Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lumbar Puncture Consent Form
Transféré par
Jann Adriel Chua Sy0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
1K vues2 pagesA lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, is a procedure where a needle is inserted into the lower back to collect cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal canal for diagnostic testing. It is most commonly performed to test for infections or the presence of cancer cells. During the procedure, the patient lies on their side while local anesthesia is administered and a needle is inserted between two lumbar vertebrae. Potential risks include temporary back pain, headache, bleeding, and very rarely, infection or neurological complications.
Description originale:
Titre original
Lumbar Puncture Consent Form Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentA lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, is a procedure where a needle is inserted into the lower back to collect cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal canal for diagnostic testing. It is most commonly performed to test for infections or the presence of cancer cells. During the procedure, the patient lies on their side while local anesthesia is administered and a needle is inserted between two lumbar vertebrae. Potential risks include temporary back pain, headache, bleeding, and very rarely, infection or neurological complications.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
1K vues2 pagesLumbar Puncture Consent Form
Transféré par
Jann Adriel Chua SyA lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, is a procedure where a needle is inserted into the lower back to collect cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal canal for diagnostic testing. It is most commonly performed to test for infections or the presence of cancer cells. During the procedure, the patient lies on their side while local anesthesia is administered and a needle is inserted between two lumbar vertebrae. Potential risks include temporary back pain, headache, bleeding, and very rarely, infection or neurological complications.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Lumbar Puncture
(Affix Patient Label)
What is a lumbar puncture?
A lumbar puncture is the insertion of a needle into the fluid space within the spinal canal. It is termed a
lumbar puncture because the needle goes into the lower back called the lumbar area.
Why is this done?
A lumbar puncture is most commonly done for diagnostic purposes, namely to obtain a sample of the
fluid in the spinal canal (cerebrospinal fluid) for tests to detect infection and/ or presence of cancer cells.
How is this procedure performed?
You will most commonly be lying down sideways for the procedure. After local anaesthesia is injected
into the lumber area, a needle is inserted in between the bony blocks (vertebrae) into the spinal canal.
The needle is usually placed between the 3
rd
and 4
th
lumbar vertebrae. The spinal fluid pressure can
then be measured. Cerebrospinal fluid is then removed for tests.
What are the risks of a lumbar puncture?
As with any medical procedure, complications may occur. Some of the most common and important
complications following lumbar puncture are:
Backache
Headache
Bleeding
Infection
Neurological deterioration
Backache
The doctor will numb the skin of your lower back before insertion of the needle. However, mild lower
back discomfort, generally lasting one or two days, might still occur. This is easily treated with simple
pain medications.
Headache
Occasionally, a headache follows lumbar puncture. This is the most common complication following a
lumbar puncture, but occurs in less than one of ten procedures. The headache can occur from hours up
to a day or so after the procedure. Remaining recumbent and avoiding walking until six hours after the
procedure may reduce the likelihood of headache. Drinking adequate water may also help reduce the
incidence or severity of headaches. Pain medications can usually relieve the headache.
Bleeding
As with any procedure involving puncture with a needle, bleeding may occur at the procedure site.
Bleeding is usually minimal in lumbar puncture, except when disorders of the blood clotting system are
present. Occasionally a blood clot that has formed under the skin at the site of the procedure called a
haematoma may cause prolonged pain. The risk of this happening can be reduced by lying flat for six
hours after the procedure.
Infection
Rarely, an infection may develop at the procedure site. In order to reduce the chances of infection, the
skin of your lower back will be cleaned with a sterilizing agent. However, it is possible that infection may
still occur.
To be continued on the next page
Neurological deterioration
In very rare situations, neurological deterioration may follow lumbar puncture. This only occurs if the
cerebrospinal fluid pressure is high and becomes reduced during the procedure, causing a part of the
brain to sink into an area of the skull resulting in coma and possible life-threatening event. The chance of
any such adverse change developing can be assessed by clinical examination and/ or radiological
procedures performed prior to the lumbar puncture.
Others (to be filled by Medical Practitioner)
Acknowledgement Section
Part I To Be Filled by Patient
I have read and understood the potential complication(s) that can arise from the surgery.
I acknowledge that the complication(s) listed are not intended to be exhaustive. I have had an
opportunity to ask for more information about any of the above-mentioned complications, as well as the
risks in general, or any specific condition of concern to me.
Part II To Be Filled by Medical Practitioner
I confirm that I have explained the reason for and the nature of potential complication(s) that may arise
from the procedure to the patient and the above-named witness.
Part III To Be Filled by Interpreter (if applicable)
I, _____________________________confirm that I have explained to the patient the reason for and the
nature of potential complication(s) that may arise from the procedure in _______________________.
* Please delete accordingly
(*Signature/Thumbprint(*Right/Left) of
*Patient/ Parent/ Guardian/ Next of kin)
(Name & NRIC of *Patient/Parent/
Guardian/Next of kin)
(Designation of Witness) (Name of Witness)
(Date of Signing) (Signature of Witness)
(Name & Signature of Medical Practitioner) (Date of Signing)
(Name of Interpreter)
(*Language / Dialect)
(Date of Signing) (Signature of Interpreter)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Vital Signs and Early Warning ScoresDocument47 pagesVital Signs and Early Warning Scoresdr_nadheem100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Autoclave GuideDocument48 pagesAutoclave GuideIman 111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook for Cssd Technicians: Understanding the Basics - Second EditionD'EverandHandbook for Cssd Technicians: Understanding the Basics - Second EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Move The Patient From The Bed To The Wheelchair How To Move The Patient From The Bed To The WheelchairDocument9 pagesHow To Move The Patient From The Bed To The Wheelchair How To Move The Patient From The Bed To The WheelchairAfniy ApriliaPas encore d'évaluation
- A P Policy & Procedure: Ntibiotic OlicyDocument24 pagesA P Policy & Procedure: Ntibiotic Olicyvijay kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tubing Misconnections Self Assessment For Healthcare FacilitiesDocument38 pagesTubing Misconnections Self Assessment For Healthcare FacilitiesAle Gastelum100% (1)
- File 571Document65 pagesFile 571RazaCreciaLastrillaMenesesPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Site Marking PolicyDocument11 pagesSurgical Site Marking PolicymiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Control in Endoscopy Unit: Safety Considerations For The PatientDocument13 pagesQuality Control in Endoscopy Unit: Safety Considerations For The PatientPamela PampamPas encore d'évaluation
- Scripps Hospital Patient Visitor Policy PDFDocument2 pagesScripps Hospital Patient Visitor Policy PDFcode4salePas encore d'évaluation
- Radiology ServicesDocument5 pagesRadiology Servicesshah007zaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital GuidelinesDocument236 pagesHospital GuidelinesMheanne Romano100% (1)
- CSSDDocument32 pagesCSSDRAHUL100% (1)
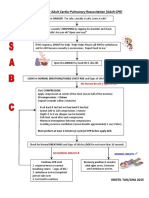
- Flow Chart For Adult Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (Adult CPR)Document1 pageFlow Chart For Adult Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (Adult CPR)Lia IshakPas encore d'évaluation
- Antimicrobial Prescribing PolicyDocument20 pagesAntimicrobial Prescribing PolicycraPas encore d'évaluation
- CLCGP030 Theatre Operating List Session Scheduling PolicyDocument19 pagesCLCGP030 Theatre Operating List Session Scheduling PolicyJeffy PuruggananPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Integrity and Wound CareDocument47 pagesSkin Integrity and Wound CareCHALIE MEQUPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency NursingDocument15 pagesEmergency NursingAshley Ishika100% (1)
- Australian Model Triage ScaleDocument3 pagesAustralian Model Triage ScaleHendraDarmawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Missing Patients ProcedureDocument16 pagesMissing Patients ProcedureAgnieszka WaligóraPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual For EndosDocument19 pagesManual For EndosVarsha MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Aseptic TechniqueDocument9 pagesAseptic Techniquebethh_6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Guidelines For Management of HTNDocument6 pagesClinical Guidelines For Management of HTNChaturangaNSenerath100% (1)
- Western Australian Patient Identification Policy PDFDocument14 pagesWestern Australian Patient Identification Policy PDFpuspadiniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Food and Its Medicinal ValueDocument9 pagesRole of Food and Its Medicinal Valueharshika tembhurnePas encore d'évaluation
- The Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Count ProcedureDocument42 pagesThe Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Count ProcedureGina AprianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Cleaning ChecklistDocument1 pageEnvironmental Cleaning ChecklistsostroPas encore d'évaluation
- Health ResearchDocument16 pagesHealth ResearchTmanoj PraveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Initial Assessment and ManagementDocument8 pagesInitial Assessment and ManagementAlvin De LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Standardized Emergency Color CodesDocument1 pageStandardized Emergency Color CodesDivya ToppoPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 2 - Healthcare Quality and Patient SafetyDocument2 pagesQuiz 2 - Healthcare Quality and Patient SafetySantosh JSEPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Manager Job Description - 09-13Document3 pagesQuality Manager Job Description - 09-13DrSaswat LincolnPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Drugs (LEAD)Document8 pagesEmergency Drugs (LEAD)RayePrudentePas encore d'évaluation
- IV Cannulation ChecklistDocument2 pagesIV Cannulation ChecklistDo0odi AlharbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Triage ProtocolDocument1 pageCentral Triage Protocolgechworkneh38Pas encore d'évaluation
- Patient Safety 1, 2Document98 pagesPatient Safety 1, 2salah salem100% (1)
- Hospital Infection Control ManualDocument59 pagesHospital Infection Control Manualابراهيم الحربيPas encore d'évaluation
- Infection Control Questions For StaffDocument3 pagesInfection Control Questions For StaffManisha maharaPas encore d'évaluation
- prehospital-EMS-COVID-19-recommendations - 4.4Document19 pagesprehospital-EMS-COVID-19-recommendations - 4.4MEONEPas encore d'évaluation
- ICAP Basic ICRA With MatrixDocument4 pagesICAP Basic ICRA With MatrixmiptahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 HandwashingDocument18 pagesChapter 2 HandwashingMylene Valdez50% (2)
- AnesthesiaDocument59 pagesAnesthesiaHasse Hasse100% (1)
- History of FluorosDocument2 pagesHistory of FluorosEvi DianPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency CodesDocument23 pagesEmergency CodesJennifer B. GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dhanusthamba/Dhanurvata/Tetanus: Dr. Mahesh C KundagolDocument19 pagesDhanusthamba/Dhanurvata/Tetanus: Dr. Mahesh C KundagolkundagolPas encore d'évaluation
- Establishing and Maintaining A Sterile Field Definition:: Action Rationale Performe D Remarks YES NODocument8 pagesEstablishing and Maintaining A Sterile Field Definition:: Action Rationale Performe D Remarks YES NOJustin AncogPas encore d'évaluation
- Policies and Procedures Radiology DepartmentDocument6 pagesPolicies and Procedures Radiology DepartmentRalph Gerard Saldajeno ValdespinaPas encore d'évaluation
- ASEPSISDocument28 pagesASEPSISDeborah AmpongPas encore d'évaluation
- Infection Control ManualDocument206 pagesInfection Control ManualJohnny DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Policies and Procedures On Disposition of Dead Bodies With Dangerous CDDocument19 pagesPolicies and Procedures On Disposition of Dead Bodies With Dangerous CDsurigao doctors'100% (2)
- Universal Precaution by FithriDocument62 pagesUniversal Precaution by FithriFithriKurniatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemotherapy Administration in Pediatric: An OverviewDocument76 pagesChemotherapy Administration in Pediatric: An OverviewMiftaa HurrahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach 4 Standard Precautions Icon PDF 672KBDocument1 pageApproach 4 Standard Precautions Icon PDF 672KBElaine MacalandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Transfusion Single Use PathwayDocument6 pagesBlood Transfusion Single Use PathwayropusanPas encore d'évaluation
- In-Patient Department: Patient Nursing Staff Ratio: RMO'S: 3 - Morning 2 - NightDocument6 pagesIn-Patient Department: Patient Nursing Staff Ratio: RMO'S: 3 - Morning 2 - NightSiddhi RanePas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 International Patient Safety GoalsDocument1 page2007 International Patient Safety GoalsElias Baraket FreijyPas encore d'évaluation
- Triage in Disaster ManagementDocument10 pagesTriage in Disaster ManagementHazel Mei MalvarPas encore d'évaluation
- Day Case Surgery 1LDocument21 pagesDay Case Surgery 1LdrhiwaomerPas encore d'évaluation
- A Clinical Study On The Efficacy of Nimbapatradi Lepa in The Management of Dushta VranaDocument7 pagesA Clinical Study On The Efficacy of Nimbapatradi Lepa in The Management of Dushta Vranamurshid AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 COSM ProgramGuide Final PDFDocument76 pages18 COSM ProgramGuide Final PDFfluffy4202011Pas encore d'évaluation
- Currículo Profissional - Tamize InglesDocument7 pagesCurrículo Profissional - Tamize InglesTamize SILVA GONCALVESPas encore d'évaluation
- A Textbook of Advanced Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument830 pagesA Textbook of Advanced Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryTabarak AdilPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomical Map of The Facial Artery For Facial 2019Document12 pagesAnatomical Map of The Facial Artery For Facial 2019letty3gapePas encore d'évaluation
- Oet 2.0 Writing Practice and Exercises Book For Nurses Vol 2Document184 pagesOet 2.0 Writing Practice and Exercises Book For Nurses Vol 2Dandlers MurrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgitoons GIT Surgitoons - Bak PDFDocument127 pagesSurgitoons GIT Surgitoons - Bak PDFAlejandra Rozo BayerPas encore d'évaluation
- Issa 2019Document6 pagesIssa 2019İbrahim DemircioğluPas encore d'évaluation
- Cataract and Surgery For Cataract: ReferencesDocument6 pagesCataract and Surgery For Cataract: ReferencesMarilyn PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Commonly Billed Codes: Spinal Cord StimulationDocument21 pagesCommonly Billed Codes: Spinal Cord StimulationKrishna KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Medisign Booklet 2013 2015 PDFDocument182 pagesMedisign Booklet 2013 2015 PDFTohid TalefifuPas encore d'évaluation
- Kea-Med Medical College 22 Campus: Title: Family Planning Project Work Surgical Contraceptive Individual AssignmentDocument13 pagesKea-Med Medical College 22 Campus: Title: Family Planning Project Work Surgical Contraceptive Individual AssignmentlahmetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Medicine Qs For GP Saudi PrometricDocument140 pagesInternal Medicine Qs For GP Saudi PrometricM A100% (4)
- Surg PlatDocument15 pagesSurg PlatElisha BernabePas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Surgeries PPT FinalDocument55 pagesCardiac Surgeries PPT FinalDumora FatmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ailing and Failing Us Dental ImplantsDocument12 pagesAiling and Failing Us Dental ImplantsCharlyBoeingPas encore d'évaluation
- Anterior Knee Pain After Intramedullary Nailing of Fractures of The Tibial ShaftDocument2 pagesAnterior Knee Pain After Intramedullary Nailing of Fractures of The Tibial ShaftasclepiuspdfsPas encore d'évaluation
- Witnesses and SponsorsDocument2 pagesWitnesses and SponsorsdiazdizzamariePas encore d'évaluation
- 1616823455876-Basic BRSingh Hospital Details 26th March 2021Document11 pages1616823455876-Basic BRSingh Hospital Details 26th March 2021Kiushik SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Wound Ostomy Continence Skills ChecklistDocument4 pagesWound Ostomy Continence Skills ChecklistnorthweststaffingPas encore d'évaluation
- Catheterization Insertion and RemovalDocument5 pagesCatheterization Insertion and RemovalArmySapphirePas encore d'évaluation
- PCNL EhDocument38 pagesPCNL EhIndra JayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Enovo Surgical TechniqueDocument9 pagesEnovo Surgical TechniqueLUNA SEQUOIAPas encore d'évaluation
- JQNMHC - Mapping Icd-9-CmDocument3 pagesJQNMHC - Mapping Icd-9-Cmsyaiful rinantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoulder DislocationDocument58 pagesShoulder DislocationSri MahadhanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthopedic EmergenciesDocument63 pagesOrthopedic EmergenciesNasser AlQadhibPas encore d'évaluation
- En SCD600Document2 pagesEn SCD600Surta DevianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advice and Exercises After A Total Hip Replacement THR - Jun21Document15 pagesAdvice and Exercises After A Total Hip Replacement THR - Jun21Julenda CintarinovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uroso18 SynopsisDocument2 pagesUroso18 SynopsiscaciorsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Procedure Listing: Procedure Proc. Code # of Procedures RequiredDocument2 pagesPediatric Procedure Listing: Procedure Proc. Code # of Procedures RequiredIsabel HigginsPas encore d'évaluation