Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Anims and Urea
Transféré par
Shivam GuptaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Anims and Urea
Transféré par
Shivam GuptaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
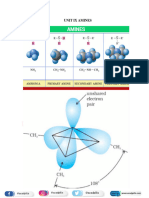
ssAmines and Urea
Introduction
Preparation
Properties of Amine
Properties of Amine
Aliphatic amines are always more basic than aromatic amines due to absence of resonance.
Aqueous solution of amines are basic in nature, express by following reaction. When this reacts with ferric chloride it forms red
precipitate of ferric hydroxide.
This reaction with benzoyl chloride is also known as
Benzoylation of amines or Schowtann Bowmanns Reaction.
(viii) Reaction with HNO
2
. (Nitrosation of aliphatic amines)
When sodium nitrite reacts with H
2
SO
4
or HCl it produces nitrous acid (HNO
2
) which works
as precursor of nitrosyl cation (N
+
O) this species is known as nitrosating agents.
When any secondary amines reacts with nitrous acid, amine work as nucleophile which is
attacking at nitrosyl cation to form yellow liquid nitroso solution.
Some other examples of nitroso products
When primary amines undergo process of nitrosation, nitroso compounds formed first and
can react further and finally produce various products where alcohols are formed as major
product.
Alkyl diazonium ion is the final product of this sequence but not any other species can be
isolated. When any primary amine is converted into diazonium species, it is known as
diazotisation of amines. These are not very much stable due to positively charged nitrogen
atom which is strained species. Its decompose rapidly where molecular nitrogen is a leaving
group and carbocations are formed.
As the nitrogen free products result from the formation and decomposition of diazonium salts
so these reactions are known as deamination reactions.
The nitrosation of tertiary alkylamines is rather complicated, and these reactions are also not
very useful in general chemistry primarilly they form addition product which breakdown on
heating and form nitrasoamine.
When primary amines reacts with excess of alkyl halide, it quaternize the starting amines to
form quaternary ammonium salt.
Above reaction is known as Hoffmanns reaction prefer less substituted alkene,
an example of kinetically control product. If we study stereochemistry a preference of trans-
periplanar (Anti)-elimination of the H and the amine. It shows, E2 mechanism with anti
stereochemistry.
By simply quaternizing the 1 amines with an excess (> 3 equivalents) of alkyl halide is also
known as Hoffmanns exhaustive alkylation. For example
In this example anti-elimination requires loss of one of the
which is trans to the nitrogen not cis
. This can be given by chair conformation where nitrogen is axial, so above product can
formed.
Some following conversions also explain the concept of Hoffmanns quaternary ammonium
salt
(xiv) Cope elimination
When tertiary alkylamine oxides in which one of alkyl group have
atom undergo thermal cleavage to form alkenes and hydroxyl amine.
This elimination does not require the presence of baseion, actually internal base already
present inside the system as N-oxide oxygen so intramolecular base promotes a Ei
elimination by path of a five membered cyclic transition state.
Above reaction follows syn stereochemistry for elimination exactly opposite to the anti
elimination in Hoffmanns regiochemistry. For example
Second isomeric cyclohexene is not formed because it is impossible for a ring hydrogen to
becomes syn to the amine oxide group unless the cyclohexane ring is severely distorted. Cope
elimination also form less substituted alkene same as Hoffmanns orientation.
UREA
Basic Character
First organic compound to be synthasized in lab from inorganic compounds thus discarding
Vital force theory
of Berzelius which said that no organic compound can be synthesized in lab. It was
synthesized by Wholars.
On the other hand acetic acid was the first organic compound to be synthesize from elements
in their free states.
Urea is a monoamide of carbamic acid (NH
2
COOH) and diamide of carbonic acid
H
2
CO
3
Preparation
Manufacture of urea
Urine contains some amount of urea so when it reacts with HNO
3
, a ppt of urea nitrate is formed which on reaction with BaCO
3
gives urea. In this process coloured impurities are removed by acidic KMnO
4
.
Properties
Breaking of urea takes place by NaOBr but Urea on Hoffmanns Hypobromite reaction forms
N
2
, CO
2
, H
2
O and NaBr while other amides furnish amines with lower homologue. Quantitative
estimation of urea done by cleavage in the presence of urease or fission by HNO
2s
Nitrosation of aromatic amines
(b) Nitrosation of aromatic amines
When aromatic amines undergo process of nitrosation by nitrosyl cation, electrophilic aromatic substitution occurs and then nitros o
derivatives are formed. For example:
Only very strong activating group, for example aniline and its derivatives can react with very weak electrophile nitrosyl with
nitrosyl cation it resemble with secondary amines where synthesis of N-alkyl nitrosoproduct takes place.
Alkyl diazomium ions are not stable due to positively charged nitrogen atom but aryl diazonium ions are much more stable due to
resonance and can be stored aqueous solution at 0C to 5C for long periods of time and loss of nitrogen form an unstable ary l
cation and is much slower than loss of nitrogen from an alkyl diazonium ion so C6H5N
+
2
immediately reacts with chloride ion to form benzene diazonium chloride.
Here NaNO2and HCl are taken in 1 : 3 so excess chloride ion quickly reacts with intermediate otherwise electrophile C6H5N
+
2
immediately reacts with nucleophilic aniline to form coupling azo product.
Aryl diazonium ions undergo a variety of reactions which makes them versatile intermediates for the preparation of many ring
substituted aromatic derivatives for example
These reactions occur only when amino group attached directly with benzene ring but when benzyl derivatives type compounds
undergo these reactions they form normal aliphatic amines type products.
When methyl amines reacts with nitrous acid they form alkoxyalkanes as major product.
(x) Separation of 1
o
, 2
o
and 3
o
Amines
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Amines, Amide and Derivatives: Edit and Compiled By: Hafiz Abdul Rafay Latif KayaniDocument26 pagesAmines, Amide and Derivatives: Edit and Compiled By: Hafiz Abdul Rafay Latif KayaniPalwasha KardarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Paper 1 FoundationDocument20 pagesChemistry Paper 1 FoundationsaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturer List - PE Pipe As Per IS 4984:2016: State Variety BrandDocument412 pagesManufacturer List - PE Pipe As Per IS 4984:2016: State Variety BrandÀVÎNÂSH RAAZPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D86Document27 pagesAstm D86dennise8100% (1)
- 12 Notes Ammines and AcidsDocument11 pages12 Notes Ammines and AcidsXyzdevuPas encore d'évaluation
- AminesDocument10 pagesAminesDUHA GORASHIPas encore d'évaluation
- AminesDocument2 pagesAminesatharvdubey29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 22Document21 pagesChapter 22AbdulhafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Amines NCERTDocument10 pagesAmines NCERTvishwak.boddukuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1-AMINES PART 2Document92 pagesGroup 1-AMINES PART 2Jana PaduaPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 AminesDocument8 pages13 AminesShesha krishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- AMINESDocument59 pagesAMINESJanna May Acierto100% (1)
- Hsslive XII Chemistry Amines NoteDocument4 pagesHsslive XII Chemistry Amines Notetrendzz youtuberPas encore d'évaluation
- Amines Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Document19 pagesAmines Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Scar LPas encore d'évaluation
- AminesDocument12 pagesAminesEmelda BanumathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Anubhav Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesAnubhav Chemistry ProjectManojPas encore d'évaluation
- Amination by ReductionDocument46 pagesAmination by ReductionSidra LiaquatPas encore d'évaluation
- Section A: 1. Testing For Functional GroupsDocument16 pagesSection A: 1. Testing For Functional GroupsGrace JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Substitution: Alkyl vs. AcylDocument10 pagesAcid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Substitution: Alkyl vs. AcylKarthik SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Substitution: Alkyl vs. AcylDocument10 pagesAcid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Substitution: Alkyl vs. AcylKarthik SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- ch20 Amines Part2Document7 pagesch20 Amines Part2kumber_singh5069Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Amines - TopperlearningDocument11 pagesRevision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Amines - TopperlearningRishabh BhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Aldehydes and Ketones .NotesDocument32 pagesAldehydes and Ketones .NotesvishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic MaterialDocument15 pagesOrganic MaterialAditya GathwalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry All Important ReactionsDocument14 pagesChemistry All Important Reactionsaayushnair2506100% (1)
- Notes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesDocument22 pagesNotes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesVanshika JainPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Amines Chapter NotesDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Amines Chapter NotesGayathiriPas encore d'évaluation
- STD XII Class Note Chapter 12 13 2021 22Document16 pagesSTD XII Class Note Chapter 12 13 2021 22Saurabh ShekharPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry: Classes Competitive Exams Buy A Course +919243500460Document10 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry: Classes Competitive Exams Buy A Course +919243500460sssPas encore d'évaluation
- AminesDocument13 pagesAminesSohamPas encore d'évaluation
- Amines WS 1 TheoryDocument3 pagesAmines WS 1 TheorytotallynotparthdubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Name ReactionsDocument10 pagesName ReactionsParam SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry Name ReactionDocument13 pagesOrganic Chemistry Name ReactionDeep GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Poc Unit-5Document9 pagesPoc Unit-5Bintoo SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bayer Test, Dan Bromine TestDocument18 pagesBayer Test, Dan Bromine TestBa'ist KhaerulPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Chemical Reactions For Class 12 ChemistryDocument10 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions For Class 12 ChemistryRitishPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch13 AminesDocument11 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch13 AminesAkPas encore d'évaluation
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocument5 pagesAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nomenclature: Chapter 19: AminesDocument5 pagesNomenclature: Chapter 19: AminesRobert GardnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Amine: The General Structure of An AmineDocument16 pagesAmine: The General Structure of An AmineCarla WashingtonPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkyl HalidesDocument20 pagesAlkyl HalidesShivam Gupta0% (1)
- Chem Notes PDFDocument8 pagesChem Notes PDFAliHassanMushtaqPas encore d'évaluation
- AminesDocument62 pagesAminesmitul muhammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming Reactions Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesNaming Reactions Organic Chemistrysaapldesign1 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amine IIDocument12 pagesAmine IIjohnsmithprayPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions of Amines and AmidesDocument7 pagesReactions of Amines and AmidesClechecyn Ella AgpadPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes AminesDocument26 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Revision Notes AminesABHISEKPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse Test Paper - 01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Amines)Document7 pagesCbse Test Paper - 01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Amines)Tamil SelviPas encore d'évaluation
- Class12 - Organichemistry - Named ReactionsDocument6 pagesClass12 - Organichemistry - Named ReactionsMᴀïᴢᴍɛɛŋ AŋꜱᴀʀïPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Name ReactionsDocument10 pages2 Name ReactionsArvindKumar100% (1)
- Important Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry With MechanismDocument9 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry With MechanismSoma SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Organic Chemistry ReactionsDocument9 pagesUnit 5 Organic Chemistry ReactionsRobbing_Hood100% (1)
- AmineDocument3 pagesAmineLinh ĐồngPas encore d'évaluation
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 20: Nitrogen CompoundsDocument9 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 20: Nitrogen CompoundsAgung Ratana Jayo Silim IPH StudentPas encore d'évaluation
- Type TextDocument16 pagesType TextDEEPAM MOHANTYPas encore d'évaluation
- M Sc-1Document12 pagesM Sc-1Shreyas BhandaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Aromatic Carboxylic Acid Preparation and ReactionDocument24 pagesAromatic Carboxylic Acid Preparation and Reactionsayyed mohsinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 202003291608409191arun Sethi Diazonium CompoundsDocument12 pages202003291608409191arun Sethi Diazonium CompoundsMarwan FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Name ReactionsDocument10 pagesName ReactionsMUKUL SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions of Aromatic AminesDocument21 pagesReactions of Aromatic Aminessayyed mohsinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic Acid Lab ReportDocument7 pagesCarboxylic Acid Lab Reportretsen30002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name RXNS: 1. Sandmeyer ReactionDocument10 pagesName RXNS: 1. Sandmeyer ReactionnitsPas encore d'évaluation
- Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument18 pagesNucleophilic SubstitutionShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jee MainDocument23 pagesJee MainKrishnagopal KunduPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Names and Geneva SystemDocument26 pagesCommon Names and Geneva SystemShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental Organic ChemistryDocument42 pagesFundamental Organic ChemistryShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- IsomerismDocument22 pagesIsomerismShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkanes Paraffins: Preparation (I) From Grignard ReagentDocument25 pagesAlkanes Paraffins: Preparation (I) From Grignard ReagentShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Al KynesDocument16 pagesAl KynesShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aldehyde and KetonesDocument45 pagesAldehyde and KetonesShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkadienes & Its PropertiesDocument24 pagesAlkadienes & Its PropertiesShivam Gupta67% (3)
- Alkyl HalidesDocument20 pagesAlkyl HalidesShivam Gupta0% (1)
- Principle of Extraction of MetalsDocument28 pagesPrinciple of Extraction of MetalsShivam Gupta100% (1)
- Alcohols, Diols, TriolsDocument32 pagesAlcohols, Diols, TriolsShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae: Shubhanshu MehrotraDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Shubhanshu MehrotraShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concave Mirrors TeacherDocument5 pagesConcave Mirrors TeacherShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 6-ADocument9 pagesGroup 6-AShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1-ADocument14 pagesGroup 1-AShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- IIT Maths Sample Paper 2: AlgebraDocument2 pagesIIT Maths Sample Paper 2: AlgebraShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basf Ucrete hf100rt TdsDocument4 pagesBasf Ucrete hf100rt TdsRana Ahmad AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Drinking Water Report 2020Document29 pagesAnnual Drinking Water Report 2020bexuxubePas encore d'évaluation
- Dienes: Reporters: Luis, Shavemil R. Mendevil, Angielyn Oquialda, Joan S. Sario, Angelo Sentillas, AljhonDocument63 pagesDienes: Reporters: Luis, Shavemil R. Mendevil, Angielyn Oquialda, Joan S. Sario, Angelo Sentillas, AljhonMICHELE REGALARIOPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 BOEKEL SCIENTIFIC 1344 (Inglés)Document1 page1 BOEKEL SCIENTIFIC 1344 (Inglés)felix bazanPas encore d'évaluation
- Compliance To Woqod GuidelinesDocument18 pagesCompliance To Woqod GuidelinesMohamedHanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gizmo Titration WorksheetDocument5 pagesGizmo Titration Worksheetapi-321107093Pas encore d'évaluation
- Indumax CLS54D EN - 0218Document12 pagesIndumax CLS54D EN - 0218Carlos LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- DIY - Soldering P36 & 37Document2 pagesDIY - Soldering P36 & 37RamavallabhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals-RocksDocument5 pagesRocks and Minerals-RocksGURU BEN PIANO STUDIO PRODUCTIONPas encore d'évaluation
- Daphne Super Coat TWDocument2 pagesDaphne Super Coat TWSuprastowo Bin SarinoPas encore d'évaluation
- CompositesDocument55 pagesCompositesali mohammed100% (1)
- Lesson PlansDocument6 pagesLesson PlansManyando MukelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermocouple Forging IndustriesDocument8 pagesThermocouple Forging IndustriesYogesh GholapPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Spatial and Temporal Controls On The Formation of Phosphate Deposits - A ReviewDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Spatial and Temporal Controls On The Formation of Phosphate Deposits - A Reviewattorig abdul goffarPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in Science 8 3RD QuarterDocument5 pagesReviewer in Science 8 3RD QuarterJillianPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomed LDH 51Document2 pagesBiomed LDH 51D Mero LabPas encore d'évaluation
- OM JSCB XXXXSB E 2020 PRINTDocument27 pagesOM JSCB XXXXSB E 2020 PRINTdirrleonardPas encore d'évaluation
- Screw Take-Up Device Ur1 Ur7: Conveyor ComponentsDocument1 pageScrew Take-Up Device Ur1 Ur7: Conveyor ComponentsDxFxPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecules: Mechanochemical and Size Reduction Machines For BiorefiningDocument22 pagesMolecules: Mechanochemical and Size Reduction Machines For BiorefiningBryan AlbornozPas encore d'évaluation
- ART Coumarins Thee Antimicrobial AgentsDocument9 pagesART Coumarins Thee Antimicrobial AgentsHECTORIBZAN ACERO SANDOVALPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso-Tc 25 N 470Document49 pagesIso-Tc 25 N 470ashey7777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book of Abstracts - Prosciba 2023Document304 pagesBook of Abstracts - Prosciba 2023Jonatas LopesPas encore d'évaluation
- BiokonjugátumokDocument54 pagesBiokonjugátumoksaif aljanabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Pollution and Control EngineeringDocument10 pagesAir Pollution and Control EngineeringVINOTHKUMAR SAMPATHPas encore d'évaluation
- RESEARCHDocument2 pagesRESEARCHLorenzo CohenPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron, FerroZine Method 8147, 02-2009, 9th Ed PDFDocument5 pagesIron, FerroZine Method 8147, 02-2009, 9th Ed PDFchemicalchouhan9303Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Processing of Textiles - I - CompressedDocument118 pagesChemical Processing of Textiles - I - CompressedOmkar Jadhav100% (1)