Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
O4Qvec - c4 Soomenx
Transféré par
KapilanNavaratnamTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
O4Qvec - c4 Soomenx
Transféré par
KapilanNavaratnamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Solomon Press
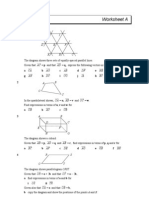
VECTORS C4 Worksheet A
1
G H I
D E F
A B C
The diagram shows three sets of equally-spaced parallel lines.
Given that AC = p and that AD = q, express the following vectors in terms of p and q.
a CA b AG c AB d DF e HE f AF
g AH h DC i CG j IA k EC l IB
2 B
O
C
In the quadrilateral shown, OA = u, AB = v and OC = w.
Find expressions in terms of u, v and w for
a OB b AC c CB
3 A B
D C
E F
H G
The diagram shows a cuboid.
Given that AB = p, AD = q and AE = r, find expressions in terms of p, q and r for
a BC b AF c DE d AG e GB f BH
4 R S
O T
The diagram shows parallelogram ORST.
Given that OR = a + 2b and that OT = a 2b,
a find expressions in terms of a and b for
i OS ii TR
Given also that OA = a and that OB = b,
b copy the diagram and show the positions of the points A and B.
A
Solomon Press
5 A
C D
O B
The diagram shows triangle OAB in which OA = a and OB = b.
The points C and D are the mid-points of OA and AB respectively.
a Find and simplify expressions in terms of a and b for
i OC ii AB iii AD iv OD v CD
b Explain what your expression for CD tells you about OB and CD.
6 Given that vectors p and q are not parallel, state whether or not each of the following pairs of
vectors are parallel.
a 2p and 3p b (p + 2q) and (2p 4q) c (3p q) and (p
1
3
q)
d (p 2q) and (4q 2p) e (
3
4
p + q) and (6p + 8q) f (2q 3p) and (
3
2
q p)
7 The points O, A, B and C are such that OA = 4m, OB = 4m + 2n and OC = 2m + 3n, where
m and n are non-parallel vectors.
a Find an expression for BC in terms of m and n.
The point M is the mid-point of OC.
b Show that AM is parallel to BC.
8 The points O, A, B and C are such that OA = 6u 4v, OB = 3u v and OC = v 3u, where
u and v are non-parallel vectors.
The point M is the mid-point of OA and the point N is the point on AB such that AN : NB = 1 : 2
a Find OM and ON .
b Prove that C, M and N are collinear.
9 Given that vectors p and q are not parallel, find the values of the constants a and b such that
a ap + 3q = 5p + bq b (2p + aq) + (bp 4q) = 0
c 4aq p = bp 2q d (2ap + bq) (aq 6p) = 0
10 A
C
O B
The diagram shows triangle OAB in which OA = a and OB = b.
The point C is the mid-point of OA and the point D is the mid-point of BC.
a Find an expression for OD in terms of a and b.
b Show that if the point E lies on AB then OE can be written in the form a + k(b a), where
k is a constant.
Given also that OD produced meets AB at E,
c find OE ,
d show that AE : EB = 2 : 1
C4 VECTORS Worksheet A continued
D
Solomon Press
VECTORS C4 Worksheet B
1 The points A, B and C have coordinates (6, 1), (2, 3) and (4, 3) respectively and O is the origin.
Find, in terms of i and j, the vectors
a OA b AB c BC d CA
2 Given that p = i 3j and q = 4i + 2j, find expressions in terms of i and j for
a 4p b q p c 2p + 3q d 4p 2q
3 Given that p =
3
4
and q =
1
2
, find
a | p | b | 2q | c | p + 2q | d | 3q 2p |
4 Given that p = 2i + j and q = i 3j, find, in degrees to 1 decimal place, the angle made with
the vector i by the vector
a p b q c 5p + q d p 3q
5 Find a unit vector in the direction
a
4
3
b
7
24
c
1
1
d
2
4
6 Find a vector
a of magnitude 26 in the direction 5i + 12j,
b of magnitude 15 in the direction 6i 8j,
c of magnitude 5 in the direction 2i 4j.
7 Given that m = 2i + j and n = i 5j, find the values of and such that
a m + n = 3i j b 2m n = 3i + 8j
8 Given that r = 6i + cj, where c is a positive constant, find the value of c such that
a r is parallel to the vector 2i + j b r is parallel to the vector 9i 6j
c | r | = 10 d | r | = 5 3
9 Given that p = i + 3j and q = 4i 2j,
a find the values of a and b such that ap + bq = 5i + 13j,
b find the value of c such that cp + q is parallel to the vector j,
c find the value of d such that p + dq is parallel to the vector 3i j.
10 Relative to a fixed origin O, the points A and B have position vectors
3
6
and
5
2
respectively.
Find
a the vector AB,
b AB,
c the position vector of the mid-point of AB,
d the position vector of the point C such that OABC is a parallelogram.
Solomon Press
11 Given the coordinates of the points A and B, find the length AB in each case.
a A (4, 0, 9), B (2, 3, 3) b A (11, 3, 5), B (7, 1, 3)
12 Find the magnitude of each vector.
a 4i + 2j 4k b i + j + k c 8i j + 4k d 3i 5j + k
13 Find
a a unit vector in the direction 5i 2j + 14k,
b a vector of magnitude 10 in the direction 2i + 11j 10k,
c a vector of magnitude 20 in the direction 5i 4j + 2k.
14 Given that r = i + 12j 4k, find the two possible values of such that | r | = 14.
15 Given that p =
1
3
1
, q =
4
2
1
and r =
2
5
3
, find as column vectors,
a p + 2q b p r c p + q + r d 2p 3q + r
16 Given that r = 2i + j + k, find the values of and such that
a r is parallel to 4i + 2j 8k b r is parallel to 5i + 20j 10k
17 Given that p = i 2j + 4k, q = i + 2j + 2k and r = 2i 4j 7k,
a find | 2p q |,
b find the value of k such that p + kq is parallel to r.
18 Relative to a fixed origin O, the points A, B and C have position vectors (2i + 7j + 4k),
(4i + j + 8k) and (6i 5j) respectively.
a Find the position vector of the mid-point of AB.
b Find the position vector of the point D on AC such that AD : DC = 3 : 1
19 Given that r = i 2j + k, and that r is parallel to the vector (2i 4j 3k),
a show that 3 + 2 = 0.
Given also that | r | = 29 2 and that > 0,
b find the values of and .
20 Relative to a fixed origin O, the points A, B and C have position vectors
6
2
4
,
12
7
4
and
6
1
8
respectively.
a Find the position vector of the point M, the mid-point of BC.
b Show that O, A and M are collinear.
21 The position vector of a model aircraft at time t seconds is (9 t)i + (1 + 2t)j + (5 t)k, relative
to a fixed origin O. One unit on each coordinate axis represents 1 metre.
a Find an expression for d
2
in terms of t, where d metres is the distance of the aircraft from O.
b Find the value of t when the aircraft is closest to O and hence, the least distance of the aircraft
from O.
C4 VECTORS Worksheet B continued
Solomon Press
VECTORS C4 Worksheet C
1 Sketch each line on a separate diagram given its vector equation.
a r = 2i + sj b r = s(i + j) c r = i + 4j + s(i + 2j)
d r = 3j + s(3i j) e r = 4i + 2j + s(2i j) f r = (2s + 1)i + (3s 2)j
2 Write down a vector equation of the straight line
a parallel to the vector (3i 2j) which passes through the point with position vector (i + j),
b parallel to the x-axis which passes through the point with coordinates (0, 4),
c parallel to the line r = 2i + t(i + 5j) which passes through the point with coordinates (3, 1).
3 Find a vector equation of the straight line which passes through the points with position vectors
a
1
0
and
3
1
b
3
4
and
1
1
c
2
2
and
2
3
4 Find the value of the constant c such that line with vector equation r = 3i j + (ci + 2j)
a passes through the point (0, 5),
b is parallel to the line r = 2i + 4j + (6i + 3j).
5 Find a vector equation for each line given its cartesian equation.
a x = 1 b y = 2x c y = 3x + 1
d y =
3
4
x 2 e y = 5
1
2
x f x 4y + 8 = 0
6 A line has the vector equation r = 2i + j + (3i + 2j).
a Write down parametric equations for the line.
b Hence find the cartesian equation of the line in the form ax + by + c = 0, where a, b and c
are integers.
7 Find a cartesian equation for each line in the form ax + by + c = 0, where a, b and c are integers.
a r = 3i + (i + 2j) b r = i + 4j + (3i + j) c r = 2j + (4i j)
d r = 2i + j + (5i + 2j) e r = 2i 3j + (3i + 4j) f r = ( + 3)i + (2 1)j
8 For each pair of lines, determine with reasons whether they are identical, parallel but not identical
or not parallel.
a r =
1
2
+ s
3
1
b r =
1
2
+ s
1
4
c r =
2
5
+ s
2
4
r =
2
3
+ t
6
2
r =
2
4
+ t
4
1
r =
1
1
+ t
3
6
9 Find the position vector of the point of intersection of each pair of lines.
a r = i + 2j + i b r = 4i + j + (i + j) c r = j + (2i j)
r = 2i + j + (3i + j) r = 5i 2j + (2i 3j) r = 2i + 10j + (i + 3j)
d r = i + 5j + (4i + 6j) e r = 2i + 11j + (3i + 4j) f r = i + 2j + (3i + 2j)
r = 2i 2j + (i + 2j) r = 3i 7j + (5i + 3j) r = 3i + 5j + (i + 4j)
Solomon Press
10 Write down a vector equation of the straight line
a parallel to the vector (i + 3j 2k) which passes through the point with position vector (4i + k),
b perpendicular to the xy-plane which passes through the point with coordinates (2, 1, 0),
c parallel to the line r = 3i j + t(2i 3j + 5k) which passes through the point with
coordinates (1, 4, 2).
11 The points A and B have position vectors (5i + j 2k) and (6i 3j + k) respectively.
a Find AB in terms of i, j and k.
b Write down a vector equation of the straight line l which passes through A and B.
c Show that l passes through the point with coordinates (3, 9, 8).
12 Find a vector equation of the straight line which passes through the points with position vectors
a (i + 3j + 4k) and (5i + 4j + 6k) b (3i 2k) and (i + 5j + 2k)
c 0 and (6i j + 2k) d (i 2j + 3k) and (4i 7j + k)
13 Find the value of the constants a and b such that line r = 3i 5j + k + (2i + aj + bk)
a passes through the point (9, 2, 8),
b is parallel to the line r = 4j 2k + (8i 4j + 2k).
14 Find cartesian equations for each of the following lines.
a r =
2
3
0
+
3
5
2
b r =
4
1
3
+
1
6
3
c r =
1
5
2
+
4
2
1
15 Find a vector equation for each line given its cartesian equations.
a
1
3
x
=
4
2
y +
= z 5 b
4
x
=
1
2
y
=
7
3
z +
c
5
4
x +
= y + 3 = z
16 Show that the lines with vector equations r = 4i + 3k + s(i 2j + 2k) and
r = 7i + 2j 5k + t(3i + 2j + k) intersect, and find the coordinates of their point
of intersection.
17 Show that the lines with vector equations r = 2i j + 4k + (i + j + 3k) and
r = i + 4j + 3k + (i 2j + k) are skew.
18 For each pair of lines, find the position vector of their point of intersection or, if they do not
intersect, state whether they are parallel or skew.
a r =
3
1
5
+
4
1
1
and r =
3
2
4
+
1
0
2
b r =
0
3
1
+
2
1
3
and r =
6
2
1
+
4
2
6
c r =
8
2
4
+
1
3
2
and r =
2
2
8
+
4
3
4
d r =
1
5
2
+
1
4
2
and r =
7
6
5
+
2
1
3
e r =
4
1
3
+
2
5
3
and r =
3
2
1
+
5
3
4
f r =
0
7
2
+
6
4
8
and r =
12
1
11
+
5
2
3
C4 VECTORS Worksheet C continued
Solomon Press
VECTORS C4 Worksheet D
1 Calculate
a (i + 2j).(3i + j) b (4i j).(3i + 5j) c (i 2j).(5i 2j)
2 Show that the vectors (i + 4j) and (8i 2j) are perpendicular.
3 Find in each case the value of the constant c for which the vectors u and v are perpendicular.
a u =
3
1
, v =
3
c
b u =
2
1
, v =
3
c
c u =
2
5
, v =
4
c
4 Find, in degrees to 1 decimal place, the angle between the vectors
a (4i 3j) and (8i + 6j) b (7i + j) and (2i + 6j) c (4i + 2j) and (5i + 2j)
5 Relative to a fixed origin O, the points A, B and C have position vectors (9i + j), (3i j)
and (5i 2j) respectively. Show that ABC = 45.
6 Calculate
a (i + 2j + 4k).(3i + j + 2k) b (6i 2j + 2k).(i 3j k)
c (5i + 2k).(i + 4j 3k) d (3i + 2j 8k).(i + 11j 4k)
e (3i 7j + k).(9i + 4j k) f (7i 3j).(3j + 6k)
7 Given that p = 2i + j 3k, q = i + 5j k and r = 6i 2j 3k,
a find the value of p.q,
b find the value of p.r,
c verify that p.(q + r) = p.q + p.r
8 Simplify
a p.(q + r) + p.(q r) b p.(q + r) + q.(r p)
9 Show that the vectors (5i 3j + 2k) and (3i + j 6k) are perpendicular.
10 Relative to a fixed origin O, the points A, B and C have position vectors (3i + 4j 6k),
(i + 5j 2k) and (8i + 3j + 2k) respectively. Show that ABC = 90.
11 Find in each case the value or values of the constant c for which the vectors u and v are
perpendicular.
a u = (2i + 3j + k), v = (ci 3j + k) b u = (5i + 3j + 2k), v = (ci j + 3ck)
c u = (ci 2j + 8k), v = (ci + cj 3k) d u = (3ci + 2j + ck), v = (5i 4j + 2ck)
12 Find the exact value of the cosine of the angle between the vectors
a
1
2
2
and
8
1
4
b
4
1
2
and
2
3
6
c
1
2
1
and
1
7
2
d
5
3
4
and
3
4
1
13 Find, in degrees to 1 decimal place, the angle between the vectors
a (3i 4k) and (7i 4j + 4k) b (2i 6j + 3k) and (i 3j k)
c (6i 2j 9k) and (3i + j + 4k) d (i + 5j 3k) and (3i 4j + 2k)
Solomon Press
14 The points A (7, 2, 2), B (1, 6, 3) and C (3, 1, 2) are the vertices of a triangle.
a Find BA and BC in terms of i, j and k.
b Show that ABC = 82.2 to 1 decimal place.
c Find the area of triangle ABC to 3 significant figures.
15 Relative to a fixed origin, the points A, B and C have position vectors (3i 2j k),
(4i + 3j 2k) and (2i j) respectively.
a Find the exact value of the cosine of angle BAC.
b Hence show that the area of triangle ABC is 3 2 .
16 Find, in degrees to 1 decimal place, the acute angle between each pair of lines.
a r =
1
3
1
+
4
4
2
and r =
5
2
1
+
8
0
6
b r =
0
3
7
+
6
1
18
and r =
4
6
3
+
4
12
3
c r =
7
1
5
+
1
1
3
and r =
2
6
3
+
2
5
3
d r =
2
3
9
+
4
6
7
and r =
11
1
2
+
5
1
8
17 Relative to a fixed origin, the points A and B have position vectors (5i + 8j k) and
(6i + 5j + k) respectively.
a Find a vector equation of the straight line l
1
which passes through A and B.
The line l
2
has the equation r = 4i 3j + 5k + (5i + j 2k).
b Show that lines l
1
and l
2
intersect and find the position vector of their point of intersection.
c Find, in degrees, the acute angle between lines l
1
and l
2
.
18 Find, in degrees to 1 decimal place, the acute angle between the lines with cartesian equations
2
3
x
=
2
y
=
5
6
z +
and
4
4
x
=
1
7
y +
=
3
4
z
.
19 The line l has the equation r = 7i 2k + (2i j + 2k) and the line m has the equation
r = 4i + 7j 6k + (5i 4j 2k).
a Find the coordinates of the point A where lines l and m intersect.
b Find, in degrees, the acute angle between lines l and m.
The point B has coordinates (5, 1, 4).
c Show that B lies on the line l.
d Find the distance of B from m.
20 Relative to a fixed origin O, the points A and B have position vectors (9i + 6j) and (11i + 5j + k)
respectively.
a Show that for all values of , the point C with position vector (9 + 2)i + (6 )j + k lies
on the straight line l which passes through A and B.
b Find the value of for which OC is perpendicular to l.
c Hence, find the position vector of the foot of the perpendicular from O to l.
21 Find the coordinates of the point on each line which is closest to the origin.
a r = 4i + 2j + 7k + (i + 3j 4k) b r = 7i + 11j 9k + (6i 9j + 3k)
C4 VECTORS Worksheet D continued
Solomon Press
VECTORS C4 Worksheet E
1 The points A and B have position vectors
1
6
4
and
5
0
6
respectively, relative to a
fixed origin.
a Find, in vector form, an equation of the line l which passes through A and B. (2)
The line m has equation
r =
5
5
3
+ t
1
4
2
.
Given that lines l and m intersect at the point C,
b find the position vector of C, (4)
c show that C is the mid-point of AB. (2)
2 Relative to a fixed origin, the points P and Q have position vectors
5
2
2
and
3
1
0
respectively.
a Find, in vector form, an equation of the line L
1
which passes through P and Q. (2)
The line L
2
has equation
r =
4
6
1
+
5
1
3
.
b Show that lines L
1
and L
2
intersect and find the position vector of their point of
intersection. (5)
c Find, in degrees to 1 decimal place, the acute angle between lines L
1
and L
2
. (3)
3 Relative to a fixed origin, the lines l
1
and l
2
have vector equations as follows:
l
1
: r =
5
0
1
+ s
2
1
2
,
l
2
: r =
7
3
7
+ t
1
1
2
.
a Show that lines l
1
and l
2
intersect and find the position vector of their point of
intersection. (5)
The points A and C lie on l
1
and the points B and D lie on l
2
.
Given that ABCD is a parallelogram and that A has position vector
9
2
5
,
b find the position vector of C. (2)
Given also that the area of parallelogram ABCD is 54,
c find the distance of the point B from the line l
1
. (4)
Solomon Press
4 Relative to a fixed origin, the points A and B have position vectors (4i + 2j 4k) and
(2i j + 2k) respectively.
a Find, in vector form, an equation of the line l
1
which passes through A and B. (2)
The line l
2
passes through the point C with position vector (4i 7j k) and is parallel to
the vector (6j 2k).
b Write down, in vector form, an equation of the line l
2
. (1)
c Show that A lies on l
2
. (2)
d Find, in degrees, the acute angle between lines l
1
and l
2
. (3)
5 The points A and B have position vectors
5
1
10
and
4
1
8
respectively, relative to a
fixed origin O.
a Find, in vector form, an equation of the line l which passes through A and B. (2)
The line l intersects the y-axis at the point C.
b Find the coordinates of C. (2)
The point D on the line l is such that OD is perpendicular to l.
c Find the coordinates of D. (4)
d Find the area of triangle OCD, giving your answer in the form 5 k . (2)
6 Relative to a fixed origin, the line l
1
has the equation
r =
1
6
2
+ s
0
4
1
.
a Show that the point P with coordinates (1, 6, 5) lies on l
1
. (1)
The line l
2
has the equation
r =
4
4
1
+ t
3
2
2
,
and intersects l
1
at the point Q.
b Find the position vector of Q. (3)
The point R lies on l
2
such that PQ = QR.
c Find the two possible position vectors of the point R. (4)
7 Relative to a fixed origin, the points A and B have position vectors (4i + 5j + 6k) and
(4i + 6j + 2k) respectively.
a Find, in vector form, an equation of the line l
1
which passes through A and B. (2)
The line l
2
has equation
r = i + 5j 3k + (i + j k).
b Show that l
1
and l
2
intersect and find the position vector of their point of intersection. (4)
c Find the acute angle between lines l
1
and l
2
. (3)
d Show that the point on l
2
closest to A has position vector (i + 3j k). (5)
C4 VECTORS Worksheet E continued
Solomon Press
VECTORS C4 Worksheet F
1 The points A and B have position vectors
2
1
5
and
0
3
4
respectively, relative to a
fixed origin.
a Find, in vector form, an equation of the line l which passes through A and B. (2)
The line m has equation
r =
6
5
1
+ 3
1
a
,
where a is a constant.
Given that lines l and m intersect,
b find the value of a and the coordinates of the point where l and m intersect. (6)
2 Relative to a fixed origin, the points A, B and C have position vectors (4i + 2j k),
(2i + 5j 7k) and (6i + 4j + k) respectively.
a Show that cos (ABC) =
1
3
. (3)
The point M is the mid-point of AC.
b Find the position vector of M. (2)
c Show that BM is perpendicular to AC. (3)
d Find the size of angle ACB in degrees. (3)
3 Relative to a fixed origin O, the points A and B have position vectors
9
5
3
and
11
7
3
respectively.
a Find, in vector form, an equation of the line L which passes through A and B. (2)
The point C lies on L such that OC is perpendicular to L.
b Find the position vector of C. (5)
c Find, to 3 significant figures, the area of triangle OAC. (2)
d Find the exact ratio of the area of triangle OAB to the area of triangle OAC. (2)
4 Relative to a fixed origin O, the points A and B have position vectors (7i 5j k) and
(4i 5j + 3k) respectively.
a Find cos (AOB), giving your answer in the form 6 k , where k is an exact fraction. (3)
b Show that AB is perpendicular to OB. (3)
The point C is such that OC =
3
2
OB.
c Show that AC is perpendicular to OA. (3)
d Find the size of ACO in degrees to 1 decimal place. (2)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- VectorsDocument26 pagesVectorsAditya Bansal0% (1)
- Finding Equations of Lines and Intersecting LinesDocument7 pagesFinding Equations of Lines and Intersecting LinesAravindh KsPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionD'EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross SectionsDocument17 pagesCross Sectionsapi-294079637Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 WMI Grade 11 Questions Part 1Document5 pages2015 WMI Grade 11 Questions Part 1Daffa Ardana100% (1)
- Topic 2 Worksheet D Exam Style Questions On Coordinate Geometry PDFDocument2 pagesTopic 2 Worksheet D Exam Style Questions On Coordinate Geometry PDFNickRazzouk100% (2)
- Solomon C4 VectorsDocument11 pagesSolomon C4 Vectorssim887Pas encore d'évaluation
- f5 c4 Vectors NewDocument9 pagesf5 c4 Vectors NewArthas Rhee HermanPas encore d'évaluation
- Plane and Fancy GeometryDocument168 pagesPlane and Fancy GeometryLucas GallindoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Maths Worksheets for Large Numbers, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and DivisionDocument7 pagesMental Maths Worksheets for Large Numbers, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Divisionbiswajit1990Pas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8: Triangle CongruenceDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8: Triangle Congruencejayjay imanPas encore d'évaluation
- E4Qvec XDocument11 pagesE4Qvec XFarisPas encore d'évaluation
- Salomon VectorsDocument2 pagesSalomon Vectorsjsy7w7z8q7Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 9 Baru 1 Tutorial and All QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 9 Baru 1 Tutorial and All QuestionsMizaZainalPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Set 16B (3-D) : Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16)Document4 pagesReview Set 16B (3-D) : Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16)Nhocticaro NhocPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.vektor 2015 (2003 - 2010)Document14 pages4.vektor 2015 (2003 - 2010)Zuraidah BasriPas encore d'évaluation
- SCALAR Product Worksheet (1) HHHHHHHHHHDocument2 pagesSCALAR Product Worksheet (1) HHHHHHHHHHSameh AllaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Scalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andDocument10 pagesScalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andFazlina MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uuur Uuur: BA BADocument8 pagesUuur Uuur: BA BASaidin AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Theory EDocument26 pagesVector Theory EthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- C4 Vectors A - QuestionsDocument2 pagesC4 Vectors A - QuestionsKevin DanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors Mixed Practice 12ıb HDocument8 pagesVectors Mixed Practice 12ıb HNil HamaviogluPas encore d'évaluation
- Expressing vectors in terms of p, q, r, u, v, m and nDocument2 pagesExpressing vectors in terms of p, q, r, u, v, m and nzainab MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- AHL 3.12 Vector DefinitionsDocument52 pagesAHL 3.12 Vector Definitionspelin petekPas encore d'évaluation
- AHL 3.13 Scalar ProductDocument53 pagesAHL 3.13 Scalar Productpelin petekPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors - SPM Questions (1) : J I K R J K I SDocument2 pagesVectors - SPM Questions (1) : J I K R J K I SAzizah Haji KamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector SPM 2003 - 2007Document4 pagesVector SPM 2003 - 2007Rosmizar AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Equations Intersecting LinesDocument4 pagesVector Equations Intersecting Linesanaseberang94Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 9 Lines and Angles Assignment 4Document11 pagesCBSE Class 9 Lines and Angles Assignment 4SarthakDiwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Juj 2009 PDFDocument36 pagesJuj 2009 PDFMohd Khir ZainunPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors 13 14Document41 pagesVectors 13 14Ramchandra MurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Science & Maths (IX)Document12 pagesScience & Maths (IX)Sundeep KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Paper 2Document3 pagesVector Paper 2Aileen Beh Chik HeangPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument56 pagesUntitledNicole WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 7 (Vector) : NCB 10103: Mathematics For Engineers 1Document12 pagesTutorial 7 (Vector) : NCB 10103: Mathematics For Engineers 1aPas encore d'évaluation
- 100 - Vectors - 9Document6 pages100 - Vectors - 9whyreadPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors 1Document5 pagesVectors 1Japhet MubaiwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors and Lines TutorialDocument6 pagesVectors and Lines TutorialAdliHakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulseb/Uleac Special Paper Pure Mathematics QuestionsDocument19 pagesUlseb/Uleac Special Paper Pure Mathematics Questionsalphamale173Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors Maths T Tingkiatan 6Document6 pagesVectors Maths T Tingkiatan 6limsiewthiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Scalar Product of VectorsDocument5 pagesScalar Product of VectorsSudibyo GunawanPas encore d'évaluation
- OC - C and OV V.: (A) (I) P Is The Point (-2, 3) - Work Out The Co-Ordinates of Q. (Ii) Work OutDocument5 pagesOC - C and OV V.: (A) (I) P Is The Point (-2, 3) - Work Out The Co-Ordinates of Q. (Ii) Work OutAyesha AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- C7 Straight Line GraphsDocument38 pagesC7 Straight Line Graphskohtabs2Pas encore d'évaluation
- f5 Additional Mathematics Revision Exercise Past Paper 20091125 Locus VectorsDocument2 pagesf5 Additional Mathematics Revision Exercise Past Paper 20091125 Locus VectorsWallStreet HKPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM F5 Ch4 PDF - UnlockedDocument11 pagesSPM F5 Ch4 PDF - UnlockedkokleongPas encore d'évaluation
- Finding Equations of Lines and GradientsDocument7 pagesFinding Equations of Lines and GradientssriniyfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors Exercises - PrintDocument6 pagesVectors Exercises - PrintMuhammad FikriPas encore d'évaluation
- VectoriDocument22 pagesVectoriStefan LucianPas encore d'évaluation
- Projg ML Milivoje LukicDocument10 pagesProjg ML Milivoje LukicPh HuyamPas encore d'évaluation
- VECTORS AND MATRICESDocument9 pagesVECTORS AND MATRICESksganPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector AlgebraDocument22 pagesVector AlgebraJB NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Paper 1 Worksheet: (217 Marks)Document44 pagesVector Paper 1 Worksheet: (217 Marks)albertPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Straight Lines and GraphDocument3 pagesRevision Straight Lines and Graphdevit siahaanPas encore d'évaluation
- MT Chapter 06 PDFDocument6 pagesMT Chapter 06 PDFWilson LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra Vectorial Vectores Nivel MedioDocument13 pagesAlgebra Vectorial Vectores Nivel MedioWilliam YundaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 6 Resultant VectorsDocument3 pagesWeek 6 Resultant VectorsVeeno DarveenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 12 - Vectors WorksheetDocument2 pagesGrade 12 - Vectors WorksheetBrandon NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- VECTORS SPM PRACTICE QUESTIONSDocument6 pagesVECTORS SPM PRACTICE QUESTIONSLee ElainePas encore d'évaluation
- FGJLKGFLKHFGFDDocument9 pagesFGJLKGFLKHFGFDIlario CutajarPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM (Q) TOPIC 6 VectorsDocument3 pagesSTPM (Q) TOPIC 6 VectorsMelody Ong0% (1)
- Hwe 3dveDocument6 pagesHwe 3dveYONGCHENG LIUPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document2 pagesChapter 5APas encore d'évaluation
- Tables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers: (Anticipation Guide and Lesson 4-1)Document18 pagesAnswers: (Anticipation Guide and Lesson 4-1)Mazahir Mohammad BakirPas encore d'évaluation
- nth term formula, profit, speed, interest, quadratic formulaDocument2 pagesnth term formula, profit, speed, interest, quadratic formulaHikmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Disha Mathematics Revision (LDocument9 pagesDisha Mathematics Revision (LDakshay AhujaPas encore d'évaluation
- t2 M 4412 Drawing Translated 2d Shapes Differentiated Activity SheetsDocument6 pagest2 M 4412 Drawing Translated 2d Shapes Differentiated Activity SheetsNguyen Thu TrangPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry Algebra Review PDFDocument16 pagesGeometry Algebra Review PDFangel anne marie jabianPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Hope 1920 Paper 1 Marking PDFDocument10 pagesGood Hope 1920 Paper 1 Marking PDFVincent haPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Marking Scheme 2020Document10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Maths Marking Scheme 2020Kiran PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 Compartment Papers 2019 Mathematics PDFDocument36 pagesClass 10 Compartment Papers 2019 Mathematics PDFSukha Uppal100% (1)
- Mathematics Tracker Atp Grade 6 Term 3 of 2021Document37 pagesMathematics Tracker Atp Grade 6 Term 3 of 2021Emily MahlanguPas encore d'évaluation
- 12th Science Model Paper 2024Document90 pages12th Science Model Paper 2024ps2616921Pas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics-FINALDocument187 pagesGeneral Mathematics-FINALDummy AccountPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratics: Twitter: @owen134866Document43 pagesQuadratics: Twitter: @owen134866CubePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4: Congruence: Congruent Numbers and Residue ClassDocument17 pagesChapter 4: Congruence: Congruent Numbers and Residue ClassMyla VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- (Rise Up) - Straight Lines - Sep 1Document238 pages(Rise Up) - Straight Lines - Sep 1prakhar100% (1)
- Complex Number DPPDocument2 pagesComplex Number DPP1 AashuPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometry exam reviewDocument4 pagesTrigonometry exam reviewmikee jane sabilloPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Solve Fractions: Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument7 pagesHow To Solve Fractions: Solving Quadratic Equationsapi-126876773Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Test 1 (QP) - AADocument3 pagesSample Test 1 (QP) - AAtp060916Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 G5 ElimDocument7 pages2015 G5 ElimMelyn BustamantePas encore d'évaluation
- 10th Maths Full Portion Test Question Paper 2022 2023 English Medium PDF DownloadDocument4 pages10th Maths Full Portion Test Question Paper 2022 2023 English Medium PDF DownloadNirmal KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Core 2C2-CDocument9 pagesMathematics Core 2C2-CEden HailuPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5 Calculus With Analytic GeometryDocument20 pagesWeek 5 Calculus With Analytic GeometryPaul John PanganibanPas encore d'évaluation
- MAT 1320 DGD WorkbookDocument120 pagesMAT 1320 DGD WorkbookAurora BedggoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiating composite and product functionsDocument61 pagesDifferentiating composite and product functionsMamo JimmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theorems on Circles, Chords, Arcs, Angles and TangentsDocument2 pagesTheorems on Circles, Chords, Arcs, Angles and TangentsRi-ann VinculadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations in One Unknown (A)Document66 pagesQuadratic Equations in One Unknown (A)luk matthewPas encore d'évaluation