Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Torsion Problems PDF
Transféré par
BlondolioTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Torsion Problems PDF
Transféré par
BlondolioDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
14 January 2011
1
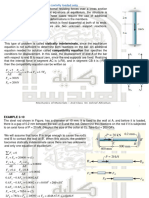
Mechanics of Materials
CIVL 3322 / MECH 3322
Torsion Problems
Homework
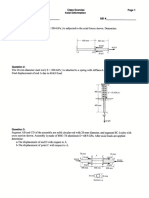
! P 6.17
! P 6.18
! P 6.20
Torsion Problems 2
14 January 2011
2
Torsion Problems 3
For the material properties shown in Figure
1, what is the Modulus of Elasticity of the
material?
260 GPa
110 GPa
800 GPa
358 GPa
Torsion Problems 4
For the material properties shown in Figure
1, what is the ultimate strength of the
material?
210 MPa
290 MPa
320 MPa
380 MPa
14 January 2011
3
Torsion Problems 5
For the material properties shown in Figure
1, what is the yield strength of the
material?
210 MPa
290 MPa
320 MPa
380 MPa
Torsion Problems 6
For the material properties shown in Figure
1, what is the fracture stress of the
material?
210 MPa
290 MPa
320 MPa
380 MPa
14 January 2011
4
Torsion Problems 7
The rigid bar shown in Figure 2 is supported by the pin at A and the rod from B
to D (1). The rod (1) has a cross sectional area of 500 mm
2
, an elastic modulus
of E = 80 GPa, and a coefficient of thermal expansion of
a= 22x10
-6
/C. Initially the bar ABC is in a horizontal position, then the
temperature of the rod (1) is reduced by 40C. What is the deflection of point C
after the temperature is reduced if the load P is equal to 0?
When rod (1) is cooled, point
B will
Torsion Problems 8
1. Move Up
2. Move Down
3. Not Move
4. Dont Know
14 January 2011
5
The magnitude of the
deflection of point C will be
_____ than the magnitude of
the deflection of point B
when Rod (1) is cooled.
Torsion Problems 9
1. Equal to
2. Less than
3. Greater than
4. Dont Know
Torsion Problems 10
The rigid bar shown in Figure 2 is supported by the pin at A and the rod from B
to D (1). The rod (1) has a cross sectional area of 500 mm
2
, an elastic modulus
of E = 80 GPa, and a coefficient of thermal expansion of
a= 22x10
-6
/C. Initially the bar ABC is in a horizontal position, then the
temperature of the rod (1) is reduced by 40C. What is the deflection of point C
after the temperature is reduced if the load P is equal to 0?
( )( )
( )( )
3
3.3 10 3.0
5.66
1.75
B AC
C
AB
m m
L
mm
L m
!
!
"
" #
= = = "
14 January 2011
6
Torsion Problems 11
The rigid bar shown in Figure 2 is supported by the pin at A and the rod from B
to D (1). The rod (1) has a cross sectional area of 500 mm
2
, an elastic modulus
of E = 80 GPa, and a coefficient of thermal expansion of
a= 22x10
-6
/C. Initially the bar ABC is in a horizontal position, then the
temperature of the rod (1) is reduced by 40C. What magnitude would P have to
be to return the rod to a horizontal orientation after the temperature is reduced?
To solve for P, you would
most likely
Torsion Problems 12
1. Sum forces in the y-direction
2. Sum forces in the x-direction
3. Sum moments about A
4. Dont Know
14 January 2011
7
To find the force in rod (1)
directly, you would most use
Torsion Problems 13
1. The deflection at C
2. The deflection at A
3. The deflection at B
4. Dont Know
Torsion Problems 14
The rigid bar shown in Figure 2 is supported by the pin at A and the rod from B
to D (1). The rod (1) has a cross sectional area of 500 mm
2
, an elastic modulus
of E = 80 GPa, and a coefficient of thermal expansion of
a= 22x10
-6
/C. Initially the bar ABC is in a horizontal position, then the
temperature of the rod (1) is reduced by 40C. What magnitude would P have to
be to return the rod to a horizontal orientation after the temperature is reduced?
( )( )
( )
( )( )
( )
1
35.2 1.75
20.53
3.0
AB
AC
F L kN m
P kN
L m
! !
= = =
14 January 2011
8
Torsion Problems 15
Two cylindrical rods, one of steel and the other of brass, are joined at C and
restrained by rigid supports at A and E. E
STEEL
= 200 GPa and E
BRASS
= 105
GPa.
What is the magnitude of the support reaction at point A?
Torsion Problems 16
Two cylindrical rods, one of steel and the other of brass, are joined at C and
restrained by rigid supports at A and E. E
STEEL
= 200 GPa and E
BRASS
= 105
GPa.
What is the magnitude of the support reaction at point
E?
37 60 40 60 40 62 .19 .81
E A
R kN kN R kN kN kN kN = + ! = + ! =
14 January 2011
9
Torsion Problems 17
Two cylindrical rods, one of steel and the other of brass, are joined at C and
restrained by rigid supports at A and E. E
STEEL
= 200 GPa and E
BRASS
= 105
GPa.
What is the deflection of point C?
Torsion Problems 18
Two cylindrical rods, one of steel and the other of brass, are joined at C and
restrained by rigid supports at A and E. E
STEEL
= 200 GPa and E
BRASS
= 105
GPa.
What is the stress in the Steel rod in the section
between points A and B?
2
62.81
49.98
1257
AB
AB
Steel
F kN
MPa
A mm
! = = =
14 January 2011
10
Torsion Problems 19
Two cylindrical rods, one of steel and the other of brass, are joined at C and
restrained by rigid supports at A and E. E
STEEL
= 200 GPa and E
BRASS
= 105
GPa.
What is the stress in the Brass rod in the section
between points D and E?
2
37.19
52.62
706.86
DE
DE
Brass
F kN
MPa
A mm
! = " = " = "
Torsion Problems 20
The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires of 1/16 -in. diameter (E =
29x10
6
psi) and a pin at D. The bar is horizontal before the load P is applied.
The load P has a magnitude of 120-lb. After P is applied
What is the tension in the wire from A to E?
14 January 2011
11
The relationship between the
deflections at A and C is
Torsion Problems 21
1. !
EA
>!
FC
2. !
EA
=!
FC
3. !
EA
>!
FC
4. Dont Know
The relationship between the
deflections at A and C is
Torsion Problems 22
1. !
EA
>!
FC
2. !
EA
=!
FC
3. !
EA
>!
FC
4. Dont Know
14 January 2011
12
Torsion Problems 23
The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires of 1/16 -in. diameter (E =
29x10
6
psi) and a pin at D. The bar is horizontal before the load P is applied.
The load P has a magnitude of 120-lb. After P is applied
What is the tension in the wire from A to E?
( )( ) ( )( ) ( )
5
8
5
16 120 24 8
8
66.21
CF AE
AE AE
AE
F F
in lb in F in F
F lb
=
! "
= +
# $
% &
=
Torsion Problems 24
The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires of 1/16 -in. diameter (E =
29x10
6
psi) and a pin at D. The bar is horizontal before the load P is applied.
The load P has a magnitude of 120-lb. After P is applied
What is the tension in the wire from C to F?
66.21
5 5
66.21 41.38
8 8
AE
CF AE
F lb
F F lb lb
=
= = =
14 January 2011
13
Torsion Problems 25
The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires of 1/16 -in. diameter (E =
29x10
6
psi) and a pin at D. The bar is horizontal before the load P is applied.
The load P has a magnitude of 120-lb. After P is applied
What is the strain in the wire from A to E?
( )( )
( )( )
3 2 6
66.21 15
0.11
3.07 10 29 10
0.11
0.0067 /
15
AE AE
AE
AE
AE
AE
lb in F L
in
AE in psi
in
in in
L in
!
!
"
#
= = =
$ $
= = =
Torsion Problems 26
The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires of 1/16 -in. diameter (E =
29x10
6
psi) and a pin at D. The bar is horizontal before the load P is applied.
The load P has a magnitude of 120-lb. After P is applied
What is the deflection of point B from the original unloaded horizontal position?
( )
( )
( )
16
0.11 0.073
24
B AE
in
BD
in in
AD in
! ! = = =
14 January 2011
14
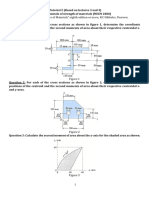
Problem 6.4
Torsion Problems 27
Problem 6.12
Torsion Problems 28
14 January 2011
15
Problem 6.16
Torsion Problems 29
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Torsion ProblemsDocument15 pagesTorsion ProblemsPrima Syahri RamadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Me218 Fa15 W3 HoDocument10 pagesMe218 Fa15 W3 HonhiuPas encore d'évaluation
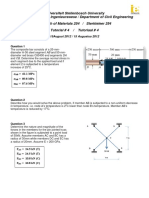
- Tutorial 2 2020Document5 pagesTutorial 2 2020AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2 Solid Mechanics PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 Solid Mechanics PDFSamiha Maysoon NooriaPas encore d'évaluation
- HW01 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHW01 SolutionsLoong Cheng NingPas encore d'évaluation
- Final April 26 10Document2 pagesFinal April 26 10Tee YeesiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Tension, Compression, and Shear: Normal Stress and StrainDocument31 pagesTension, Compression, and Shear: Normal Stress and Strainmelkis_darkPas encore d'évaluation
- LE1 Problem Set PDFDocument14 pagesLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapPas encore d'évaluation
- Axial LoadingDocument4 pagesAxial LoadingAnonymous mXicTi8hBPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 2Document5 pages1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 2onenoteforlocadPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set: Strain and Thermal StressesDocument5 pagesProblem Set: Strain and Thermal StressesClint Charles P. BrutasPas encore d'évaluation
- Statically Indeterminate Members (Axially Loaded Only: F F FyDocument11 pagesStatically Indeterminate Members (Axially Loaded Only: F F FyHafiz NordinPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Exam 2: E.S. 13 - Mechanics of Deformable Bodies I 2 Semester, A.Y. 2010-2011Document2 pagesLong Exam 2: E.S. 13 - Mechanics of Deformable Bodies I 2 Semester, A.Y. 2010-2011Junhong BapPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple StrainDocument36 pagesSimple StrainMartina CelsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1jermainpeart4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2anonymouschePas encore d'évaluation
- 06 ES13 Axially Loaded MembersDocument22 pages06 ES13 Axially Loaded MembersMich Angeles100% (1)
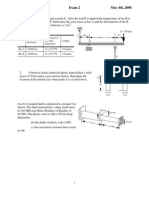
- EM 440 Exam 2 May 4th, 2000: P 20 KipsDocument2 pagesEM 440 Exam 2 May 4th, 2000: P 20 KipsRayleight SilversPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsDocument3 pagesSheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsAhmed AlaaPas encore d'évaluation
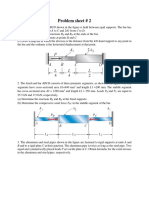
- Problem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarDocument7 pagesProblem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarYatharth KhicharPas encore d'évaluation
- AXIALLY LOADED MEMBER: Statically Determinate: (Note: You Can Only Have Displacement/s at Axis/axes With No Support)Document4 pagesAXIALLY LOADED MEMBER: Statically Determinate: (Note: You Can Only Have Displacement/s at Axis/axes With No Support)Marsha Fatima PascualPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 03Document2 pagesHW 03Andy BayuPas encore d'évaluation
- MEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial QuestionsDocument7 pagesMEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial Questionsha haPas encore d'évaluation
- JC Physics Semestral Assessment QuestionsDocument25 pagesJC Physics Semestral Assessment QuestionsLelouch1337Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mec32 HW3Document4 pagesMec32 HW3Isabelle LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tut4 PDFDocument3 pagesTut4 PDFGregorPas encore d'évaluation
- تقريرخرسانهDocument4 pagesتقريرخرسانهmohammedyarub1998Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios en Clase Deformaciones PDFDocument3 pagesEjercicios en Clase Deformaciones PDFOscar LeonardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce-221 Solid Mechanics End-Sem Exam 07/11/16 Paper Code: DDocument7 pagesCe-221 Solid Mechanics End-Sem Exam 07/11/16 Paper Code: DAshutosh AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Problems & SolutionsDocument41 pagesMechanics Problems & Solutionsdjhazard100% (2)
- Tutorial 2 Chapter 2: Axial Load: (Ans 73.7 Gpa)Document12 pagesTutorial 2 Chapter 2: Axial Load: (Ans 73.7 Gpa)ha haPas encore d'évaluation
- Es 13 Thy Prob Set 1 I. Stresses: Max MaxDocument5 pagesEs 13 Thy Prob Set 1 I. Stresses: Max MaxMichael Sean DeangPas encore d'évaluation
- Tsu m18 Practice Problems Smat1Document2 pagesTsu m18 Practice Problems Smat1Mark Lester ValdozPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGN 36 HomeworkDocument50 pagesENGN 36 Homework082292fer67% (3)
- Physics IJSO Stage-1Document14 pagesPhysics IJSO Stage-1Sonal Gupta83% (12)
- 02-01 Chap GereDocument17 pages02-01 Chap GereTortelliniTimPas encore d'évaluation
- PEC ERyRM I PDFDocument11 pagesPEC ERyRM I PDFAlejandro serrano pozoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 ENGG317 Assignment2Document2 pages2015 ENGG317 Assignment2Anonymous xUb9GnoFPas encore d'évaluation
- Axial Load 2022Document48 pagesAxial Load 2022Feriawan HambalangPas encore d'évaluation
- TLA3 (CO1) : Word Problem Set - Topic 2A, 2B, and 2CDocument1 pageTLA3 (CO1) : Word Problem Set - Topic 2A, 2B, and 2CPeter Adrian NgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Mechanics Assigment 1Document2 pagesSolid Mechanics Assigment 1DALOJr.0% (1)
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Nguyen Trong SonPas encore d'évaluation
- CH-3 Equilibrium ExamplesDocument30 pagesCH-3 Equilibrium ExamplesHaftamu HilufPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsDocument6 pages2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsMartin MugoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 3 2003 ProblemsDocument9 pagesExam 3 2003 ProblemsNURI ONUR CATAKPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2.1 Analysis of Strain - Concepts and Definitions-2 - CE 205-CE22S2 - Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument12 pagesModule 2.1 Analysis of Strain - Concepts and Definitions-2 - CE 205-CE22S2 - Mechanics of Deformable BodiesRUSSELPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems On StrainDocument16 pagesProblems On StrainRalph Evidente33% (3)
- Determine average stresses and strains in beams, rods, wires and other structural elementsDocument17 pagesDetermine average stresses and strains in beams, rods, wires and other structural elementsLam TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises in Chapter 3Document40 pagesExercises in Chapter 3Lam TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Score 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerDocument5 pagesScore 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerChristian M. MortelPas encore d'évaluation
- AEAS 205 Lecture 2 - Axial LoadingDocument73 pagesAEAS 205 Lecture 2 - Axial LoadingSamiha Maysoon NooriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Statically Indeterminate Structures & Thermal StressesDocument24 pagesStatically Indeterminate Structures & Thermal StressesBuddy SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsYan NiePas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5A SкPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages4 41 To 52 PDFDocument12 pagesPages4 41 To 52 PDFIsmael de PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesD'EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisD'EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisPas encore d'évaluation
- See Catalog: Get A QuoteDocument4 pagesSee Catalog: Get A QuoteahnafPas encore d'évaluation
- General Guidelines For Design and Construction of Concrete Diaphram (Slurry) WallsDocument108 pagesGeneral Guidelines For Design and Construction of Concrete Diaphram (Slurry) WallsharleyPas encore d'évaluation
- SPECIFIC GRAVITY - DENSITY OF HYDRAULIC CEMENT (IS - 4031-Part 11-1988)Document6 pagesSPECIFIC GRAVITY - DENSITY OF HYDRAULIC CEMENT (IS - 4031-Part 11-1988)Pritha DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Information for 2x660 MW Lube Oil PumpsDocument93 pagesProject Information for 2x660 MW Lube Oil PumpsghostamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Rizal's Allegorical Play 'El Consejo de Los DiosesDocument9 pagesRizal's Allegorical Play 'El Consejo de Los DiosesAlexiahree ChaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Transaxle PDFDocument50 pagesAutomatic Transaxle PDFdemos70100% (1)
- St. John of The Cross - UnknownDocument19 pagesSt. John of The Cross - UnknownthepillquillPas encore d'évaluation
- Convection: Example 3.1Document5 pagesConvection: Example 3.1MChobind RivaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Focus Shooting Method CourseDocument48 pagesThe Focus Shooting Method CourseKobiXDPas encore d'évaluation
- Mic ProjectDocument12 pagesMic Projectsarthakjoshi012Pas encore d'évaluation
- Matlab For SolidworksDocument18 pagesMatlab For SolidworksAle' AmoudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hufenus 2006 Geotextiles GeomembranesDocument18 pagesHufenus 2006 Geotextiles Geomembranesbkollarou9632Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experimental Design and Optimization MethodsDocument38 pagesExperimental Design and Optimization MethodssudalaiyandiPas encore d'évaluation
- HTTP Verbs GET POST PUT PATCH DELETE (39Document12 pagesHTTP Verbs GET POST PUT PATCH DELETE (39Jefferson EducacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Canadian Wood Council Publications and Tools For Wood Design Robertson RocchiDocument62 pagesCanadian Wood Council Publications and Tools For Wood Design Robertson RocchiDj MacPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual de Uso Ecografo GE Logiq e PDFDocument192 pagesManual de Uso Ecografo GE Logiq e PDFDaniel CortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Shri Durga Chalisa 1Document25 pagesShri Durga Chalisa 1gsameeriitdPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Flight Recorder - OcrDocument19 pages5 - Flight Recorder - OcrtmhoangvnaPas encore d'évaluation
- STP Manual Final PDFDocument862 pagesSTP Manual Final PDFrudiPas encore d'évaluation
- WIP CaseStudyDocument3 pagesWIP CaseStudypaul porrasPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes Short Notes PDFDocument2 pagesSTPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes Short Notes PDFbendanPas encore d'évaluation
- Meditations on Ancient Astrology Principles from Brihat Parashari HorāDocument87 pagesMeditations on Ancient Astrology Principles from Brihat Parashari HorāPrasanna KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB Price Book 714Document1 pageABB Price Book 714EliasPas encore d'évaluation
- 0580 w15 QP 42Document16 pages0580 w15 QP 42Shahrizan Noor100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Design and Drawing FundamentalsDocument11 pagesHeat Exchanger Design and Drawing Fundamentalsjeevanantham 5846Pas encore d'évaluation
- PENERAPAN ARSITEKTUR TROPIS PADA HOTEL RESORT DI PANTAI KRAKALDocument12 pagesPENERAPAN ARSITEKTUR TROPIS PADA HOTEL RESORT DI PANTAI KRAKALleo adoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ammonia Tech Manual 2002Document28 pagesAmmonia Tech Manual 2002Talha Bin Zubair0% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise 2 Mole-Mole Mass-Mass: Sorsogon State CollegeDocument2 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise 2 Mole-Mole Mass-Mass: Sorsogon State CollegeJhon dave SurbanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 5-in-1 Document Provides Lessons on Trees and Environmental ConservationDocument45 pages5-in-1 Document Provides Lessons on Trees and Environmental ConservationPriya DharshiniPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Scoring Materials Math g6Document119 pages2017 Scoring Materials Math g6KRAPas encore d'évaluation