Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Formatted Food Assignment
Transféré par
DylanRichardsDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Formatted Food Assignment
Transféré par
DylanRichardsDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Food and Nutrition
Dylan Richards
M5
21st May 2014
Ms. Rogers
CONTENTS
TASK 1 NUTRIENTS
SECTION 1.1 - DEFINITION OF NUTRIENTS 4
SECTION 1.2 SIX MAIN NUTRIENTS
TASK 2 MACRONUTRIENTS
SECTION 2.1 PROTEIN 5
SECTION 2.1.1 ROLE IN BODY
SECTION 2.1.2 DAILY REQUIREMENTS
SECTION 2.1.2 FOOD SOURCES
SECTION 2.2 - CARBOHYDRATES
SECTION 2.2.1 ROLE IN BODY
SECTION 2.2.2 DAILY REQUIREMENTS
SECTION 2.2.3 FOOD SOURCES
SECTION 2.3 LIPIDS
SECTION 2.3.1 ROLE IN BODY
SECTION 2.3.2 DAILY REQUIREMENTS
SECTION 2.3.3 FOOD SOURCES
TASK 3 MICRONUTRIENTS
SECTION 3.1 FOUR MICRONUTRIETS AND FOOD SOUCES 6
SECTION 3.2 ROLE IN BODY WITHR EXAMPLES
TASK 4 WATER
SECTION 4.1 ROLE IN BODY 7
SECTION 4.2 FOUR FOOD SOURCES
TASK 5 FOOD SELECTION MODELS
SECTION 5.1 HEALTHY LIVING PYRAMID 8
SECTION 5.1.1 PURPOSE
SECTION 5.1.2 FEATURES
SECTION 5.1.3 DISADVANTAGES AND ADVANTAGES
SECTION 5.2 AUSTRALIAN GUIDE TO HEALTHY EATING 9
SECTION 5.2.1 PURPOSE
SECTION 5.2.2 FEATURES
SECTION 5.2.3 DISADVANTAGES AND ADVANTAGES
TASK 6 CONSUMPTION IN LAST 24 HOURS
SECTION 6.1 TABLE 10
SECTION 6.2 FOOD SELECTION MODEL
TASK 7 DIETING
SECTION 7.1 DESCRIPTION 11
SECTION 7.2 COMPARISON WITH FOOD SELECTION MODEL
SECTION 7.3 SUGARS AFFECT ON HEALTH
BIBLIOGRAPHY 12
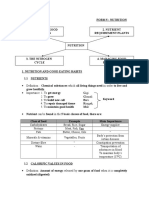
TASK 1 NUTRIENTS
1.1 A Nutrient is a source of nourishment
1.2 Food sources include carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, minerals and
water.
TASK 2 MACRONUTRIENTS
2.1 PROTEIN
2.1.1 Proteins function in the human body is to build new cells and fix damaged
cells in the body. During certain stages of human life, protein is especially
significant for growth. They also maintain muscle mass, hormone production,
enzyme production, maintenance of immune system and to provide energy when
carbohydrates are not available.
2.1.2 10-35% protein is required for a healthy diet.
2.1.3 - Protein is found in egg and beans
2.2 CARBOHYDRATE
2.2.1 - Carbohydrates function in the human body is to provide energy.
Carbohydrates are significant for your brain, nervous system, kidneys and
muscles.
2.2.2 45-65% carbohydrates is required for a healthy diet.
2.2.3 Carbohydrates are found in potatoes and watermelon.
TASK 3 MICRONUTRIENTS
3.1 Iron red meat
Copper nuts
Chromium wheat bread
Zinc Beans
3.2 Micronutrients help with healthy growth and development. Calcium
contributes to development of bones and teeth. Iron contributes to metabolism
and energy balance. Magnesium contributes to the prevention of heart disease
by controlling the rhythm of heartbeats and muscular activity in the heart.
TASK 4 WATER
4.1 - Waters role in the human body is essential because it helps nearly ever part
of the human body to work well. Water brings nutrients and oxygen to all cells in
the human body; water moistens oxygen and is required for breathing.
4.2 Food sources containing water include: cucumber, pineapples, grapefruit
and strawberries
TASK 5 FOOD SELECTION MODELS
5.1 HEALTHY LIVING PYRAMID
5.1.1 - The healthy living pyramid is a guideline to show what type of foods we
should have in our diet and in what proportions we should eat them, it is
presented in a pyramid. There are guidelines to indicate that exercise is needed
in a healthy diet, the amount of water needed in our diet and how much salt.
5.1.2 - The bottom layer of the pyramid features the healthiest food and that are
essential to a healthy diet. These foods must be eaten more than both of the
above sections. Another feature of this pyramid is the feet underneath the
pyramid and the white text Move More.Move More, which indicates that
exercise is essential for a healthy diet. A 3
rd
feature of this pyramid is the tap and
saltshaker along the side of the pyramid which is encouraging water
consumption and to not use salt in order to sustain a healthy diet.
5.1.3 - An advantage of this diagram is that it is providing guidelines on how to
have a healthy diet and if it is followed the outcome will be beneficial. A
disadvantage however is that the diagram does not include an exact amount of
how much of each section can be eaten, how much water should be drunk and
how much
exercise is
required for a
healthy diet.
TASK 5 FOOD SELECTION MODELS
5.2 AUSTRALIAN GUIDE TO HEALTHY EATING
5.2.1 - The Australian guide to healthy eating is a guideline that groups different
types of foods to show how to maintain a healthy diet, it is presented in a circle
diagram. It also indicates how much of an array of unhealthy foods should be
eaten and how often.
5.2.2 - The yellow section of the circle presents a variety of foods that are
classified as grain (cereal) foods. The yellow section is bigger than a quarter of
the circle meaning that more than a quarter of your diet should consist of cereals
high in fiber. There is a small section on the bottom left corner that indicates that
canola oil, olive oil, vegetable oil and margarine that should be used in small
amounts. Another feature of this diagram is the glass of water in the top right
corner and should be consumed as much as vegetables and beans.
5.2.3 - An advantage of this diagram is that the main categories of food and how
much should be consumed in a healthy diet are shown. A disadvantage of this
diagram is that there is no exact amount of how much food should be consumed.
TASK 6 FOOD SELECTION MODELS
6.1 -
6.2 - Fish is a difficult food to place into the food selection model. This is because
not every fish will be equal in size, which can alter the amount of protein,
carbohydrate, and fat the consumer is consuming. If the food selection model
provides an exact weight/length to categorize how much should be eaten, it
would be heard for the consumer to match those measurements exactly.
Australian guide to healthy eating Healthy living pyramid
Water, carrots, lamb, lettuce, tomatoes,
cheese, cucumber, white-bread, egg,
bacon, butter, milk
Egg, bacon, carbonated soft drinks,
lettuce, corn chips, avocado, carrots,
lamb, tomatoes, cheese, cucumber,
white-bread, water, butter, milk, tuna
TASK 7 DIETING
7.1 Dieting is the act of consuming a regulated amount of food usually to
control ones body weight.
7.2 Day 1 for the Jenny Craig 5000kj planned menu is: oven baked muesli,
cup non fat milk, 1 orange, hearty beef pie, garden salad, 1 carrot, cheese twists,
1 apple, chicken fettuccine, 1 cup broccoli, 1 cup green beans, 1 cup zucchini, 2/3
cup fat free yoghurt. When compared to the healthy living pyramid we see that
every section of the pyramid is used in this diet.
7.3 The overconsumption of eating foods high in sugar regularly has a negative
affect on physical health. Sugar can cause tooth decay and can overload the liver.
Overloading the liver with sugar can cause liver diseases. Sugar also has the
ability to give you cancer, it is addictive and can cause you too put on excess
weight.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
First reference: http://www.thefreedictionary.com/Nutrients
Second reference: http://healthyeating.sfgate.com/6-essential-nutrients-
functions-4877.html
Third reference: http://www.worldofmolecules.com/foods/
Fourth reference: http://www.self.com/blogs/flash/2011/08/6-high-fat-foods-
that-are-good.html
Fifth reference: http://www.marieclaire.com/health-fitness/advice/water-rich-
foods-to-beat-bloat
Sixth reference: http://www.livestrong.com/article/355090-what-are-
functions-of-proteins-carbohydrates-fats-water-vitamins-and-minerals/
Seventh reference: http://www.livestrong.com/article/436094-what-role-do-
micronutrients-play-in-the-body/
Eighth reference:
http://www.nutritionaustralia.org/national/resource/healthy-living-
pyramid#.U4SJ4pSSxsY
Ninth reference: http://www.eatforhealth.gov.au/guidelines/australian-guide-
healthy-eating
Tenth reference:
http://www8.nationalacademies.org/onpinews/newsitem.aspx?RecordID=1049
0
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basic Nutrition ToolsDocument48 pagesBasic Nutrition ToolsRednax 0912Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nutritional and Health Aspects of Food in South Asian CountriesD'EverandNutritional and Health Aspects of Food in South Asian CountriesJamuna PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- FSM 113Document113 pagesFSM 113ccatiishs100% (1)
- Mediterranean diet cookbook for beginners 2024: Discover the art of healthy living: A guide to the Mediterranean dietD'EverandMediterranean diet cookbook for beginners 2024: Discover the art of healthy living: A guide to the Mediterranean dietPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is NutritionDocument11 pagesWhat Is NutritionWing Yeng TanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3 Food Guide Pyramid PDFDocument47 pages1.3 Food Guide Pyramid PDFaisyah fauziPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 1 Macronutrients - CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesExercise 1 Macronutrients - CarbohydratesBabs tvPas encore d'évaluation
- FST 307 Basic NutritionDocument47 pagesFST 307 Basic NutritionNur Ayu Nadhirah Bt YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Science 1Document240 pagesFood Science 1Anas AhmedhPas encore d'évaluation
- Balanced Diet - Class 6, Components of FoodDocument3 pagesBalanced Diet - Class 6, Components of FoodPriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Balance DietDocument9 pagesBalance DietUshna KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Macro and MicronutrientsDocument11 pagesMacro and Micronutrientsharshika tembhurnePas encore d'évaluation
- MAPEH 7 Q1 M2 Health 1Document10 pagesMAPEH 7 Q1 M2 Health 1Shamson AbantasPas encore d'évaluation
- NDT Exercise No.2 For BSN 2Document20 pagesNDT Exercise No.2 For BSN 2Celline Isabelle ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Isabela State University City of Ilagan CampusDocument27 pagesIsabela State University City of Ilagan CampusCharlz ZipaganPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 105 Modules NCM 105Document33 pagesNCM 105 Modules NCM 105Duran JustinePas encore d'évaluation
- Anc-01 Solved Assignment 2020-2021Document15 pagesAnc-01 Solved Assignment 2020-2021Priyanka BediPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition LectureDocument11 pagesNutrition LectureAngelo P. VeluzPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Chem Module 1 2ND QTRDocument4 pagesApplied Chem Module 1 2ND QTRJustine ZablanPas encore d'évaluation
- NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY PowerpointDocument367 pagesNUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY Powerpointcarlos poncePas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Science 2021/2022 Term 1: Ms Ramdehal 2.6&2.4Document9 pagesIntegrated Science 2021/2022 Term 1: Ms Ramdehal 2.6&2.4Naseeb AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition Nursing: CarbohydratesDocument36 pagesNutrition Nursing: CarbohydratesAngelyka Nicole Bengco DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- PATHFIT UNIT 4 - Nutrition and NutrientsDocument2 pagesPATHFIT UNIT 4 - Nutrition and NutrientsRhea Mae PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy PowerpointDocument379 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy PowerpointRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stop Dieting Start Eating Healthy: Chris Brandell NF-25 B. Crocker MT Sac Fall 2013Document141 pagesStop Dieting Start Eating Healthy: Chris Brandell NF-25 B. Crocker MT Sac Fall 2013cbigggsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 10 - Live Life WellDocument5 pagesLesson 10 - Live Life Wellaarnathakour101010Pas encore d'évaluation
- NDT LecDocument13 pagesNDT LecAia RecaidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dwnload Full Contemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Contemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manual PDFcatamiddler4rn7100% (16)
- Chapter 5 Grade-12Document5 pagesChapter 5 Grade-12umamahfarooq75Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise - 6 - NCM-105A Group 1 2FDocument4 pagesExercise - 6 - NCM-105A Group 1 2FRALPH ELVIN MACANLALAYPas encore d'évaluation
- LifestyleDocument32 pagesLifestyleMidz SalipPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrients and Nutrional Requirements For ChildrenDocument11 pagesNutrients and Nutrional Requirements For ChildrenSANAPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 21 Food and Nutrition: StructureDocument16 pagesUnit 21 Food and Nutrition: StructureanonymousPas encore d'évaluation
- FST01 Unit 21 To 30Document151 pagesFST01 Unit 21 To 30sumit prajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Diet Design Tools and GuidelinesDocument68 pagesDiet Design Tools and GuidelinescheriemoorePas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Dietary Tools 1Document38 pages2 Dietary Tools 1Camille GrefaldiaPas encore d'évaluation
- ABRERA, Lucky Lynn R. - Laboratory - Activity - CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesABRERA, Lucky Lynn R. - Laboratory - Activity - CarbohydratesLucky Lynn AbreraPas encore d'évaluation
- College of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityDocument20 pagesCollege of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityRUSSEL AQUINOPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition - 754 755Document40 pagesNutrition - 754 755775.Debidutta MohapatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Form 5 ScienceDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Form 5 ScienceSubashini Muniandy100% (1)
- Basic ToolsDocument47 pagesBasic ToolsCesca Medina100% (1)
- Nutrients Can Be Divided Into 2 Categories: Macronutrients (Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats)Document5 pagesNutrients Can Be Divided Into 2 Categories: Macronutrients (Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats)mildred alidonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy: UNP College of NursingDocument379 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy: UNP College of NursingrnrmmanphdPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Nutrition For LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Nutrition For LifeVraj PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO MT3 ProjectDocument16 pagesBIO MT3 ProjectNikil J.PPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5Document24 pagesLesson 5hk_scribdPas encore d'évaluation
- PetrofskyDocument15 pagesPetrofskyNestor BalboaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 105 Nutrition and Diet Therapy:: Ferkiya A. Abduwa, R.NDocument29 pagesNCM 105 Nutrition and Diet Therapy:: Ferkiya A. Abduwa, R.NLouie Pangilinan LanajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Meal ManagementDocument13 pagesModule 1 Meal Managementrachellegalit2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Health Education Part 1Document20 pages4 Health Education Part 1Julie DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition-Principles FinalDocument9 pagesNutrition-Principles FinalRikkard AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- FSN 101 Lecture NotesDocument140 pagesFSN 101 Lecture NotesMothika SPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Nutrition TransDocument7 pagesBiochem Nutrition TransCyril Dayne Marie BaldePas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition Chapter 1-5Document49 pagesNutrition Chapter 1-5Maria MariePas encore d'évaluation
- Session - 3 - Balanced Diets For Normal Individuals.Document16 pagesSession - 3 - Balanced Diets For Normal Individuals.Sagar KrupaPas encore d'évaluation
- Apply Basics of Sport Nutrition and HydrationDocument68 pagesApply Basics of Sport Nutrition and HydrationsimachewPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Download Contemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesFull Download Contemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manualalojlyhol3100% (35)
- Lesson 2a Pregnancy LacDocument72 pagesLesson 2a Pregnancy LacDenise Joy15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6: Nutrition Tarikh Topik Catatan 6.1 Types of NutritionDocument4 pagesChapter 6: Nutrition Tarikh Topik Catatan 6.1 Types of NutritionPutri MalayaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd QUARTER MAPEH 10 RegularDocument7 pages2nd QUARTER MAPEH 10 RegularCharles Jayson OropesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 2 - Abisha AliDocument7 pagesPaper 2 - Abisha Aliapi-269596566Pas encore d'évaluation
- PEBC Qualifying Exam References and Resources ListDocument5 pagesPEBC Qualifying Exam References and Resources ListAnkit ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyromania-The Urge To Set Fires For Pleasure, Gratification, or Release of Tension Ezhae SymptomsDocument2 pagesPyromania-The Urge To Set Fires For Pleasure, Gratification, or Release of Tension Ezhae SymptomsptbarnabicPas encore d'évaluation
- ZXXZDocument6 pagesZXXZfei cuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Emergencies in Dental Practice: A Review: July 2016Document18 pagesMedical Emergencies in Dental Practice: A Review: July 2016AnushkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Site167 26375 en File1Document11 pagesSite167 26375 en File1Cao Minh TríPas encore d'évaluation
- Inglés II Nivel B 2017 PP 32 43Document12 pagesInglés II Nivel B 2017 PP 32 43MariaVLPas encore d'évaluation
- SMR August 19 (Rengat - Tembilahan, Sect 2) PDFDocument28 pagesSMR August 19 (Rengat - Tembilahan, Sect 2) PDFDoo PLTGUPas encore d'évaluation
- Testicular CancerDocument3 pagesTesticular CancerSherief MansourPas encore d'évaluation
- Schuessler Tissue Salts HandbookDocument52 pagesSchuessler Tissue Salts HandbookBashir Ahmed100% (2)
- Safety Data Sheet: Chevron (Malaysia) Unleaded GasolineDocument12 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Chevron (Malaysia) Unleaded GasolineaminPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Analysis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Analysis Planning Implementation EvaluationJeffrey LumacangPas encore d'évaluation
- Distinguishes Aerobic From MuscleDocument2 pagesDistinguishes Aerobic From MuscleVolley PilgrimsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasonido en El Paciente Crítico Daniel Lichtenstein PDFDocument33 pagesUltrasonido en El Paciente Crítico Daniel Lichtenstein PDFVallejo Romo Alberto CristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Sal Mvlex WebDocument35 pagesSal Mvlex WebCarlos EcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Multigrade Lesson Plan in English3Document13 pagesMultigrade Lesson Plan in English3Nick Bantolo100% (11)
- Professional Development Plan PPT 1Document10 pagesProfessional Development Plan PPT 1api-355484042Pas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiology Course For 3 Yrs Midwifery Students: Yibekal .M (PHA, PH and MPH/Specialty Epidemiology)Document326 pagesEpidemiology Course For 3 Yrs Midwifery Students: Yibekal .M (PHA, PH and MPH/Specialty Epidemiology)Yoseph KassaPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Data Sheet: Blue DyeDocument13 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Blue DyeAsh BuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Restraint Reduction For Older AdultsDocument11 pagesPhysical Restraint Reduction For Older Adultsantariksa tedyPas encore d'évaluation
- American Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoDocument50 pagesAmerican Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoLightPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Nursing ProcessDocument10 pagesCommunity Nursing Processbuhari rabiuPas encore d'évaluation
- K5 - Sistem Informasi KesehatanDocument29 pagesK5 - Sistem Informasi KesehatanPusvaNurmalaSariPas encore d'évaluation
- MWF Community Resource Guide - Atlanta - 2014Document32 pagesMWF Community Resource Guide - Atlanta - 2014MuslimWellnessPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical DiagnosticsDocument3 pagesMedical DiagnosticsDlorrie879Pas encore d'évaluation
- OmeprazoleDocument2 pagesOmeprazoleIvan Matthew SuperioPas encore d'évaluation
- Nature's Pathways Oct 2012 Issue - Northeast WI EditionDocument116 pagesNature's Pathways Oct 2012 Issue - Northeast WI EditionNature's PathwaysPas encore d'évaluation
- Addisons DiseaseDocument1 pageAddisons DiseaseAndreia Palade100% (1)
- Pranic Psychotherapy Session 1Document57 pagesPranic Psychotherapy Session 1Aryan Anand80% (5)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainD'EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (38)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellD'EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietD'EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyD'EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Eat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessD'EverandEat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessPas encore d'évaluation
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsD'EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (49)
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)D'EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (40)
- The Noom Kitchen: 100 Healthy, Delicious, Flexible Recipes for Every DayD'EverandThe Noom Kitchen: 100 Healthy, Delicious, Flexible Recipes for Every DayPas encore d'évaluation
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonD'EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (33)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarD'EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (352)
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthD'EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomD'EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookD'EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeD'EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Rapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: Deep Sleep Your Way to Rapid Weight Loss, Healing Your Body and Self Esteem with Guided Meditations and Positive AffirmationsD'EverandRapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: Deep Sleep Your Way to Rapid Weight Loss, Healing Your Body and Self Esteem with Guided Meditations and Positive AffirmationsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (7)
- The Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthD'EverandThe Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthPas encore d'évaluation
- Foods That Cause You to Lose Weight: The Negative Calorie EffectD'EverandFoods That Cause You to Lose Weight: The Negative Calorie EffectÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (5)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeD'EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifePas encore d'évaluation
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingD'EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Eat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthD'EverandEat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellD'EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (83)
- The Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodD'EverandThe Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleD'EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyD'EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyPas encore d'évaluation
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouD'EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeD'EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)