Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
WK 9
Transféré par
autumntait0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
29 vues3 pagesOperations
Titre original
Wk 9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentOperations
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
29 vues3 pagesWK 9
Transféré par
autumntaitOperations
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Developing New Products and New Services
Innovation: putting anything new into practice
within a firm, irrespective of whether it is new
to the world, copied from competitors, or
adapted from existing products and services
Innovation may apply to: products, services,
processes, organisations
Importance of Innovation:
In operations resources: rapid technology
change, means of building capabilities
In market requirements: increased
competitiveness, shortened lifecycles, fragmented markets
Innovation can be
- Radical step change (Kaikaku): not always sustainable as the operation
becomes fatigued
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): small increments may not be substantial
enough to keep up with market requirements over time
- Combination of the two: optimum and sustainable improvement
Six Levels of Novelty
Design is the configuration of the product or service, whereas innovation is anything new that a
company does (products, services, processes)
- Both can lead to a competitive advantage
- Both follow a broadly similar process
Design: concept generation, screening, preliminary design, evaluation and prototyping
Innovation also includes: business evaluation and management of change to deliver new design
15 Stages of New Product or Service Development Process
1. Objectives and Strategy
a. Specific objectives with regards the the number and nature of new products and
services that they will develop over the coming months or years
2. Structure
a. Does it support ideas and innovation?
b. Is there a large R+D department?
3. Idea Generation and Screening
a. Internal sources: employees, sales force, reverse engineering
b. External sources: customers, competitors, legislative requirements,
environmental pressures, technology advances
c. Screening: level of investment needed, ease of implementation, demand from
customers, fit with existing product/service range
4. Concept Development
a. Required that the ideas that go forward are expanded into fully fledged concepts,
especially if there is a significant service element
5. Concept Testing
a. Research technique designed to evaluate whether a prospective user
understands the idea of the proposed product or service
b. Do they react favourably to it and feel it offers benefits
c. Done by talking directly to users, sales staff or service providers
6. Business Analysis
a. Involved a comprehensive investigation into business implications of each
concept
b. Market assessment and budget drafting for development and introduction of each
proposed new product/service
7. Project Authorisation
a. When top management commits corporate resources to the implementation
8. Service Design and Testing
a. Conversion of the concept into an operational entity
b. Products largely centres around a specialist team
c. Service involves input of prospective users and co-operation of operations
personnel who will ultimately be delivering the service
9. Process and System Design and Testing
a. Applicable to both products and services
b. Products: new production processes or develop new equipment
c. Services: totality of the delivery process, not just experience of customer
10. Marketing program Design and Testing
a. Services: devised in conjunction with the service department
b. Product: marketing program may be entirely separate from development process
11. Personnel Training
a. Mainly applies to service development, employees familiarised with new service
12. Product/Service Testing
a. Determines potential customers acceptance while pilot run ensures smooth
functioning
13. Test Marketing
a. Saleability of new service and field tests sample a limited number of customers
14. Launch
a. Production or delivery and marketing in place and testing, begin full scale launch
15. Post Launch Review
a. Determines whether the strategic objectives were achieved or if further
adjustments are needed
Factors Influencing NPD and NSD
Product/Service Features
- Originality
- Degree of protection from competitors
- Amount of capital investment required
Organisational Characteristics
- Size of company
- Organisational structure
- Degree of in-house capacity
Environmental Factors
- Maturity of marketplace
- Nature of supply chain
- Industry Association Sponsorship
- Formal or informal process
Likely to follow a formal process if:
- new products with major process impact
are developed
- number of interrelated innovations being
developed simultaneously
- new product is protected by licence or
patent
- product life cycles are long
- competitors unlikely to enter maker with a
similar product/service
- innovation is original or new to the world
Ethical Innovation
Patent: provides a legally protected right to exploit an invention. Only granted to something that
is novel (new to the world) but must also have a practical application
- Typically last 20 years
- Prevents others from submitting identical patent requests
- Ensures new knowledge is shared
Design Rights: enabled an organisation to legally protect the appearance of a product, so that the
design cannot be copied by others
- Coca Colas contour shaped bottle
Copyright: how creative works like books, plays, software and artwork can be legally protected
- Creator given exclusive right to use the copyright material, usually granted for the lifetime
of the author, plus a farther 70 years after their death
Trademarks: distinctive mark that identifies a product, service or organisation
Successful NPD and NSDs
Likely Success Barriers to Success
- Development teams are well led and
include creative people (called Plants
by Belbin)
- Top management isolation
- Development teams are a culture of
trust and sharing information
- Innovation seen as too risky
- Effective Knowledge Management - Short term financial horizons
- Inclusion of suppliers and distributors
in decision making process
- Intolerance of fanatics, inappropriate
culture
- Innovation seen as change/chaos
- Excessive bureaucracy (delays)
Likely to follow informal process if:
- simple modifications to existing
product/service
- innovation is not part of major
change program
- there is no licence or patent
protection
- competitors are actively innovating
- the new product is largely a copy of
a competitors product
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Structuring Your Novel Workbook: Hands-On Help For Building Strong and Successful StoriesDocument16 pagesStructuring Your Novel Workbook: Hands-On Help For Building Strong and Successful StoriesK.M. Weiland82% (11)
- ToonHub - Articles of PartnershipDocument13 pagesToonHub - Articles of PartnershipKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Negotiating For SuccessDocument11 pagesNegotiating For SuccessRoqaia AlwanPas encore d'évaluation
- ! Sco Global Impex 25.06.20Document7 pages! Sco Global Impex 25.06.20Houssam Eddine MimounePas encore d'évaluation
- Cookery-10 LAS-Q3 Week5Document7 pagesCookery-10 LAS-Q3 Week5Angeline Cortez100% (1)
- WK 1-3 Financial AccountingDocument1 pageWK 1-3 Financial AccountingautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
- The Accounting SystemDocument1 pageThe Accounting SystemautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
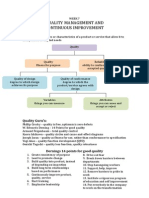
- Managing Quality and Continuous ImprovementDocument6 pagesManaging Quality and Continuous ImprovementautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Quality and Continuous ImprovementDocument6 pagesManaging Quality and Continuous ImprovementautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
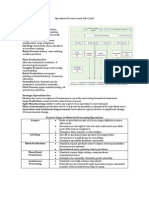
- Mass Customisation: Mass Customisation Strategies Lean and Agile Strategies Generic' Operations StrategiesDocument3 pagesMass Customisation: Mass Customisation Strategies Lean and Agile Strategies Generic' Operations StrategiesautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Supply Chain Relationships and StrategiesDocument2 pagesManaging Supply Chain Relationships and StrategiesautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Jobs and Managing PeopleDocument4 pagesDesigning Jobs and Managing PeopleautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
- WK 6Document3 pagesWK 6autumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
- WK 3Document2 pagesWK 3autumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
- Location and Layout DesignDocument2 pagesLocation and Layout DesignautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
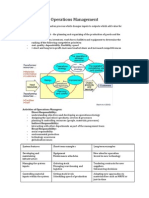
- Operations ManagementDocument4 pagesOperations ManagementautumntaitPas encore d'évaluation
- Intentional Replantation TechniquesDocument8 pagesIntentional Replantation Techniquessoho1303Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd YearDocument5 pages2nd YearAnbalagan GPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-Library - IJLSR - Information - SumanDocument10 pages2-Library - IJLSR - Information - SumanTJPRC PublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron FoundationsDocument70 pagesIron FoundationsSamuel Laura HuancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Assignment Topics - BEO6500 Economics For ManagementDocument3 pagesGroup Assignment Topics - BEO6500 Economics For ManagementnoylupPas encore d'évaluation
- Arcmap and PythonDocument29 pagesArcmap and PythonMiguel AngelPas encore d'évaluation
- CERTIFICATE - Guest Speaker and ParentsDocument4 pagesCERTIFICATE - Guest Speaker and ParentsSheryll Eliezer S.PantanosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adverbs of Frequency Board GameDocument1 pageAdverbs of Frequency Board GameIsmi PurnamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prep - VN: Where Did The Polo Family Come From?Document1 pagePrep - VN: Where Did The Polo Family Come From?Phương LanPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Manual: Control Cabinet M2001Document288 pagesProduct Manual: Control Cabinet M2001openid_6qpqEYklPas encore d'évaluation
- PRI Vs SIP Trunking WPDocument3 pagesPRI Vs SIP Trunking WPhisham_abdelaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Kristine Karen DavilaDocument3 pagesKristine Karen DavilaMark anthony GironellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chengyang Li Archive Cra 23Document32 pagesChengyang Li Archive Cra 23Li ChengyangPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifting Plan FormatDocument2 pagesLifting Plan FormatmdmuzafferazamPas encore d'évaluation
- Kepler's Law 600 Years Before KeplerDocument7 pagesKepler's Law 600 Years Before KeplerJoe NahhasPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Vehicles PresentationDocument10 pagesElectric Vehicles PresentationKhagesh JoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts of Human Development and Poverty: A Multidimensional PerspectiveDocument3 pagesConcepts of Human Development and Poverty: A Multidimensional PerspectiveTasneem RaihanPas encore d'évaluation
- Robots Template 16x9Document13 pagesRobots Template 16x9Danika Kaye GornesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ivan PavlovDocument55 pagesIvan PavlovMuhamad Faiz NorasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lucid Motors Stock Prediction 2022, 2023, 2024, 2025, 2030Document8 pagesLucid Motors Stock Prediction 2022, 2023, 2024, 2025, 2030Sahil DadashovPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidaat Alem The Medical Rights and Reform Act of 2009 University of Maryland University CollegeDocument12 pagesHidaat Alem The Medical Rights and Reform Act of 2009 University of Maryland University Collegepy007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dues & Scholarship Section: NotificationDocument6 pagesDues & Scholarship Section: NotificationMUNEEB WAHEEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Transpetro V 5 PDFDocument135 pagesTranspetro V 5 PDFadityamduttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vipinesh M K: Career ObjectiveDocument4 pagesVipinesh M K: Career ObjectiveJoseph AugustinePas encore d'évaluation
- Zeng 2020Document11 pagesZeng 2020Inácio RibeiroPas encore d'évaluation