Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sensory Disorders
Transféré par
Kory Christina0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
51 vues2 pagesNursing Study Guide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentNursing Study Guide
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
51 vues2 pagesSensory Disorders
Transféré par
Kory ChristinaNursing Study Guide
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
CH 43 Sensory Disorders
Sensory Disorders Information
Definitions Sensation- Ability to receive & process stimuli through
sensory organs
Perception: Ability to experience, recognize, organize
& interpret sensory stimuli
Sensory Perception: ability to receive sensory
impressions & relate the stimuli to past experiences.
Anatomy & Physiology *Nervous System: 12 Cranial nerves & 31 Spinal nerves.
Components of Cognition:
Consciousness: awareness (verbal & tactile).
Consciousness may be altered by drugs, trauma, &
metabolic factors.
Arousal: State of wakefulness & alertness.
Memory: IMMEDIATE (retention of information for a
specific & short period of time). RECENT (Ability to
recall events from the past 24 hours). REMOTE
(Retention of experiences that occurred earlier in life
such as childhood). ** Remote memory is accurately
assessed ONLY when patient responses about past
events can be validated, either by others or written
account.
Affect: expression of mood or feeling, (mood can affect
ones thinking ability).
Judgment: ability to compare or evaluate alternatives
to come to a conclusion, based on reasoning &
supported by evidence.
Perception: Individuals awareness of reality. ILLUSION
(Inaccurate perception). HALLUCINATION (not based
on reality). DISOREINTATION (mentally confused
state).
CH 43 Sensory Disorders
Language: Spoken words, reading, writing, &
comprehension. *Most complex cognitive function.
Assessment *Senses protect us from danger & keep us safe.
5 SENSES:
Hear (Auditory)
Sight (Visual)
Smell (Olfactory)
Taste (Gustatory)
Touch (Tactile)
Sensory Deficit
(Change in perception of sensory
stimuli)
This affects all 5 senses. Examples are hearing or vision loss. Deficits can occur over time
as someone ages, or can occur suddenly & without warning. Patient must be able to
accommodate to the changes and compensate for it by strengthening one or more
senses.
Sensory Deprivation
(Reduced sensory input from
internal or external environment)
This can be a result of illness, trauma, or isolation. Individuals who are sensatory
deprived may exhibit: poor concentration, poor memory, confusion, impaired problem
solving, depression, irritability & boredom.
Taste Gustation. Taste sensations are altered secondary to neurological disorders or trauma.
Medication, antibiotics, & smoking can decrease taste. **Bitterness declines with age but
sweetness stays. Tastes are: Sweet, Salty, Bitterness, & Sour.
Smell Olfaction. Guardian from danger. Receptors for sense smell are located in the roof of the
nasal cavity. If these cells are damaged then the sense of smell is impaired. The body
cannot regenerate olfactory cells.
Touch Tactile. Cutaneous sensations of touch: pressure, vibration, cold, heat, and pain. Patients
with reduced or lost tactile sensation are at risk for decubitus ulcers. Reposition patient
Q2 hours.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Why Men Want Sex and Women Need Love by Barbara and Allen Pease - ExcerptDocument27 pagesWhy Men Want Sex and Women Need Love by Barbara and Allen Pease - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group62% (34)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Evidence Based DesignDocument4 pagesEvidence Based Designmartinadam82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tryout Consent Form - 2014 - Sign and ReturnDocument2 pagesTryout Consent Form - 2014 - Sign and ReturnSanjeevan BaraPas encore d'évaluation
- ASK-M 72cells Monocrystalline Module: Key FeaturesDocument2 pagesASK-M 72cells Monocrystalline Module: Key FeaturesNam Tran HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 Uptown Parksuites D3 PDFDocument54 pages2016 Uptown Parksuites D3 PDFArafat Domado100% (1)
- HEAS 1000 Health Assessment: Reflection of PracticeDocument4 pagesHEAS 1000 Health Assessment: Reflection of PracticePreet ChahalPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 4-H Show & Sale CatalogDocument53 pages2015 4-H Show & Sale CatalogFauquier NowPas encore d'évaluation
- Self Reflection 1Document5 pagesSelf Reflection 1api-270873994Pas encore d'évaluation
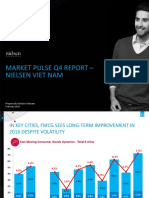
- Market Pulse Q4 Report - Nielsen Viet Nam: Prepared by Nielsen Vietnam February 2017Document8 pagesMarket Pulse Q4 Report - Nielsen Viet Nam: Prepared by Nielsen Vietnam February 2017K57.CTTT BUI NGUYEN HUONG LYPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing ProjectDocument82 pagesMarketing ProjectSumit GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Celltac MEK 6500Document3 pagesCelltac MEK 6500RiduanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 PolarographyDocument20 pages1 PolarographyRiya Das100% (1)
- Soft Tissue SarcomaDocument19 pagesSoft Tissue SarcomaEkvanDanangPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Lines SMART EDGE VILLARUEL For April 2024 v1Document89 pagesTransmission Lines SMART EDGE VILLARUEL For April 2024 v1mayandichoso24Pas encore d'évaluation
- EBANX Beyond Borders 2020Document71 pagesEBANX Beyond Borders 2020Fernanda MelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbo Hi DratDocument11 pagesCarbo Hi DratILHAM BAGUS DARMA .NPas encore d'évaluation
- 365 Days (Blanka Lipińska)Document218 pages365 Days (Blanka Lipińska)rjalkiewiczPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 10 - Reinforced - Concrete - Fundamentals and Design ExamplesDocument143 pagesCH 10 - Reinforced - Concrete - Fundamentals and Design ExamplesVeronica Sebastian EspinozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hema Lec HematopoiesisDocument8 pagesHema Lec HematopoiesisWayne ErumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cariprazine PDFDocument162 pagesCariprazine PDFige zaharaPas encore d'évaluation
- CatalogDocument12 pagesCatalogjonz afashPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4: Health and Fitness AdvertisingDocument4 pagesLesson 4: Health and Fitness AdvertisingCatherinePas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Operative Check Up of Farm Tools, ImplementsDocument19 pagesPre-Operative Check Up of Farm Tools, ImplementsLaurence Fabiala50% (2)
- Evidence-Based Strength & HypertrophyDocument6 pagesEvidence-Based Strength & HypertrophyAnže BenkoPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbes in Human Welfare PDFDocument2 pagesMicrobes in Human Welfare PDFshodhan shettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparing Polymers For The Jar TestDocument5 pagesPreparing Polymers For The Jar Testarvin4dPas encore d'évaluation
- S108T02 Series S208T02 Series: I (RMS) 8A, Zero Cross Type Low Profile SIP 4pin Triac Output SSRDocument13 pagesS108T02 Series S208T02 Series: I (RMS) 8A, Zero Cross Type Low Profile SIP 4pin Triac Output SSRnetiksPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 7-8: Health 9 Module 4Document8 pagesWEEK 7-8: Health 9 Module 4Heidee BasasPas encore d'évaluation
- Intraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor DynamicsDocument36 pagesIntraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor DynamicsIntan EkarulitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Usp 1078 Good Manufacturing Practices For Bulk Pharmaceutical Excipients PDFDocument13 pagesUsp 1078 Good Manufacturing Practices For Bulk Pharmaceutical Excipients PDFMayson BaliPas encore d'évaluation