Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Final Project of EE210
Transféré par
tol51870 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
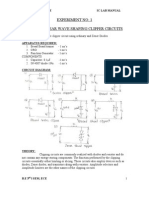
650 vues10 pagesFinal project of EE210 Tianyu Li, Section 004. BLOCK 1 1. Purpose: To combine 2 input into one and to control the output voltage range from 10 mVpp to 400 mVpp.
Description originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentFinal project of EE210 Tianyu Li, Section 004. BLOCK 1 1. Purpose: To combine 2 input into one and to control the output voltage range from 10 mVpp to 400 mVpp.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
650 vues10 pagesFinal Project of EE210
Transféré par
tol5187Final project of EE210 Tianyu Li, Section 004. BLOCK 1 1. Purpose: To combine 2 input into one and to control the output voltage range from 10 mVpp to 400 mVpp.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 10
Final Project of EE210
Tianyu Li, Section 004
BLOCK 1
1. Purpose:
To combine 2 input into one and to control the output voltage range from 10
mVpp to 400 mVpp.
2. Schematic of the circuit:
3. Supporting mathematical derivation:
4. Description/explanation of the function of the design:
With the help of the potentiometer and fixed resistors, we can control the gain of
the circuit. And each potentiometer can change the current go through the
voltage source, we can change the gain of both sources respectively.
5. Graphs/plots:
*CH1: Right Channel (440Hz, 500mV)
*CH2: Left Channel (3520Hz, 500mV)
*CH3: Output of Block1
Potentiometer at their maximum resistance:
Potentiometer at their minimum resistance:
BLOCK 2
1. Purpose:
To produce a variable gain for high audio frequency and low one.
2. Schematic of the circuit:
3. Supporting mathematical derivation:
No
4. Description/explanation of the function of the design:
When the potentiometer is at its minimum value, the circuit acts as low pass.
When the potentiometer is at its maximum value, the circuit acts as high pass
5. Graphs/plots:
*CH1: output from Block1/input to Block2 (440Hz, 400mVpp)
*CH2: output of Block2
High pass
Low pass
Middle
BLOCK 3
1. Purpose:
Control the output of the block varied between 1.2Vpp and 0Vpp with a
typical 400mVpp (absolute max 1.2Vpp) input.
2. Schematic of the circuit:
3. Supporting mathematical derivation:
4. Description/explanation of the function of the design:
When potentiometer is at its extreme (lets say at its minimum value), the output
is connected to input directly. So at this time Vout = Vin. When potentiometer is
at the other extreme, the output is connected to ground directly. So at this time
Vout = 0V.
5. Graphs/plots:
Not required.
BLOCK 4
1. Purpose:
To create a voltage level meter and to light the LEDs
2. Schematic of the circuit:
3. Supporting mathematical derivation:
4. Description/explanation of the function of the design:
R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 are design to divide the voltage to produce the expected
voltage level. The op-amps are used as comparators, which compare the voltage
at the non-inverting terminal and the one at the inverting terminal. Since the
input voltage varies from 0 to 400mVpp, with this design, LEDs will be lit respect
to different voltage input. And the R
limit
is calculated with V
turn-on
=3.3V given in
the supplement.
5. Graphs/plots:
BLOCK 5
1. Purpose:
To overcome the loading effect and work up to currents on the order of a couple
tens of milliamps.
2. Schematic of the circuit:
3. Supporting mathematical derivation:
4. Description/explanation of the function of the design:
The TDA7051A audio power amplifier chip (replaced with a voltage controlled
source here) can overcome the loading effect.
5. Graphs/plots:
*CH1: Output from Block 3 /Input to Block 5(440Hz, 600mVp)
*CH2: Output of Block 5
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lab. Exercise PL1 CC/CC Converters: Electrònica de Potència Grau en Enginyeria Electrònica Industrial I AutomàticaDocument8 pagesLab. Exercise PL1 CC/CC Converters: Electrònica de Potència Grau en Enginyeria Electrònica Industrial I AutomàticageovannyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual Analog Electronics-B.tech-Eee-3rdDocument32 pagesLab Manual Analog Electronics-B.tech-Eee-3rdKiranmai KonduruPas encore d'évaluation
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocument21 pagesADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-3 - Function Generator Using IC 8038Document10 pagesUnit-3 - Function Generator Using IC 8038yp2401553Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- LIC Lab ManualDocument43 pagesLIC Lab ManualManoj DPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 352 Ec Ii LabDocument61 pagesEe 352 Ec Ii LabSatya SandeepPas encore d'évaluation
- IC and ECAD LabDocument88 pagesIC and ECAD LabVeerayya JavvajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Eca Lab-Manual PDFDocument87 pagesEca Lab-Manual PDFdedoga9086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Open Ended 1Document12 pagesOpen Ended 1AneeshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Silicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationDocument21 pagesSilicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationMangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lic May-June 2017Document15 pagesLic May-June 2017santhosh sekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Lab ManualDocument38 pagesLab ManualsivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nollido Acee6l Exp6 Ee2hDocument10 pagesNollido Acee6l Exp6 Ee2hrusselpagaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Working Sinewave InverterDocument10 pagesWorking Sinewave InverterxenotargetPas encore d'évaluation
- 566 LIC Expt 2Document22 pages566 LIC Expt 2Hrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)Pas encore d'évaluation
- AE Lab Manual For EeeDocument53 pagesAE Lab Manual For EeeSRUJANA VPas encore d'évaluation
- EE222 Exercise 4Document3 pagesEE222 Exercise 4Raju MundruPas encore d'évaluation
- 13.8 V 15 A From A PC Power SupplyDocument8 pages13.8 V 15 A From A PC Power SupplyTibor NemethPas encore d'évaluation
- EE2003-E03 Operational AmplifierDocument6 pagesEE2003-E03 Operational AmplifierntldvlaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiDocument28 pagesLaboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiAtul SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ica Lab AmnualDocument14 pagesIca Lab AmnualNaga RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- IIT BH DNC Lab EE Manual Expt 4Document6 pagesIIT BH DNC Lab EE Manual Expt 4Priyesh PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No: DateDocument24 pagesExperiment No: DateChaitanya ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications QtyDocument0 pageCommon Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications Qtyagama1188Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices: What You Should Learn From This PracticalDocument11 pagesPractical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices: What You Should Learn From This PracticalDevesh GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex05 Lim OpampDocument9 pagesEx05 Lim OpampLIM Sheryl M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Co-3 MaterialDocument35 pagesCo-3 MaterialMLM TELUGU GAMERSPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsD'EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Linear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantityDocument61 pagesLinear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantitySainadh YerrapragadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics Lab ManualDocument92 pagesElectronics Lab ManualVolodya SmolyakPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Amplifier Circuits With Bipolar Transistors: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesBasic Amplifier Circuits With Bipolar Transistors: ObjectivesKhalid W Al-sheakhPas encore d'évaluation
- Audio Oscillator CircuitDocument3 pagesAudio Oscillator CircuitwiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Edc Lab Manuals Third SemesterDocument56 pagesEdc Lab Manuals Third SemesterSprout GigsPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 - Experiment Diode j09Document19 pages01 - Experiment Diode j09Ahmed Sobhy KhattabPas encore d'évaluation
- Lica Unit-1 Notes (3-1 ECE)Document52 pagesLica Unit-1 Notes (3-1 ECE)vasantha_btech90% (20)
- List of ExperimentsDocument22 pagesList of ExperimentsloganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ic Lab ManaulDocument73 pagesIc Lab Manaulsreenath1729Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of A High Voltage Pulse Circuit For Exciting Ultrasonic TransducersDocument7 pagesDesign of A High Voltage Pulse Circuit For Exciting Ultrasonic TransducersDavid Isaias Jaimes ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Power Supply For Electro-Optics Applications: IJRRAS 3Document5 pagesHigh Voltage Power Supply For Electro-Optics Applications: IJRRAS 3mishithPas encore d'évaluation
- Op-Amp Lab KitDocument44 pagesOp-Amp Lab KitQodor MubarakPas encore d'évaluation
- Ica WithoutreadingsmanualDocument90 pagesIca WithoutreadingsmanualAhmed Al MansurPas encore d'évaluation
- EDC II Lab ManualDocument46 pagesEDC II Lab Manualshreeyak841Pas encore d'évaluation
- BasicsOfPowerElectronicCircuits ConvertersDocument9 pagesBasicsOfPowerElectronicCircuits ConvertersDhananjay LimayePas encore d'évaluation
- Ic Applications Lab NewDocument12 pagesIc Applications Lab NewSandy RonaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ica Withoutreadingsmanual PDFDocument90 pagesIca Withoutreadingsmanual PDFKimharly VersozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment Number 6 Digital Phase DetectorDocument2 pagesExperiment Number 6 Digital Phase DetectorakhilPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 8 Buck ConverterDocument7 pagesExp 8 Buck Converterusmpowerlab50% (2)
- Op AmpDocument18 pagesOp AmpminhobaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector Amplifier5611 M.Mubeen M.yaseenPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 MarksDocument25 pages2 MarksAnnapurna CheruvuPas encore d'évaluation
- Inverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsDocument13 pagesInverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsBereket TsegayePas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector Amplifier5611 M.Mubeen M.yaseenPas encore d'évaluation
- AEC Lab ManualDocument70 pagesAEC Lab ManualRohan BosePas encore d'évaluation
- Design Concept of Transformerless Solar InverterDocument3 pagesDesign Concept of Transformerless Solar InverterdragonjahirshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3Document5 pagesLab 3معتصم الكاملPas encore d'évaluation
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1D'EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Lab 2 Report of TeamAteDocument11 pagesLab 2 Report of TeamAtetol5187Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rhetorical Analysis Tianyu LiDocument3 pagesRhetorical Analysis Tianyu Litol5187Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reflective MemoDocument2 pagesReflective Memotol5187Pas encore d'évaluation
- Folding Paper Cranes For A SenbazuruDocument7 pagesFolding Paper Cranes For A Senbazurutol5187Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab8 Opamp Dssign AmpDocument13 pagesLab8 Opamp Dssign Amptol518750% (2)
- EE 310 Lab3 ReportDocument10 pagesEE 310 Lab3 Reporttol5187100% (1)
- 2.introduction Sensors TransducerDocument15 pages2.introduction Sensors TransducerRaunaq SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis and Design of A Functional Electric Motorcycle PrototypeDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Functional Electric Motorcycle PrototypearielguerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- isoHV425 D00082 D XXENDocument8 pagesisoHV425 D00082 D XXENwakasPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual SPAA 341 C2 PDFDocument160 pagesManual SPAA 341 C2 PDFGustavo TrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Prima: Grid SolutionsDocument8 pagesPrima: Grid SolutionsPraneeth Madhushan BandaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Antena TV ShakespeareDocument4 pagesAntena TV ShakespearenachoborjasPas encore d'évaluation
- MNRE ALMM Dated 18.08.22Document43 pagesMNRE ALMM Dated 18.08.22Minal MimaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment #2: Parallel Plate Capacitors and Dielectric ConstantsDocument2 pagesExperiment #2: Parallel Plate Capacitors and Dielectric ConstantsMari KuljanishviliPas encore d'évaluation
- Protective Relaying Principles and Applications 4th Blackburn Solution ManualDocument24 pagesProtective Relaying Principles and Applications 4th Blackburn Solution ManualAnitaCareyfemy100% (36)
- WET PCB Fabrication ProcessDocument14 pagesWET PCB Fabrication Processwebip33713100% (1)
- DOD Gonkulator How It Works OriginalDocument1 pageDOD Gonkulator How It Works OriginaltttymonPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp #3: Temperature Transducers: Objectives: To Understand The Operation of Thermistors and Realization of A TemperatureDocument15 pagesExp #3: Temperature Transducers: Objectives: To Understand The Operation of Thermistors and Realization of A TemperatureKhawar RiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Polycab HT Cable SpecificationDocument36 pagesPolycab HT Cable Specificationranjish_007100% (2)
- WP-L Instalation ManualDocument12 pagesWP-L Instalation ManuallaksonoismiputrantoPas encore d'évaluation
- 09.04.01 Informatics and Computer Engineering: MPEI Master Programs 2018Document4 pages09.04.01 Informatics and Computer Engineering: MPEI Master Programs 2018tarek_bouzayaniPas encore d'évaluation
- DNR-DNRW DataSheet A05-0422Document4 pagesDNR-DNRW DataSheet A05-0422HAMDYPas encore d'évaluation
- Ese Undergraduate LaboratoryDocument6 pagesEse Undergraduate LaboratoryRirinPas encore d'évaluation
- Medium Voltage CableDocument7 pagesMedium Voltage Cableakheel201Pas encore d'évaluation
- ESTWire GuideDocument106 pagesESTWire GuideMarlon100% (1)
- Electrical Substation Interlock System-2Document24 pagesElectrical Substation Interlock System-2yassir zyadahPas encore d'évaluation
- 300B Parallel SET AmplifierDocument8 pages300B Parallel SET Amplifierandree wPas encore d'évaluation
- Nidek YC-1600 Service ManualDocument111 pagesNidek YC-1600 Service Manualqwertyu100% (2)
- LR MK4 User Issue 5.1Document64 pagesLR MK4 User Issue 5.1rich ballPas encore d'évaluation
- The Revised en 13463-1 Standard For Non-Electrical Equipment For Use in Potentially Explosive AtmospheresDocument11 pagesThe Revised en 13463-1 Standard For Non-Electrical Equipment For Use in Potentially Explosive Atmospheresibson045001256Pas encore d'évaluation
- DTEx Marine Series QSG v1.6Document6 pagesDTEx Marine Series QSG v1.6Zafar YabPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit BreakerDocument23 pagesCircuit BreakerCedrick100% (2)
- Ficha Tecnica MG 5000Document1 pageFicha Tecnica MG 5000mazzingerzPas encore d'évaluation
- ZVP2110A ZVP2110C: P-Channel Enhancement Mode Vertical Dmos Fet P-Channel Enhancement Mode Vertical Dmos FetDocument3 pagesZVP2110A ZVP2110C: P-Channel Enhancement Mode Vertical Dmos Fet P-Channel Enhancement Mode Vertical Dmos Fet19aldo97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Typical Noise Levels in Power SubstationDocument2 pagesTypical Noise Levels in Power SubstationRobert GalarzaPas encore d'évaluation