Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
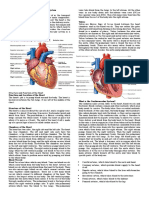
Heart:: Membrane. Similarly Ventricles Are Divided Into Right and Left Ventricles by A Thick Membrane Called
Transféré par
ianglennTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Heart:: Membrane. Similarly Ventricles Are Divided Into Right and Left Ventricles by A Thick Membrane Called
Transféré par
ianglennDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
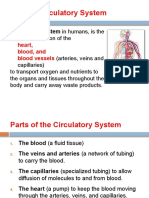
Circulatory System
The circulatory system is made up of the heart, blood and blood vessels known as arteries,
capillaries and veins. The heart pumps blood throughout your body through the blood vessels.
Blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to cells and carries away carbon dioxide and other waste
materials.
The Human Circulatory System and How it works
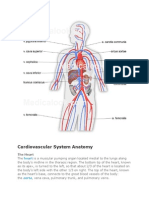
1. Heart:
Heart is of the size of the fist and is built with the muscles which is situated in the rib cage between
the lungs.
Chambers of the Heart:
It consists of four chambers of which upper two chambers are called as auricles and lower two
chambers as ventricles.
Auricles are divided as right and left auricles by a thin membrane know as intra auricular
membrane. Similarly ventricles are divided into right and left ventricles by a thick membrane called
as intraventricular membrane. Auricles and ventricles are separated by a auriculoventricular
membrane. Pacemakers namely sinoauricular node (SA node) and auriculoventricular node (AV
node) are present which stimulate the functioning of the heart.
Right auricle receives the deoxygentaed blood from various parts of the body. Oxygentaed blood
from lungs is brought to left auricle by the pulmonary vein. Deoxygentaed blood from right auricle is
pumped into right ventricle and this blood is pumped to lungs by the pulmonary artery. Oxygentaed
blood from left auricle is pumped to left ventricle and this blood is supplied to all body parts.
2. Blood Vessels:
Blood vessels are thin pipe like structures which supply the blood to the heart and receives impure
blood from body parts. Blood vessels are of two types namely arteries and veins.
Arteries:
Arteries supply oxygentaed blood from the left ventricle to all parts of the body. These arteries divide
into arterioles and end as capillaries in the cells. Pulmonary artery supplies deoxygenated blood from
right ventricle to lungs.
Veins:
Veins collect deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body. They start as capillaries, then to veinlets
and to larger veins finally. Pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from lungs to left auricle.
3. Blood:
Blood is a fluid connective tissue which is red in colour due to the presence of haemoglobin. Our
body contains 5-6 litres of blood. The main components of the blood are plasma and blood cells.
Plasma:
Plasma constitutes 55% of the blood and is light yellow coloured liquid containing water, salts and
plasma proteins.
Blood cells:
Blood cells constitute 45% of the blood. They float in plasma and are of three types. They are red
blood cells, white blood cells and blood platelets.
Red Blood Corpuscles:
They are also known as erythrocytes. RBC are round in shape and disc shaped with constriction in
the middle. They contain a pigment called as haemoglobin. They do not contain nucleus. The life
span of RBC is 120 days.
White Blood Corpuscles:
They are also known as leukocytes. They are of differenet shapes. WBC contains nucleus. WBC are
classified as granulocytes and agranulocytes based on the presence of granules in their cells. They do
not contain haemoglobin and hence are white in colour. They attack the microorganisms which enter
our body and protects us from diseases. Their lifespan is 12 days.
Agranulocytes:
Lymohocytes and monocytes belongs to agranulocytes as they do not contain granules in their cells.
Kidney shaped nucleus is present in them. Monocytes are called as macrophages.
Granulocytes:
Eosinophils (acidophils), basophils and neutrophils belong to granulocytes as they contain granules.
Their nucleus is lobed.
Blood platelets:
Blood platelets are called as thrombocytes and are small and oval in shape. They do not contain the
pigment and are white in colour. The life span is 3 -10 days. Blood platelets are useful for formation
of the blood clot during bleeding when wound occurs in the body.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint DysfunctionDocument46 pagesTreatment of Sacroiliac Joint DysfunctionMichel Bakker100% (5)
- Fitness Calculator Python ProjectDocument12 pagesFitness Calculator Python ProjectNishitha NeelamPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood and Circulation, iGCSE BiologyDocument4 pagesBlood and Circulation, iGCSE BiologyMisterBlueSky89% (9)
- Emergency Care (Hemophilia)Document30 pagesEmergency Care (Hemophilia)Nica Georgelle Maniego SamontePas encore d'évaluation
- Traditional Healers in South AfricaDocument8 pagesTraditional Healers in South AfricaTraditional Healer100% (1)
- Lymphatic System: Parts of The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesLymphatic System: Parts of The Circulatory Systemdownfree28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemEvansPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Notes: Human Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesClass Notes: Human Circulatory SystemAnurag SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesBlood Circulatory SystemstephanietoppoPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument27 pages07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans100% (2)
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 pagesKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemSarada KasyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System in Finfish and ShellfishDocument27 pagesCirculatory System in Finfish and ShellfishDr. Abir IshtiaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 pagesBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation 1 PDFDocument9 pagesTransportation 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in HumansDocument10 pagesTransport in Humanseugene_970418755Pas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Unit 4 3esoDocument9 pagesSummary Unit 4 3esoMeneses Oriano SaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System: Review of Related LiteratureDocument15 pagesCardiovascular System: Review of Related LiteratureCha AlegriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation in AnimalsDocument6 pagesTransportation in AnimalskrovrainkPas encore d'évaluation
- Competitive Exams: Heart: ExamraceDocument3 pagesCompetitive Exams: Heart: Examraceathira vijayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory - System EditedfocusssnoteDocument136 pagesCirculatory - System Editedfocusssnoteamir kingPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions of The Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesFunctions of The Circulatory SystemJulliane OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart and Blood NotesDocument3 pagesHeart and Blood NotesarjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer Science Grade 9Document43 pagesReviewer Science Grade 9Earl AndreiPas encore d'évaluation
- Presidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationDocument8 pagesPresidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationSaniya nebPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal TransportDocument20 pagesAnimal TransportFeranmi AkinboboyePas encore d'évaluation
- Lec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesLec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemHimanshu JindalPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 9 1.3 LessonDocument31 pagesScience 9 1.3 LessonHdisbdbd NfjdnbdncPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument13 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyDwi Junita SariPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemkristinePas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument44 pagesCirculatory SystemAdonai Jireh Dionne BalitePas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System NotesDocument10 pagesCirculatory System Notesadriann strakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombePas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesCirculatory SystemKalev MaricqPas encore d'évaluation
- For Quiz AnaphyDocument26 pagesFor Quiz AnaphyRuel AlejandroPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument39 pagesScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in Animals o Level2018Document12 pagesTransport in Animals o Level2018MuneebPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezPas encore d'évaluation
- Function of The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Circulatory SystemChristine SegundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Excellup Class TenDocument3 pagesExcellup Class TenHemant KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Body Systems (Autosaved)Document17 pagesHuman Body Systems (Autosaved)K. Thenuja MihinPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation NotesDocument12 pagesTransportation NotesavanishPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemSaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesCirculatory SystemMaria Theresa DemeterioPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelompok 2: Sirkulasi DarahDocument14 pagesKelompok 2: Sirkulasi DarahjokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartSyafiq RozaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper Cardiovaskuler System: Institute of Health Science Pekanbaru Medical Center 2018Document7 pagesPaper Cardiovaskuler System: Institute of Health Science Pekanbaru Medical Center 2018Rismala RAPas encore d'évaluation
- English 1 Final ExamDocument5 pagesEnglish 1 Final ExamMariam AbesadzePas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation Notes Class 10thDocument10 pagesTransportation Notes Class 10thKrishna SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyJona Addatu0% (1)
- TRANSPORTATIONDocument9 pagesTRANSPORTATIONAnonymousPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument34 pagesCirculatory SystemMHAR CHRISTOPHER MAMASIGPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidDocument8 pagesCirculatory System: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidTanaka muzuwaPas encore d'évaluation
- The HearthDocument1 pageThe HearthRaffaela CerronePas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 Revision Notes PDFDocument8 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 7 Revision Notes PDFNayla Masroor 9BPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in AnimalsDocument6 pagesTransport in Animals2027dpatel.studentPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Document9 pagesBIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Jv Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Grade 9 - Lesson NoteDocument9 pagesBiology Grade 9 - Lesson NotemicahxPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of CirculationDocument7 pagesTypes of Circulationhow are you?Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionD'EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Research 2: 4Th QuarterDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2: 4Th Quartergamms upPas encore d'évaluation
- Genitourinary SystemDocument27 pagesGenitourinary SystemDanica FrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tricks To Remember Important Days-All-MonthsDocument2 pagesTricks To Remember Important Days-All-MonthsSenthikumar MuraliPas encore d'évaluation
- USHK - A - Clean - Environment - Healthy - Me - EngDocument24 pagesUSHK - A - Clean - Environment - Healthy - Me - EngBeaa BeaaPas encore d'évaluation
- AET-301-Pests of Crops and Stored Grain and Thier ManagementDocument158 pagesAET-301-Pests of Crops and Stored Grain and Thier ManagementAvinash S MPas encore d'évaluation
- Transgenic AnimaliaDocument4 pagesTransgenic AnimaliaGalino Julia Cristine A.Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Detailed Analysis of 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene SegmentsDocument10 pagesA Detailed Analysis of 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene SegmentsCharith NikahetiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Netically Modified Crops Their Development, Uses, and Risks by G.H. LiangDocument416 pagesNetically Modified Crops Their Development, Uses, and Risks by G.H. LiangbiokanagasundarPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof Rika - Konsep Dasar Biologi Sel Dan MolekularDocument33 pagesProf Rika - Konsep Dasar Biologi Sel Dan MolekularTiaradestiana AbeePas encore d'évaluation
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 pagesBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- 2 Upper Airway Disorders PDFDocument33 pages2 Upper Airway Disorders PDFMonica BorjaPas encore d'évaluation
- ForrestDocument4 pagesForrestAbulHasan Idrus IstarPas encore d'évaluation
- Unidirctional Anti Covid-19 Gate Using Motion SensorDocument45 pagesUnidirctional Anti Covid-19 Gate Using Motion SensorMuhammad SalmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of CT Scan in Diagnosis of Acute AppendicitisDocument6 pagesRole of CT Scan in Diagnosis of Acute AppendicitisIndahPas encore d'évaluation
- Norsyahira Binti Abdullah - hs245 4cDocument8 pagesNorsyahira Binti Abdullah - hs245 4cMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Experience of Dental Caries in Mother/child Pairs: Association Between Risk Indicators and Dental CariesDocument8 pagesExperience of Dental Caries in Mother/child Pairs: Association Between Risk Indicators and Dental CariesRisky Anita OktavianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 8 - Hand Shao-Yang San-Jiao ChannelDocument89 pagesClass 8 - Hand Shao-Yang San-Jiao ChannelFrancisco VilaróPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Review On Vegetable OilDocument8 pagesLiterature Review On Vegetable Oilbteubwbnd100% (1)
- Glossary of Commonly Used Dental Terms: 14212 Ambaum Boulevard Southwest Suite #101, Burien, WA 98166Document10 pagesGlossary of Commonly Used Dental Terms: 14212 Ambaum Boulevard Southwest Suite #101, Burien, WA 98166Mayra RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Street Corner Secrets by Svati ShahDocument71 pagesStreet Corner Secrets by Svati ShahDuke University Press100% (2)
- Alkaloids - Biosynthesis Biological Roles and HealthDocument285 pagesAlkaloids - Biosynthesis Biological Roles and HealthPrakash PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 4biomechanics of Removable Partial DenturesDocument15 pages4biomechanics of Removable Partial DenturesDemilyadioppy AbevitPas encore d'évaluation
- Bright Adjei B.A. (Hons.)Document136 pagesBright Adjei B.A. (Hons.)gideon A. owusuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effect of Physiotherapy Intervention by Using Ultrasound and Piriformis Stretching in Management To Reduce Pain in Piriformis SyndromeDocument3 pagesThe Effect of Physiotherapy Intervention by Using Ultrasound and Piriformis Stretching in Management To Reduce Pain in Piriformis SyndromeInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 The Circulatory System of MammalsDocument30 pagesChapter 6 The Circulatory System of MammalsRethenaPas encore d'évaluation
- GHH Horoscope PDFDocument46 pagesGHH Horoscope PDFRakesh Kumar BeheraPas encore d'évaluation