Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Fabrication Process 1
Transféré par
Mahabub Hossain0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues7 pagesFabrication, Silicon manufacture, oxidation, process
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentFabrication, Silicon manufacture, oxidation, process
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues7 pagesFabrication Process 1
Transféré par
Mahabub HossainFabrication, Silicon manufacture, oxidation, process
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
Semiconductor Fabrication
Md. Mahabub Hossain
Oxidation
Lithography &
Etching
Ion Implantation
Annealing &
Diffusion
Introduction
Silicon Growth
& Wafer
Quartz, or silica, consists of silicon dioxide
Sand contains many tiny grains of quartz
Silicon can be artificially produced by combining silica and carbon in electric furnace
Gives polycrystalline silicon (multitude of crystals)
Practical integrated circuits can only be fabricated from single-crystal material
Silicon Crystal & Growth
Growth
A solid seed crystal is rotated and
slowly extracted from a pool of
molten Si.
Requires careful control to give
crystals desired purity and
dimensions.
Czochralski process is a technique in making single-crystal silicon.
Wafer Manufacturing
The silicon crystal is sliced in ingot by using a diamond-tipped saw into thin wafers
Sorted by thickness
Damaged wafers removed during lapping
Etch wafers in chemical to remove any remaining crystal damage
Polishing smoothes uneven surface left by sawing process
Oxidation of Silicon
SiO
2
growth is a key process step in
manufacturing all Si devices
- Thick (~1m) oxides are used for field
oxides (isolate devices from one another )
- Thin gate oxides (~100 ) control MOS
devices
- Sacrificial layers are grown and removed to
clean up surfaces
The stability and ease of SiO
2
formation is one
of the reasons that Si replaces Ge as the
semiconductor of choice.
The simplest method of
producing an oxide layer
consists of heating a silicon
wafer in an oxidizing
atmosphere.
Dry oxide - Pure dry oxygen is employed
Si + O
2
SiO
2
Disadvantage
- Dry oxide grows very slowly.
Advantage
- Oxide layers are very uniform.
- Relatively few defects exist at the oxide-
silicon interface.
- It has especially low surface state charges and
thus make ideal dielectrics.
Wet oxide - Same way as dry oxides, but
steam is injected
Si +2H
2
O SiO
2
+ 2H
2
Disadvantage
-Hydrogen atoms liberated by the
decomposition of the water molecules
produce imperfections that may degrade the
oxide quality.
Advantage
-Wet oxide grows fast.
-Useful to grow a thick layer of field oxide.
Oxidation of Silicon
Si Wafers
O
2
N
2
H
2
O or TCE(trichloroethylene)
Quartz tube
Resistance-heated furnace
Flow
controller
Oxidation of Silicon
Estimation
(a) How long does it take to grow
0.1m of dry oxide at 1000
o
C ?
(b) How long will it take to grow
0.2m of oxide at 900
o
C in a wet
ambient ?
Solution:
(a) From the 1000
o
C dry curve, it
takes 2.5 hr to grow 0.1m of oxide.
(b) Use the 900
o
C wet curve only. It
would have taken 0.7hr to grow the
0.1 m oxide and 2.4hr to grow 0.3
m oxide from bare silicon. The
answer is 2.4hr0.7hr = 1.7hr.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Capillary Pen Part1Document4 pagesCapillary Pen Part1Mahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- BiCMOS FabricationDocument7 pagesBiCMOS FabricationMahabub Hossain100% (1)
- Semiconductor FabricationDocument20 pagesSemiconductor FabricationMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Pauli Exclusion PrincipleDocument3 pagesPauli Exclusion PrincipleMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Fabrication Process 2Document5 pagesFabrication Process 2Mahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Pinned PhotodiodeDocument6 pagesPinned PhotodiodeMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Developments in Lens DesignDocument12 pagesCurrent Developments in Lens DesignMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Reluctance: I. Magnetic Circuit ConceptDocument12 pagesReluctance: I. Magnetic Circuit ConceptMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Book of Class 9-10Document308 pagesMath Book of Class 9-10boidamataPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Focusing Via An Oscillating Liquid Lens: Group MembersDocument13 pagesFast Focusing Via An Oscillating Liquid Lens: Group MembersMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Alcohol and Pork Is Prohibited in Islam?Document9 pagesWhy Alcohol and Pork Is Prohibited in Islam?Mahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Appl MOS DesignDocument9 pagesAppl MOS DesignMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Imdad-Sitara Khan Scholarship RulesDocument3 pagesImdad-Sitara Khan Scholarship RulesMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratelist GreyDocument711 pagesRatelist GreyMahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics InvertersDocument37 pagesPower Electronics Inverterskupps65Pas encore d'évaluation
- Why Alcohol and Pork Is Prohibited in Islam?Document9 pagesWhy Alcohol and Pork Is Prohibited in Islam?Mahabub HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- ZoologyDocument46 pagesZoologyRahul Kumar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 3071 2020 Textiles-Determination of PH of Aqueous Extract BZ-244Document12 pagesISO 3071 2020 Textiles-Determination of PH of Aqueous Extract BZ-244tsing takPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Instruction For Pluging Redundant Holes in Structural MembersDocument5 pagesWork Instruction For Pluging Redundant Holes in Structural MembersRakesh RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQsDocument8 pagesMCQsAsad MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Res Guide Electromagnetic WavesDocument8 pagesRes Guide Electromagnetic WavesbrsreddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics For Chemists, GlasstoneDocument533 pagesThermodynamics For Chemists, GlasstoneRowie Carpio100% (2)
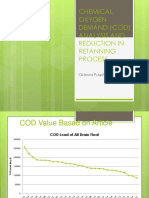
- COD Anaysis and ReductionDocument13 pagesCOD Anaysis and ReductionelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gymcol Adhezive IdeasDocument68 pagesGymcol Adhezive Ideasdanalin_ursu_8976885Pas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Conv Belt - 1800-ST2250-8+6 FR-LRR-TKIL-NK ProjectDocument1 pageSteel Conv Belt - 1800-ST2250-8+6 FR-LRR-TKIL-NK ProjectCaspian DattaPas encore d'évaluation
- NIA Mechanical Insulation Appraisal: NAIMA 3E Plus ProgramDocument7 pagesNIA Mechanical Insulation Appraisal: NAIMA 3E Plus ProgramAvi NashPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Sixteen Cell SignalingDocument96 pagesChapter Sixteen Cell SignalingRu LiliPas encore d'évaluation
- 12ME2201 - ENGINEERING MECHANICS - SolutionsDocument6 pages12ME2201 - ENGINEERING MECHANICS - SolutionsgkgjPas encore d'évaluation
- AFR - Turbine PDFDocument20 pagesAFR - Turbine PDFChetanPrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Hemp Shiv On Cement Setting and HardeningDocument10 pagesImpact of Hemp Shiv On Cement Setting and HardeningscottalumilePas encore d'évaluation
- TSL 230Document7 pagesTSL 230alexmradPas encore d'évaluation
- ItpDocument2 pagesItpVinay YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Experimental Investigation On Black Cotton Soil Treated With Terrabind Chemical and Glass PowderDocument12 pagesExperimental Investigation On Black Cotton Soil Treated With Terrabind Chemical and Glass PowderIJRASETPublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalase Lab Project PosterDocument1 pageCatalase Lab Project Posterapi-411085091Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cdna12526enc 001Document170 pagesCdna12526enc 001Anonymous 1hOgJqwZuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiberglass TerminologyDocument13 pagesFiberglass Terminologystang2001gurlPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Thermodynamics Y: David A. KatzDocument44 pagesChemical Thermodynamics Y: David A. Katztheodore_estradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Propagation in Fluid-Filled Single-Walled Carbon PDFDocument13 pagesWave Propagation in Fluid-Filled Single-Walled Carbon PDFhmsedighi459Pas encore d'évaluation
- PSV 430066 PDFDocument41 pagesPSV 430066 PDFErikikoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ensival MoretDocument6 pagesEnsival MoretPatricia J ÁngelesPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Reinforcement and Glass Fibre Reinforced PolymerDocument9 pagesConcrete Reinforcement and Glass Fibre Reinforced PolymerchanakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Portland Limestone CementDocument38 pagesPortland Limestone CementNajeeb Manhanpally M100% (3)
- PPU NotesDocument38 pagesPPU Noteswadhwachirag524Pas encore d'évaluation
- Princípio de Babinet 1Document3 pagesPrincípio de Babinet 1josh16kalebPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Fusion PowerDocument11 pagesNuclear Fusion PowerAndré RebelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Chemistry Sk025 (Ain Bashirah - b3t9) - 2Document23 pagesAssignment Chemistry Sk025 (Ain Bashirah - b3t9) - 223005852Pas encore d'évaluation