Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Air Conditioning System
Transféré par
NurFarahinZakariah0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
121 vues46 pagesabout the sysetem of airconditioning
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentabout the sysetem of airconditioning
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
121 vues46 pagesAir Conditioning System
Transféré par
NurFarahinZakariahabout the sysetem of airconditioning
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 46
AIR-CONDITIONING SYSTEM
MOHD SAFWAN SAIFFUDIN AB100039 (Leader)
LOW HUI CHING AB100038
MUHAMMAD AZIZI BIN HAMZAH AB100042
SITI NURMAZIAN BINTI HASIM AB100051
TANG ZHI LIN AB100054
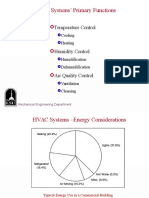
Introduction
Air conditioning- process of conditioning closed spaces and
places:
AIR
CONDITIONING
Air
temperature
Humidity Air purity
Distribution
Humidification
Dehumidification
Heating
Cooling
Requires
mechanical
ventilation
(eg. AHU) to
distribute
treated air
To ensure
air purity
*heating does not take place in tropical countries
Reasons for Air-conditioning
To ensure stable comfort level
Normal ventilation is not suitable under
certain circumstances,
compact spaces (eg. Cinemas, theatres
and halls)
Limited spaces (eg. Offices)
A) COMFORT
B) Performance
C) Health
D) Sensitive Equipment
Reasons for Air-conditioning
To improve the comfort of workers
improving productivity
Production process in factories
Chocolate factories require refrigeration to avoid
chocolate from melting
B) PERFORMANCE
A) Comfort
C) Health
D) Sensitive Equipment
Reasons for Air-conditioning
Pollution, rapid urbanization and
industrialization, noise pollution, raised air
temperatures
Isolated indoor spaces from outdoor, free
from contaminants and noise
C) HEALTH
A) Comfort
B) Performance
D) Sensitive Equipment
Reasons for Air-conditioning
Computers, electronic equipment, lenses
Equipment that are used in the production
of micro-chips and photonics components
D) SENSITIVE
EQUIPMENT
A) Comfort
B) Performance
C) Health
Importance of air-conditioning
Remove excess heat
Provide sufficient ventilation
Humidity control
Air distribution to achieve human comfort
Unit System
Plant System
Multi Space
System
Solar Powered
Systems
Window Unit
Packaged Unit
Split Unit
Centralised
Plant
Decentralised
Plants
Types of Air Conditioning Systems
CENTRALISED UNIT
SPLIT UNIT
A) Split Unit
Comprises of two parts
i. Outdoor Condensing Unit
ii. Indoor Fan Coil Unit
Use in
Outdoor
Condensing
Unit
Indoor Fan Coil Unit
Air cond controller:
-control indoor temperature
-turn on or off of the air con
B) CENTRALISED SYSTEM
One outdoor unit to cool multiple indoor units
Comprises of cooling tower, Ahu room, Chiller room etc.
Indoor units: using same type of indoor unit
Used for almost all spaces provided in Angsana, except
2 types of
indoor unit
found in
Angsana
Only maintenance and staff office is using split unit air conditioning system. Other spaces using
Central air conditioning system.
Building Management
System
The centralised system is controlled
by BMS. The control room is located
in ground floor level, which is beside
the admin office.
Almost all building services system is
controlled in that room, including
air-con
Building service system is taken control in Security room.
I) Cooling Tower
Cooling towers are used in central air conditioning systems.
The function of the cooling tower is to cool the warm water
from the chiller condenser.
The cooling tower is at the final point of the heat transfer.
There are basically 2 types of designs:
-Cross Flow
-Counter Flow
Cross Flow Design
The cooling tower for this type of design is usually shaped like a
box.
This process happens over and over.
Roof Plan
Water tank for
air conditioning system
Sodium hydroxide:
- treatment for rust on the
inside walls of the towers.
- to maintain recirculated
water pH
Water Treatment
In cooling towers, the cooling effect is achieved by
evaporation of a portion of the water passing through it.
If the contaminants are not controlled, they can cause scaling,
corrosion, and sludge accumulations which can reduce heat
transfer efficiencies.
In order to control the concentrations, it is necessary to bleed
a small amount of circulating water from the system and top
up with fresh water.
The growth of algae, and other microorganisms can reduce
system efficiency and may even contribute to potentially
health hazards.
Biocides are used to treat the water to control the biological
growths.
AHU
*known as air handler, or air
handling unit
* is a device used to condition
and circulate air as part of a
heating, ventilating, and air-
conditioning (HVAC) system.
* a large metal box containing a
blower, heating or cooling
elements, filter racks or
chambers, sound attenuators,
and dampers.
* connect to a ductwork
ventilation system that
distributes the conditioned air
through the building and returns
it to the AHU. Sometimes AHUs
discharge (supply) and admit
(return) air directly to and from
the space served without
ductwork.
ducting of air distribution in Angsana plaza is confidential.
But the AHU only distribute cold air to particular area.
Construction
*Air handler is
normally constructed
around a framing
system with metal infill
panels as required to
suit the configuration
of the components.
* This may be done by means
of a visual display using a
pressure gauge, or by a
pressure switch linked to an
alarm point on the building
control system.
* Failure to replace a filter
may eventually lead to its
collapse, as the forces
exerted upon it by the fan
overcome its inherent
strength, resulting in collapse
and thus contamination of
the air handler and
downstream ductwork.
Cooling elements
*Indirect coils chilled
water for cooling (prime
energy for heating and
cooling is provided by
central plant elsewhere
in the building).
* Coils are typically
manufactured from
copper for the tubes,
with copper or
aluminium fins to aid
cold transfer.
* Cooling coils will also
employ eliminator plates
to remove and drain
condensate., and the
chilled water is provided
by a central chiller.
Blower/fan
Mechanical fan
*Air handlers
typically employ
a large squirrel
cage blower
driven by an AC
induction
electric moto.
Chiller Room
Basement
6 chillers
- 5 chillers with
500 tan
- 1 chiller with
300 tan
Chilled water pump
Condenser water
pump
Air conditioning
main board
Chiller
Machine that removes heat from a liquid via a vapor-compression
or absorption refrigeration cycle. This liquid can then be circulated
through a heat exchange to cool air or equipment as required.
Chiller
In air conditioning systems, chilled water is typically
distributed to heat exchangers, or coils, in air handling units,
or other type of terminal devices which cool the air in its
respective space
Chilled water is re-circulated back to the chiller to be cooled
again.
Cooling coils transfer heat from the air to the chilled water,
thus cooling and usually dehumidifying the air stream.
A typical chiller for air conditioning applications is rated
between 15 to 1500 tons (180,000 to 18,000,000 BTU/h or 53
to 5,300 kW) in cooling capacity.
Chilled water temperatures can range from 35 to 45 degrees
Fahrenheit (1.5 to 7 degrees Celsius).
3 units of cooling tower for a functioning chiller.
Air Conditioning Main Board
Main board
Over current relay
- maintain every two
years
- programmable inputs
and outputs
- comprehensive self-
monitoring
- compact multi-function
numerical relay
Busbar Coupler
Main board for 300 tan
chiller
Main board for 500 tan
Chiller, overcurrent relay,
Busbar coupler
Overcurrent relay Manual switch for chillers
Basic Chilled Water Pumping System
Keeping pressure in the chilled water network constant and
to suck the chilled water from the chillers.
Chilled Water Pump
Control strategy
Enabled chilled water pump when outside air temperature is
above setpoint and at least 1 chilled water coil control valve is
open to coil.
Enable chiller after flow is proven. Chiller operates to
maintain leaving chilled water temperature at setpoint.
Coil valves modulate to maintain comfortable space
conditions.
Chilled Water Pump
6 chilled water pumps
The number and the
running speed of the
pumps are determined by
the cooling load of the
building at the particular
time. Eg. How much
chilled water is needed.
Chiller Room
Related Services
For an efficient air-conditioning system, 3 building services are
important:
Electricity supply (The electric bill for Angsana is around RM
460,000 , and air con system comprises 60% of them)
for air-conditioning systems need to be 3 phase.
To avoid high starting current
Switch on certain AHU at each level
And then chiller
Air conditioning system controlled by BMS (Building
Management Service)
Start with the AHU for office at 7.30am
9.30am for other AHU
Not all AHU switch whole day. Certain AHU certain time.
Related Services
Water supply for larger systems like plant rooms water is used
to remove heat.
Water is distributed to the cooling tower under 1420 atm.
Related Services
DUCTING
Spaces necessary for equipment and ducting.
The ducts connect to indoor air con are situated above ceiling.
SOUND INSULATION
Sound insulation wall was constructed in AHU and chiller room.
Chiller room is located at basement to avoid noise transmission.
Air conditioning flow
Chiller Plant Room
Security
Room
Floor Plan
Level One
The floor plan of Angsana is almost the same. Only the
top floor is different.
Maintenance
The technician check on the air conditioning system monthly.
Follow the schedule they have made
Take about 2 weeks to finish checking the whole system.
When there is a breakdown, report and repair follow the grid.
Conclusion
Extensive use of air-conditioning give rise to heat island
Outdoor areas becomes unsuitable in terms of human
comfort
Passive systems should be used where appropriate
Spaces should be provided for air-con equipment such as
cooling tower, AHU room and chiller room especially for
highrise.
Thank you
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Learn About Central Air Conditioning Systems in Under 2 MinutesDocument39 pagesLearn About Central Air Conditioning Systems in Under 2 Minutesmonica singh100% (1)
- Unit-Iv-Air Water SystemDocument6 pagesUnit-Iv-Air Water SystemManjeet CinghPas encore d'évaluation
- ENERGY-EFFICIENT AIR CONDITIONING PRINCIPLESDocument49 pagesENERGY-EFFICIENT AIR CONDITIONING PRINCIPLESShubha100% (1)
- Integration of HVAC SystemsDocument8 pagesIntegration of HVAC SystemsRiya Bansal0% (1)
- Heating Ventilation and Air ConditioningDocument14 pagesHeating Ventilation and Air ConditioningMiahsaheb Rafeeq100% (1)
- Hvac - Centralized AC SystemDocument21 pagesHvac - Centralized AC SystemVala Vraj M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- HVACDocument72 pagesHVACvarshneyrk@rediffmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Air Conditioning UnitsDocument10 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning Unitssnowgalvez44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On AC SystemDocument33 pagesSeminar On AC SystemHassan Elattar0% (1)
- Variable Refrigerant Flow Systems PDFDocument38 pagesVariable Refrigerant Flow Systems PDFRafael SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Air Conditioning Systems PDFDocument29 pages1 - Air Conditioning Systems PDFMayaPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Equipment Guide for Heating and Cooling SystemsDocument16 pagesHVAC Equipment Guide for Heating and Cooling SystemsRahul Prajapati100% (1)
- Residential Cooling Load CalculationDocument24 pagesResidential Cooling Load CalculationAngeloTomalonPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigerants: Engr. William R. Salazar, Pme InstructorDocument45 pagesRefrigerants: Engr. William R. Salazar, Pme InstructorWilliam SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumble DryersDocument20 pagesTumble DryersGrover CondoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Air Conditioning Systems ReviewDocument23 pagesCentral Air Conditioning Systems ReviewlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC System OverviewDocument150 pagesHVAC System OverviewSeth Patrick ArceoPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIC 1: Air-Conditioning Systems: Subtopic: Types of HVAC SystemsDocument32 pagesTOPIC 1: Air-Conditioning Systems: Subtopic: Types of HVAC SystemsMuhammad Fadhil Hilmi NasutionPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC SystemDocument16 pagesHVAC SystemAswini Kumar KhuntiaPas encore d'évaluation
- What is HVAC? Introduction to Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning SystemsDocument50 pagesWhat is HVAC? Introduction to Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Systemssohail parachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classifications of Air Conditioning System: Based On Major FunctionDocument67 pagesClassifications of Air Conditioning System: Based On Major Functionjet latorrePas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigerant Recovery and Recharge of A Room Air Conditioner 170280VDocument9 pagesRefrigerant Recovery and Recharge of A Room Air Conditioner 170280VMathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Testimg Adjusting and Balancing For HVACDocument14 pagesTestimg Adjusting and Balancing For HVACAbdullah.N FAAliPas encore d'évaluation
- Compressors: Basic Classification and Design Overview andDocument20 pagesCompressors: Basic Classification and Design Overview andshihabPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC SystemsDocument20 pagesHVAC SystemsMoshira Abo ElȜellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Humidification Operation and Cooling Tower: Introduction, Performance, and DesignDocument31 pagesHumidification Operation and Cooling Tower: Introduction, Performance, and DesignSafyan ManzoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhPas encore d'évaluation
- Air-Cooled Chillers Maintenance & Inspection ChecklistDocument3 pagesAir-Cooled Chillers Maintenance & Inspection ChecklistdjukalPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument34 pagesAir Conditioning Systemshnslave100% (1)
- Refrigeration SystemDocument38 pagesRefrigeration SystemAdrian Derek IvashkovePas encore d'évaluation
- Air+Conditioning IntroductionDocument59 pagesAir+Conditioning IntroductionKanika PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychrometric ChartDocument63 pagesPsychrometric ChartCutekarthik Subramanian100% (1)
- Heat Wheel: Mohammad Yusuf 13PKB380Document10 pagesHeat Wheel: Mohammad Yusuf 13PKB380Haider Ali100% (1)
- HVAC and Lighting Control PresentationDocument52 pagesHVAC and Lighting Control PresentationEDUARD VI DANDAPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Spec for AHUDocument6 pagesTechnical Spec for AHUreddyrioPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Design I - Class 8Document7 pagesHVAC Design I - Class 8Wyatt C. Lewis100% (1)
- HVAC Design SyllabusDocument6 pagesHVAC Design SyllabusRanganathan .kPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimization of Pumping Systems in HVACDocument30 pagesOptimization of Pumping Systems in HVACBalasundaramSrinivasaRajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- AIR SYSTEM BASICS: THE FUNDAMENTALSDocument11 pagesAIR SYSTEM BASICS: THE FUNDAMENTALSpbhat83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument41 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioningrejeesh_rajendranPas encore d'évaluation
- Fan Coil UnitDocument99 pagesFan Coil UnitUmer FarooqPas encore d'évaluation
- Bsim - VRV - Rishiraj & MoulikDocument11 pagesBsim - VRV - Rishiraj & MoulikRishiraj GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Training - Updated PDFDocument80 pagesHVAC Training - Updated PDFmohamed sharief100% (1)
- Hvac SystemsDocument6 pagesHvac Systems2742481Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic HvacDocument31 pagesBasic HvacRahul Jatrothu NaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Articles About HVAC - Fresh Air and OccupancyDocument13 pagesArticles About HVAC - Fresh Air and OccupancyAnonymous DjWqKpZ1Pas encore d'évaluation
- AHU CHW Coil ConnectionDocument1 pageAHU CHW Coil ConnectionMULTIKARTHI07100% (1)
- Hvac QuestionsDocument4 pagesHvac Questionssyedkaleem55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Air Conditioning Processes Illustrated On A Psychrometric ChartDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning Processes Illustrated On A Psychrometric Chartvv260513Pas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration: "Refrigeration Is The Process of Removing Heat From An Enclosed Space, orDocument16 pagesRefrigeration: "Refrigeration Is The Process of Removing Heat From An Enclosed Space, ordjgondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Air ConditioningDocument22 pagesAir ConditioningEmmanuel BuhwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Conditioning Is The Removal of Heat FromDocument8 pagesAir Conditioning Is The Removal of Heat FromShee JaPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Conditioning SystemsDocument19 pagesAir Conditioning SystemskatherinewingettPas encore d'évaluation
- Hvac System: Lecture No 1Document55 pagesHvac System: Lecture No 1Pankaj AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Group Presentation: History, Components, and ApplicationsDocument36 pagesHVAC Group Presentation: History, Components, and Applicationsaishwarya903100% (2)
- Air Conditioning PPT of EMEDocument24 pagesAir Conditioning PPT of EMEDineshKumar VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Equipment: MAE 406 Energy Conservation in Industry Stephen TerryDocument29 pagesHVAC Equipment: MAE 406 Energy Conservation in Industry Stephen TerrySuresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Conditioning of Small BuildingsDocument26 pagesAir Conditioning of Small BuildingsAADIL AHMED APas encore d'évaluation
- Hvac System and Fire Sprinkerler SystemsDocument14 pagesHvac System and Fire Sprinkerler SystemsTatheer ZahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengan Nama Allah Yang Maha Pemurah Lagi Maha Penyayang.Document68 pagesDengan Nama Allah Yang Maha Pemurah Lagi Maha Penyayang.Krisyen Murali TharanPas encore d'évaluation
- TNB Guideline To Build Carpark Under PylonDocument4 pagesTNB Guideline To Build Carpark Under PylonNurFarahinZakariahPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Filling CCC Forms May08Document9 pagesGuide To Filling CCC Forms May08JohnyReubenPas encore d'évaluation
- China HK ConsCostBook 2K3Document64 pagesChina HK ConsCostBook 2K3NurFarahinZakariahPas encore d'évaluation
- Documentation Projects, Part 1Document34 pagesDocumentation Projects, Part 1NurFarahinZakariahPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.2 BiophiliaDocument24 pages5.2 BiophiliaNurFarahinZakariahPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of DPWH Standard Specs and Min Test RequirmentDocument34 pagesSummary of DPWH Standard Specs and Min Test Requirmentcharlee_05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Servo Coat 120Document1 pageServo Coat 120BhaveshBalasPas encore d'évaluation
- Conte O Conte: NewgreenDocument2 pagesConte O Conte: NewgreenajoilhamPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.buettner, D.R. & Becker, R.JDocument141 pages1.buettner, D.R. & Becker, R.Jchetcuti_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- FoundryDocument17 pagesFoundryMuhd Shabeeb APas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Properties of SteamDocument35 pages01 Properties of SteamDeepanshu Sehgal100% (1)
- Pushover AnalysisDocument12 pagesPushover AnalysisabdulmananPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Insights Into The Effect of ITZ and Aggregate Strength On Concrete PropertiesDocument11 pagesNumerical Insights Into The Effect of ITZ and Aggregate Strength On Concrete PropertiesAndres ForeroPas encore d'évaluation
- IG Seismic Design HousesDocument36 pagesIG Seismic Design HousesmarkPas encore d'évaluation
- Deformation R01Document1 pageDeformation R01famfu94Pas encore d'évaluation
- P Tel LST 970 30002 3 Rlmu F - SDocument8 pagesP Tel LST 970 30002 3 Rlmu F - SBenkhira HoucinePas encore d'évaluation
- Tec066 6700 PDFDocument2 pagesTec066 6700 PDFExclusivo VIPPas encore d'évaluation
- KONE Indo Elevator Technical Spec Project TambunDocument2 pagesKONE Indo Elevator Technical Spec Project TambunSaidAnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- EductorsDocument1 pageEductorscesar luis gonzalez rodriguez100% (1)
- C17 Raapdx CDocument12 pagesC17 Raapdx ClavyPas encore d'évaluation
- As 2601 en E Series Valves and ManifoldsDocument52 pagesAs 2601 en E Series Valves and ManifoldsdbmingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast-5211 NT PdsDocument2 pagesFast-5211 NT PdsGino TironiPas encore d'évaluation
- Kwality Cable India: Manufacturer Quality PlanDocument3 pagesKwality Cable India: Manufacturer Quality PlanTrivesh SPas encore d'évaluation
- Muthalagu 2021Document9 pagesMuthalagu 2021Mechanical Engg. Alagappa Poly College,KaraikudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimum Design of Wide Span Cable-Stayed Roof StructuresDocument13 pagesOptimum Design of Wide Span Cable-Stayed Roof StructuresAndrés Juárez SánchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Rubber Pad FormingDocument15 pagesRubber Pad FormingAdula Rajasekhar67% (3)
- Do Mai Lam PHD Thesis. Vapor Phase SolderingDocument105 pagesDo Mai Lam PHD Thesis. Vapor Phase SolderingDo Mai LamPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspen Flare System AnalyzerDocument10 pagesAspen Flare System Analyzerharyonodaniel50% (2)
- Tribology in OrthopaedicsDocument60 pagesTribology in OrthopaedicsRavishanker Baliga100% (1)
- Technical Guide enDocument56 pagesTechnical Guide enCioplea Zamfirescu MihaelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ual2018 M08014300061Document78 pagesUal2018 M08014300061Bayu SetiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic House PackageDocument3 pagesBasic House PackageSudheer KmPas encore d'évaluation
- Method of Statement For Sealing Off The Unused Existing Slab OpeningDocument3 pagesMethod of Statement For Sealing Off The Unused Existing Slab OpeningAzumiPas encore d'évaluation
- Science GR 345 1st Quarter MG Bow 1Document10 pagesScience GR 345 1st Quarter MG Bow 1api-359551623Pas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee Department of Civil Engineering CEN 305 Design of Steel Elements Tutorial No. 1Document1 pageIndian Institute of Technology Roorkee Department of Civil Engineering CEN 305 Design of Steel Elements Tutorial No. 1Mayank RajPas encore d'évaluation