Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Power of Youth
Transféré par
Soni Mishra TiwariCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Power of Youth
Transféré par
Soni Mishra TiwariDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Power of Youth
Power of Youth when this topic comes we get examples of youth of Metro cities. We
event dont get news of youth of towns and we totally forget villages.
As we have studied in our schools that India is a country of villages. As per Census
2011 Indias
Population in Urban areas
And in Rural area
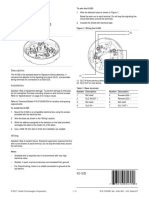
One can see from the chart
Around 70% population of India leaves in rural area. And out of this more than 65% of
population below the age of 35.
Indias Population
as per Census 2011
65% of It Youth of Gujarat
1210569573.00 786870222.5 Around 225 Lacs
121 Carore Say
78,68,70,223.00
78 Carore
By far the most significant impact of the JGS has been improving the quality of life of
rural people who had never experienced uninterrupted 24 h, three-phase power supply.
Rural,
83,34,63,448
68.85%
Urban,
37,71,06,125
31.15%
Population of India
( 1,21,05,69,573 Nos)
Census 2011
Rural
Urban
School teachers and students can use laboratory equipments, computers, television
sets more than they could do before due to long and frequent interruptions in rural
power supply. The JGS also has modified migration. Prior to implementing the JGS,
many wealthier, rural families migrated to towns, where the power supply was better.
This temptation, especially among the young, has declined as village life has become
more comfortable with implementation of the JGS. Improved power supply has led to
improved services such as drinking water supply, street lighting and telecommunication.
The JGS paved the way for better functioning of schools, primary health centers, dairy
cooperatives and other village institutions. It has also enhanced access to television,
radio, kitchen gadgets and fans.
The JGS has given impetus to tailoring, knitting, vending cool drinks, welding, small oil
mills in villages. According to a local leader in Bhavnagar district, thanks to JGS, our
villages have witnessed more progress and better incomes during the last 3 years than
in 50 years before. According to another, JGS has good and bad things for farmers;
but it has only good things for the village as a whole.
In most districts, electronic and electrical repair shops experienced major improvements
in efficiency and speed. Welding machine owners and tire puncture shops improved
their businesses substantially. Rural demand for electronic products TV sets, DVD
players, tape recorders increased rapidly. Cold drink and frozen food shops have
experienced 10% to _20% increases in business, especially during the summer. Tailors
have improved their productivity and income. Housewives, students, commuters, non-
farm workers, and cottage industry owners are unreservedly positive about the
beneficial impacts of the JGS.
In many areas, diamond polishing units have been shifting to villages to save on
expensive space in towns, creating new employment for village youth.
Around the world, the English terms youth, adolescent, teenager, kid, and young
person are interchanged, often meaning the same thing, but they are occasionally
differentiated. Youth can refer to the entire time of life when one is young, including
childhood, but often refers specifically to the time of life that is neither childhood nor
adulthood but rather somewhere in between.
[5][6]
Youth also identifies a particular
mindset of attitude, as in "He is very youthful". The term youth is also related to
being young.
[7]
The term also refers to individuals between the ages of 16-24.
[8]
Current Population of India 2013
Rank State or union territory Population (2011 Census) Density (per km) Sex ratio
01 Uttar Pradesh 199,581,477 828 908
02 Maharashtra 112,372,972 365 946
03 Bihar 103,804,637 1102 916
04 West Bengal 91,347,736 1029 947
05 Andhra Pradesh 84,665,533 308 992
06 Madhya Pradesh 72,597,565 236 930
07 Tamil Nadu 72,138,958 555 995
08 Rajasthan 68,621,012 201 926
09 Karnataka 61,130,704 319 968
10 Gujarat 60,383,628 308 918
11 Odisha 41,947,358 269 978
12 Kerala 33,387,677 859 1,084
13 Jharkhand 32,966,238 414 947
14 Assam 31,169,272 397 954
15 Punjab 27,704,236 550 893
16 Haryana 25,353,081 573 877
17 Chhattisgarh 25,540,196 189 991
18 Jammu and Kashmir 12,548,926 56 883
19 Uttarakhand 10,116,752 189 963
20 Himachal Pradesh 6,856,509 123 974
21 Tripura 3,671,032 350 961
22 Meghalaya 2,964,007 132 986
23 Manipur 2,721,756 122 987
24 Nagaland 1,980,602 119 931
25 Goa 1,457,723 394 968
26 Arunachal Pradesh 1,382,611 17 920
27 Mizoram 1,091,014 52 975
28 Sikkim 607,688 86 889
UT1 Delhi 16,753,235 9,340 866
UT2 Puducherry 1,244,464 2,598 1,038
UT3 Chandigarh 1,054,686 9,252 818
UT4 Andaman and Nicobar Islands 379,944 46 878
UT5 Dadra and Nagar Haveli 342,853 698 775
UT6 Daman and Diu 242,911 2,169 618
UT7 Lakshadweep 64,429 2,013 946
Total India 1,210,193,422 382 940
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Standard Costing: (Problems On - Labour Cost Variances)Document2 pagesStandard Costing: (Problems On - Labour Cost Variances)Soni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.A) Material Cost Variance - ProblemsDocument2 pages1.A) Material Cost Variance - ProblemsSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Access Point BrochureDocument2 pagesWireless Access Point BrochureSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- AbductedDocument160 pagesAbductedSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Red 10 Blue 2 Pink 4 Yellow 5Document1 pageRed 10 Blue 2 Pink 4 Yellow 5Soni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Origami Poodle Face PDFDocument1 pageOrigami Poodle Face PDFSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA AssignmentDocument2 pagesMBA AssignmentSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Sheet Format - 2Document5 pagesCost Sheet Format - 2Soni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Income Tax MCQDocument15 pagesIncome Tax MCQSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA MCOB SyllabusDocument2 pagesMBA MCOB SyllabusSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Required For 66KV SSDocument1 pageMaterial Required For 66KV SSSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Required For 66KV SS-IIDocument1 pageMaterial Required For 66KV SS-IISoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Morse Code Sheet 01Document2 pagesMorse Code Sheet 01Soni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Broken WingsDocument3 pagesBroken WingsSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- PranayamDocument5 pagesPranayamSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- GK IndiaDocument4 pagesGK IndiaSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Tourism in IndiaDocument3 pagesTourism in IndiaSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Books and SiteDocument3 pagesList of Books and SiteSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Robotics PDFDocument29 pagesFull Robotics PDFmajesticdharma1985Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01 IndustrialRobots PDFDocument53 pages01 IndustrialRobots PDFchandu naikPas encore d'évaluation
- Met 1Document46 pagesMet 1Ahmed AbdelhamedPas encore d'évaluation
- 700Document6 pages700Soni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- DRDO RAC Recruitment Advt.Document4 pagesDRDO RAC Recruitment Advt.Soni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear ProgrammingDocument32 pagesLinear ProgrammingLeomard SilverJoseph Centron LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Jyoti GramDocument2 pagesJyoti GramSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- CL - Aprin XTL: Nxaminattons (I) Departmental Examinations in AccountsDocument24 pagesCL - Aprin XTL: Nxaminattons (I) Departmental Examinations in AccountsSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Kaise Bataun MainDocument1 pageKaise Bataun MainSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Main Ek JaldharaDocument1 pageMain Ek JaldharaSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument1 pageApplied Hydraulics and PneumaticsSoni Mishra Tiwari0% (1)
- GATE Subject Vise WeigtageDocument1 pageGATE Subject Vise WeigtageSoni Mishra TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Species Diversity in Lentic and Lotic Systems of Lake Tamblyn and The Mcintyre RiverDocument21 pagesSpecies Diversity in Lentic and Lotic Systems of Lake Tamblyn and The Mcintyre Riverapi-393048315Pas encore d'évaluation
- PB PWR e R1 PDFDocument8 pagesPB PWR e R1 PDFnallinikanth sivalankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 6 Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDocument7 pagesWeek 6 Blood and Tissue FlagellatesaemancarpioPas encore d'évaluation
- Reference For Biology AssignmentDocument2 pagesReference For Biology Assignmentdhanieya ganeishPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod 6 Soft Tissue InjuriesDocument5 pagesMod 6 Soft Tissue Injuriesrez1987100% (1)
- Strauss Dental Catalog 2013Document74 pagesStrauss Dental Catalog 2013d3xt3rokPas encore d'évaluation
- NCMA 217 - Newborn Assessment Ma'am JhalDocument5 pagesNCMA 217 - Newborn Assessment Ma'am JhalMariah Blez BognotPas encore d'évaluation
- BCM Continuous ImprovementDocument22 pagesBCM Continuous ImprovementnikoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapid Cycling in Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageRapid Cycling in Bipolar Disorderdo leePas encore d'évaluation
- Maual de Servicio TV LG 32lf15r-MaDocument31 pagesMaual de Servicio TV LG 32lf15r-MaJaime E FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Micdak BackgroundDocument3 pagesMicdak Backgroundappiah ernestPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of Motivation and Child Moral DevelopmentDocument5 pagesTheories of Motivation and Child Moral DevelopmentPamela mirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Base para Detectores de Humo y Temperatura KIDDE KI-SBDocument2 pagesBase para Detectores de Humo y Temperatura KIDDE KI-SBAnderson CastañedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Family MedicineDocument156 pagesFamily MedicinedtriggPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenna LecDocument31 pagesAntenna Lecjosesag518Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual of Physics by Arthur BeiserDocument145 pagesSolution Manual of Physics by Arthur BeiserManuull71% (49)
- The Secret of The House WTDocument22 pagesThe Secret of The House WTPetr -50% (2)
- Allium CepaDocument90 pagesAllium CepaYosr Ahmed100% (3)
- 2016.05.16 - Org ChartDocument2 pages2016.05.16 - Org ChartMelissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Criminal Justice IssuesDocument132 pagesCritical Criminal Justice IssuesAnnamarella Amurao CardinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Upk B Inggris PKBM WinaDocument11 pagesSoal Upk B Inggris PKBM WinaCuman MitosPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Capital FormationDocument9 pagesHuman Capital Formationtannu singh67% (6)
- Canada's Health Care SystemDocument11 pagesCanada's Health Care SystemHuffy27100% (2)
- Job Satisfaction RRLDocument39 pagesJob Satisfaction RRLMarie Tiffany100% (1)
- History of The Stethoscope PDFDocument10 pagesHistory of The Stethoscope PDFjmad2427Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual de Referencia PlanmecaDocument288 pagesManual de Referencia PlanmecaJorge Escalona Hernandez100% (2)
- Abstract - Tropen Tag 2011 PDFDocument634 pagesAbstract - Tropen Tag 2011 PDFzmoghesPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: Distinction From ICD Pre-DSM-1 (1840-1949)Document25 pagesDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: Distinction From ICD Pre-DSM-1 (1840-1949)Unggul YudhaPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Kumar Aswamy Job Offer LetterDocument1 pageA. Kumar Aswamy Job Offer LetterHimanshu PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurons and Nerve Impulses: Nandika Arora and Risa Gaikwad (11 G2)Document17 pagesNeurons and Nerve Impulses: Nandika Arora and Risa Gaikwad (11 G2)RisaPas encore d'évaluation