Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
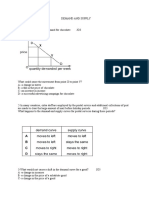
Determinants of Demand
Transféré par
Naeem HaiderCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Determinants of Demand
Transféré par
Naeem HaiderDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Determinants of Market
Demand
IGCSE Economics
Key Issues
! How the price mechanism works
! Law of demand
! Determinants (Factors that influence) of
demand
! Joint demand, effective demand
! The demand curve and shifts in demand curve
Functions of Prices
! The Price Mechanism
Prices provide the main method through which
scarce resources are allocated between
competing uses in virtually all modern economies
! The Signalling Function
Prices signal what is available, conveying
information to producers and consumers alike
If prices signal wrong or misleading information,
then markets may perform inefficiently or break
down completely
Functions of Prices
! The Incentive Function
Prices create incentives for agents to behave in
ways consistent with their self-interest. For
example, the rising price of a good may:
Result in a firm expanding production of that good
in its pursuit of profit-maximisation
Result in a consumer contracting demand as she
tries to maximise her overall utility with her limited
income
Demand: Buyers in the Market
! Demand:
The quantity of a product consumers are willing
and able to buy at different prices in a specified
time period
Normally there is an inverse relationship between
the price of good X and the quantity demanded of
good X
Demand: Buyers in the Market
! Factors that affect demand
Consumer tastes and preferences
Income available to the consumer
Prices of other goods and services
Substitute goods
Complementary goods
Consumer population Age distribution and size
Advertising
Demand for New Cars
The Price of New
Cars
Interest Rates
Relative prices of
second-hand
vehicles
Cost of fuel
Road Charges /
Tax
Consumer
Confidence
Relative costs of
travelling on public
transport
Availability of
Credit
Costs of car
insurance and
servicing etc
Effective Demand
! Effective Demand
When a consumers' desire to buy a product is
backed up by an ability to pay for it
They must have sufficient real purchasing power
Consider the market for pay-per-view boxing
events the companies promoting these events
must price carefully so that they tap into the
largest possible market
Effective demand
Demand is only effective if
backed up with an ability to
pay for the product
Latent Demand
! Latent Demand
Latent demand exists when there is willingness to
purchase a good, but where the consumer lacks
the real purchasing power to be able to afford the
product
Latent demand is affected by persuasive
advertising where the producer is seeking to
influence consumer tastes and preferences
Latent demand
Derived Demand (Joint Demand)
! The demand for a product X might be strongly
linked to the demand for a related product Y
giving rise to the idea of a derived demand
! For example, the demand for coal is derived in
part on the demand for fossil fuels to burn in
the process of generating energy
! Demand for steel is strongly linked to the
demand for new vehicles and many other
manufactured products
Derived demand
The housing market is a good example of the idea of
derived demand. When construction of new homes
rises, so too does the demand for materials used in
new properties as well as demand for labour
Demand for steel
! The
construction
of a new
steel roof
! Global
demand for
steel is
strongly
linked to the
world
economic
cycle
Complementary Demand
! As the demand for
mobile phone handsets
increases, so too does
demand for phone calls
! Mobile phone
companies often sell
handsets at very low
prices because they
can recoup revenues
from the calls made by
subscribers to their
network
The Demand Curve
Quantity
Demanded
Demand
P1
Q1 Q3 Q2
P2
P3
Price
A contraction of demand
Quantity
Demanded
Demand
P1
Q1 Q3 Q2
P2
P3
A contraction of demand
due to a higher price
Price
An expansion of demand
Quantity
Demanded
Demand
P1
Q1 Q3 Q2
P2
P3
An expansion of demand
due to a lower price
Price
Falling Prices and Demand
! Many goods and services are cheaper now in
both money and real terms than they were a
few years ago
Flights/holidays overseas
Audio-visual equipment TVs, DVD Players
Laptop computers
New car prices
! When prices are falling, we see a rise in the
quantity demanded as consumers respond to
the change in price
Price trends for selected items
Downward-sloping demand curve
! For normal goods, more is demanded as price falls
! Firstly at lower prices, consumers can afford to
purchase more with their income
! Secondly, a fall in price makes one good relatively
cheaper than a substitute
! Thirdly, a fall in price means that the consumer derives
more benefit per pound spent on the product than they
did before
! The demand curve is normally drawn in textbooks as a
straight line suggesting a linear relationship between
price and demand, but in reality, the demand curve will
be non-linear
Shifts in the demand curve
Changes in the conditions of
demand
Shifts in Demand
Quantity
Demanded
D1
P1
Q1 Q2 Q3
D2
D3
Increase in
Demand
Decrease in
Demand
Price
An outward shift in demand
! A rise in the real incomes of consumers
! An increase in the price of a substitute good (i.e. a
competing product)
! A fall in the price of a complementary good
! A change in consumers preferences towards the good
! An increase in the size of the total population
! A fall in interest rates
! A rise in consumer confidence
! Social changes which affect total demand for a product
Substitutes
! Substitutes are goods in competitive demand
They are replacements for another product
For example, a rise in the price of Esso petrol
(other factors held constant) should cause a
substitution effect away from Esso towards Shell
or other competing brands
Complements
! Complements are said to be in joint demand
Examples include: fish and chips, DVD players
and DVDs, iron ore and steel
A rise in the price of a complement to Good X
should cause a fall in the demand for X
Normal and Inferior Goods
! For normal products, more is demanded as
income rises, and less as income falls
! There are exceptions called inferior products
! They are often cheaper poorer quality
substitutes for some other good
! With a higher income a consumer can switch
from the cheaper substitute to preferred
alternative
! As a result, less of the inferior product is
demanded at higher levels of income
Income Elasticity of Demand
! For some products
there is a strong link
between income and
demand
New cars
Expensive furniture
Overseas holidays
Changes in price of Substitutes
P1
Q1 Q2
Demand
Output (Q)
Price of
Texaco
petrol
P1
Q1 Q2
D1
Output (Q)
Price of
Shell
petrol
P2
D2
Changes in tastes and preferences
! Market demand in nearly every market is often affected
by changes in consumer preferences
! One persons preferences can affect those of others
! This is a very powerful force in digital markets e.g.
iTunes, demand for DVDs
! But it is also powerful when influencing the demand for
meals at restaurants, hotels in holiday destinations et
al
! Advertising and marketing are explicitly designed to
influence consumer tastes and preferences
What factors are influencing market
demand for smoothies?
Exceptions to the law of demand
! Ostentatious consumption
! Some goods are luxurious items where satisfaction
comes from knowing both the price of the good and
being able to flaunt consumption of it to other people!
! Speculative Demand
! The demand for a product can be affected by
speculative demand. Here, potential buyers are
interested not just in the satisfaction they may get from
consuming the product, but also the potential rise in
market price leading to a capital gain or profit
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- FA - Financial Accounting: Chapter 2 - Regulatory FrameworkDocument23 pagesFA - Financial Accounting: Chapter 2 - Regulatory FrameworkSumiya YousefPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Microeconomics TheoryDocument37 pagesApplications of Microeconomics TheoryCharlie Magne G. Santiaguel100% (1)
- Tutorial: Tuesday 8.00-9.00a.m Group: T1G1: CIX1002: Principles of MacroeconomicsDocument22 pagesTutorial: Tuesday 8.00-9.00a.m Group: T1G1: CIX1002: Principles of MacroeconomicsYongAnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand NumericalsDocument2 pagesDemand Numericalsmahesh kumar0% (1)
- CVP AnalysisDocument3 pagesCVP AnalysisEjaz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition by Sayre and Morris Solution ManualDocument67 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition by Sayre and Morris Solution Manualkevaxt100% (1)
- Stock Market Barometer of The Economy 1Document12 pagesStock Market Barometer of The Economy 1Raval ashilPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Marketing Strategy of Mountain DewDocument30 pagesReport On Marketing Strategy of Mountain DewSanchit Taksali40% (5)
- Money Banking Finance MBF Notes B.com Part 1 Punjab University PDFDocument85 pagesMoney Banking Finance MBF Notes B.com Part 1 Punjab University PDFEraj Ahmed100% (2)
- Demand and Supply-Market EquilibriumDocument30 pagesDemand and Supply-Market EquilibriumGomathiRachakondaPas encore d'évaluation
- Page 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandDocument4 pagesPage 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandRumana AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Applications of Macroeconomics Theory As A Basis For Understanding The Key Economic Variables Affecting The BusinessDocument52 pagesChapter 6 Applications of Macroeconomics Theory As A Basis For Understanding The Key Economic Variables Affecting The Businessaladdin oidacraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Market StructureDocument14 pagesChapter 7 Market StructureMissDang100% (1)
- Grade 8 Demand Supply mcq-1Document26 pagesGrade 8 Demand Supply mcq-1Prayrit JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Net Present Value and Other Investment CriteriaDocument33 pagesChapter 8 Net Present Value and Other Investment CriteriaPaul Adrian BalascanPas encore d'évaluation
- Balance of Payment PPT Presentation 1Document12 pagesBalance of Payment PPT Presentation 1HEMANTH KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Aggregate Supply and DemandDocument13 pagesAggregate Supply and DemandkayejamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Determinants of DemandDocument9 pagesDeterminants of DemandTina Antony100% (1)
- The Theory of Consumer BehaviourDocument30 pagesThe Theory of Consumer BehaviourMiswar ZahriPas encore d'évaluation
- BDI3C Evaluation Rubric For Entrepreneurial Venture PlanDocument3 pagesBDI3C Evaluation Rubric For Entrepreneurial Venture PlanRenante DeseoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Volume ProfitDocument73 pagesCost Volume ProfitAsiiyah100% (1)
- CA Final Case Study NewDocument185 pagesCA Final Case Study NewRaja100% (1)
- The Tobin's Q Theory of InvestmentDocument3 pagesThe Tobin's Q Theory of InvestmentGodwinUddinPas encore d'évaluation
- IS-LM FrameworkDocument54 pagesIS-LM FrameworkLakshmi NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2-Scarcity, Choice and Opportunity CostDocument32 pagesChapter 2-Scarcity, Choice and Opportunity CostNuriIzzatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.1 International Trade and Specialization: Igcse /O Level EconomicsDocument10 pages6.1 International Trade and Specialization: Igcse /O Level EconomicsAvely AntoniusPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 1 Managerial Accounting BasicsDocument53 pagesCH 1 Managerial Accounting BasicsIra AdraPas encore d'évaluation
- Keynesian Theory of Income DeterminationDocument15 pagesKeynesian Theory of Income DeterminationVivek SharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch07 Incremental AnalysisDocument47 pagesCh07 Incremental Analysisعبدالله ماجد المطارنهPas encore d'évaluation
- Elesticity of DemandDocument48 pagesElesticity of DemandDr.Ashok Kumar Panigrahi100% (1)
- Chapter01 Managers, Profits, and MarketsDocument47 pagesChapter01 Managers, Profits, and MarketsMohammad Raihanul HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Theory of ProductionDocument5 pagesChapter 5 Theory of ProductionYus Linda100% (1)
- WEEK3 LESSON 4 Production FunctionDocument4 pagesWEEK3 LESSON 4 Production FunctionSixd WazninePas encore d'évaluation
- Decision Under CertaintyDocument30 pagesDecision Under Certaintymd1008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Price Adjustment Strategies: Discount and Allowance PricingDocument6 pagesPrice Adjustment Strategies: Discount and Allowance Pricinghashaam khatriPas encore d'évaluation
- Foreign Exchange Market NotesDocument49 pagesForeign Exchange Market Notesderekleung1992Pas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Edexcel AS Level Microeconomics GlossaryDocument7 pagesEconomics Edexcel AS Level Microeconomics Glossarymarcodl18Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 1 - Introduction MicroeconomicsDocument45 pagesCH 1 - Introduction MicroeconomicsAchmad TriantoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.0 Introduction To EconomicsDocument48 pages1.0 Introduction To Economicsrajai farwagiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Demand and SupplyDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Demand and SupplyAbdul-Mumin AlhassanPas encore d'évaluation
- BBS Macroeconomics 2nd YearDocument3 pagesBBS Macroeconomics 2nd YearIsmith Pokhrel0% (1)
- Keynes Law of ConsumptionDocument7 pagesKeynes Law of ConsumptionMohammedAhmedRazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermediate Macro Economics - Assignment 1 PDFDocument12 pagesIntermediate Macro Economics - Assignment 1 PDFTriple HPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors of ProductionDocument19 pagesFactors of ProductionRinky Talwar100% (1)
- Market StructuresDocument100 pagesMarket Structuresapi-3825580100% (9)
- Law of SupplyDocument32 pagesLaw of SupplyMahavir BhatiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2api-234284411100% (2)
- Lecture 5 - Growth and ProductivityDocument54 pagesLecture 5 - Growth and ProductivityAli Ali100% (1)
- Is LM ModelDocument3 pagesIs LM ModelAaquib AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet Unit 3 SupplyDocument4 pagesWorksheet Unit 3 SupplyPriya Yadav100% (1)
- Weighted Average Cost of Capital: Confidential and Legally PrivilegedDocument15 pagesWeighted Average Cost of Capital: Confidential and Legally PrivilegedBet RomanPas encore d'évaluation
- Eonomics Questions That May Be On A Business ExamDocument8 pagesEonomics Questions That May Be On A Business ExamVic Burrack100% (1)
- IB Business - 2.3 Leadership and ManagementDocument22 pagesIB Business - 2.3 Leadership and ManagementadrianaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECP5702 MBA ManagerialEconomics ROMANO SPR 16Document4 pagesECP5702 MBA ManagerialEconomics ROMANO SPR 16OmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)Document13 pagesProduction Possibilities Curve (PPC)Dhawal GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Valuation and Rate of ReturnsDocument42 pagesValuation and Rate of ReturnsMadCube gamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Macro-Economics: You No Longer Live in A Society You Live in An Economy!Document37 pagesMacro-Economics: You No Longer Live in A Society You Live in An Economy!Jayant MohapatraPas encore d'évaluation
- 0000001635-Macroeconomics For ManagersDocument19 pages0000001635-Macroeconomics For ManagersVigneshVardharajanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.2 and 2.5 Demand and Linear Demand RSDocument41 pages2.2 and 2.5 Demand and Linear Demand RSSyed HaroonPas encore d'évaluation
- Price Mechanism and ElasticityDocument72 pagesPrice Mechanism and ElasticityRaniya ShoukPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 DemandDocument25 pages2.1 DemandGrace GePas encore d'évaluation
- Demond Thoery - NotesDocument10 pagesDemond Thoery - Noteschikkegowda k gPas encore d'évaluation
- Nicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesNicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourNaeem HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Polya E ThesisDocument34 pagesPolya E ThesisNaeem HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Diminishing Marginal Utility: Can You Get Too Much of Something?Document24 pagesDiminishing Marginal Utility: Can You Get Too Much of Something?Naeem HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Monetary Policy On Indian IndustryDocument13 pagesImpact of Monetary Policy On Indian IndustryVikalp Saxena50% (2)
- Entrepreneurship 101 - How To Become EnterpreneurDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurship 101 - How To Become EnterpreneurNaeem HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Services Marketing 117 2Document37 pagesServices Marketing 117 2Naeem HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Paper BagDocument79 pagesProject On Paper BagDimple Kanojia67% (3)
- Pricing Assignment c2Document5 pagesPricing Assignment c2Naveendar RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Fresher JuicesDocument26 pagesProject On Fresher JuicesMuhammad Mohsin Shahzad Kahloon100% (1)
- Class Notes Cases and Laws: SalesDocument9 pagesClass Notes Cases and Laws: Salesjane ling adolfoPas encore d'évaluation
- Merchandising Costing - Dft.ranjanDocument24 pagesMerchandising Costing - Dft.ranjanRavi SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 22 General Equilibrium Theory: A. Interdependence in The EconomyDocument3 pagesChapter 22 General Equilibrium Theory: A. Interdependence in The EconomyishtiaqlodhranPas encore d'évaluation
- SOL BA Program 1st Year Economics Study Material and Syllabus in PDFDocument87 pagesSOL BA Program 1st Year Economics Study Material and Syllabus in PDFShamim Akhtar100% (1)
- Rights of Consumer Under Consumer Protection ActDocument10 pagesRights of Consumer Under Consumer Protection ActShimantika AdhikariPas encore d'évaluation
- Negative Prices in Electricity MarketDocument4 pagesNegative Prices in Electricity MarketWalter_Djuric_9539Pas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Price Index: Significance of CPIDocument10 pagesConsumer Price Index: Significance of CPInitish kumar twariPas encore d'évaluation
- Pricing Strategies.: Objectives.Document29 pagesPricing Strategies.: Objectives.Narsingh Das AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Let's Check: Regine Mae L. Yaniza - Bsce 2 Year CEE 109 - 3351Document6 pagesLet's Check: Regine Mae L. Yaniza - Bsce 2 Year CEE 109 - 3351Regine Mae Lustica YanizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument41 pagesSupply Chain ManagementVenkat KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Arithmetic: Problems For PracticeDocument3 pagesArithmetic: Problems For PracticeArchit HingePas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Importance of Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pages12 Importance of Price Elasticity of DemandVom Samourais50% (2)
- Market StructureDocument81 pagesMarket StructuresuryaabhimaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Seller Questionnaire (2017!09!20)Document60 pagesSeller Questionnaire (2017!09!20)vinod3511Pas encore d'évaluation
- 486 Assignment 1 AnDocument24 pages486 Assignment 1 AnNguyễn Thị Thu AnPas encore d'évaluation
- 4BDocument12 pages4BdagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap. II) (Appendix 2.13Document23 pagesChap. II) (Appendix 2.13Harish Kumar MahavarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1831 RulesDocument21 pages1831 RulestobymaoPas encore d'évaluation
- t113 PDFDocument151 pagest113 PDFViswanathan VPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes V3265, 2016 PDFDocument173 pagesLecture Notes V3265, 2016 PDFmangesh_morePas encore d'évaluation
- Vat On Sales of Goods or PropertiesDocument10 pagesVat On Sales of Goods or Propertiesgoerginamarquez100% (1)
- Tendernotice 1Document44 pagesTendernotice 1Raja G Circles SafetyPas encore d'évaluation
- Vsmart Academy CA Vishal Bhattad 09850850800Document5 pagesVsmart Academy CA Vishal Bhattad 09850850800ghksfskdhj vjbvkjvPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 - IIFT Managing Contracts & Negotiations PDFDocument43 pages06 - IIFT Managing Contracts & Negotiations PDFWahib WaqasPas encore d'évaluation
- Enterepreneurship PPT Ch-5Document53 pagesEnterepreneurship PPT Ch-5Mulu AlemPas encore d'évaluation