Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Neurotransmitters and Their Functions
Transféré par
literatelemon59320 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
166 vues5 pagesTitre original
Neurotransmitters and their Functions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
166 vues5 pagesNeurotransmitters and Their Functions
Transféré par
literatelemon5932Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 5
Neurotransmitters and their Functions
Did You Know?
Acetylcholine is the first neurotransmitter to be discovered. It was isolated in 1921 by the German
pharmacologist Otto Loewi.
The transmission of signals from one neuron to another, across the synapse was earlier thought to
be electrical. In 1921, it was confirmed that neurons mostly communicate by releasing certain
chemicals. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters.
So, neurotransmitters allow the nerve impulses or signals to travel across the synapse. A synapse is
a small gap or junction between two neurons, or a neuron and a muscle cell. The credit for
discovering the chemical transmission of nerve impulses goes to Sir Henry Dale (an English
pharmacologist and physiologist) and Otto Loewi (a German pharmacologist). Both of them shared
the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1936 for their work on neurotransmitters.
Types of Neurotransmitters
There are several types of neurotransmitters, and each one of them is responsible for some specific
functions. Neurotransmitters are usually classified as amino acids, peptides, and monoamines.
The neurotransmitters that fall into the category of amino acids are:
? Glutamate
? Aspartate
? Glycine
? D-serine
? Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
The most important monoamines or other biogenic amines that are considered as neurotransmitters
are:
? Serotonin
? Norepinephrine
? Epinephrine
? Histamine
? Melatonin
A large number of neurotransmitters fall into the category of peptides, of which a few important
ones are:
? Beta-endorphin
? Opioid peptides
? Somatostatin
? Calcitonin
? Vasopressin
? Oxytocin
? Glucagon
Apart from these, there are several other important neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine,
dopamine, adenosine, and nitric oxide. So far, about 50 neuroactive peptides have been discovered.
Sometimes, neurotransmitters are also classified as excitatory and inhibitory. This classification
is based on their actions on the neurons. Excitatory neurotransmitters are those that excite the
neurons and stimulate the brain, while inhibitory neurotransmitters are known for having a calming
effect on the brain.
Neurotransmitters like, GABA and serotonin come under the category of inhibitory
neurotransmitters, while epinephrine and norepinephrine are the excitatory neurotransmitters.
Dopamine on the other hand, can act as an excitatory, as well as an inhibitory neurotransmitter.
However, the effect of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell depends on the receptors
present in it. For some neurotransmitters, like glutamate, the important receptors have excitatory
properties. On the other hand, most of the important receptors produce an inhibitory effect for
GABA. But there are some neurotransmitters, for which both types of receptors exist.
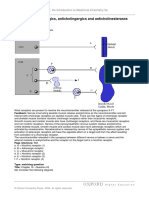
Neurotransmitters and the Transmission of Nerve Impulses
Nerve cells or neurons communicate messages by transmitting nerve impulses. The impulses
travel from one neuron to another neuron or body cell by the movement of the neurotransmitters. A
nerve impulse traveling through the axon (a long, slender projection arising from the nerve cell)
eventually reaches the axon terminal, and then the synaptic knob or terminal button.
The synaptic knobs are the slightly swollen tips of the branches that arise from an axon. They
contain the neurovesicles, which store and release neurotransmitters. For transmitting impulses,
neurons form a specialized structure, called synapse. It serves as a junction where impulses or
information can flow from one neuron to another.
There are basically three elements of a synapse, a presynaptic membrane of the signal-passing
neuron (usually found in the synaptic knob of an axon), the postsynaptic membrane found in a
dendrite or a target cell, and a synaptic cleft. A synaptic cleft is the space between the presynaptic
and post synaptic membranes.
When an impulse reaches the synaptic knob of the signal-passing or presynaptic neuron,
neurotransmitter molecules are released into the synaptic cleft by the neurovesicles. The
neurotransmitter molecules then diffuse and float across the synaptic cleft, in order to bind to the
receptors embedded in the postsynaptic membrane. The neurotransmitter molecules are then
internalized by the postsynaptic cell, and thus the nerve impulse is carried forward.
Important Neurotransmitters & Their Functions
As mentioned already, about 50 neurotransmitters have been discovered so far. Out of these, a few
of the most important neurotransmitters and their functions are discussed below.
Acetylcholine
This neurotransmitter was discovered in the year 1921, by Otto Loewi. It is mainly responsible for
stimulating muscles. It activates the motor neurons that control the skeletal muscles. It is also
concerned with regulating the activities in certain areas of the brain, which are associated with
attention, arousal, learning, and memory. People with Alzheimer's disease are usually found to have
a substantially low level of acetylcholine.
Dopamine
Dopamine is the neurotransmitter that controls voluntary movements of the body, and is associated
with the reward mechanism of the brain. In other words, dopamine regulates the pleasurable
emotions.
It is not a top secret that being overweight has become a planet-large epidemic. Along with typical
concerns of clothes not fitting, insufficient power, and low confidence, being above-weight can cause
dramatic boosts in diabetic issues, heart disease, stroke, arthritis and cancer and despression
symptoms.
This product is an amazing product and will get you awesome results. Try it and see!
Drugs like cocaine, heroin, nicotine, opium, and even alcohol increase the level of this
neurotransmitter. A significantly low level of dopamine is associated with Parkinson's disease, while
the patients of schizophrenia are usually found to have excess dopamine in the frontal lobes of their
brain.
Serotonin
Serotonin is an important inhibitory neurotransmitter, which can have a profound effect on emotion,
mood, and anxiety. It is involved in regulating sleep, wakefulness, and eating. It plays a role in
perception as well. The hallucinogenic drugs like LSD actually bind to the serotonin receptor sites,
and thereby block the transmission of nerve impulses, in order to alter sensory experiences.
A significantly low level of serotonin is believed to be associated with conditions like depression,
suicidal thoughts, and obsessive compulsive disorder. Many antidepressants work by affecting the
level of this neurotransmitter.
Gamma-aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that slows down the activities of the neurons, in order to
prevent them from getting over excited. When neurons get over excited, it can lead to anxiety. GABA
can thus help prevent anxiety.
GABA is a non-essential amino acid, that is produced by the body from glutamate. A low level of
GABA can have an association with anxiety disorders. Drugs like Valium work by increasing the level
of this neurotransmitter. Alcohol and barbiturates can also influence GABA receptors.
Glutamate
Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter that was discovered in 1907 by Kikunae Ikeda of Tokay
Imperial University. It is the most commonly found neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
Glutamate is mainly associated with functions like learning and memory. An excess of glutamate is
however, toxic for the neurons. An excessive production of glutamate may be related to the disease,
known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or Lou Gehrig's disease.
http://plexuslafayette.com/
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
Epinephrine (also known as adrenaline) is an excitatory neurotransmitter, that controls attention,
arousal, cognition, and mental focus. Norepinephrine is also an excitatory neurotransmitter, and it
regulates mood and physical and mental arousal. An increased secretion of norepinephrine raises
the heart rate and blood pressure.
Endorphins
Endorphins are the neurotransmitters that resemble opioid compounds, like opium, morphine, and
heroin in structure. The effects of endorphins on the body are also quite similar to the effects
produced by the opioid compounds. In fact, the name 'endorphin' is actually the short form for
'endogenous morphine'.
Like opioids, endorphins can reduce pain, stress, and promote calmness and serenity. The opioid
drugs produce similar effects by attaching themselves to the endorphin receptor sites. Endorphins
enable some animals to hibernate by slowing down their rate of metabolism, respiration, and heart
rate.
Melatonin
It is the hormone produced by the pineal gland that also acts as a neurotransmitter. It basically
controls the sleep-wake cycle. It is also associated with controlling mood and sexual behavior. The
production of melatonin is dependent on light. Light to the retina inhibits the production of
melatonin, while darkness has a stimulating effect on its production.
Nitric Oxide
It is a gas that acts both as a hormone and neurotransmitter, depending on the specific requirement.
It can cause the blood vessels to dilate, besides preventing the formation of clots. This in turn, can
promote the circulation of blood. Nitric oxide can increase the level of oxygen in the body, and
improve memory, learning, alertness, and concentration. It is also responsible for causing the
smooth gastrointestinal muscles to relax.
To sum up, neurotransmitters are chemicals that allow the nerves to communicate with each other,
and thus, regulate the various functions of the body. A substantially high or low level of these
chemicals can alter the functions of the entire nervous system.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- NeurotransmittersDocument2 pagesNeurotransmittersShaheen Mogral ArimalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Med Surg Chapter 65 Flashcards - QuizletDocument17 pagesMed Surg Chapter 65 Flashcards - QuizletMonica JubanePas encore d'évaluation
- CNS NeurotransmittersDocument30 pagesCNS Neurotransmittersdevanshi_582262183100% (1)
- H1 - Neural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionDocument9 pagesH1 - Neural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionAlexandra Nicole EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Psychopathology Book NotesDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Psychopathology Book NotesZohaib Ahmad100% (1)
- Spiritual Karma Magazine 68. Published by Swamiji Sri Selvam Siddhar-Dr Commander Selvam-Shiva Vishnu TempleDocument72 pagesSpiritual Karma Magazine 68. Published by Swamiji Sri Selvam Siddhar-Dr Commander Selvam-Shiva Vishnu Templetexastemple100% (2)
- Fall Final Exam Concepts ReviewDocument9 pagesFall Final Exam Concepts ReviewColeton GPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell ReceptorsDocument10 pagesCell ReceptorsMaria PavalPas encore d'évaluation
- PSYC 3600 Final Exam Questions (Spring 2021Document23 pagesPSYC 3600 Final Exam Questions (Spring 2021Sandip AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Quizzes: Physiology Prelims Compiled SamplexDocument67 pagesPost Quizzes: Physiology Prelims Compiled SamplexMcycy Mi100% (1)
- Discussion Questions - Chapter 2Document6 pagesDiscussion Questions - Chapter 2nlenz94Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsDocument35 pagesLecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsakramuddaulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem1. revisionSLDocument84 pagesSem1. revisionSLRawanMazen SharifPas encore d'évaluation
- Biopsycho QuestionsDocument4 pagesBiopsycho QuestionsArianne PicanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 Q3 Week 3Document10 pagesScience 10 Q3 Week 3John ver PitaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Neural DarwinismDocument11 pagesNeural DarwinismRodrigoPristaPas encore d'évaluation
- MDMA PowerpointDocument16 pagesMDMA Powerpointapi-26938624Pas encore d'évaluation
- Personality Theory Paper Ted BundyDocument19 pagesPersonality Theory Paper Ted Bundyapi-34679413550% (2)
- Neurophysiology: Dr. Irbab HawariDocument32 pagesNeurophysiology: Dr. Irbab Hawaritrisna satriana100% (1)
- Exploring Theories of Archean-Age Gold-Quartz Vein Systems FormationDocument16 pagesExploring Theories of Archean-Age Gold-Quartz Vein Systems FormationAhmed ElhadadPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurotransmisson AVSDocument1 pageNeurotransmisson AVSHeliodor van ScriverPas encore d'évaluation
- Asi - Helen Shen - The Hard Science of OxytocinDocument3 pagesAsi - Helen Shen - The Hard Science of OxytocinOza ArikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutritionalmanagementof Behaviorandbrain DisordersindogsandcatsDocument17 pagesNutritionalmanagementof Behaviorandbrain Disordersindogsandcatsluqui guzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- H-Unit 05-B.Pharmacy 4th Semester - Pharamcology.Document3 pagesH-Unit 05-B.Pharmacy 4th Semester - Pharamcology.raviomj100% (1)
- In Silico Studies Predict Amaranthus tricolor's Effect on Alzheimer's PathwaysDocument13 pagesIn Silico Studies Predict Amaranthus tricolor's Effect on Alzheimer's PathwaysvinayPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Paper 3 TZ1 HL Markscheme PDFDocument26 pagesBiology Paper 3 TZ1 HL Markscheme PDFXiang SizhePas encore d'évaluation
- 06.a Happy HormonesDocument2 pages06.a Happy Hormones박소이Pas encore d'évaluation
- Η Ενδογενής Διμεθυλοτρυπταμίνη (DMT) ως πιθανός βιολογικός μεσολαβητής της σχέσης μεταξύ Στρες και των θετικών συμπτωμάτων της ΨύχωσηςDocument7 pagesΗ Ενδογενής Διμεθυλοτρυπταμίνη (DMT) ως πιθανός βιολογικός μεσολαβητής της σχέσης μεταξύ Στρες και των θετικών συμπτωμάτων της ΨύχωσηςGrigoris DeoudisPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 19 Test Bank PatrickDocument41 pagesChapter 19 Test Bank PatrickAmir ali WalizadehPas encore d'évaluation
- Per Brodal - The Central Nervous System - Structure and Function (2004, Oxford University Press)Document532 pagesPer Brodal - The Central Nervous System - Structure and Function (2004, Oxford University Press)AlejandroPas encore d'évaluation