Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
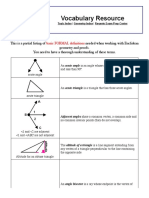
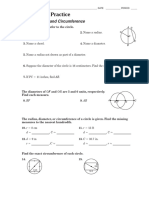
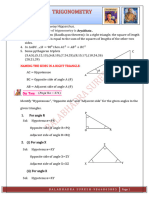
Roar'Ks Properties of Sections
Transféré par
Raine HopeCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Roar'Ks Properties of Sections
Transféré par
Raine HopeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
TABLE A.
1 Properties of sections
NOTATION: A area length
2
; y distance to extreme ber (length); I moment of inertia length
4
; r radius of gyration (length); Z plastic section modulus length
3
; SF shape factor. See
Sec. 8.15 for applications of Z and SF
Form of section
Area and distances from
centroid to extremities
Moments and products of inertia
and radii of gyration about central axes
Plastic section moduli,
shape factors, and locations
of plastic neutral axes
1. Square
A a
2
y
c
x
c
a
2
y
0
c
0:707acos
p
4
a
_ _
I
x
I
y
I
0
x
1
12
a
4
r
x
r
y
r
0
x
0:2887a
Z
x
Z
y
0:25a
3
SF
x
SF
y
1:5
2. Rectangle
A bd
y
c
d
2
x
c
b
2
I
x
1
12
bd
3
I
y
1
12
db
3
I
x
> I
y
if d > b
r
x
0:2887d
r
y
0:2887b
Z
x
0:25bd
2
Z
y
0:25db
2
SF
x
SF
y
1:5
3. Hollow rectangle
A bd b
i
d
i
y
c
d
2
x
c
b
2
I
x
bd
3
b
i
d
3
i
12
I
y
db
3
d
i
b
3
i
12
r
x
I
x
A
_ _
1=2
r
y
I
y
A
_ _
1=2
Z
x
bd
2
b
i
d
2
i
4
SF
x
Z
x
d
2I
x
Z
x
db
2
d
i
b
2
i
4
SF
y
Z
y
b
2I
y
8
0
2
F
o
r
m
u
l
a
s
f
o
r
S
t
r
e
s
s
a
n
d
S
t
r
a
i
n
[
A
P
P
.
A
4. Tee section
A tb t
w
d
y
c
bt
2
t
w
d2t d
2tb t
w
d
x
c
b
2
I
x
b
3
d t
3
d
3
3
b t
w
Ad t y
c
2
I
y
tb
3
12
dt
3
w
12
r
x
I
x
A
_ _
1=2
r
y
I
y
A
_ _
1=2
If t
w
d5bt, then
Z
x
d
2
t
w
4
b
2
t
2
4t
w
btd t
2
Neutral axis x is located a distance bt=t
w
d=2
from the bottom.
If t
w
d4bt, then
Z
x
t
2
b
4
t
w
dt d t
w
d=2b
2
Neutral axis x is located a distance t
w
d=b t=2
from the top.
SF
x
Z
x
d t y
c
I
1
Z
y
b
2
t t
2
w
d
4
SF
y
Z
y
b
2I
y
5. Channel section
A tb 2t
w
d
y
c
bt
2
2t
w
d2t d
2tb 2t
w
d
x
c
b
2
I
x
b
3
d t
3
d
3
3
b 2t
w
Ad t y
c
2
I
y
d tb
3
12
db 2t
w
3
12
r
x
I
x
A
_ _
1=2
r
y
I
y
A
_ _
1=2
If 2t
w
d5bt, then
Z
x
d
2
t
w
2
b
2
t
2
8t
w
btd t
2
Neutral axis x is located a distance
bt=2t
w
d=2 from the bottom.
If 2t
w
d4bt, then
Z
x
t
2
b
4
t
w
d t d
t
w
d
b
_ _
Neutral axis x is located a distance t
w
d=b t=2
from the top.
SF
x
Z
x
d t y
c
I
x
Z
y
b
2
t
4
t
w
db t
w
SF
y
Z
y
b
2I
y
A
P
P
.
A
]
P
r
o
p
e
r
t
i
e
s
o
f
a
P
l
a
n
e
A
r
e
a
8
0
3
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
Form of section
Area and distances from
centroid to extremities
Moments and products of inertia
and radii of gyration about central axes
Plastic section moduli,
shape factors, and locations
of plastic neutral axes
6. Wide-ange beam with
equal anges
A 2bt t
w
d
y
c
d
2
t
x
c
b
2
I
x
bd 2t
3
12
b t
w
d
3
12
I
y
b
3
t
6
t
3
w
d
12
r
x
I
x
A
_ _
1=2
r
y
I
y
A
_ _
1=2
Z
x
t
w
d
2
4
btd t
SF
x
Z
x
y
c
I
x
Z
y
b
2
t
2
t
2
w
d
4
SF
y
Z
y
x
c
I
y
7. Equal-legged angle
A t2a t
y
c1
0:7071a
2
at t
2
2a t
y
c2
0:7071a
2
2a t
x
c
0:7071a
I
x
a
4
b
4
12
0:5ta
2
b
2
a b
I
y
a
4
b
4
12
where b a t
r
x
I
x
A
_ _
1=2
r
y
I
y
A
_ _
1=2
Let y
p
be the vertical distance from the top corner to
the plastic neutral axis. If t=a50:40, then
y
p
a
t
a
t=a
2
2
_ _
1=2
Z
x
Ay
c1
0:6667y
p
If t=a40:4, then
y
p
0:3536a 1:5t
Z
x
Ay
c1
2:8284y
2
p
t 1:8856t
3
8. Unequal-legged angle
A tb d t
x
c
b
2
dt t
2
2b d t
y
c
d
2
bt t
2
2b d t
I
x
1
3
bd
3
b td t
3
Ad y
c
2
I
y
1
3
db
3
d tb t
3
Ab x
c
2
I
xy
1
4
b
2
d
2
b t
2
d t
2
Ab x
c
d y
c
r
x
I
x
A
_ _
1=2
r
y
I
y
A
_ _
1=2
8
0
4
F
o
r
m
u
l
a
s
f
o
r
S
t
r
e
s
s
a
n
d
S
t
r
a
i
n
[
A
P
P
.
A
9. Equilateral triangle A 0:4330a
2
y
c
0:5774a
x
c
0:5000a
y
0
c
0:5774acos a
I
x
I
y
I
x
0 0:01804a
4
r
x
r
y
r
x
0 0:2041a
Z
x
0:0732a
3
; Z
y
0:0722a
3
SF
x
2:343; SF
y
2:000
Neutral axis x is 0:2537a from the base.
10. Isosceles triangle
A
bd
2
y
c
2
3
d
x
c
b
2
I
x
1
36
bd
3
I
y
1
48
db
3
I
x
> I
y
if d > 0:866b
r
x
0:2357d
r
y
0:2041b
Z
x
0:097bd
2
; Z
y
0:0833db
2
SF
x
2:343; SF
y
2:000
Neutral axis x is 0:2929d from the base.
11. Triangle
A
bd
2
y
c
2
3
d
x
c
2
3
b
1
3
a
I
x
1
36
bd
3
I
y
1
36
bdb
2
ab a
2
I
xy
1
72
bd
2
b 2a
y
x
1
2
tan
1
db 2a
b
2
ab a
2
d
2
r
x
0:2357d
r
y
0:2357
b
2
ab a
2
_
12. Parallelogram
A bd
y
c
d
2
x
c
1
2
b a
I
x
1
12
bd
3
I
y
1
12
bdb
2
a
2
I
xy
1
12
abd
2
y
x
1
2
tan
1
2ad
b
2
a
2
d
2
r
x
0:2887d
r
y
0:2887
b
2
a
2
_
A
P
P
.
A
]
P
r
o
p
e
r
t
i
e
s
o
f
a
P
l
a
n
e
A
r
e
a
8
0
5
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
Form of section
Area and distances from
centroid to extremities
Moments and products of inertia
and radii of gyration about central axes
Plastic section moduli,
shape factors, and locations
of plastic neutral axes
13. Diamond
A
bd
2
y
c
d
2
x
c
b
2
I
x
1
48
bd
3
I
y
1
48
db
3
r
x
0:2041d
r
y
0:2041b
Z
x
0:0833bd
2
; Z
y
0:0833db
2
SF
x
SF
y
2:000
14. Trapezoid
A
d
2
b c
y
c
d
3
2b c
b c
x
c
2b
2
2bc ab 2ac c
2
3b c
I
x
d
3
36
b
2
4bc c
2
b c
I
y
d
36b c
b
4
c
4
2bcb
2
c
2
ab
3
3b
2
c 3bc
2
c
3
a
2
b
2
4bc c
2
I
xy
d
2
72b c
c3b
2
3bc c
2
b
3
a2b
2
8bc 2c
2
15. Solid circle A pR
2
y
c
R
I
x
I
y
p
4
R
4
r
x
r
y
R
2
Z
x
Z
y
1:333R
3
SF
x
1:698
8
0
6
F
o
r
m
u
l
a
s
f
o
r
S
t
r
e
s
s
a
n
d
S
t
r
a
i
n
[
A
P
P
.
A
16. Hollow circle A pR
2
R
2
i
y
c
R
I
x
I
y
p
4
R
4
R
4
i
r
x
r
y
1
2
R
2
R
2
i
_
Z
x
Z
y
1:333R
3
R
3
i
SF
x
1:698
R
4
R
3
i
R
R
4
R
4
i
17. Very thin annulus
A 2pRt
y
c
R
I
x
I
y
pR
3
t
r
x
r
y
0:707R
Z
x
Z
y
4R
2
t
SF
x
SF
y
4
p
18. Sector of solid circle A aR
2
y
c1
R 1
2 sina
3a
_ _
y
c2
2Rsina
3a
x
c
Rsina
I
x
R
4
4
a sina cos a
16 sin
2
a
9a
_ _
I
y
R
4
4
a sina cos a
Note: If a is small; a sina cos a
2
3
a
3
2
15
a
5
r
x
R
2
1
sina cos a
a
16 sin
2
a
9a
2
_
r
y
R
2
1
sina cos a
a
_
If a 454:3
, then
Z
x
0:6667R
3
sina
a
3
2 tana
_ _
1=2
_ _
Neutral axis x is located a distance
R0:5a= tana
1=2
from the vertex.
If a 554:3
, then
Z
x
0:6667R
3
2sin
3
a
1
sina where the
expression 2a
1
sin2a
1
a is solved for the value
of a
1
.
Neutral axis x is located a distance Rcos a
1
from
the vertex.
If a 473:09
, then SF
x
Z
x
y
c2
I
x
If 73:09
4a 490
, then SF
x
Z
x
y
c1
I
x
Z
y
0:6667R
3
1 cos a
If a 490
, then
SF
y
2:6667sina
1 cos a
a sina cos a
If a 590
, then
SF
y
2:6667
1 cos a
a sina cos a
A
P
P
.
A
]
P
r
o
p
e
r
t
i
e
s
o
f
a
P
l
a
n
e
A
r
e
a
8
0
7
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
Form of section
Area and distances from
centroid to extremities
Moments and products of inertia
and radii of gyration about central axes
Plastic section moduli,
shape factors, and locations
of plastic neutral axes
19. Segment of solid circle
(Note: If a 4p=4, use
expressions from case 20)
A R
2
a sina cos a
y
c1
R 1
2 sin
3
a
3a sina cos a
_ _
y
c2
R
2sin
3
a
3a sina cos a
cos a
_ _
x
c
Rsina
I
x
R
4
4
a sina cos a 2 sin
3
a cos a
16 sin
6
a
9a sina cos a
_ _
I
y
R
4
12
3a 3sina cos a 2 sin
3
a cos a
r
x
R
2
1
2 sin
3
a cos a
a sina cos a
16 sin
6
a
9a sina cos a
2
_
r
y
R
2
1
2 sin
3
a cos a
3a sina cos a
_
20. Segment of solid circle
(Note: Do not use if
a > p=4
A
2
3
R
2
a
3
1 0:2a
2
0:019a
4
y
c1
0:3Ra
2
1 0:0976a
2
0:0028a
4
y
c2
0:2Ra
2
1 0:0619a
2
0:0027a
4
x
c
Ra1 0:1667a
2
0:0083a
4
I
x
0:01143R
4
a
7
1 0:3491a
2
0:0450a
4
I
y
0:1333R
4
a
5
1 0:4762a
2
0:1111a
4
r
x
0:1309Ra
2
1 0:0745a
2
r
y
0:4472Ra1 0:1381a
2
0:0184a
4
21. Sector of hollow circle
A at2Rt
y
c1
R 1
2 sina
3a
1
t
R
1
2 t=R
_ _ _ _
y
c2
R
2 sina
3a2 t=R
1
t
R
_ _
2sina 3a cos a
3a
_ _
x
c
Rsina
I
x
R
3
t 1
3t
2R
t
2
R
2
t
3
4R
3
_ _ _
a sina cos a
2 sin
2
a
a
_ _
t
2
sin
2
a
3R
2
a2 t=R
1
t
R
t
2
6R
2
_ _
_
I
y
R
3
t 1
3t
2R
t
2
R
2
t
3
4R
3
_ _
a sina cos a
r
x
I
x
A
_
; r
y
I
y
A
_
(Note: If t=R is small, a can
exceed p to form an
overlapped annulus)
8
0
8
F
o
r
m
u
l
a
s
f
o
r
S
t
r
e
s
s
a
n
d
S
t
r
a
i
n
[
A
P
P
.
A
Note: If a is small:
sina
a
1
a
2
6
a
4
120
; a sina cos a
2
3
a
3
1
a
2
5
2a
4
105
_ _
;
sin
2
a
a
a 1
a
2
3
2a
4
45
_ _
cos 1
a
2
2
a
4
24
; a sina cos a
2 sin
2
a
a
2a
5
45
1
a
2
7
a
4
105
_ _
22. Solid semicircle
A
p
2
R
2
y
c1
0:5756R
y
c2
0:4244R
x
c
R
I
x
0:1098R
4
I
y
p
8
R
4
r
x
0:2643R
r
y
R
2
Z
x
0:3540R
3
; Z
y
0:6667R
3
SF
x
1:856; SF
y
1:698
Plastic neutral axis x is located a distance 0:4040R
from the base.
23. Hollow semicircle
Note: b
RR
i
2
t RR
i
A
p
2
R
2
R
2
i
y
c2
4
3p
R
3
R
2
i
R
2
R
2
i
or
y
c2
2b
p
1
t=b
2
12
_ _
y
c1
Ry
c2
x
c
R
I
x
p
8
R
4
R
4
i
8
9p
R
3
R
3
i
2
R
2
R
2
i
or
I
x
0:2976tb
3
0:1805bt
3
0:00884t
5
b
I
y
p
8
R
4
R
4
i
or
I
y
1:5708b
3
t 0:3927bt
3
Let y
p
be the vertical distance from the bottom to the
plastic neutral axis.
y
p
0:7071 0:2716C 0:4299C
2
0:3983C
3
R
Z
x
0:8284 0:9140C 0:7245C
2
0:2850C
3
R
2
t
where C t=R
Z
y
0:6667R
3
R
3
i
24. Solid ellipse
A pab
y
c
a
x
c
b
I
x
p
4
ba
3
I
y
p
4
ab
3
r
x
a
2
r
y
b
2
Z
x
1:333a
2
b; Z
y
1:333b
2
a
SF
x
SF
y
1:698
A
P
P
.
A
]
P
r
o
p
e
r
t
i
e
s
o
f
a
P
l
a
n
e
A
r
e
a
8
0
9
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
Form of section
Area and distances from
centroid to extremities
Moments and products of inertia
and radii of gyration about central axes
Plastic section moduli,
shape factors, and locations
of plastic neutral axes
25. Hollow ellipse
A pab a
i
b
i
y
c
a
x
c
b
I
x
p
4
ba
3
b
i
a
3
i
I
y
p
4
ab
3
a
i
b
3
i
r
x
1
2
ba
3
b
i
a
3
i
ab a
i
b
i
_
r
y
1
2
ab
3
a
i
b
3
i
ab a
i
b
i
_
Z
x
1:333a
2
b a
2
i
b
i
Z
y
1:333b
2
a b
2
i
a
i
SF
x
1:698
a
3
b a
2
i
b
i
a
a
3
b a
3
i
b
i
SF
y
1:698
b
3
a b
2
i
a
i
b
b
3
a b
3
i
a
i
Note: For this case the inner and outer perimeters are both ellipses and the wall
thickness is not constant. For a cross section with a constant wall thickness see
case 26.
26. Hollow ellipse with
constant wall thickness t.
The midthickness
perimeter is an ellipse
(shown dashed).
0:2 < a=b < 5
A pta b 1 K
1
a b
a b
_ _
2
_ _
where
K
1
0:2464 0:002222
a
b
b
a
_ _
y
c
a
t
2
x
c
b
t
2
I
x
p
4
ta
2
a 3b 1 K
2
a b
a b
_ _
2
_ _
p
16
t
3
3a b 1 K
3
a b
a b
_ _
2
_ _
where
K
2
0:1349 0:1279
a
b
0:01284
a
b
_ _
2
K
3
0:1349 0:1279
b
a
0:01284
b
a
_ _
2
For I
y
interchange a and b in the expressions
for I
x
; K
2
, and K
3
Z
x
1:3333taa 2b 1 K
4
a b
a b
_ _
2
_ _
t
3
3
where
K
4
0:1835 0:895
a
b
0:00978
a
b
_ _
2
For Z
y
interchange a and b in the expression for Z
x
and K
4
.
See the note on maximum
wall thickness in case 27.
8
1
0
F
o
r
m
u
l
a
s
f
o
r
S
t
r
e
s
s
a
n
d
S
t
r
a
i
n
[
A
P
P
.
A
27. Hollow semiellipse with
constant wall thickness t.
The midthickness
perimeter is an ellipse
(shown dashed).
0:2 < a=b < 5
Note: There is a limit on the
maximum wall thickness
allowed in this case. Cusps
will form in the perimeter at
the ends of the major axis
if this maximum is exceeded.
If
a
b
41; then t
max
2a
2
b
If
a
b
51; then t
max
2b
2
a
A
p
2
ta b 1 K
1
a b
a b
_ _
2
_ _
where
K
1
0:2464 0:002222
a
b
b
a
_ _
y
c2
2a
p
K
2
t
2
6pa
K
3
where
K
2
1 0:3314C 0:0136C
2
0:1097C
3
K
3
1 0:9929C 0:2287C
2
0:2193C
3
Using C
a b
a b
y
c1
a
t
2
y
c2
x
c
b
t
2
I
X
p
8
ta
2
a 3b 1 K
4
a b
a b
_ _
2
_ _
p
32
t
3
3a b 1 K
5
a b
a b
_ _
2
_ _
where
K
4
0:1349 0:1279
a
b
0:01284
a
b
_ _
2
K
5
0:1349 0:1279
b
a
0:01284
b
a
_ _
2
I
x
I
X
Ay
2
c2
For I
y
use one-half the value for I
y
in case 26.
Let y
p
be the vertical distance from the bottom to the
plastic neutral axis.
y
p
C
1
C
2
a=b
C
3
a=b
2
C
4
a=b
3
_ _
a
where if 0:25 < a=b 41, then
C
1
0:5067 0:5588D 1:3820D
2
C
2
0:3731 0:1938D 1:4078D
2
C
3
0:1400 0:0179D 0:4885D
2
C
4
0:0170 0:0079D 0:0565D
2
or if 1 4a=b < 4, then
C
1
0:4829 0:0725D 0:1815D
2
C
2
0:1957 0:6608D 1:4222D
2
C
3
0:0203 1:8999D 3:4356D
2
C
4
0:0578 1:6666D 2:6012D
2
where D t=t
max
and where 0:2 < D41
Z
x
C
5
C
6
a=b
C
7
a=b
2
C
8
a=b
3
_ _
4a
2
t
where if 0:25 < a=b 41, then
C
5
0:0292 0:3749D
1=2
0:0578D
C
6
0:3674 0:8531D
1=2
0:3882D
C
7
0:1218 0:3563D
1=2
0:1803D
C
8
0:0154 0:0448D
1=2
0:0233D
or if 1 4a=b < 4, then
C
5
0:2241 0:3922D
1=2
0:2960D
C
6
0:6637 2:7357D
1=2
2:0482D
C
7
1:5211 5:3864D
1=2
3:9286D
C
8
0:8498 2:8763D
1=2
1:8874D
For Z
y
use one-half the value for Z
y
in case 26.
A
P
P
.
A
]
P
r
o
p
e
r
t
i
e
s
o
f
a
P
l
a
n
e
A
r
e
a
8
1
1
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections (Continued)
TABLE A.1 Properties of sections Continued)
Form of section
Area and distances from
centroid to extremities
Moments and products of inertia
and radii of gyration about central axes
Plastic section moduli,
shape factors, and locations
of plastic neutral axes
28. Regular polygon with n
sides
A
a
2
n
4 tana
r
1
a
2 sina
r
2
a
2 tana
If n is odd
y
1
y
2
r
1
cos a
n 1
2
_ _
p
2
_ _
If n=2 is odd
y
1
r
1
; y
2
r
2
If n=2 is even
y
1
r
2
; y
2
r
1
I
1
I
2
1
24
A6r
2
1
a
2
r
1
r
2
1
24
6r
2
1
a
2
_
For n 3, see case 9. For n 4, see cases 1 and 13.
For n 5, Z
1
Z
2
0:8825r
3
1
. For an axis perpen-
dicular to axis 1, Z 0:8838r
3
1
. The location of this
axis is 0.7007a from that side which is perpendicular
to axis 1. For n56, use the following expression for a
neutral axis of any inclination:
Z r
3
1
1:333 13:908
1
n
_ _
2
12:528
1
n
_ _
3
_ _
29. Hollow regular polygon
with n sides
A nat 1
t tana
a
_ _
r
1
a
2 sina
r
2
a
2 tana
If n is odd
y
1
y
2
r
1
cos a
n 1
2
p
2
_ _
If n=2 is odd
y
1
r
1
; y
2
r
2
If n=2 is even
y
1
r
2
; y
2
r
1
I
1
I
2
na
3
t
8
1
3
1
tan
2
a
_ _
1 3
t tana
a
4
t tana
a
_ _
2
2
t tana
a
_ _
3
_ _
r
1
r
2
a
8
p
1
3
_ _
1
tan
2
a
1 2
t tana
a
2
t tana
a
_ _
2
_ _
_
8
1
2
F
o
r
m
u
l
a
s
f
o
r
S
t
r
e
s
s
a
n
d
S
t
r
a
i
n
[
A
P
P
.
A
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Ead - 330030 00 06.01 Fastener For Wall CladdingDocument26 pagesEad - 330030 00 06.01 Fastener For Wall CladdingRaine HopePas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Credit Card Authority-NLEXDocument1 pageCredit Card Authority-NLEXRaine HopePas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- A Slightly Longer Look at Prying July 2016Document11 pagesA Slightly Longer Look at Prying July 2016Raine HopePas encore d'évaluation
- E177 13 Standard Practice For Use of The Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test MethodsDocument10 pagesE177 13 Standard Practice For Use of The Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test MethodsRaine HopePas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Tapcon (Screws To CMU Wall)Document2 pagesTapcon (Screws To CMU Wall)Raine HopePas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Heuns.m 1 of 2 C:/Users/Std User/Downloads February 28, 2016Document2 pagesHeuns.m 1 of 2 C:/Users/Std User/Downloads February 28, 2016Raine HopePas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- ASCII CharactersDocument1 pageASCII CharactersRaine HopePas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Worksheet - Areas Related To CirclesDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Mathematics Worksheet - Areas Related To CirclesSandyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Worksheet 5.1A: Area of A Triangle 2 1Document41 pagesWorksheet 5.1A: Area of A Triangle 2 1g8f27w5ywgPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Babers - FormulasDocument171 pagesBabers - Formulasharoub_nasPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Unit 8Document9 pagesUnit 8Haitham HashimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Visualising Solid Shapes Class 8 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 10 (PDF)Document4 pagesVisualising Solid Shapes Class 8 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 10 (PDF)Manoj SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Math 9 Q4 Week 1Document10 pagesMath 9 Q4 Week 1Rocky Parinas DuquePas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (Flores Tyronne Exequiel P.)Document2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (Flores Tyronne Exequiel P.)KULU GOPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabulary List of Geometry TermsDocument5 pagesVocabulary List of Geometry Termsvks gamerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Answer Enhance MergeDocument99 pagesAnswer Enhance MergeAllen RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument24 pagesAssignmentyge070806Pas encore d'évaluation
- TalesFromtheGermanofHeinrichZschokke 10149581 PDFDocument487 pagesTalesFromtheGermanofHeinrichZschokke 10149581 PDFjurebiePas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Notes Slope, Distance, MidpointDocument6 pagesNotes Slope, Distance, MidpointAbhilash Reddy100% (1)
- Milestones ReviewDocument11 pagesMilestones Reviewapi-344048921Pas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Ncert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Ex 1Document3 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Ex 1shubham kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Percubaan PMR Perak 2008 - Maths Paper 2 (Ans)Document5 pagesPercubaan PMR Perak 2008 - Maths Paper 2 (Ans)plgan100% (3)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS in ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS by Venancio I. Besavilla, Jr. VOL1Document38 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS in ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS by Venancio I. Besavilla, Jr. VOL1John DelrosarioPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - Flaws in EuclidDocument32 pages02 - Flaws in EuclidRiemann SolivenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Trigonometric Functions - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesTrigonometric Functions - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadaniyalhassan2789Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jacobs Vocabulary LepDocument3 pagesJacobs Vocabulary Lepapi-378960179Pas encore d'évaluation
- A LESSON PLAN For "Pythagorean Theorem" By: February 2019Document10 pagesA LESSON PLAN For "Pythagorean Theorem" By: February 2019Fave Chlair Misha FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- CE 2121 Simple Curve PDFDocument2 pagesCE 2121 Simple Curve PDFEnriquez Martinez May AnnPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- X Class2023 24 11.trigonometry Notes WM 1Document31 pagesX Class2023 24 11.trigonometry Notes WM 1omsaiboggala811Pas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activity Sheet No. 2Document4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet No. 2Mariel PastoleroPas encore d'évaluation
- Jee Main 2021 PYQDocument422 pagesJee Main 2021 PYQAnant JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Talent Test For MATHDocument4 pagesTalent Test For MATHsaihruthikPas encore d'évaluation
- Prelim Exam 4th Quarter Grade 9Document4 pagesPrelim Exam 4th Quarter Grade 9Vanessa PinarocPas encore d'évaluation
- ' Maths - Stage 8 - 01 - 5RP - AFP - tcm143-639975Document16 pages' Maths - Stage 8 - 01 - 5RP - AFP - tcm143-639975Teng Xuen Chan100% (1)
- Math Section B ProjectDocument9 pagesMath Section B ProjectGeni StarPas encore d'évaluation
- DLLDocument15 pagesDLLRams Polledorep50% (2)
- Mathworld AssignmentDocument11 pagesMathworld AssignmentJoy BallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)