Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Transformer: Symbol of A Transformer
Transféré par
hill_me87Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Transformer: Symbol of A Transformer
Transféré par
hill_me87Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
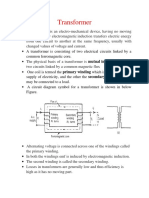
Transformer
Symbol of A Transformer
The figure on the left shows the transformer while the figure in the right is the symbol
of a transformer. The 2 lines in between the coil denote the core.
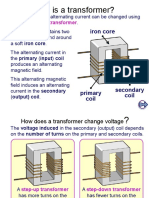
What is a transformer?
A transformer is a device that is used to raise or lower down the potential difference
of an alternating current.
Function:
The function of a transformer is to increase or decrease the potential difference of an
alternating current supply.
Structure and Technical Terms
A transformer consist of 3 parts, namely
1. The primary circuit
2. The core
3. The secondary Circuit
The primary circuit is the circuit that connected to the input energy source. The
current, potential difference and coil (winding in the primary circuit are called the
primary current (!p, primary potential difference ("p and primary coil respectively.
Core:
The core is the ferromagnetic metal wound by the primary and secondary coil. The
function of the core is to transfer the changing magnetic flu# from the primary coil to
the secondary coil.
Secondary Circuit:
The secondary circuit is the circuit that connected to the output of the transformer.
The current, potential difference and coil (winding in the secondary circuit are called
the secondary current (!s, secondary potential difference ("s and secondary coil
respectively.
Working Principle of A Transformer
1. A transformer consists of a primary coil and a secondary coil wound on a soft
iron core.
2. $hen an alternating current flows in the primary coil, a changing magnetic
flu# is generated around the primary coil.
3. The changing magnetic flu# is transferred to the secondary coil through the
iron core.
%. The changing magnetic flu# is cut by the secondary coil, hence induces an
e.m.f. in the secondary coil.
&. The magnitude of the output voltage can be controlled by the ratio of the
number of primary coil and secondary coil.
Types of Transformer
There are 2 types of transformer, namely
1. the step up transformer
2. the step down transformer
Step-up Transformer
1. A step'up transformer is one where the e.m.f. in the secondary coil is greater
than the e.m.f. in the primary coil. !t is used to increases the potential
difference.
2. The number of windings in the secondary winding is greater than the number
of windings in the primary coil.
3. The current in the primary coil is greater than the current in the secondary coil.
Step-don transformer
1. Conversely, a step'down transformer is one where the e.m.f. in the secondary
coil is less than the e.m.f. in the primary coil. !t is used to reduce the potential
difference.
2. The number of windings in the primary winding is greater than the number of
windings in the secondary coil.
3. The current in the primary coil is lesser than the current in the secondary coil.
!elationship "eteen #umber of Turns $n Coils With %oltage $n an $deal
Transformer
"p ( input (primary potential difference
"s ( output (secondary potential difference
)p ( )umber of turns on the primary coil
)s ( )umber of turns on the secondary coil
!elationship "eteen &utput Poer and $nput Poer of an $deal Transformer
"p ( input (primary potential difference
"s ( output (secondary potential difference
!p ( Current flows in primary coil
!s ( Current flows in secondary coil
Efficiency of a Transformer
IsVs ' IpVp
"p ( input (primary potential difference
"s ( output (secondary potential difference
!p ( Current flows in primary coil
!s ( Current flows in secondary coil
Factors That Affect the Efficiency of a Transformer (Power Loss)
() The heating effect of current in a coil)
All coils will have resistance. *eat is produced when current flows through them.
*ethods to impro+e the efficiency
' +se thic, copper wires of low resistance.
' +se coolant to decrease the temperature of the transformer.
,) -ddy current in the core
The changing magnetic field will also induces current in the iron core. This induced
current is called eddy current. -ddy current cause heat to be produced in the iron
cores.
*ethods to impro+e the efficiency
+se a laminated iron core whereby each layer is insulated with enamel paint to
prevent the flow of eddy currents. The high resistance between layers of the iron core
decrease the prevalence of eddy currents and heat.
.) *agneti/ation of the $ron Core)
The energy used in the magneti.ation and de'magneti.ation of the iron core each time
current changes its direction is ,nown as hysterisis. This energy is lost as heat which
subse/uently heats up the iron core.
*ethods to impro+e the efficiency
+se a soft iron core that is easily magneti.ed and de'magneti.ed.
0) Flu1 leakage)
0ome of the induced magnetic flu# from the primary coil is not transmitted to the
secondary coil, therefore the e.m.f in the secondary coil is decreased. The secondary
coil(windings are intertwined tightly with the primary coils. The iron core should
form a closed loop.
*ethods to impro+e the efficiency
The secondary coil (windings is intertwined tightly with the primary coils. The iron
core should form a closed loop.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Factors That Affect The Efficiency TransformersDocument7 pagesFactors That Affect The Efficiency TransformersSalmizam Izam100% (1)
- Phy ProjectDocument7 pagesPhy ProjectRohith SivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mutual InductionDocument20 pagesMutual InductionMohammad Wajeeh MohsinPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigate The RelationDocument4 pagesInvestigate The RelationArvind KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy InvsDocument12 pagesPhy InvsHasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesInvestigatory ProjectAryan WarathePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit:2: 1. Transformers and Its Operation 2Document64 pagesUnit:2: 1. Transformers and Its Operation 2Agent SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument7 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectHarshith YendapallyPas encore d'évaluation
- 325 04 TransformersDocument31 pages325 04 TransformersNurullah MertelPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 3 - Chap 6Document14 pagesForm 3 - Chap 6vimallkannatPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pagesSingle Phase TransformerSkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of TransformersDocument16 pagesTypes of TransformersTahamee SHAIKHPas encore d'évaluation
- TransformerDocument18 pagesTransformerEid MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IV TransformerDocument31 pagesUnit IV TransformerParikshit SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Investigatory - TransformersDocument28 pagesPhysics Investigatory - TransformersSanskriti83% (18)
- Hysteresis Eddy Current Iron or Core Losses and Copper Loss in Transformer - Electrical4uDocument4 pagesHysteresis Eddy Current Iron or Core Losses and Copper Loss in Transformer - Electrical4usauravPas encore d'évaluation
- TRANSFORMERSDocument24 pagesTRANSFORMERStmmbonelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Bim CH 01 Part 01Document16 pagesMachine Bim CH 01 Part 01bkmmizanPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction & WorkingDocument22 pagesConstruction & WorkingShah Aizat Razali100% (1)
- Transformer EceDocument12 pagesTransformer EceKaranpal Singh100% (1)
- Ac TransformerDocument10 pagesAc Transformermpravin kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics ProjectRajat UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 3 Transformer BEEDocument18 pagesUNIT 3 Transformer BEElakshya purbiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformers and Logic GatesDocument4 pagesTransformers and Logic GatesCåłłmėĎäddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Project On "Transformers"Document17 pagesPhysics Project On "Transformers"Jaÿ Üx100% (1)
- Physics ProjectDocument24 pagesPhysics ProjectSnigdha ChaudhryPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetism Part 4 StudentsDocument16 pagesElectromagnetism Part 4 StudentsSharvinder SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- TransformerDocument7 pagesTransformersivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3: Transformer: Electrical MachineDocument39 pagesChapter 3: Transformer: Electrical MachineThe zeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Elegant Education Pack For Students Blue by SlidesgoDocument6 pagesElegant Education Pack For Students Blue by Slidesgoselena leePas encore d'évaluation
- AC AC TransformerDocument4 pagesAC AC TransformerKevin GianePas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ProjectDocument4 pagesPhysics ProjectAnjan MandalPas encore d'évaluation
- EE313 Class5Document14 pagesEE313 Class5Zahid MarwatPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Phase TransformerDocument23 pagesSingle Phase TransformerShreyash SargarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Transformer?: Table of ContentDocument9 pagesWhat Is Transformer?: Table of ContentShreedaPas encore d'évaluation
- EE352 Chapter #4 Ideal Transformers and Real Equivalent CircuitsDocument31 pagesEE352 Chapter #4 Ideal Transformers and Real Equivalent CircuitsCan ARABACIPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 MSDocument42 pagesChapter 3 MSRounak ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- TRANSFORMERDocument52 pagesTRANSFORMERNaty SeyoumPas encore d'évaluation
- BoostYourChess2 ExcerptDocument16 pagesBoostYourChess2 ExcerptThe Smart Boy KungFuPawnPas encore d'évaluation
- Working Principle of Transformer: Definition of Transformer. Since There Is No Rotating or Moving Part SoDocument33 pagesWorking Principle of Transformer: Definition of Transformer. Since There Is No Rotating or Moving Part SoBrahmpal BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Investiatory PRJDocument20 pagesPhy Investiatory PRJarjunjr101Pas encore d'évaluation
- X Raygenerators 220817141451 9e83c41aDocument40 pagesX Raygenerators 220817141451 9e83c41asspcontractionPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview & Energy Optimization of Power Distribution TransformersDocument47 pagesOverview & Energy Optimization of Power Distribution TransformershadrienPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Investigatory Project 12Document19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project 12BatmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical TransformerDocument19 pagesElectrical Transformer164ec1f5100% (1)
- Siddharth PhyDocument12 pagesSiddharth Physiddharthdeuri476Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Porject Report Class 12th MathsDocument22 pagesPhysics Porject Report Class 12th MathsAaditya TomarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Transformer?Document7 pagesWhat Is A Transformer?Rahul SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Transformer Seminar TopicDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Transformer Seminar TopicSatya Yadav100% (3)
- Transformer 2Document3 pagesTransformer 2mohammadham242Pas encore d'évaluation
- Index 20240115 170022 0000Document14 pagesIndex 20240115 170022 0000Sony Shailesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- PhyDocument11 pagesPhyKrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Presentasi TransformatorDocument21 pagesTugas Presentasi TransformatorTimothy LumbanrajaPas encore d'évaluation
- TransformerDocument22 pagesTransformerIF21 Minit ChitrodaPas encore d'évaluation
- ContentDocument12 pagesContentHarishPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Construction of TransformerDocument17 pagesBasic Construction of TransformerRudra DeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit4 Application Notes EMDocument17 pagesUnit4 Application Notes EMYoke Hock SeowPas encore d'évaluation
- Genaral Details of A TransformerDocument3 pagesGenaral Details of A TransformershaluPas encore d'évaluation
- TrnasformerDocument21 pagesTrnasformer19M647 - SRIRAM APas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsD'EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Buku Manual Mesin Kisar UniversalDocument26 pagesBuku Manual Mesin Kisar Universalhill_me87Pas encore d'évaluation
- PPC NotesDocument44 pagesPPC Noteshill_me870% (1)
- Standard Paper Sizes: U.S. Name U.S. Size Metric EquivalentDocument1 pageStandard Paper Sizes: U.S. Name U.S. Size Metric Equivalenthill_me87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quantity Represented by The Gradient of A Graph Quantity Represented by The Area Under A GraphDocument10 pagesQuantity Represented by The Gradient of A Graph Quantity Represented by The Area Under A Graphhill_me87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6: Gradient and Area Under A Graph.. Form 5Document1 pageChapter 6: Gradient and Area Under A Graph.. Form 5hill_me87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDocument9 pagesFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- A Model of Student College ChoiceDocument17 pagesA Model of Student College Choicehill_me87Pas encore d'évaluation
- CENTRALIZATION Vs DEVOLUTIONDocument12 pagesCENTRALIZATION Vs DEVOLUTIONhill_me87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bhel TG RollingDocument26 pagesBhel TG RollingAnand Swami100% (2)
- CP4 AHU's Energy Saving Data 18.05.21Document4 pagesCP4 AHU's Energy Saving Data 18.05.21SalmanPas encore d'évaluation
- PPTDocument49 pagesPPTyunimulia100% (1)
- Consistent Use of The Standard Model Effective Potential PDFDocument5 pagesConsistent Use of The Standard Model Effective Potential PDFJoão Paulo da MataPas encore d'évaluation
- Igcse Physics FormulasDocument5 pagesIgcse Physics Formulasmohammad affan merchantPas encore d'évaluation
- Ena Design Standard For Earthing SystemDocument110 pagesEna Design Standard For Earthing SystemNADEEM KHALID100% (1)
- Industrial Chemistry and Tribology Topic 5Document18 pagesIndustrial Chemistry and Tribology Topic 5Gonzales Frank Lioyd Bhong100% (1)
- Datasheet Argo Diode Battery Isolators enDocument1 pageDatasheet Argo Diode Battery Isolators enDavor GiaconiPas encore d'évaluation
- AT Kearney Energy Transition Institute Media Presentation180606aDocument9 pagesAT Kearney Energy Transition Institute Media Presentation180606aAyesha Khan JamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical English LessonsDocument18 pagesTechnical English LessonsabdeldjalildaraniunivPas encore d'évaluation
- Submersible SubstationDocument7 pagesSubmersible SubstationWill AchuPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Proposal For The Proton BatteryDocument4 pagesResearch Proposal For The Proton BatteryStacey SkibaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFBillPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2 ME-241Document6 pagesAssignment 2 ME-241Naman KansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Irf3207 MOSFETDocument12 pagesIrf3207 MOSFETKennedy IruPas encore d'évaluation
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 6 Electromagnetism in Everyday LifeDocument68 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 6 Electromagnetism in Everyday LifeJacob Dy67% (3)
- 01 - First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument20 pages01 - First Law of ThermodynamicsFabio BosioPas encore d'évaluation
- Instruction - Resistance Heating Element ProjectDocument6 pagesInstruction - Resistance Heating Element Projectarg0nautPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Transmitter With Ceramic Sensor, Accuracy 0,5%Document2 pagesPressure Transmitter With Ceramic Sensor, Accuracy 0,5%essameldinPas encore d'évaluation
- StaticDocument49 pagesStaticmrccahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics WSDocument19 pagesKinematics WSMadhav JainPas encore d'évaluation
- School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Aait, Aau Ceng 2161: Hydraulics I Home Work No. 1Document2 pagesSchool of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Aait, Aau Ceng 2161: Hydraulics I Home Work No. 1zablonPas encore d'évaluation
- ExpVDS JHEDocument8 pagesExpVDS JHERob616Pas encore d'évaluation
- DCMT Lecture Notes Full - 230406 - 110711Document111 pagesDCMT Lecture Notes Full - 230406 - 1107114402 Ajesh RPas encore d'évaluation
- NullDocument10 pagesNullapi-25932525Pas encore d'évaluation
- RCA Power Transistors Applications 1983Document290 pagesRCA Power Transistors Applications 1983Paulo Ricardo MendelPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction Transistors Talha Syed NaqviDocument51 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors Talha Syed NaqviMuhammad AwaisPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review of Current Electrostatic Measurement TechniquesDocument7 pagesA Review of Current Electrostatic Measurement TechniquesJan Posvic100% (2)
- UntitledDocument41 pagesUntitledSushant Kumar JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- PIP-LC User ManualDocument31 pagesPIP-LC User ManualPelusaGurmendezPas encore d'évaluation