Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
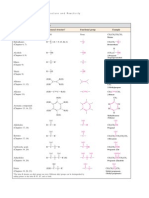
Types of Acids and Bases
Transféré par
Jadie Barringer III0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
99 vues3 pagesOverview of acids and bases for MCAT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentOverview of acids and bases for MCAT
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
99 vues3 pagesTypes of Acids and Bases
Transféré par
Jadie Barringer IIIOverview of acids and bases for MCAT
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
1
Acids & Bases
An acid is any chemical that will
react with a base
There are 3 types of acids and
bases that we commonly identify:
o Arrhenius acids & bases
o Brnsted-Lowry acids &
bases
o Lewis acids & bases
Arrhenius acids dissociate in
solution to yield H
+
ions
o i.e. HCl
Arrhenius bases dissociate in
solution to yield OH
-
ions
o i.e. NaOH
Arrhenius Acids and Bases
Arrhenius acids, like HCl, form H
+
ions in
solution. Arrhenius bases, like NaOH, form OH
-
ions in solution.
During our studies of acids and
bases, we will come across the
hydronium ion: H
3
O
+
o When you see it, treat it
as a H
+
ion
Also, a H
+
ion is a hydrogen
atom thats lost its only electron
o That leaves behind just a
proton, and so H
+
ions are
commonly called protons
Brnsted-Lowry acids donate H
+
ions; they are proton donors
Brnsted-Lowry bases accept H
+
ions; they are proton acceptors
In a reaction between HCl and
NaHCO
3
, the HCl donates a
proton to NaHCO
3
o This makes HCl a
Brnsted-Lowry acid and
NaHCO
3
a Brnsted-
Lowry base
Brnsted-Lowry Acid/Base Reaction
In a reaction between HCl and NaHCO
3
, HCl
acts as a proton donor and NaHCO
3
acts as a
proton acceptor. This makes HCl a Brnsted-
Lowry acid and NaHCO
3
a Brnsted-Lowry
base.
From the above illustration,
notice that HCl yields H+ ions in
solution
o So, in addition to being a
Brnsted-Lowry acid, its
also an Arrhenius acid
But also notice that NaHCO
3
does not yield OH
-
ions in
solution
o So it is not an Arrhenius
base
Lewis acids are electron
acceptors
Lewis bases are electron donors
As a mnemonic, recall that Lewis
deals with electrons
Again consider the reaction
between HCl and NaHCO
3
o Notice that NaHCO
3
acts
as an electron donor,
making it a Lewis base
o And, HCl acts as an
electron acceptor, making
it a Lewis acid
Types of Acids and Bases | MCAT
J Co Review, Inc., Accessed by jadie2@mac.com on 06-01-2014
2
Lewis Acid/Base Reaction
In the reaction between HCl and NaHCO
3
,
sodium bicarbonate acts as an electron donor,
making it a Lewis base. HCl, the recipient of
those electrons, is an electron acceptor, making it
a Lewis acid.
All Arrhenius acids/bases are
Brnsted-Lowry acids/bases
And, all Brnsted-Lowry
acids/bases are Lewis acids/bases
Acid/Base Type Overlap
All Arrhenius acids/bases are Brnsted-Lowry
acids/base, which are all Lewis acids/bases.
Conjugate Pairs
Again take a look at the reaction
between HCl and NaHCO
3
Reaction between HCl and NaHCO
3
An acid- HCl- reacts with a base-
NaHCO
3
-
If the reaction is run in reverse,
notice that H
2
CO
3
would act as
an acid by donating a proton to
NaCl
o This makes H
2
CO
3
an
acid and NaCl a base
So during the acid/base reaction,
our acid becomes a base, and our
base becomes an acid
o When an acid reacts, we
say that it becomes its
conjugate base
o Likewise, when a base
reacts, it becomes its
conjugate acid
Together, an acid and its
conjugate base are known as a
conjugate pair
Conjugate Pairs
When HCl reacts, it becomes its conjugate base-
NaCl. When NaHCO
3
reacts, it becomes its
conjugate acid- H
2
CO
3
.
In general, conjugate acids and
bases differ by just a H
+
But then why are HCl & NaCl
conjugates? They differ by more
than a H
+
o In solution, positively
charged ions like Na
+
and
K
+
rapidly dissociate, so
in actuality, that NaCl
would quickly become a
Cl
-
Once you recognize that NaCl
dissociates, its easy to see that
HCl and Cl
-
differ by only a H
+
ion, making them conjugates
Conjugate Acid/Base Strengths
Strong acids have weak
conjugate bases, and vice versa
o After all, a strong acid
really wants to donate its
hydrogen
Types of Acids and Bases | MCAT
J Co Review, Inc., Accessed by jadie2@mac.com on 06-01-2014
3
o Once the H
+
is donated,
the molecule wont want
the H
+
back
Itll be a poor
hydrogen
acceptor, making
it a weak base
Acid/Base Conjugate Strengths
A strong acid will have a weak conjugate base,
and vice versa.
Look back at our reaction
between HCl and NaHCO
3
o Notice that NaHCO
3
is a
weak base, meaning that
its conjugate acid will be
strong
Acid/Base Conjugate Strengths
NaHCO
3
is a weak base, and so its conjugate
acid, H
2
CO
3
, must be strong.
Its no surprise that H
2
CO
3
is a
strong acid
o After all, it has 2 protons
to donate
Amphoteric Substances
Amphoteric substances are
capable of acting as acids or
bases, depending upon their
environment
In a highly basic environment,
water is acidic relative to its
environment
o It will be capable of
donating a proton,
becoming OH
-
In a highly acidic environment,
water will be basic relative to its
environment
o It will be capable of
accepting a proton,
becoming H
3
O
+
o
Types of Acids and Bases | MCAT
J Co Review, Inc., Accessed by jadie2@mac.com on 06-01-2014
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- DAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield DAT General Chemistry QuestionsD'EverandDAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield DAT General Chemistry QuestionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsD'EverandSterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Gen Chem NotesDocument8 pagesMCAT Gen Chem NotesViviana PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Biochemistry I NotesDocument3 pagesMCAT Biochemistry I NotesTaylor JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Test PDFDocument53 pagesTest PDFKarina SandersPas encore d'évaluation
- Mcat Questions TestDocument14 pagesMcat Questions TestBrandon DeveaultPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryDocument25 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryLora100% (1)
- Functional GroupsDocument2 pagesFunctional GroupsshostevePas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Physics ReviewDocument57 pagesMCAT Physics ReviewrinieroxPas encore d'évaluation
- EK Schedule - 4 MonthDocument14 pagesEK Schedule - 4 MonthLauraAlexandraPas encore d'évaluation
- E2 Mechanism and Examples: BY - Tejaswini B.VDocument9 pagesE2 Mechanism and Examples: BY - Tejaswini B.VTejaswini ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Chemistry ReviewDocument9 pagesMCAT Chemistry ReviewStellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Mcat 3: Ken Evans, MSC, MD Charlene Bramwell, MedDocument47 pagesPractice Mcat 3: Ken Evans, MSC, MD Charlene Bramwell, MedNaomi RyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical NotesDocument25 pagesAnalytical NotesRyan BoodramlallPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT PrepDocument1 pageMCAT Prepherbertgur777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Leah4Sci OrgChem Cheat Sheet PDFDocument32 pagesLeah4Sci OrgChem Cheat Sheet PDFhPas encore d'évaluation
- Master AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsDocument30 pagesMaster AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsSukhvir AujlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Backwards ReasoningDocument40 pagesBackwards Reasoningharshit chaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Arterial Blood GasDocument55 pagesArterial Blood GasRathis Dasan100% (1)
- Chemical Foundations of Biological SystemsDocument30 pagesChemical Foundations of Biological SystemsKarla PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemPhysics MCAT NotesDocument14 pagesChemPhysics MCAT NotesChris HuebnerPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Physics Equations SheetDocument4 pagesMCAT Physics Equations SheetAshley ShanaéPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation Review - MathDocument24 pagesFoundation Review - MathThe LightPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT 2014 Biology Portion Answer Key: WhiteDocument14 pagesMCAT 2014 Biology Portion Answer Key: WhiteMuhammad ShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Organic Chemistry ReviewDocument43 pagesMCAT Organic Chemistry ReviewVetina LirioPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Test For AkuDocument12 pagesMCAT Test For AkuKamran ParvezPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Review SilberbergDocument26 pagesMCAT Review SilberbergGuy La100% (1)
- Electrochemistry - A Branch of Chemistry That Deals With The Exploitation of Spontaneous OxidationDocument17 pagesElectrochemistry - A Branch of Chemistry That Deals With The Exploitation of Spontaneous OxidationWaraeyPas encore d'évaluation
- EK 101 Test 6 Passages 1-4Document15 pagesEK 101 Test 6 Passages 1-4AyodejiES1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System and Development W. SolutionsDocument12 pagesReproductive System and Development W. SolutionsFrank RaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- 1e Aldehyde & KetoneDocument48 pages1e Aldehyde & KetoneJonathan Wyatt100% (1)
- MCAT ReviewDocument162 pagesMCAT ReviewYukiC123Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Physics Reference NotesDocument16 pagesMCAT Physics Reference NotesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Mcat Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesMcat Organic Chemistryhussai7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology and Behaviour: Unit 1 Semester 2 BA PsychologyDocument21 pagesBiology and Behaviour: Unit 1 Semester 2 BA PsychologyAteesh SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer SolutionDocument14 pagesBuffer SolutionSony0% (1)
- Confusing MCQS in MCAT Preparation BioDocument7 pagesConfusing MCQS in MCAT Preparation BioMuhammad Ajmal Malik50% (2)
- General Chemistry Discretes Test W. SolutionsDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry Discretes Test W. SolutionsCodie SimoneauxPas encore d'évaluation
- The Berkeley Review: MCAT Chemistry Atomic Theory PracticeDocument37 pagesThe Berkeley Review: MCAT Chemistry Atomic Theory Practicerenjade1516Pas encore d'évaluation
- DAT QuizletDocument78 pagesDAT QuizletJihee YoonPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Lab TechniquesDocument18 pagesMCAT Lab TechniquesJames Huynh100% (1)
- Electron Delocalization, Resonance Structures Orbital Theory PDFDocument4 pagesElectron Delocalization, Resonance Structures Orbital Theory PDFbencleesePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrochemistry 494 PDFDocument55 pagesElectrochemistry 494 PDFHarsh SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Practice PsDocument4 pagesMCAT Practice PsStephen CampbellPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology OutlinesDocument21 pagesBiology OutlinesKyle Broflovski100% (1)
- Jack Westin MCAT Content Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content Organic ChemistryLoraPas encore d'évaluation
- OChem MasterDocument6 pagesOChem MasterDelixae PhoinixPas encore d'évaluation
- Nomenclature of Chemical Compounds: Inorganic ChemistryDocument1 pageNomenclature of Chemical Compounds: Inorganic ChemistrybasimPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Hormones SummaryDocument1 pageMCAT Hormones Summaryrvar839Pas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry MCAT - 1Document63 pagesGeneral Chemistry MCAT - 1pparik10100% (2)
- Orgo Cheat Sheets 08 2019 PDFDocument34 pagesOrgo Cheat Sheets 08 2019 PDFKobe AcobPas encore d'évaluation
- McatDocument50 pagesMcatbebbuwebbuPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling Test Prep DAT General Chemistry Review: Complete Subject ReviewD'EverandSterling Test Prep DAT General Chemistry Review: Complete Subject ReviewPas encore d'évaluation
- OAT General Chemistry Review: Complete Subject ReviewD'EverandOAT General Chemistry Review: Complete Subject ReviewPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling Test Prep OAT Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT Organic Chemistry QuestionsD'EverandSterling Test Prep OAT Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT Organic Chemistry QuestionsPas encore d'évaluation
- PHARMACY COLLEGE ADMISSION TEST (PCAT): Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandPHARMACY COLLEGE ADMISSION TEST (PCAT): Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- GRE Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield GRE Chemistry Questions with Detailed ExplanationsD'EverandGRE Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield GRE Chemistry Questions with Detailed ExplanationsPas encore d'évaluation
- GRE Chemistry: Inorganic Chemistry Review for GRE Chemistry Subject TestD'EverandGRE Chemistry: Inorganic Chemistry Review for GRE Chemistry Subject TestPas encore d'évaluation
- Interest Groups Collective Action, Power, and RepresentationDocument27 pagesInterest Groups Collective Action, Power, and RepresentationJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- The Media: New Technologies, Enduring LessonsDocument29 pagesThe Media: New Technologies, Enduring LessonsJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- PluribusDocument4 pagesPluribusJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Cherokee 140 B ChecklistDocument7 pagesCherokee 140 B ChecklistJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Brutus XV, New York Journal, 20 March 1788Document5 pagesBrutus XV, New York Journal, 20 March 1788Jadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- The Federal Judiciary Politics, Power, and The "Least Dangerous" BranchDocument18 pagesThe Federal Judiciary Politics, Power, and The "Least Dangerous" BranchJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Commercial Pilot SyllabusDocument12 pagesCommercial Pilot SyllabusJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Read An OpinionDocument16 pagesHow To Read An OpinionCC8527563Pas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Physiology All and Complete PDFDocument86 pagesRespiratory Physiology All and Complete PDFSikandar LodhiPas encore d'évaluation
- US Army Medical Course MD0577-100 - The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument49 pagesUS Army Medical Course MD0577-100 - The Musculoskeletal SystemGeorgesPas encore d'évaluation
- Faa-Ct-8080-3 IfrDocument209 pagesFaa-Ct-8080-3 Ifrpapa_danny100% (2)
- US Army Medical The Central Nervous SystemDocument123 pagesUS Army Medical The Central Nervous SystemSpace_Hulker100% (2)
- The Federalist 67, New York Packet, 11 March 1788Document4 pagesThe Federalist 67, New York Packet, 11 March 1788Jadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- US Army Medical The Central Nervous SystemDocument123 pagesUS Army Medical The Central Nervous SystemSpace_Hulker100% (2)
- Atlas of Emergency Medicine Procedures 1st Ed 2016 Edition UnitedVRG PDFDocument718 pagesAtlas of Emergency Medicine Procedures 1st Ed 2016 Edition UnitedVRG PDFJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- US Army Medical Course MD0575-100 - Integumentary SystemDocument97 pagesUS Army Medical Course MD0575-100 - Integumentary SystemGeorgesPas encore d'évaluation
- US Army Medical Course MD0564-200 - Blood, Electrolytes, and Intravenous InfusionsDocument80 pagesUS Army Medical Course MD0564-200 - Blood, Electrolytes, and Intravenous InfusionsGeorgesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 StdraftppcluesDocument16 pages1 Stdraftppcluesvp6148Pas encore d'évaluation
- Swift Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSwift Cheat SheetJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- US Army Medical Course MD0575100 Integumentary SystemDocument97 pagesUS Army Medical Course MD0575100 Integumentary SystemJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Airway Management: Leaugeay Webre, BS, CCEMT-P, Nremt-PDocument35 pagesAdvanced Airway Management: Leaugeay Webre, BS, CCEMT-P, Nremt-Pbasic100% (4)
- Paramedic NREMTDocument88 pagesParamedic NREMTJadie Barringer III100% (2)
- S1 2014 P1 Set 3 Questions PDFDocument5 pagesS1 2014 P1 Set 3 Questions PDFNancy MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- What America's Gun Fanatics Won't Tell You - MarketWatchDocument10 pagesWhat America's Gun Fanatics Won't Tell You - MarketWatchJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbal Reasoning Test12 SolutionsDocument2 pagesVerbal Reasoning Test12 SolutionsJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbal - Reasoning Test13 Solutions PDFDocument21 pagesVerbal - Reasoning Test13 Solutions PDFJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Before Back N PDFDocument5 pagesPDF Before Back N PDFJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Algo Postarrest PDFDocument1 pageAlgo Postarrest PDFdewita wahyu kemalasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Neuroanatomy and Stroke Syndromes PDFDocument15 pagesBasic Neuroanatomy and Stroke Syndromes PDFFrancisco A. Villegas-López100% (2)
- Interpretation: Compensated and Uncompensated Blood Gas AnalysisDocument30 pagesInterpretation: Compensated and Uncompensated Blood Gas AnalysisJadie Barringer IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Effect:: General Organic Chemistry-IDocument15 pagesElectronic Effect:: General Organic Chemistry-IKrishna SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter # 12Document82 pagesChapter # 12Kamil Rasheed SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Blade Calculations For Water Turbines of The Banki Type: Citation For Published Version (APA)Document24 pagesBlade Calculations For Water Turbines of The Banki Type: Citation For Published Version (APA)Anonymous Hy5Ir9QXPas encore d'évaluation
- LAB 5 VibrationDocument6 pagesLAB 5 Vibrationmohdiqbal930% (1)
- Semiconductor Laser Experiment Lab ReportDocument11 pagesSemiconductor Laser Experiment Lab ReportSeema ChahalPas encore d'évaluation
- Effective ApertureDocument10 pagesEffective ApertureLeo HambirepiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fowles, Grant R. - Introduction To Modern Optics-Dover Publications (1975)Document349 pagesFowles, Grant R. - Introduction To Modern Optics-Dover Publications (1975)Elias BojagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Postlab Protein ConcnDocument25 pagesPostlab Protein ConcnMarie Elexis P. RevillezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 6-7 ElectrostaticsDocument10 pagesClass 6-7 ElectrostaticsChandraKiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Generator ProtectionDocument5 pagesGenerator ProtectionThirumalPas encore d'évaluation
- Organometallic CompoundsDocument40 pagesOrganometallic CompoundsDezta Fandity' VantycaPas encore d'évaluation
- CE 407 Final ExamDocument2 pagesCE 407 Final ExamSteve BariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus For Eee 801Document3 pagesSyllabus For Eee 801Eze UkiwePas encore d'évaluation
- Proton 200 220 WebDocument2 pagesProton 200 220 WebLUIS CORDOVA ZANCHESPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 1 PDFNama Desalew100% (1)
- Mohr CircleDocument5 pagesMohr CircleSteeve JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Sciences Baseline Test Gr11Document7 pagesPhysical Sciences Baseline Test Gr11Midyondzi ngobeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Friday 15 May 2020: PhysicsDocument28 pagesFriday 15 May 2020: PhysicsAyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Propagation and Dispersion Characteristics in Anisotropic MediumDocument15 pagesWave Propagation and Dispersion Characteristics in Anisotropic MediumqwerrfsPas encore d'évaluation
- ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Mixing Elbow PDFDocument13 pagesANSYS Fluent Tutorial Mixing Elbow PDFShangkaran RadakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Venturi, Orifice, RotameterDocument34 pagesVenturi, Orifice, RotameterVinod VadithyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves and Sound Waves PDFDocument11 pagesWaves and Sound Waves PDFSanatan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Et M Zulassungspruefung PDFDocument5 pagesEt M Zulassungspruefung PDFmuhammad bilalPas encore d'évaluation
- TorsionDocument17 pagesTorsionkalpanaadhi100% (1)
- A Is Shear Stress Momentum FluxDocument21 pagesA Is Shear Stress Momentum FluxPamela MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acids, Bases and BuffersDocument29 pagesAcids, Bases and BuffersTayba KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics: MarkschemeDocument42 pagesKinematics: MarkschemePremium DongPas encore d'évaluation
- Bearing Dynamic Static Load Carrying Capacity PDFDocument11 pagesBearing Dynamic Static Load Carrying Capacity PDFmanimeczPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Balance For Nonreactive Processes-P1Document12 pagesEnergy Balance For Nonreactive Processes-P1Aby JatPas encore d'évaluation