Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Thalumas & Diancephalon
Transféré par
sssaji0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
36 vues4 pagesMedicine lecture notes
Titre original
thalumas & diancephalon
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMedicine lecture notes
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
36 vues4 pagesThalumas & Diancephalon
Transféré par
sssajiMedicine lecture notes
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
1
Repeat campaign A/L 2008
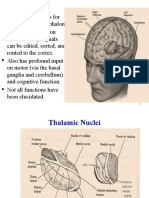
Thalamus
Mass of gray matter, egg shaped
Two thalami, on either side of 3
rd
ventricle- connected by interthalamic connection.
Relays all sensations except olfactory
Important in crude sensation (for detailed localization & interpretation cerebral cortex)
Relations
Anterior Interventricular foramen
Posterior pineal body, posterior commissure
Superior tela choroidia, fornix (midline)
choroid plexus of lateral ventricle
(thalamus forms a part of the floor of the lateral ventricle)
Inferior hypothalamus, tegmentum of mid brain
Medial 3
rd
ventricle, interthalamic connection
Lateral internal capsule, lentiform nucleus
Cerebrum
Diencephalon
3
rd
ventricle
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Cerebral hemisphere
Cortex (grey matter)
Internal white matter
Basal ganglia
Cerebrum
2
Repeat campaign A/L 2008
Important thalamic nuclei
lateral geniculate body(LGB)relays vision(optic tract)
medial geniculate body(MGB)relays hearing(lateral leminiscusinferior colliculus)
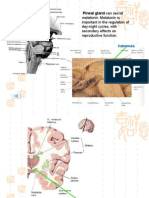
Hypothalamus
Controls autonomic nervous system
Controls endocrine system
Maintains body homeostasis
Contributes to the limbic system-Emotion & behavior, memory, sexual drive.
Relations
Anterior optic chiasma, lamina terminalis, anterior commissure
Posterior tegmentem of the mid brain
Superior thalamus
Inferior (AP)optic chiasma, tuber cinerium & infundibulum, mammilary bodies
Medial 3
rd
ventricle
Hypophyseal portal system
Carries releasing & release inhibitory hormones to the pituitary (eg. GnRH, GHRH, GHIH)
Formed by a branch of the internal carotid artery.
1)Ventral posterior nucleus
Ventral posterolateral
Relays spinal & medial leminisci
Ventral posteromedial
Relays trigerminal & taste
1)Ventral posterior nucleus
Ventral posterolateral
Relays spinal & medial leminisci
Ventral posteromedial
Relays trigerminal & taste
Ventral posterior nucleus
Ventral posterolateral(VPL)
Relays spinal & medial leminisci
(sensations from the body)
Ventral posteromedial(VPM)
Relays trigerminal & taste
(sensations from face)
3
Repeat campaign A/L 2008
Q. Regarding the thalamus,
a) Has the body of the fornix on its superior aspect.
b) Is separated from the lentiform nucleus by the external capsule.
c) Has bands of gray matter connecting the thalami of both sides.
d) Has the medial leminiscus ending in its VPL.
e) Has the anterior pole forming the posterior boundary of the interventricular foraman.
CEREBELLUM
Posterior cranial fossa
Posterior to 4
th
ventricle, pons & medulla oblongata.
Two cerebellar hemispheres joined by the median vermis
3 lobes
-anterior
primary fissure
-middle
(posterior)
Uvulonodular fissure
-flocculonodular -
Outer-grey cortex
Inner-white matter
Intracerebellar nuclei-masses of grey matter embedded in white matter
Cortex
3 layers (outerinner)
-molecular layer
-purkinje cell layer-purkinje cells
-granular layer
Functional areas
1. Cortex of the vermis-movements of the long axis of the body
2. Intermediate zone-controls muscles of distal parts of limbs
3. Lateral zone-planning of sequential movements of the entire body
Intracerebellar nuclei
Afferent
Intracerebellar nuclei cortex(purkinje cells)
efferent
4
Repeat campaign A/L 2008
Functions of cerebellum
Cerebellum has no direct neuronal connections with the lower motor neurons, but excerts its
influence indirectly through the cerebral cortex and brainstem.
Coordination of precise movements
How?
By continuously compairing the output of the motor area of cerebral cortex with the
proprioceptive information received from the site of muscle action.
Brings about necessary adjustment by influencing the activity of the lower motor
neurons.
CLINICAL
-Signs & symptoms are limited to the same side of the body.
-No Paralysis ,sensory loss or atrophy.
Signs of cerebellar lesion - A2 R2 D3 TiN
1. Ataxia- disturbance of voluntary movement.
2. Atonia (*hypotonia)
3. Reflex disturbances-eg. Pendular knee jerk
4. Rebound phenomenon.
5. Dysdiadochokinasia-inability to perform alternating movements regularly and rapidly
6. Disarthria (slurred speech)
7. Dismetria eg.past pointing
8. Tremor intentional (tremor in fine movements)
9. Nystagmus-rythmical oscillations of eyes)
Vermis syndrome- fall forwards or backwards
Cere. hemisphere syndrome- fall to the side of the lesion
Cerebellar
peduncle
Superior
(with midbrain)
Middle
(with pons)
Inferior
(with medulla oblongata)
Afferent
pathways
Ant.spinocerebellar o Corticopontocerebellar
o Cerebroreticulocerebellar
o Post. spinocerebellar
o Cerebro-olivocerebellar
o Cerebroreticulocerebellar
o Cuneocerebellar
o From vestibular nerve
Efferents
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- MED (Neuro) - NeuroanatomyDocument6 pagesMED (Neuro) - NeuroanatomyFlora XuPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy 1 - Sensory PathwaysDocument8 pagesAnatomy 1 - Sensory PathwaysAnthony BrownPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Surgical Nursing NotesDocument66 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Notessimon92% (12)
- Basal GangliaDocument38 pagesBasal GangliaKhalid AlhemyariPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nervous System: Ian Van V. Sumagaysay, RN, MAN St. Anthony's CollegeDocument182 pagesThe Nervous System: Ian Van V. Sumagaysay, RN, MAN St. Anthony's CollegeAlibasher MacalnasPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument85 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebasePas encore d'évaluation
- NervousSystem (6) &Document67 pagesNervousSystem (6) &Irfan Nur Fathur Rahman100% (1)
- Npte - Neuroanatomy Lec 2Document31 pagesNpte - Neuroanatomy Lec 2Densen Raphael C. Antonio100% (2)
- LECTURE On Spinal CordDocument11 pagesLECTURE On Spinal CordElijah KamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical SurgicalDocument119 pagesMedical SurgicalTammy TamPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Eyad M. Hussein: Anatomy of The Cerebellum, Basal Nuclei & DiencephalonDocument68 pagesDr. Eyad M. Hussein: Anatomy of The Cerebellum, Basal Nuclei & Diencephalonأمال داودPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO 342 Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Lecture Notes 11 - Nervous System The Vertebrate Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesBIO 342 Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Lecture Notes 11 - Nervous System The Vertebrate Nervous SystemAitor LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurolocalization In Pediatrics: Localizing Neurologic Lesions In ChildrenDocument66 pagesNeurolocalization In Pediatrics: Localizing Neurologic Lesions In ChildrenNigussie MershaPas encore d'évaluation
- ThalamusDocument21 pagesThalamusTem GemechuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Nervous System Conduction: B. Pathophysiology 1.) Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesFundamentals of Nervous System Conduction: B. Pathophysiology 1.) Anatomy and PhysiologyJanine P. Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain and Behaviour 1-2Document11 pagesBrain and Behaviour 1-2Jagoda KamińskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiologymhel03_chickmagnetPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinothalamic Tract - WikipediaDocument23 pagesSpinothalamic Tract - WikipediaManish Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Cheat Sheet - MIDTERMDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet - MIDTERMmeganbb02Pas encore d'évaluation
- ue 1-Broc s Are ʹ an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involvedDocument31 pagesue 1-Broc s Are ʹ an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involvedMhmd IrakyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Vphy112-Nervous SystemDocument76 pages1 Vphy112-Nervous SystemJohn Jephet RamiscalPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology CVADocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CVAmaryrose_jordan100% (6)
- CEREBELLUM (Physiotherapy)Document44 pagesCEREBELLUM (Physiotherapy)Richmond tohPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum 4 - 5Document45 pagesCerebellum 4 - 5sridhar100% (1)
- Diencephalon: Rabbia Yousaf (Pharm-D) Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument32 pagesDiencephalon: Rabbia Yousaf (Pharm-D) Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro Ppt. Lec. 1Document49 pagesNeuro Ppt. Lec. 1Jay successPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System GuideDocument59 pagesNervous System GuideDR Archana Agarwal100% (2)
- Learn Neuroscience & Anatomy 23Document3 pagesLearn Neuroscience & Anatomy 23rajad100% (2)
- Understanding Human Anatomy and Brain FunctionDocument61 pagesUnderstanding Human Anatomy and Brain Functionjustice88_639020831Pas encore d'évaluation
- Frog's Nervous System ExplainedDocument4 pagesFrog's Nervous System ExplainedJesi QuiambaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum Anatomy and FunctionsDocument43 pagesCerebellum Anatomy and FunctionsHarmas Novryan FarezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thalamus: - Dr. Sachin A. AdukiaDocument56 pagesThalamus: - Dr. Sachin A. AdukiaNairda TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum & DiencephalonDocument21 pagesCerebellum & Diencephalonprasun_vPas encore d'évaluation
- K3. Anatomi Sistem Limbik, ARAS, Saraf Tepi, Dalam Aspek Neurologis (Dr. Ahmad Azmi Nasution, M.Biomed)Document112 pagesK3. Anatomi Sistem Limbik, ARAS, Saraf Tepi, Dalam Aspek Neurologis (Dr. Ahmad Azmi Nasution, M.Biomed)AmesyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Organization Neuro ScienceDocument45 pagesOrganization Neuro SciencePrathyu ShaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellar Function TestDocument37 pagesCerebellar Function TestAdrian Paolo Malamug100% (1)
- Nervous System - All NotesDocument6 pagesNervous System - All NotesJPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord LesionsDocument110 pagesSpinal Cord Lesionsgtaha80100% (1)
- Presentation 3 (Information) Major Descending (Motor) Pathway and Spinal Cord Tracts March 25, 2012Document23 pagesPresentation 3 (Information) Major Descending (Motor) Pathway and Spinal Cord Tracts March 25, 2012bsittPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesCentral Nervous SystemJaybelle MadolariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System and Muscle OverviewDocument15 pagesNervous System and Muscle OverviewGordana DimeskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 6 Revision - Cognitive Impairment: Central SulcusDocument7 pagesCase 6 Revision - Cognitive Impairment: Central SulcusCharlie WalkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Corticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesCorticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsAlexaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Learning Assessment 4Document24 pagesAnatomy Learning Assessment 4Jay Lure Gomez BaguioPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction and Overview of Neuroanatomy (Presentation) Author Al Muqsith, Ervi SuminarDocument55 pagesIntroduction and Overview of Neuroanatomy (Presentation) Author Al Muqsith, Ervi Suminarsari dianitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesNervous SystemSuvalari Mimi JonathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Structures and their Functions ExplainedDocument6 pagesBrain Structures and their Functions ExplainedUjjal Kumar Sarker100% (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyssairej06Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neuroanatomy, Cerebellar Dysfunction: Gross AnatomyDocument5 pagesNeuroanatomy, Cerebellar Dysfunction: Gross AnatomyANISA RIFKA RIDHOPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3Document4 pagesLesson 3JessiePas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1Document8 pagesModule 1laaraybmehmood1503Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro 1Document26 pagesNeuro 1Iris BakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor SystemDocument49 pagesMotor SystemAhaisibwe GordonPas encore d'évaluation
- The Human Nervous System - 71911Document49 pagesThe Human Nervous System - 71911Rome Voltaire GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Thalamus: RD THDocument9 pagesThalamus: RD THDr santoshPas encore d'évaluation
- White Matter Classification and TractsDocument48 pagesWhite Matter Classification and TractsEma MocanPas encore d'évaluation
- SNC EEG MalmivuoDocument10 pagesSNC EEG MalmivuoAdam SamenezesPas encore d'évaluation
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyD'EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar DisorderDocument5 pagesBipolar DisordersssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- BLS MCQ CoagulationDocument4 pagesBLS MCQ CoagulationsssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal MassDocument8 pagesAbdominal MasssssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Spleen. Liver, PancreaseDocument7 pagesSpleen. Liver, PancreasesssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary CalculiDocument6 pagesUrinary CalculisssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy - CAT 3 Neuro & EmbryoDocument7 pagesAnatomy - CAT 3 Neuro & EmbryosssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy - CAT 3Document11 pagesAnatomy - CAT 3sssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Thalumas & DiancephalonDocument4 pagesThalumas & DiancephalonsssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid FunctionDocument6 pagesThyroid FunctionArun Kumar GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy - Upper Limb Q Bank MCQDocument19 pagesAnatomy - Upper Limb Q Bank MCQsssaji88% (17)
- Lipids: What Are The Building Blocks of LipidsDocument2 pagesLipids: What Are The Building Blocks of LipidssssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal CapsuleDocument4 pagesInternal CapsulesssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- ANS AnatomyDocument2 pagesANS AnatomysssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Glomerulo Nephritis PathologyDocument3 pagesGlomerulo Nephritis PathologysssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Glomerulo Nephritis PathologyDocument3 pagesGlomerulo Nephritis PathologysssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral CavityDocument5 pagesOral CavitysssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- UTI in ChildrenDocument4 pagesUTI in ChildrensssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- ImmunodeficiencyDocument10 pagesImmunodeficiencysssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Constipation and IncontinenceDocument8 pagesConstipation and IncontinencesssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Palmar Aspect of The HandDocument2 pagesPalmar Aspect of The HandsssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain StemDocument6 pagesBrain StemsssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal CapsuleDocument4 pagesInternal CapsulesssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting 3Document1 pageAnorexia, Nausea and Vomiting 3sssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergencies in GITDocument7 pagesEmergencies in GITsssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting 2Document1 pageAnorexia, Nausea and Vomiting 2sssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal MassDocument8 pagesAbdominal MasssssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting 1Document5 pagesAnorexia, Nausea and Vomiting 1sssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental MilestonesDocument3 pagesDevelopmental MilestonessssajiPas encore d'évaluation
- NephrologyDocument38 pagesNephrologysssajiPas encore d'évaluation