Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Scalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature and
Transféré par
Fazlina MustafaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Scalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature and
Transféré par
Fazlina MustafaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Notes 4.
1 VECTOR
4.1 .1 Vector and scalar quantities
A quantity that only has a size, known as magnitude, is called a
scalar quantity, such as area, volume, mass, temperature and
pressure.
A quantity that has a magnitude and a direction is called a vector
quantity, such as force, displacement, velocity, acceleration,
momentum and impulse.
EXAMPLE
Answers:
a) A scalar quantity ( magnitude only )
b) A vector quantity ( magnitude and direction )
c) A vector quantity ( magnitude and direction )
d) A scalar quantity ( magnitude only )
4.1.2 Magnitude and direction of vectors
The symbol || is used to denote the magnitude of a vector.
For example, |PQ| and |u| denote the magnitude of vectors PQ
and u respectively.
A vector with magnitude of zero and no direction is known as zero
vector. It is denoted as 0.
A negative sign ( - ) is used to denote a vector in the opposite
direction. For example the negative vector for a is a.
4.1.3 Determining whether two vectors are equal
Two vectors are equal if and only if they have the same magnitude
and the same direction.
For negative vectors, PQ = - QP and PQ = QP
Determine whether each of the following quantities is a
scalar or a vector quantity.
a) 40 ms
-1
b) 10E towards the east
c) 20 ms
-2
towards the west
d) 6m
2
a
b
Vector a and b are equal.
4.1.4 Determining whether two vectors are parallel
Two vectors, a and b are parallel if and only if a = mb where m is a
constant meaning
a) If a =mb then vectors a and b are parallel,
b) If vectors a and b are parallel, then a =mb.
If P,Q and R are three collinear points, then vectors PQ and QR are
parallel, meaning that PQ =mQR where m is a constant.
If vectors a and b are not parallel, and ha =kb, then h=k=0
EXAMPLES
Given that PQ = 2v and AB =- -
v, determine whether vectors PQ
and AB are parallel.
Steps Solution
Write down the value of PQ PQ=2v
Then find the value of v
v =
PQ
Write down the value of AB
AB = -
v
= -
PQ )
= -
PQ
Therefore vectors PQ and AB are
parallel.
Given that ( 3 ) p = ( 2 + 7 ) q where and are constants, find
the values of and if vectors p and q are non- zero and non-
parallel.
Steps Solution
Write down the equation ( 3 ) p = ( 2 + 7 ) q
Vectors p and q are non-zero
and non-parallel
3 = 0
= 3 and
2 + 7 = 0
= -
Given that MN = 4u and NP = 7u, show that points M,N and P are
collinear.
Steps Solution
Write down the value of MN MN = 4u
Then find the value of u
u =
MN
Write down the value of NP NP = 7u
= 7 (
MN )
=
MN
Therefore, vectors MN and
NP are parallel.
Since N is a common point, points
M,N and P are collinear.
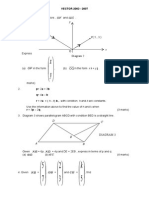
4.2 ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION OF VECTORS
When two or more vectors are combined and represented by a
single vector, the single vector is known as the resultant vectors.
In the diagram above, PQRS is a trapezium . PQ is parallel to SR.
Given that PQ =
SR, PQ = 5m and |m| = 6, find
a) Vector PQ + SR in terms of m,
b) |PQ = SR|.
Steps Solution
Write down the value of PQ
PQ=
SR
Then find the value of SR
SR =
PQ ( PQ and SR are parallel)
=
( 5m )
= 3m
Find the value of PQ + SR PQ + SR = 5m + 3m
= 8m
Find the value | PQ + SR | |PQ + SR | = |8m|
= 8 |m|
= 8 ( 6 )
= 48 units
The diagram shows a triangle OAB. OA = a , OB = b and M is the
midpoint of OA. State in terms of a and/or b,
(a) MA (b) MB (c) AB
Steps Solution
(a) OM = MA because M is the
midpoint.
OA = a
MA =
OA
=
a
(b) In MOB, express MB in
terms of a and b.
MB = MO + OB
M
-a
O B
b
MB = MO + OB
= - OM + OB
= - -
a + b
(c) In AOB, express AB in
terms of a and b.
AB = AO + OB
AB = - AO + OB
= - a + b
j
5m
S
R
P Q
b
a
O B
A
M
In the diagram above, PQRS is a trapezium. PQ is parallel to SR.
Given that PQ = 2a, PR = 5b and SR = 2PQ.
a) Determine each of the following vectors in terms of a.
i) PR QR
ii) SR
b) Find the vector which is equal to vector 4a 5b.
Steps Solution
a i)
PR QR = PR + ( - QR )
= PR + RQ
= PQ
= 2a
ii) SR = 2PQ ( PQ and SR are parallel)
= 2 ( 2a )
= 4a
b) 4a 5b = 4a + ( - 5b )
= SR + ( - PR )
= SR + RP
= SP
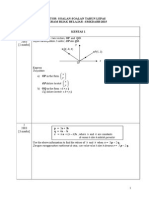
In the diagram above, PTR and QSR are straight lines. Points S and T
lie on QR and PR respectively such that S is the midpoint of QR and
3PT = PR. Given That PQ = 4a and PR = 6b, express each of the
following vectors in terms of a and b.
a) QR b) RS c) PS d) QT
Steps Solution
a) In PQR, find QR
QR = QP + PR
= - PQ + PR
= - 4a + 6b
b) Find RS
S is the midpoint of QR
RS and RQ are parallel
RS =
RQ
RS =
( - QR )
=
( 4a 6b)
= 2a - 3b
c) In PQS, find PS
PS = PQ + QS
= PQ + SR (QS = SR)
= PQ + ( - RS )
= 4a + ( 3b 2a )
= 2a + 3b
2a
5b
S
P
Q
R
2a
5b
P
R
Q
P
R
Q
S
T
P
R
Q
P
Q
S
d) Given 3PT = PR
PT and PR are parallel
In PQT, find QT
3PT = PR
PT =
PR
=
(6b)
= 2b
QT = QP + PT
= - PQ + PT
= - 4a + 2b
4.3 VECTORS IN A CARTESIAN PLANE
a) In the form x + y or (
)
b) vector units I = (
) and j = (
)
The vector in a Cartesian plane which proceeds from point A( x
1
, y
1
)
to point B( x
2
, y
2
) is given by
= (
)
Given points P ( 5 , 1 ) and Q ( -2 , 4 ), express vector PQ in the form
x + y and in the form of (
)
Steps Solution
Use the formula
PQ = (
)
PQ = (-2 5 )I + ( 4 1 )j
= -7i + 3j
PQ = -7i + 3j
= (
)
Given that u = (
) and v = (
), find the value of p such that 2pu - v
is parallel to the x-axis.
Steps Solution
Write down the value of 2pu v
2pu v = 2p (
) - (
)
= (
) - (
)
= (
)
y= 0 ( parallel to x-axis ) 8p + 4 = 0
P =
4.3.1 UNIT VECTOR S IN A GIVEN PLANE
The unit vector in the direction of a is denoted as
If a = x + y, then the unit vector in the direction of a is given by
=
x + y
EXAMPLE
a) Determine the unit vector in the direction of u if u = 4 - 7.
b) Given that v = (
), find
a ) =
x + y
=
4 -7
=
P Q
T
b) =
)
=
)
=
)
= (
)
EXERCISES
SPM 2003
PAPER 1
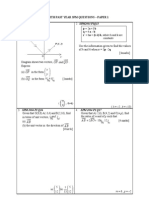
Diagram 3 shows a parallelogram ABCD with BED as a straight line.
Given that AB = 6p, AD = 4q and DE = 2EB, express, in terms of p
and q
a) BD
b) EC
PAPER 2
6 Given that AB = (
), OB = (
) and CD = (
), find
a) the coordinates of A,
b) the unit vector in the direction of OA,
c) the value of k, if CD is parallel to AB
SPM 2004
PAPER 1
16. Given that O (0,0), A(-3,4) and B(2,16), find in terms of the unit
vectors, i and j ,
a) AB
b) the unit vector in the direction of AB
17. Given that A(-2,6), B(4,2) and C(m,p), find the value of m and of
p such that,AB + 2BC = 10i 12j.
Diagram 3
D C
B
A
E
PAPER 2
8 Diagram 3 shows OAB. The straight AP intersects the straight line
OQ at R. It is given that OP =
OB, AQ =
AB, OP = 6x and OA = 2y.
a) Express in terms of x and / or y :
i) AP
ii) OQ
b) I) given that AR = hAP, state AR in terms of h,x and y
ii) given that RQ = kOQ, state RQ in terms of k,x and y.
c) Using AR and RQ from b), find the value of h and of k.
SPM 2005
PAPER 1
15 Diagram 4 shows vector OA drawn on a Cartesian plane.
a) Express OA in the form (
).
b) Find the unit vector in the direction of OA.
16. Diagram 5 shows a parallelogram, OPQR drawn on a Cartesian
plane.
It is given that OP = 6i + 4j and PQ = -4i +5j.
Find PR.
PAPER 2
6 In diagram 3, ABCD is a quadrilateral. AED and EFC are straight
lines.
R
Diagram 3
O
B
A
P
Q
8
6
4
2
-2
-4
-6
-8
y
-15 -10 -5 5 10 15 x
A
6
4
2
-2
-4
-6
-8
-10
y
-15 -10 -5 5 10 15 x
Diagram 5
O
R
Q
P
F
Diagram 3
D
A B
C E
It is given that AB = 20x, AE = 8y, DC = 25x 24y, AE =
AD and
EF =
EC.
a) Express in terms of x and/ or y :
i) BD ,
ii) EC.
b) Show that the points B, F and D are collinear.
c) If = 2 and = 3, find
SPM 2006
PAPER 1
13 Diagram 6, shows 2 vectors, OA and AB.
Express
a) OA in the form of (
),
b) AB in the form xi + yj
14 The points P,Q and R are collinear. It is given that PQ = 4a 2b
and QR = 3a + (1 + k)b, where k is a constant. Find
a) The value of k
b) the ratio of PQ :QR
PAPER 2
5 Diagram 1 shows a trapezium ABCD.
It is given that AB = 2y, AD = 6x, AE =
AD and BC =
AD.
a) Express AC, in terms of x and y.
b) Point F lies inside the trapezium ABCD such that 2EF = mAB,
and m is a constant.
i) Express AF, interms of m, x and y.
ii) Hence, if the points A,F and C are collinear, find the value
of m.
Diagram 6
x
y
(4,3)
-5
A
O
B
Diagram 1
A
D
B
C
F
E
SPM 2007
PAPER 1
15 Diagram 3 shows a rectangle OABC and the point D lies on
the straight line OB.
It is given that OD = 3DB. Express OD, in terms of x and y.
16. The following information refers to the vectors a and b.
a= (
) and b = (
)
Find a) the vector 2a b
b) the unit vector in the direction of 2a b
PAPER 2
8 Diagram 3 shows AOB . The point P lies on OA and the point Q
lies on AB. The straight line BP intersects the straight line OQ at
point S.
It is given that
OA : OP = 4 : 1, AB : AQ = 2 : 1, OA = 8x, OB = 6y.
a) Express in terms of x and/or y:
i) BP
ii) OQ
b) Using OS = hOQ and BS = kBP, where h and k are constants,
find the value of h and k.
c) Given that = 2 units, = 3 units and AOB = 90
0.
Find
Diagram3
5y
9x
O
A
B
C
D
Diagram 3
S
B
O
A
P
Q
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CHAPTER 4a VectorDocument44 pagesCHAPTER 4a VectormakiyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Juj 2009 PDFDocument36 pagesJuj 2009 PDFMohd Khir ZainunPas encore d'évaluation
- O4Qvec - c4 SoomenxDocument11 pagesO4Qvec - c4 SoomenxKapilanNavaratnamPas encore d'évaluation
- E4Qvec XDocument11 pagesE4Qvec XFarisPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Theory EDocument26 pagesVector Theory EthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- VectorsDocument26 pagesVectorsAditya Bansal0% (1)
- CHAPTER 9 Baru 1 Tutorial and All QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 9 Baru 1 Tutorial and All QuestionsMizaZainalPas encore d'évaluation
- Solomon C4 VectorsDocument11 pagesSolomon C4 Vectorssim887Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 9 Lines and Angles Assignment 4Document11 pagesCBSE Class 9 Lines and Angles Assignment 4SarthakDiwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector SPM 2003 - 2007Document4 pagesVector SPM 2003 - 2007Rosmizar AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.vektor 2015 (2003 - 2010)Document14 pages4.vektor 2015 (2003 - 2010)Zuraidah BasriPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Year SPM QuestionsDocument6 pagesPast Year SPM QuestionsLee ElainePas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Coordinates GeometryDocument5 pagesExercise Coordinates GeometryFatin HayalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Coordinates GeometryDocument5 pagesExercise Coordinates GeometryFatin HayalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Find The Midpoints of Each Side Connect Them in OrderDocument23 pagesFind The Midpoints of Each Side Connect Them in OrderRedzuan Saidi0% (1)
- Vectors - SPM Questions (1) : J I K R J K I SDocument2 pagesVectors - SPM Questions (1) : J I K R J K I SAzizah Haji KamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Past YearDocument8 pagesVector Past YearWan AfiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulseb/Uleac Special Paper Pure Mathematics QuestionsDocument19 pagesUlseb/Uleac Special Paper Pure Mathematics Questionsalphamale173Pas encore d'évaluation
- VectorsDocument5 pagesVectorsZahid RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cordinate GeometryDocument14 pagesCordinate GeometryShalini GaneshPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors 13 14Document41 pagesVectors 13 14Ramchandra MurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Dimensional Geometry: Coordinate of A Point in SpaceDocument35 pagesThree Dimensional Geometry: Coordinate of A Point in SpacethinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesCoordinate Geometrynaisha kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordinate GeometryDocument32 pagesCoordinate GeometrythinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- RD Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 14 Co Ordinate Geometry Exercise 14.3Document17 pagesRD Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 14 Co Ordinate Geometry Exercise 14.3bandarisairishikesh971Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Chapter 6Document4 pagesExercise Chapter 6Shafiqah SamsuriPas encore d'évaluation
- F3 Challenging Exercise 11Document3 pagesF3 Challenging Exercise 11pgkbgjrh5pPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordinate PP KEY 2021Document11 pagesCoordinate PP KEY 2021Mayur GowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 C4 Vectors: Louis Brooks April 11, 2008Document5 pages1 C4 Vectors: Louis Brooks April 11, 2008alawi1889Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 7Document18 pagesChap 7sameerchopadePas encore d'évaluation
- Review Set 16B (3-D) : Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16)Document4 pagesReview Set 16B (3-D) : Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16)Nhocticaro NhocPas encore d'évaluation
- Oordinate EometryDocument18 pagesOordinate EometryNITISH KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM F5 Ch4 PDF - UnlockedDocument11 pagesSPM F5 Ch4 PDF - UnlockedkokleongPas encore d'évaluation
- Salomon VectorsDocument2 pagesSalomon Vectorsjsy7w7z8q7Pas encore d'évaluation
- AHL 3.12 Vector DefinitionsDocument52 pagesAHL 3.12 Vector Definitionspelin petekPas encore d'évaluation
- Jemh 107Document18 pagesJemh 107myPas encore d'évaluation
- VectorsDocument9 pagesVectorsImash MinokaPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 10 14 - IMOGeom2Document13 pages06 10 14 - IMOGeom2Atithaya Chinchalongporn100% (1)
- Vector AlgebraDocument22 pagesVector AlgebraJB NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Coordinate Geometry: Ms. Ghia RelucioDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Coordinate Geometry: Ms. Ghia RelucioDamian Juan100% (1)
- Grade 9 Unit 7Document3 pagesGrade 9 Unit 7NatayPas encore d'évaluation
- BarycentricDocument10 pagesBarycentricRohit KaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors - Algebra and Geometry May 29, 2011: 1 Algebraic DefinitionsDocument19 pagesVectors - Algebra and Geometry May 29, 2011: 1 Algebraic DefinitionssuccessinmpPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors Worksheet (A+Astar) - Clip 180Document5 pagesVectors Worksheet (A+Astar) - Clip 180Dominic Bonkers StandingPas encore d'évaluation
- Point D.P.P SubjectiveDocument5 pagesPoint D.P.P SubjectiveMukesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Key Points of VectorsDocument5 pagesSome Key Points of VectorsAkshay MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.plane Coordinate GeometryDocument10 pages1.plane Coordinate GeometryPoh Koon Seng100% (1)
- Geometry Practice First Sem - 2021Document5 pagesGeometry Practice First Sem - 2021Shivaji ThubePas encore d'évaluation
- Maths-Straight Line IIIDocument7 pagesMaths-Straight Line IIIShubham JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Addmath VectorDocument4 pagesAddmath Vectornurhayati8860Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maths - Coord. Geometry - Part 2Document1 pageMaths - Coord. Geometry - Part 2pmagrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 LinesDocument16 pages5 Linesamanda_edithPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 8: The Distance FormulaDocument17 pagesLesson 8: The Distance FormulaMarquez FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Coordinate GeometryDocument19 pagesCoordinate GeometryFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Seri Rompin 26810 Kuala Rompin Peperiksaan Penilaian 3 Tingkatan 4 2014Document2 pagesSMK Seri Rompin 26810 Kuala Rompin Peperiksaan Penilaian 3 Tingkatan 4 2014Fazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul 1 Asas NomborDocument3 pagesModul 1 Asas NomborFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jadual KebarangkalianDocument1 pageJadual KebarangkalianFazlina Mustafa100% (1)
- Solve The Equation - Selesaikan Persamaan (3 Marks/markah) Answer/JawapanDocument11 pagesSolve The Equation - Selesaikan Persamaan (3 Marks/markah) Answer/JawapanFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Slot 1: Matrices Mathematical ReasoningDocument1 pageSlot 1: Matrices Mathematical ReasoningFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Graph OA - Object Move With Constant Speed Graph AB - Object Is Not MovingDocument8 pagesGraph OA - Object Move With Constant Speed Graph AB - Object Is Not MovingFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- StatisticsDocument11 pagesStatisticsFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 2 Given That N (G H) 4, N (G) 15 and N (H) 12, Find N (G H)Document3 pages1 2 Given That N (G H) 4, N (G) 15 and N (H) 12, Find N (G H)Fazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Reasoning AnswerDocument3 pagesMathematical Reasoning AnswerFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Set K2Document7 pagesSet K2Fazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Which Graph Represent y - 3x - 5 ? A.: Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Satu Garis Lurus JKDocument3 pagesWhich Graph Represent y - 3x - 5 ? A.: Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Satu Garis Lurus JKFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulae Given in ExamDocument2 pagesFormulae Given in ExamFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors N TrigoDocument20 pagesVectors N TrigoFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Expression1Document1 pageQuadratic Expression1Fazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Selesaikan Persamaan Kuadratik Selesaikan Persamaan Kuadratik BerikutDocument4 pagesSelesaikan Persamaan Kuadratik Selesaikan Persamaan Kuadratik BerikutFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kebarangkalian Hujung Atas Q Bagi Taburan NormalDocument4 pagesKebarangkalian Hujung Atas Q Bagi Taburan NormalFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mind Map VectorDocument1 pageMind Map VectorFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul Matematik Tambahan Form 5 (JPNP)Document110 pagesModul Matematik Tambahan Form 5 (JPNP)Fazlina Mustafa0% (1)
- Modul Matematik Tambahan Form 4 JPNPDocument162 pagesModul Matematik Tambahan Form 4 JPNPFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Up1 f5 SMKSR 2014 k1 SkemaDocument6 pagesUp1 f5 SMKSR 2014 k1 SkemaFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- 19ProbablityDistributionsF5 BinomialDocument6 pages19ProbablityDistributionsF5 BinomialFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors (PPD)Document11 pagesVectors (PPD)Fazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional Mathematics F5 Probability DistributionDocument9 pagesAdditional Mathematics F5 Probability DistributionFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document24 pagesChapter 6Fazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emg 211 Module 1 Fut MinnaDocument13 pagesEmg 211 Module 1 Fut MinnaAbdlHameed FareedahPas encore d'évaluation
- Localization Theory For Triangulated CategoriesDocument56 pagesLocalization Theory For Triangulated CategoriesCartan AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Sex Zones: Intimacy, Citizenship and Public SpaceDocument22 pagesSex Zones: Intimacy, Citizenship and Public SpaceValeria PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Big Bang TheoryDocument9 pagesAnti-Big Bang TheoryrlcaPas encore d'évaluation
- LM Pre - Calculus Q2 M10 V2-RoberontaDocument20 pagesLM Pre - Calculus Q2 M10 V2-RoberontaTERESA N. DELOS SANTOSPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Csikos Differential GeometryDocument354 pages01 Csikos Differential GeometryAqua100% (1)
- Technical Drawing Worksheet: Teacher: Mrs. Di SclafaniDocument4 pagesTechnical Drawing Worksheet: Teacher: Mrs. Di SclafaniEarl Caesar100% (1)
- Vector and Tensor Otation': AppendixDocument16 pagesVector and Tensor Otation': AppendixshubhamPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Math Studies - Triangle Trigonometry Practice Key: MarkschemeDocument45 pagesIB Math Studies - Triangle Trigonometry Practice Key: MarkschemeRafael Tayo0% (1)
- Stereographic ProjectionDocument30 pagesStereographic ProjectionYeabsira AdebabayPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 S4 Emath (Bring Home Exam) Emath Test 1Document12 pages2021 S4 Emath (Bring Home Exam) Emath Test 1George ChooPas encore d'évaluation
- Elliptic CurvesDocument66 pagesElliptic Curvesjax21esPas encore d'évaluation
- WS-Y10 Upper and Lower BoundsDocument2 pagesWS-Y10 Upper and Lower BoundsridwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gauss KrugerDocument7 pagesGauss KrugerFernandaRiberaAnteloPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Mechanics and The Analysis of Behavior - Reflections and SDocument14 pagesQuantum Mechanics and The Analysis of Behavior - Reflections and SSamuel AraujoPas encore d'évaluation
- Denavit-Hartenberg Parameters - WikipediaDocument19 pagesDenavit-Hartenberg Parameters - Wikipediavikas16051998Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math10 - Q2 - Module 6 - Lessons 1-4 - v2Document106 pagesMath10 - Q2 - Module 6 - Lessons 1-4 - v2erraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3-BalancingDocument30 pagesChapter 3-BalancingHafzal GaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-Sss Sas Asa and Aas CongruenceDocument4 pages4-Sss Sas Asa and Aas CongruenceSohel MozidPas encore d'évaluation
- Training PPT at Honda Activa ShowroomDocument17 pagesTraining PPT at Honda Activa ShowroomArpit SatijaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hilbert EngDocument6 pagesHilbert EngRaphaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Routine and Non Routine ProblemsDocument14 pagesRoutine and Non Routine ProblemsAmanda HodgesPas encore d'évaluation
- Samvida Rai-r0688220-Existence-by-Invention-and-ExperimentationDocument9 pagesSamvida Rai-r0688220-Existence-by-Invention-and-ExperimentationSamvida11Pas encore d'évaluation
- I. Graphs of Sin X, Cos X, and Tan X Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesI. Graphs of Sin X, Cos X, and Tan X Practice ProblemsStevenPas encore d'évaluation
- Math10 - Q2 - Week 3Document12 pagesMath10 - Q2 - Week 3Venice Gwyn ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of A ForceDocument4 pagesMoment of A ForceReesePas encore d'évaluation
- AnglesDocument44 pagesAnglesIrfan AfzalPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7: Read The Following PassageDocument8 pagesUnit 7: Read The Following PassageNovri Anggraini Margareta TPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Math ReviewDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Math ReviewnobPas encore d'évaluation