Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mountain Formation
Transféré par
Charles Cornelius0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
35 vues1 pageMountain Formation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMountain Formation
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
35 vues1 pageMountain Formation
Transféré par
Charles CorneliusMountain Formation
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
CLIL360 2014 All rights reserved. May be photocopied for use in the classroom.
Images are from Wikimedia Commons and are in public domain
unless stated.
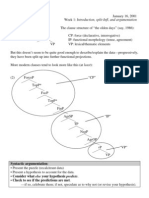
The Earths surface is broken into many pieces called
tectonic plates. The plates move because of heat from
the inside of the Earth. They move very slowly just a
few millimetres a year - but when they push against
another plate, mountain ranges are often formed. It
takes millions of years to form mountains.
Fold Mountains
When two plates push against each other, the land
along the edge of the plates is pushed upwards. This
is why many mountain ranges are long and narrow.
Many mountain ranges of the world were formed this
way.
The Himalayas were formed when the Indian Plate
pushed against the Eurasian Plate. In fact, the
Himalayas are still being formed: The Indian Plate is
moving north into the Eurasian Plate and the
Himalayas are rising by about a millimetre a year.
The Alps were formed when the African Plate pushed
against the Eurasian Plate. The Alps are still being
formed. In millions of years, the Alps will be as high as
the Himalayas and the Mediterranean Sea will
disappear.
Fault-Block Mountains
When tectonic plates move, large cracks, called faults,
are formed in the Earth's surface. Sometimes, huge
blocks of rock, often hundreds of kilometres long, are
formed inside these faults. Sometimes, these huge
blocks of rock are pushed upwards by the movement
of tectonic plates. Sometimes the blocks move apart,
forming a valley in between. The Sierra Nevada
Mountains in the USA, and the Black Forest in
Germany, are examples of block mountain ranges.
Volcanoes
Volcanoes are formed when hot rock (magma) below
the surface of the Earth is pushed up and through the
surface of the Earth. This often happens when one
tectonic plate slides under another plate, and when two
tectonic plates move away from each other.
Dome Mountains
Dome mountains are formed when magma rises from
inside the Earth but does not come through the
surface. Instead, the magma pushes up the Earth's
crust. Eventually, the magma cools and goes hard. A
dome mountain usually forms a dome shape. Dome
mountains are usually surrounded by flat land.
Sometimes magma rises over a large area, such as
the Llano Uplift in Texas.
Plateau Mountains
Plateau mountains are large areas of high, flat land
(plateaus) which have been eroded by wind, water and
ice. For example, valleys will be formed by streams
and rivers over thousands of years, and mountains will
be formed either side of the valley. The Cook
Mountains in New Zealand and the Catskill Mountains
of New York State are examples of plateau mountains.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Platinum English FAL Grade 5 Lesson PlansDocument64 pagesPlatinum English FAL Grade 5 Lesson Planskonanani73% (33)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Ten Lessons On ArabicDocument84 pagesTen Lessons On ArabicKamran Haikal100% (3)
- Climbing Everest DiaryDocument1 pageClimbing Everest DiaryCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Man On The MoonDocument1 pageMan On The MoonCharles Cornelius100% (1)
- The AlpsDocument1 pageThe AlpsCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Mountain ClimateDocument1 pageMountain ClimateCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- James CookDocument1 pageJames CookCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Ibn BattutaDocument1 pageIbn BattutaCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Mount EverestDocument1 pageMount EverestCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Everest ConqueredDocument1 pageEverest ConqueredCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Ascent of MatterhornDocument1 pageAscent of MatterhornCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Ferdinand MagellanDocument1 pageFerdinand MagellanCharles Cornelius100% (1)
- HimalayasDocument1 pageHimalayasCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Christopher ColumbusDocument1 pageChristopher ColumbusCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- European Mountain RangesDocument1 pageEuropean Mountain RangesCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Mountain RangesDocument1 pageMountain RangesCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- VoyagerDocument1 pageVoyagerCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Marco PoloDocument1 pageMarco PoloCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 001 - Russian LanguageDocument4 pagesLesson 001 - Russian LanguageYiannis KaminisPas encore d'évaluation
- Roald AmundsenDocument1 pageRoald AmundsenCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Technologies in Use For Second Language Learning. by Mike LevyDocument15 pagesTechnologies in Use For Second Language Learning. by Mike LevyCharles Cornelius100% (2)
- Rod Ellis 1995 Interpretation Tasks For Grammar Teaching TESOL QuarterlyDocument19 pagesRod Ellis 1995 Interpretation Tasks For Grammar Teaching TESOL QuarterlyCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Lewis and ClarkDocument1 pageLewis and ClarkCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Amelia EarhartDocument1 pageAmelia Earhartclil360100% (1)
- Zoltan Dornyei 1995 On The Teachability of Communication Strategies TESOL QuarterlyDocument31 pagesZoltan Dornyei 1995 On The Teachability of Communication Strategies TESOL QuarterlyCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Vivian Cook 1999, Going Beyond The Native Speaker in The Language ClassroomDocument26 pagesVivian Cook 1999, Going Beyond The Native Speaker in The Language ClassroomCharles Cornelius100% (2)
- Criticism On Communicative ApproachDocument11 pagesCriticism On Communicative ApproachisabelprofeatalPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabulary Notebooks: Theoretical Underpinnings and Practical Suggestions Norbert Schmitt and Diane SchmittDocument11 pagesVocabulary Notebooks: Theoretical Underpinnings and Practical Suggestions Norbert Schmitt and Diane SchmittCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Widdowson - Against Dogma - Reply To SwanDocument4 pagesWiddowson - Against Dogma - Reply To SwanCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- What We Know About Second Language Acquisition: A Synthesis From Four PerspectivesDocument58 pagesWhat We Know About Second Language Acquisition: A Synthesis From Four PerspectivesCharles CorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Swan A Critical Look at The Communicative Approach 2Document12 pagesSwan A Critical Look at The Communicative Approach 2Charles Cornelius100% (1)
- Past Tense of The VerbDocument5 pagesPast Tense of The VerbTanya FloreaPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGLISH MELCs Grade 3Document3 pagesENGLISH MELCs Grade 3EvelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Diego Collado's Grammar of The Japanese Language by Collado, Diego, - 1638Document118 pagesDiego Collado's Grammar of The Japanese Language by Collado, Diego, - 1638Gutenberg.org100% (7)
- Gim Causative Have and GetDocument4 pagesGim Causative Have and GetLorena Cepeda Espinoza-GavilánPas encore d'évaluation
- JSU & Skema Jawapan BAHASA INGGERIS PEMAHAMAN PKSR 2Document2 pagesJSU & Skema Jawapan BAHASA INGGERIS PEMAHAMAN PKSR 2Izzurah WasliPas encore d'évaluation
- Guía Verb To Be 6to BásicoDocument2 pagesGuía Verb To Be 6to BásicoOvalle Ojeda MaricelPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument9 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechYuli SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- MODAL VERBS Table PDFDocument1 pageMODAL VERBS Table PDFKarolis BilskisPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix: Glossary TermsDocument23 pagesAppendix: Glossary TermsguyPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent Simple Vs Present ContinuousLEIDY TATIANA CAVIEDES ZUTAPas encore d'évaluation
- How to Adjust Language for Different AudiencesDocument11 pagesHow to Adjust Language for Different AudiencesSatomi Sta AnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Quiz g9Document2 pagesLong Quiz g9nurainaPas encore d'évaluation
- PronounsDocument2 pagesPronounsNajoie Khalaf Abbas100% (1)
- SyntaxII 1 IP PollockDocument10 pagesSyntaxII 1 IP PollockFacestar KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar videos: Exercises on this, that, these and thoseDocument2 pagesGrammar videos: Exercises on this, that, these and thoseyuraima100% (1)
- Grammar 4 - As If As ThoughDocument13 pagesGrammar 4 - As If As ThoughAyu Endah Pertiwi100% (1)
- Pronouns in EnglishDocument2 pagesPronouns in EnglishAchmad FauzanPas encore d'évaluation
- The English VerbDocument127 pagesThe English Verbmmm_popa6222100% (1)
- Discussion On Year 6 Summative Test 1 Paper 2Document18 pagesDiscussion On Year 6 Summative Test 1 Paper 2yusmyunPas encore d'évaluation
- Syntax1 PDFDocument7 pagesSyntax1 PDFfarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3A Position of Adverbs of Frequency: Adverbs Words That Describe Verbs, Sentences And/Or Adjectives ExamplesDocument6 pages3A Position of Adverbs of Frequency: Adverbs Words That Describe Verbs, Sentences And/Or Adjectives ExamplesAlexander FarezPas encore d'évaluation
- By Zain ImranDocument14 pagesBy Zain ImranZainImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Patterns: - Ing, ToDocument3 pagesVerb Patterns: - Ing, ToKatarina JovanovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Morphemes: Free vs Bound Morphemes ExplainedDocument5 pagesTypes of Morphemes: Free vs Bound Morphemes ExplainedSafkat Al FayedPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Study Korean - Lesson 1 - Basic Korean SentencesDocument12 pagesHow To Study Korean - Lesson 1 - Basic Korean SentencesS_ghazal100% (1)
- Grammar Book Level B2Document125 pagesGrammar Book Level B2luisPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic and Derived StructureDocument14 pagesBasic and Derived StructureRisnu Laila67% (3)
- Traditional GrammarDocument20 pagesTraditional GrammarMessatsu DZPas encore d'évaluation