Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 1
Transféré par
Hamood AhmadCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Assignment 1
Transféré par
Hamood AhmadDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Separation Lab
Assignment No: 1
Assignment Topic: Steam Generation, Boiler and Steam traps.
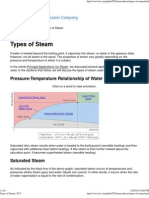
Steam:
1. Definition:
When water is heated it gets converted into vapors. These vapors create a white mist of water droplets in
air, and are called as steam.
Steam is being used widely in process industries and in power generation units as a source of heat as
well as energy source for running turbines. In addition to it, steam is also being employed in the
manufacturing of some chemical products in chemical industries. For example, in ammonia (NH
3
)
manufacturing, steam is used as one of the raw materials.
2. Properties:
When water is heated at atmospheric pressure it starts boiling at 100
o
C. The heat transferred to
water which increases its temperature up to its boiling point is known as sensible heat. When further
heated, the heat provided is utilized in changing the water into its vapor form and no increase in
temperature takes place. This heat provide is not visible and is thus named latent heat.
At high pressure water boils at higher temperatures. For instance, at 1000 kPa, water boils at 187
o
C.
Therefore, at increased pressure conditions, greater amount of sensible heat is required for boiling water.
Hence, steam generated at high pressure stores greater energy than the steam heated at atmospheric
pressure.
Steam carries energy in the form of heat as well as in its ability to do work, which it performs during
increase in its volume, as in case of steam turbines. This energy carrying ability of steam makes it a very
important heat and energy carrier in modern industries.
3. Steam Types:
Steam is generally classified in two types:
a) Saturated Steam
Steam which condenses readily as soon as it transfers heat is named as saturated steam.
When water in a closed container is heated, it starts boiling as soon as its boiling point temperature
is reached. With further addition of heat, no increase in temperature is detected and the heat added is
utilized in the phase change process. If we continue heating, a point comes when even the last drop of water
is vaporized. Steam which is present at this point is named as saturated steam. This steam, as soon as it
transfers some of its heat content, changes into liquid water.
b) Superheated Steam:
Steam which at given pressure is well above its saturation temperature is termed as superheated
steam.
When saturated steam in a system is further heated, the heat entering increases the temperature of
the saturated steam. This type of steam has the ability of transferring heat energy without condensing to
liquid phase. Superheated steam is used in power generation units for running/rotating the turbine due to
its ability to do work during expansion.
4. Uses of Steam:
In modern industries steam is being utilized as an indirect medium for transferring heat to the
process taking place or for space heating purposes. Steam is being used for sterilizing equipment and also for
humidification. The use of steam as a heating medium is favored because it can be controlled easily, also the
rate of heat transfer for steam as heating medium is high even at relatively low temperatures.
Use of steam is common in following processes:
Food processing
Beverage production
Brewing
Pharmaceutical processes
Petro-chemical processes.
In the above mentioned applications of steam, it only transfers heat while being contained in a heat
exchanger and direct contact of steam and product being heated does not takes place. While during
sterilization, steam comes in direct contact with the product to be heated. Steam is being used in modern
buildings for maintaining the humidity of air.
Steam Traps:
Definition:
A steam trap is a liquid-vapor separator, which is used for separating steam from the steam condensate formed
while latent heat of vaporization is transferred from steam to the system.
Working Principle:
A simple steam trap is constructed such that it has a small opening at the bottom of a disc or pipe which
allows the flow of steam condensate but prevents the flow of steam through it because of greater volume occupied
by steam.
Types:
Majorly three types of steam traps are present, which are classified on the basis of the mechanism by which
they operate.
1. Thermostatic Traps: Such steam traps are based on the principles of thermal expansion of materials when
heat is supplied to them and similarly the contraction of materials as soon as their temperature decreases. A
valve which is turned off/on based on the thermal expansion/contraction is used to control the flow of
steam.
Examples of thermostatic traps are
2. Mechanical Traps: These functioning of such traps is based on the difference in the density of the steam and
its condensate.
3. Kinetic Traps: The flow characteristics of steam and its condensate are used as a function in operating this
type of traps.
Mechanical Traps:
Mechanical Steam Trap as understood by the name consists of a mechanical apparatus which separates
steam from steam condensate using a float or an open bucket which is in connection with a valve using which we
regulate the discharge.
Examples:
Float Traps
Bucket Traps
Thermostatic Traps:
In thermostatic trap steam and steam condensate are differentiated on the basis of temperature difference
between the steam and condensate. As soon as the temperature of the condensate decreases than that of steam,
the stopping element contracts and allow it to pass. In such types of steam traps, condensate must be stopped for an
interval of time so that its temperature decreases than that of steam.
Examples:
Balanced pressure design
Bimetallic steam trap
Thermodynamic Steam Trap:
Such type of traps consist of a disc, which is controlled (i.e., rises and falls) due to the pressure changes
caused due to condensate formation.
Materi
al of
Constru
ction:
Industrial Application:
The use of steam traps helps in preventing of water hammering which may occur due to excess formation of
condensate
Steam traps are also used to save the system parts from erosion which is caused due to high velocity water
generated.
They also help in preventing corrosion.
They help in improving the overall economy of the system.
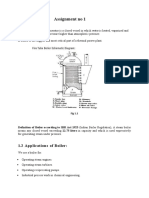
Boiler:
Boiler is a closed vessel in which vapors of water or some other liquid are generated at desired pressure
In modern process industries, steam is required during various processes and operations. It is used for heat
transferring, high pressure generation, as well as raw material in various processes. Steam is also being used to
control the humidity of the air in modern buildings. The equipment/device which is used for generating steam at
desired pressure is called a boiler. The pressure at which the steam is generated is of extreme importance, since
during a process steam loses its energy either due to losses in pipes or during heat transfer. Sometimes, it is our
need to prevent the condensation of steam which saves the equipment from corrosion. In such cases, we use steam
which is at high pressure so that its condensation does not occur. Hence, boilers play a very important role in the
functioning of modern industries.
Construction:
Although, various types of boilers are available in the market, most of them have some basic parts in their
construction. Some of them are explained below:
1. Furnace: A furnace is present in every boiler where some fuel is burned for heating water which is to be
converted into steam.
2. Water Inlet: An inlet is present for the introduction of water to be boiled into the boiler.
3. Flue gas discharge: A discharge is present for the used flue gases to leave the system i.e., boiler after they
have transferred their heat to the water present.
4. Check Valve: Various check valves are used to prevent any type of accidents. Check valves are there to
regulate the pressure within the boiler. If under some conditions, the pressure of the boiler reaches a
dangerous value, check valves open to relax the system and hence avoid any explosion.
5. Tubes: Tubes are also present in the boilers to increase the amount of heat transfer. Depending upon the
type of the boilers, either the flue gases or water move in the tubes present.
Working:
A boiler is a closed vessel. Fuel is burned in the furnace, and the heat generated is used to vaporize the
water present in the boiler. As water reaches its boiling temperature it starts changing into its vapor form. After
certain time interval, whole of the water is converted to vapor form and no liquid is present in the system. Under
these conditions the steam produced is said to be saturated steam. When further heated, the temperature and
pressure of the steam increases and it becomes superheated. The heat present in flue gases rising from the furnace
can also be used to economize the process. For this, we use tube sheets to increase heat transfer area, and hence
the amount of heat transferred to the liquid.
Types:
Boilers are generally classified by keeping in mind the way in which the flue gases and the water stream flow
within the boilers. On these basis boilers are generally classified as:
1. Water tube boilers
2. Fire tube boilers
Sometimes, the heat source is also used in classifying the boilers into various types for example:
1. Oil-fired boilers use oil in furnace for generating heat
2. Gas-fired boilers use gas
3. Coal-fired boilers use coal as heating source.
Fire Tube Boilers:
In fire tube boilers, water to be heated is present in the tank outside the tubes. Inside the tubes, flue gases
pass, transferring their heat to the water and changing it to vapors. This type of boilers have low initial cost but
cannot operate at high pressures and high capacity requirements.
Water Tube Boilers:
Water tube boilers have water inside the tube channels, while hot flue gases outside in the shell of the
boiler. Such boilers are used in places where high capacity and high steam pressures are required.
Safety:
It must be checked that all the safety valves are working properly.
Gloves should be used when working near pipes containing steam generated.
Steam containing pipes are painted silver for their identification.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Introduction to Steam Generation and Boiler Types for Textile IndustryDocument26 pagesIntroduction to Steam Generation and Boiler Types for Textile IndustryEngr Mujahid MehdiPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Basics of SteamDocument29 pages01 Basics of SteamEjubPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1. Marine Boilers PDFDocument48 pages2.1. Marine Boilers PDFBasong San67% (3)
- Tugas Util (Boiler)Document4 pagesTugas Util (Boiler)AkhmadSumarnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument9 pagesPower Plant EngineeringBlessyJoyPunsalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Thermo AssignmentDocument6 pagesBoiler Thermo AssignmentBassam0% (2)
- BoilerDocument77 pagesBoilerChoudhry Waqas Uddin.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment-Ali RazaDocument12 pagesAssignment-Ali RazaahsanPas encore d'évaluation
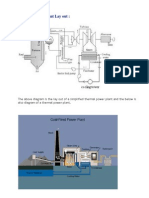
- JJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemDocument9 pagesJJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemAh Tiang86% (7)
- Thermal Power Plant Lay OutDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plant Lay OutSaheli ChoudhuriPas encore d'évaluation
- A Report On BoilersDocument5 pagesA Report On BoilersHarsh NigamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 02 FinalDocument13 pagesLab 02 FinalAsh DenemPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Design and Operation PDFDocument8 pagesBoiler Design and Operation PDFChungNguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Book PDFDocument44 pagesBoiler Book PDFmpgzyah100% (5)
- Boiler Research: Types, Systems, Failures & SafetyDocument3 pagesBoiler Research: Types, Systems, Failures & SafetyJonathan MalamulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler TypesDocument9 pagesBoiler TypesSharif Muhammad HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Boiler: Introduction To BoilersDocument1 pageWhat Is A Boiler: Introduction To BoilersThivin RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Heating by Steam (Kabaale)Document5 pagesWater Heating by Steam (Kabaale)OKIDI Thomas BecketPas encore d'évaluation
- The Boiler System Is Made Up ofDocument1 pageThe Boiler System Is Made Up ofThivinrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Steam Boiler: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesIndustrial Steam Boiler: ObjectiveM. Hassan HaidderPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler:: Working Principle of A BoilerDocument22 pagesBoiler:: Working Principle of A BoilerZeshan AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam BasicsDocument7 pagesSteam BasicsJohn RajPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Boiler? What Are Parts of A Boiler?Document24 pagesWhat Is A Boiler? What Are Parts of A Boiler?dharanistrikezPas encore d'évaluation
- #Lecture 3 - Steam GeneratorsDocument22 pages#Lecture 3 - Steam Generatorsmohamed EldesokyPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment # 7 Objective:: Fig: 7.1 (Steam Boiler)Document4 pagesExperiment # 7 Objective:: Fig: 7.1 (Steam Boiler)AkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 - Steam Generators: Mechanics of Steam BoilersDocument7 pagesLecture 7 - Steam Generators: Mechanics of Steam BoilersIjazzzAliPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Water ConditioningDocument59 pagesBoiler Water ConditioningShikderPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 - Steam GeneratorsDocument6 pagesLecture 7 - Steam GeneratorsHussain Abbas100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant Layout and OperationDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plant Layout and OperationRAJENDRA TELVEKARPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler and Boiler CalculationsDocument7 pagesBoiler and Boiler CalculationsChaya Stia ClaluiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire-tube Boiler Guide: Types, Components & UsesDocument7 pagesFire-tube Boiler Guide: Types, Components & Usesgalih prasetyo aji gumelarPas encore d'évaluation
- BoilersDocument3 pagesBoilersatikulPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal LabDocument38 pagesThermal LabKRRISH MAHESHWARIPas encore d'évaluation
- HRSG BoilersDocument40 pagesHRSG BoilersNadeem KhanPas encore d'évaluation
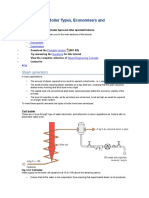
- Miscellaneous Boiler Types, Economisers and Superheaters ExplainedDocument4 pagesMiscellaneous Boiler Types, Economisers and Superheaters ExplainedsenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment No 1Document16 pagesAssignment No 1AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Boilers: Espiritu, Christopher James Managuit, John Jeruel Querubin, Russel JohnDocument43 pagesBoilers: Espiritu, Christopher James Managuit, John Jeruel Querubin, Russel JohnRussel John Morillo Querubin100% (1)
- Boiler Basics: Design, Operation, Components & SystemsDocument5 pagesBoiler Basics: Design, Operation, Components & SystemsEng Waleed MouhammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Pressure PartsDocument9 pagesBoiler Pressure PartsManikandan Vijayan50% (2)
- Jericho Hyansalem Wicaksono - 5019201004Document3 pagesJericho Hyansalem Wicaksono - 5019201004Lucas JerichoPas encore d'évaluation
- Expo Calor InglesDocument3 pagesExpo Calor InglesJessica Andrea CalderonPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To BoilersDocument25 pagesIntroduction To BoilersDamith Buddhika Sri WimalarathnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Torrejas Review 1Document2 pagesTorrejas Review 1Arnel Belza TorrejasPas encore d'évaluation
- Armstrong - Trapping Super Heated SteamDocument7 pagesArmstrong - Trapping Super Heated SteamLarry HoffmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Alter Polymerization Reactors for Enhanced Heat TransferDocument7 pagesAlter Polymerization Reactors for Enhanced Heat TransferafifiPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Steam ExplainedDocument6 pagesTypes of Steam ExplainedMohammad Ali ZamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Boiler: Water Tube Boiler Fire Tube BoilerDocument4 pagesTypes of Boiler: Water Tube Boiler Fire Tube BoilerRahul PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Heat Boiler Plate Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesWaste Heat Boiler Plate Heat ExchangerskondusamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Cont.Document9 pagesBoiler Cont.adnan mukhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ornos, Janlyn Z. MEL 2 Assessment 1Document4 pagesOrnos, Janlyn Z. MEL 2 Assessment 1Janlyn OrnosPas encore d'évaluation
- De-superheating steam for greater efficiencyDocument5 pagesDe-superheating steam for greater efficiencypriyanka236Pas encore d'évaluation
- High Pressure BoilerDocument8 pagesHigh Pressure BoilerAnand KalaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Operating Procedure of A Fire Tube BoilerDocument10 pagesSafety Operating Procedure of A Fire Tube BoilerJan Marvin Tamse0% (1)
- Chapter 21: Evaporation - Principles, Types of EvaporatorsDocument7 pagesChapter 21: Evaporation - Principles, Types of EvaporatorssdfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesD'EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesPas encore d'évaluation
- How it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useD'EverandHow it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common usePas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewD'EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewPas encore d'évaluation
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialD'EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialPas encore d'évaluation
- Soda Ash (Na CO)Document5 pagesSoda Ash (Na CO)Hamood AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- VALVESDocument153 pagesVALVESHamood Ahmad100% (1)
- Dimensionless Numbers & Their ApplicationDocument24 pagesDimensionless Numbers & Their ApplicationHamood AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive SystemHamood AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Hybrid Cycle Mod 3Document27 pagesAir Hybrid Cycle Mod 3Parveen Kumar100% (1)
- Re 79093Document4 pagesRe 79093Anonymous lIJl27QBXLPas encore d'évaluation
- Honda Gs390 Owners Manual (Powerwasher)Document60 pagesHonda Gs390 Owners Manual (Powerwasher)Nate SpaydPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of Material Lab ManualDocument64 pagesMechanics of Material Lab ManualMOAZPas encore d'évaluation
- Hoop StressDocument3 pagesHoop Stresskarthikraja21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Innovative Bridge Bearing SolutionsDocument12 pagesInnovative Bridge Bearing SolutionsyhszaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pc3 Clamp DrawingDocument4 pagesPc3 Clamp DrawingSujin SujiPas encore d'évaluation
- Man P2862 Le ProjectDocument406 pagesMan P2862 Le ProjectMuhammad Subhan IrfandyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pauselli 700 Solar Pile Driver BrochureDocument4 pagesPauselli 700 Solar Pile Driver BrochureJaouad Id BoubkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Technology of Heat Treating-Straightening of Long Shafts With Low RigidityDocument8 pagesTechnology of Heat Treating-Straightening of Long Shafts With Low RigidityShariq KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Multi Stage Parabolic Leaf SpringDocument13 pagesMulti Stage Parabolic Leaf SpringahiremanojPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleed Air Manual Control Modes Task CardDocument34 pagesBleed Air Manual Control Modes Task CardTony GarrisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigation of building collapse in AbujaDocument15 pagesInvestigation of building collapse in AbujaEmeso OjoPas encore d'évaluation
- DR650SEL2 Catalogo Partes PDFDocument75 pagesDR650SEL2 Catalogo Partes PDFEderPas encore d'évaluation
- Powerplant Quizlet 492Document63 pagesPowerplant Quizlet 492Jecah Angelu S. SaquianPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Controlador Lae MTR 6Document3 pagesManual Controlador Lae MTR 6Anonymous 6VCG1YRd100% (2)
- Alfa Laval BioPharm Fittings Catalog PDFDocument102 pagesAlfa Laval BioPharm Fittings Catalog PDFcneo59Pas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Furnace DefectsDocument4 pagesBoiler Furnace DefectskrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Service Tool 2015A v2Document3 pagesElectronic Service Tool 2015A v2Nacer ZehaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynapac f1800w En-20220822.134322Document2 pagesDynapac f1800w En-20220822.134322Fredrik ÅkessonPas encore d'évaluation
- Conditionals 20.3.Document32 pagesConditionals 20.3.Stefan PetrovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Centrifugal Pump Lab ReportDocument16 pagesCentrifugal Pump Lab Reportapi-31051928380% (5)
- Pumps HighPressureDrainage D42AB D53AB DatasheetDocument2 pagesPumps HighPressureDrainage D42AB D53AB DatasheetMohammad ZeeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Risk Based Inspection (RBI)Document7 pagesIntroduction To Risk Based Inspection (RBI)Alejandro LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Water Hammering in Pipeline and Its CFD SimulationDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Water Hammering in Pipeline and Its CFD SimulationDuzzysPas encore d'évaluation
- SD 14 eDocument12 pagesSD 14 eseaqu3stPas encore d'évaluation
- Date: Drawn Trac. Scale Checked Apprd.: Replacement: Replaced By: DWG: Rev.Document1 pageDate: Drawn Trac. Scale Checked Apprd.: Replacement: Replaced By: DWG: Rev.Deepak DasPas encore d'évaluation
- SFD & BMDDocument44 pagesSFD & BMDAltaf Hossain100% (2)
- Ec T30 PDFDocument1 500 pagesEc T30 PDFNorman Valle Sáenz100% (1)
- ITT CONTROLS Barton Chart Recorders 202e User Manual 1Document52 pagesITT CONTROLS Barton Chart Recorders 202e User Manual 1Edbaac BAPas encore d'évaluation