Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Helfritch CSAT 2011 Helfritch
Transféré par
ycwbycwbDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Helfritch CSAT 2011 Helfritch
Transféré par
ycwbycwbDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Victor Champagne, Dennis Helfritch, Matthew Trexler
Army Research Laboratory
Aberdeen proving Ground, MD
Dennis Helfritch
DSI at Army Research Laboratory
unclassified
Economics of Cold Spray-Cost Analysis
Procedure
1. Define coating dimensions (area, thickness)
2. Define operating conditions (pressure, temperature, etc.)
3. Define material characteristics (particle size, melting point, etc.)
4. Calculate deposition efficiencies
5. Input costs rates (powder, gas, labor)
6. Calculate cost
unclassified
Classical isentropic gas dynamics (adiabatic, frictionless)
Particles do not influence gas conditions
( ) | |
( ) | |
( )
( ) 1 2
1
2
2
2
1
1
2
2
1
2 / 1 1
2 / 1 1
+
+
+
=
M
M
M
M
A
A
( ) ( )
2 2
8 /
p g g D
p
V V d C
dt
dV
m = t
Particle drag/velocity
relationship
Isentropic flow
area/Mach number
relationship
( )( )( )
p g p p u
p
p
T T m A d k N
dt
dT
c = / /
Particle temperature/gas
temperature relationship
Aerodynamics and Deposition
Critical velocity for
deposition
unclassified
Criteria for Deposition
unclassified
The Affect of Powder Loading
unclassified
Copper particles in air from Gilmore, et al, JTST, 1999
Interactive Calculator
unclassified
throat diameter 2.7 mm area 144 sq inch
nitrogen (0) helium (1) 0 thickness 20 mil
feed rate 10 pound/hour overspray 10 %
raster speed 400 mm/sec time for completion 0.4 hours
increment 1 mm number layers 6.7
gas temp after heating 500 degree C powder usage 4.3 pounds
compressed gas pressure 500 psig electricity usage 15.9 kWhr
geometric mean diameter 40 micron powder cost/wt 200 $/pound
standard deviation 1.5 nitrogen cost/SCF 0.4 $/100 SCF
shape factor 1.2 helium cost/SCF 20 $/100 SCF
material density 8.9 gm/cc set-up time per piece 0.10 hours
melting point 1453 degree C hourly labor rate 125 $/hr
specific heat 450 J/kg-K
ultimate stress 195 Mpa powder cost $861
gas cost $5
gas flow 47.8 SCFM labor cost $66
wt% powder to gas 4.5 % unit cost $934
deposition efficiency 23.9 %
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 20 40 60 80 100
P
r
o
b
a
b
i
l
i
t
y
Particle Diameter, micron
Particle Size Distribution
0
500
1000
1500
2000
0 20 40 60 80 100 I
m
p
a
c
t
V
e
l
,
m
/
s
&
T
e
m
p
,
C
Particle Diameter
Particle Impact Conditions
velocity
temperature
critical velocity
Recommendations
unclassified
1. Use nitrogen when spraying inexpensive powders
2. Use helium when spraying expensive powders
3. Use the highest possible feed rate
4. Use powders with small diameter particles
5. A narrow particle size distribution (small SD) is best
6. Irregularly shaped particles are better than spherical
? Questions ?
unclassified
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Additive Manufacturing For Defense and Government (CTC)Document36 pagesAdditive Manufacturing For Defense and Government (CTC)ycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Erosion of A Chromium-Plated Tank Gun BarrelDocument16 pagesErosion of A Chromium-Plated Tank Gun BarrelycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Additive Material Repairs: The Changing Nature of SustainmentDocument28 pagesAdditive Material Repairs: The Changing Nature of SustainmentycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- 3di Workshop Presentations Public ReleaseDocument177 pages3di Workshop Presentations Public ReleaseycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Findings and Developments in Chromium Plated Gun TubesDocument29 pagesRecent Findings and Developments in Chromium Plated Gun TubesycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- State-Of-The-Art Survey On Hot Corrosion in Marine Gas Turbine EnginesDocument11 pagesState-Of-The-Art Survey On Hot Corrosion in Marine Gas Turbine EnginesycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Electroplated Chromium in Gun BarrelsDocument41 pagesUse of Electroplated Chromium in Gun BarrelsycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Materials Test Methods For Wear Resistance in Oil and Mining IndustryDocument2 pagesStudy of Materials Test Methods For Wear Resistance in Oil and Mining IndustryycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- A Systems Engineering Modeling and Simulation Approach For Rotorcraft Drive System OptimizationDocument12 pagesA Systems Engineering Modeling and Simulation Approach For Rotorcraft Drive System OptimizationycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Oilfield Metals - Better Outcomes PDFDocument19 pagesAdvanced Oilfield Metals - Better Outcomes PDFycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Erosion of A Chromium-Plated Tank Gun Barrel PDFDocument16 pagesErosion of A Chromium-Plated Tank Gun Barrel PDFycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Materials Test Methods For Wear Resistance in Oil and Mining Industry PDFDocument11 pagesStudy of Materials Test Methods For Wear Resistance in Oil and Mining Industry PDFycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Honeywell CLEEN Projects Briefing 2011Document33 pagesHoneywell CLEEN Projects Briefing 2011ycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Warm Spray Technology For Ti, Ti6Al4V and WC-CoDocument46 pagesWarm Spray Technology For Ti, Ti6Al4V and WC-CoycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 18ni-300 Maraging Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser MeltingDocument7 pagesMicrostructure and Mechanical Properties of 18ni-300 Maraging Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser MeltingycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- AMC Advanced Mould Coatings 2017Document4 pagesAMC Advanced Mould Coatings 2017ycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Degradation of HVOF, Fe3Al Coatings in Simulated Coal AshDocument20 pagesDegradation of HVOF, Fe3Al Coatings in Simulated Coal AshycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Thermal Barrier Coatings - A ReviewDocument10 pagesYttria-Stabilized Zirconia Thermal Barrier Coatings - A ReviewycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- CMAS Corrosion and Thermal Cycle of Al-Modified PS-PVD Environmental Barrier CoatingDocument19 pagesCMAS Corrosion and Thermal Cycle of Al-Modified PS-PVD Environmental Barrier CoatingycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser Surface Modification of HVOF Coatings For Improvement of Corrosion and Wear PerformanceDocument293 pagesLaser Surface Modification of HVOF Coatings For Improvement of Corrosion and Wear PerformanceycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- HVOF Thermal Spray TiC-TiB2 Coatings For AUSC Boiler-Turbine Components For Enhanced Corrosion Protection PDFDocument24 pagesHVOF Thermal Spray TiC-TiB2 Coatings For AUSC Boiler-Turbine Components For Enhanced Corrosion Protection PDFycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Low Conductivity Thermal Barrier Coatings PDFDocument39 pagesAdvanced Low Conductivity Thermal Barrier Coatings PDFycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Durability of Gadolinium Zirconate-YSZ Double-Layered Thermal Barrier Coatings Under Different Thermal Cyclic Test Conditions PDFDocument14 pagesDurability of Gadolinium Zirconate-YSZ Double-Layered Thermal Barrier Coatings Under Different Thermal Cyclic Test Conditions PDFycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Additive Manufacturing - Next Generation OEM & Sustainment SolutionsDocument15 pagesAdditive Manufacturing - Next Generation OEM & Sustainment SolutionsycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Abrasive Resistant Coatings-A ReviewDocument24 pagesAbrasive Resistant Coatings-A ReviewsumohiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine Coatings Eddy Current Quantitative and Qualitative EvaluationDocument10 pagesGas Turbine Coatings Eddy Current Quantitative and Qualitative EvaluationycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Characterization of Thin Coatings Using High Frequency Eddy Current TechnologyDocument6 pagesMaterial Characterization of Thin Coatings Using High Frequency Eddy Current TechnologyycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Rev.I 112014 HTK Ultra Strip 100 EnglDocument1 pageRev.I 112014 HTK Ultra Strip 100 EnglycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- EP2511396 Guided Non-Line of Sight CoatingDocument13 pagesEP2511396 Guided Non-Line of Sight CoatingycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of High Frequency Eddy Current Technology For Material Characterization of Thin CoatingsDocument7 pagesApplications of High Frequency Eddy Current Technology For Material Characterization of Thin CoatingsycwbycwbPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Thermo EngineeringDocument68 pagesThermo EngineeringAsmaa WajeahPas encore d'évaluation
- 9709 Y20-22 SW Mechanics v2Document19 pages9709 Y20-22 SW Mechanics v2Akram ZaraiPas encore d'évaluation
- D06 Parametric WorksheetDocument3 pagesD06 Parametric WorksheetEverett StimlerPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Baghdad Fluid Mechanics Research ReportsDocument6 pagesUniversity of Baghdad Fluid Mechanics Research ReportsAnmar HamidPas encore d'évaluation
- Conductor Galloping BasicsDocument16 pagesConductor Galloping BasicsDaniel Marginean100% (1)
- Numerical Investigation on Lateral Capacity of Helical PilesDocument21 pagesNumerical Investigation on Lateral Capacity of Helical PilesGK Ramya ShreePas encore d'évaluation
- Diagram roll angle calculationsDocument3 pagesDiagram roll angle calculationsSanjay ShelarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dipole Magnet 2017Document3 pagesDipole Magnet 2017MrWolf23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Loading on Concrete, Steel, and TimberDocument8 pagesEffects of Loading on Concrete, Steel, and TimberAshok JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Subshells and OrbitalsDocument29 pagesSubshells and OrbitalsRhythm's PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- 83120-On The Dynamics of The Friction CoefficientDocument7 pages83120-On The Dynamics of The Friction CoefficientVitor JardimPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 3 Lecture on Buoyancy Forces and StabilityDocument20 pagesQuiz 3 Lecture on Buoyancy Forces and StabilityAlyssa AmistosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Strength and Applied Stress AnalysisDocument951 pagesAdvanced Strength and Applied Stress AnalysisEng W Ea100% (5)
- Thermal EquilibriumDocument9 pagesThermal EquilibriumHarsh WaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Forces and DeflectionsDocument77 pagesInternal Forces and DeflectionsSrinivas VogguPas encore d'évaluation
- A 3D Constitutive Wood Model Using The Concepts of Continuum Damage MechanicsDocument19 pagesA 3D Constitutive Wood Model Using The Concepts of Continuum Damage MechanicsAnonymous 7MdZQn1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline Crossing CalculationsDocument2 pagesPipeline Crossing CalculationsFabianArmazaPas encore d'évaluation
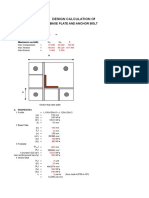
- Ook Base Plate, Anchor & Foundation (Angle) - Modified With Extra MomentDocument36 pagesOok Base Plate, Anchor & Foundation (Angle) - Modified With Extra MomentcoreteamPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate of ChangeDocument22 pagesRate of ChangeTrisha MariehPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear TrainDocument26 pagesGear TraingowthamarajPas encore d'évaluation
- A Novel Methodology For Analyzing Modal Dynamics of Multirotor Wind Turbinesjournal of Sound and VibrationDocument18 pagesA Novel Methodology For Analyzing Modal Dynamics of Multirotor Wind Turbinesjournal of Sound and VibrationMahmoud MoussaPas encore d'évaluation
- SMT1 Nature of Force KeyDocument2 pagesSMT1 Nature of Force KeyRoan Tapia AntiquenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics of Vibrations and WavesDocument2 pagesPhysics of Vibrations and WavesRashid JalalPas encore d'évaluation
- LRB Non-LinearDocument24 pagesLRB Non-LinearJames McguirePas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulics Lab Experiment on Center of PressureDocument6 pagesHydraulics Lab Experiment on Center of PressureAmiruddinMohktarPas encore d'évaluation
- TPDocument3 pagesTPDolly PriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model For Record Report PROBLEM 1Document3 pagesModel For Record Report PROBLEM 1Siddhartha Harsha OmmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrals 5 QuestionsDocument3 pagesIntegrals 5 QuestionsJoseph Neil TacataniPas encore d'évaluation
- Shear Wall Design and Analysis in RC BuildingsDocument69 pagesShear Wall Design and Analysis in RC BuildingsLizi CasperPas encore d'évaluation