194810 Lva1 App6891Navid KhPas encore d'évaluation
- Helminths (Tapeworm, Pinworm) - NavarroDocument26 pagesHelminths (Tapeworm, Pinworm) - NavarroThaddeus Dalagan NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Anclynostoma Duodenale Ancylostoma Duodenale Ancylostoma Ancylostoma Duodenale Necator Americanus Ancylostoma DuodenaleDocument3 pagesAnclynostoma Duodenale Ancylostoma Duodenale Ancylostoma Ancylostoma Duodenale Necator Americanus Ancylostoma DuodenaleMarwin OditaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hymenolepsis Nana LabDocument3 pagesHymenolepsis Nana LabMary Jane TiangsonPas encore d'évaluation
- This Article Previously Appeared in General Practice Update 2008Document8 pagesThis Article Previously Appeared in General Practice Update 2008gopscharanPas encore d'évaluation
- MorkzzzzDocument22 pagesMorkzzzzjd llobreraPas encore d'évaluation
- M2 Hookworms (Apik)Document4 pagesM2 Hookworms (Apik)Zulfan RifqiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Insecta: Group 2: Calma, de Los Santos, Delfin, DemontañoDocument21 pagesClass Insecta: Group 2: Calma, de Los Santos, Delfin, DemontañoShanaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Roun WormsDocument24 pagesRoun WormsBalach JanPas encore d'évaluation
- ToxocariasisDocument3 pagesToxocariasisRochelle ThompsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Trichuris TrichiuraDocument3 pagesTrichuris TrichiuraTwish BeraldePas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum NematodaDocument24 pagesPhylum NematodaFetejohn Seño AbrencilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Pinworm Infection Is Caused by A Small - For MergeDocument5 pagesPinworm Infection Is Caused by A Small - For MergeZingara VelanPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 4Document55 pagesDay 4Amanuel MaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitic Roundworm DiseaseDocument53 pagesParasitic Roundworm DiseaseRaja Alfian IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies Guideline Sept 07 PDFDocument10 pagesScabies Guideline Sept 07 PDFMira ApriliaPas encore d'évaluation
- المحاضرة 7 مادة الطفيلياتDocument5 pagesالمحاضرة 7 مادة الطفيلياتdyabw6430Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases & Conditions: Contact Us AppointmentsDocument14 pagesDiseases & Conditions: Contact Us AppointmentsRohit Kumar AllaparthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies Management: Community Control of ScabiesDocument3 pagesScabies Management: Community Control of Scabiespet_trinPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies NotesDocument9 pagesScabies NotesAvi ePas encore d'évaluation
- Para-Lab Practicals PDFDocument15 pagesPara-Lab Practicals PDFRizzy VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Deworming: Fit For SchoolDocument9 pagesDeworming: Fit For SchoolLark SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- COMMON WORM INFESTATION DrASBDocument54 pagesCOMMON WORM INFESTATION DrASBDr AMAL S BABUPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediculosis (Lice Infestation) : Oklahoma State Department of Health 01-2015 ReviewedDocument8 pagesPediculosis (Lice Infestation) : Oklahoma State Department of Health 01-2015 ReviewedAgung PermanajatiPas encore d'évaluation
- ThreadwormsDocument1 pageThreadwormsDavid HylandPas encore d'évaluation
- Ringworm Procedures v1Document10 pagesRingworm Procedures v1Shams AlzamanPas encore d'évaluation
- BAB I Selesai SemuaDocument10 pagesBAB I Selesai SemuaZminasariPas encore d'évaluation
- ScabiesDocument8 pagesScabiesJessica Dumayas Dela RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual For Small Animal Care and Management 4th Edition Warren 1285425529 9781285425528Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Small Animal Care and Management 4th Edition Warren 1285425529 9781285425528victorwestkdobjnwrep100% (23)
- Aljas&Bama (Microbm9evaluate)Document8 pagesAljas&Bama (Microbm9evaluate)Mary Clare Fuentes BamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 18. Pinworm InfectionDocument12 pagesChapter 18. Pinworm InfectionMonica CiorneiPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Memo Head Lice Eng-SpanDocument4 pagesHealth Memo Head Lice Eng-Spanapi-285009559Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cocci Dia of SheepDocument11 pagesCocci Dia of Sheepmazhr_bzuPas encore d'évaluation
- Hymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpDocument7 pagesHymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpSusan GachukiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies GuidelineJanuary 2013Document13 pagesScabies GuidelineJanuary 2013anisarahma718Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class 7:systems of Housing-Single Row System-Double Row System-Head To Head and Tail To Tail-Merits and DemeritsDocument15 pagesClass 7:systems of Housing-Single Row System-Double Row System-Head To Head and Tail To Tail-Merits and DemeritsAjay kuhirePas encore d'évaluation
- 336 ScabiesDocument2 pages336 ScabiesrozanfikriPas encore d'évaluation
- Flea ControlDocument4 pagesFlea ControlwandererPas encore d'évaluation
- Papular Urticaria: Diagnosis by SCRATCHDocument2 pagesPapular Urticaria: Diagnosis by SCRATCHanisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pest ControlDocument41 pagesPest ControlMakrand ShirsatPas encore d'évaluation
- Canfamphys00240 0140Document4 pagesCanfamphys00240 0140Abbas KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Immediate Care of The NewbornDocument10 pagesImmediate Care of The NewbornRaffy100% (2)
- SCABIESDocument14 pagesSCABIESNom Kumar Naik Rathod100% (1)
- Thrush / Vaginitis / Candidiasis / Yeast Infection: Contributing FactorsDocument6 pagesThrush / Vaginitis / Candidiasis / Yeast Infection: Contributing FactorsIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- MS Word Paging TipDocument3 pagesMS Word Paging TipIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Creating Great Powerpoint PresentationDocument25 pagesCreating Great Powerpoint PresentationIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Constipation: Constipation Fewer Than Three Bowel Movements Per WeekDocument8 pagesConstipation: Constipation Fewer Than Three Bowel Movements Per WeekIbrahim Abdullah100% (1)
- CystitisDocument3 pagesCystitisIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Warts (Verruca) : Local Growth SurfaceDocument4 pagesWarts (Verruca) : Local Growth SurfaceIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Lice (Singular Louse) : Pediculus Humanus Capitis Parasitic Wingless InsectsDocument4 pagesHead Lice (Singular Louse) : Pediculus Humanus Capitis Parasitic Wingless InsectsIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Acne Vulgaris / Pimples / Spots / Zits: CommonDocument14 pagesAcne Vulgaris / Pimples / Spots / Zits: CommonIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- DermatitisDocument9 pagesDermatitisIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- DiarrhoeaDocument3 pagesDiarrhoeaIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Scabies: Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesScabies: Signs and SymptomsIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Medicines ListDocument163 pagesMedicines ListIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion SicknessDocument5 pagesMotion SicknessIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- English - Simple Present Tense PDFDocument6 pagesEnglish - Simple Present Tense PDFIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Compliance and ConcordanceDocument17 pagesCompliance and ConcordanceIbrahim AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Vildagliptin-Metformin and Glimepiride-Metformin Treatments in Type 2 Diabetic PatientsDocument7 pagesComparison of Vildagliptin-Metformin and Glimepiride-Metformin Treatments in Type 2 Diabetic PatientsGregory VeintimillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Minnesota Fall School Planning Guide - Minnesota Department of HealthDocument16 pagesMinnesota Fall School Planning Guide - Minnesota Department of HealthPatch Minnesota100% (1)
- MOH-National Antimicrobial GuidelinesDocument65 pagesMOH-National Antimicrobial GuidelinesHamada Hassan AlloqPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study..Document4 pagesDrug Study..Micah SalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Proposal 1 - DengueDocument8 pagesSample Proposal 1 - Dengueazliothman100% (1)
- MED2 Tut1 Inflammation Healing Quiz NG 2021Document2 pagesMED2 Tut1 Inflammation Healing Quiz NG 2021joshPas encore d'évaluation
- Childrens Colour Trail TestDocument5 pagesChildrens Colour Trail Testsreetama chowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Number FourDocument5 pagesCase Study Number FourYessamin Paith RoderosPas encore d'évaluation
- Anesthesia in The FutureDocument11 pagesAnesthesia in The FuturesayednourPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic Act No. 6675: Reporter: Manamparan Hosny MDocument17 pagesRepublic Act No. 6675: Reporter: Manamparan Hosny Mkhara teanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Draft Examination Timetable For Msu Mid-Semester Examination, February 2016 SessionDocument279 pagesDraft Examination Timetable For Msu Mid-Semester Examination, February 2016 SessionRebecca ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Rational Use of MedicineDocument30 pagesRational Use of MedicineJareena BegumPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide Grade 8 3rd QuarterDocument16 pagesSlide Grade 8 3rd Quartermanuel a. pinlacPas encore d'évaluation
- Providing First Aid and Emergency ResponseDocument161 pagesProviding First Aid and Emergency ResponseTHE TITANPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical FormDocument4 pagesPhysical Formapi-352931934Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toxoigg ArcDocument8 pagesToxoigg Arctesteste testePas encore d'évaluation
- BPHDocument20 pagesBPHHerly KakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventilator Draeger Evita V300 - Spesifikasi Teknis PDFDocument4 pagesVentilator Draeger Evita V300 - Spesifikasi Teknis PDFArifyadin SudonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Insan Anatomisi Atlasi Mcminn 1515167549Document18 pagesInsan Anatomisi Atlasi Mcminn 1515167549Müslüm ŞahinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease - Clinical Manifestations and DiagnosisDocument13 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease - Clinical Manifestations and DiagnosisJavier Manuel Escobedo CalderónPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspirin Plus Clopidogrel As Secondary Prevention After Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument13 pagesAspirin Plus Clopidogrel As Secondary Prevention After Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisshevmyrPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialog Bahasa Inggris Sehat Itu MahalDocument4 pagesDialog Bahasa Inggris Sehat Itu Mahaljusniati puwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Visiting A DoctorDocument12 pagesVisiting A DoctorНаталіяPas encore d'évaluation
- Ano Rectal ExaminationDocument12 pagesAno Rectal ExaminationSnehal SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 12TH Postgraduate Course Program PDFDocument2 pages12TH Postgraduate Course Program PDFOliver VirataPas encore d'évaluation
- OligohydramniosDocument4 pagesOligohydramniossalamredPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Course InstructorsDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan: Course InstructorsFatema AlsayariPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Head Trauma: PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPediatric Head Trauma: Pathophysiologyherman76Pas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical EpidemiologyDocument64 pagesAnalytical EpidemiologyQueency Dangilan100% (1)
- Case 11-2009 - A 47-Year-Old Man With Fever, Headache, Rash, and VomitingDocument9 pagesCase 11-2009 - A 47-Year-Old Man With Fever, Headache, Rash, and VomitingcmirceaPas encore d'évaluation