Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ME503 Tut-1
Transféré par
Deepak Agrawal0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues2 pagesThis document provides tutorial problems for an automatic control course. It includes 5 problems involving modeling dynamic systems using state space representations. Problem 1 asks to determine the order of two systems and write their state space models. Problem 2 models a DC motor driving a load. Problem 3 models a cart-disk system and asks for the state variables and output equations. Problem 4 asks for the state space model of a fluid system. Problem 5 models two connected carts and asks for the state space model with position as the output.
Description originale:
tutorial of automatic control -1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document provides tutorial problems for an automatic control course. It includes 5 problems involving modeling dynamic systems using state space representations. Problem 1 asks to determine the order of two systems and write their state space models. Problem 2 models a DC motor driving a load. Problem 3 models a cart-disk system and asks for the state variables and output equations. Problem 4 asks for the state space model of a fluid system. Problem 5 models two connected carts and asks for the state space model with position as the output.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues2 pagesME503 Tut-1
Transféré par
Deepak AgrawalThis document provides tutorial problems for an automatic control course. It includes 5 problems involving modeling dynamic systems using state space representations. Problem 1 asks to determine the order of two systems and write their state space models. Problem 2 models a DC motor driving a load. Problem 3 models a cart-disk system and asks for the state variables and output equations. Problem 4 asks for the state space model of a fluid system. Problem 5 models two connected carts and asks for the state space model with position as the output.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
MOTILAL NEHRU NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ALLAHABAD
Automatic Control (ME503)
Faculty: Dr. Samir Saraswati and Dr. Praveen Kumar Agarwal (Course Coordinator)
Tutorial Sheet - 1
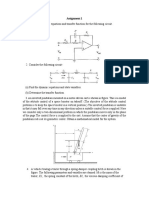
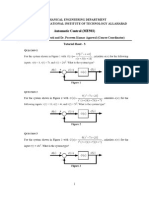
1. For the systems shown in figure 1(a) and (b):
a) Find the order of the system.
b) Obtain the state space representation if, input is force F(t) and outputs of interest are
1
x : displacement and
2
x : velocity. Indicate the A, B, C and D matrices.
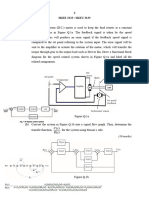
2. The figure 2 represents an armature controlled DC motor with a fixed field being used to drive a
rotational inertial load. The motor armature circuit is being driven by a voltage source, V. The torque
generated by the motor is proportional to the armature current:
T = K.i
The back electromotive force voltage, V
a
, is proportional to the motor speed:
V
a
= K
m
Derive the state equations assuming that all elements in the system are linear and ideal. Take the system
input as source voltage V
in
and output as rotor speed
j.
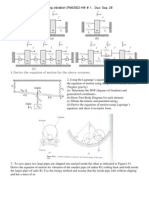
3. Consider the mechanical system illustrated in figure 3. The mass of disk is M
d
and it is uniformly
distributed. There is no friction between the cart and the ground. There is also no friction between the
disk and the cart. We are interested in horizontal motion only and assume that the rotational angle of the
disk is very small. The outputs that we are interested in are the spring force caused by spring K
2
and the
damping force caused by damper B
3
. Choosing the appropriate set of state variables, represent system
model in state space equation. Make sure that output equation is also presented,
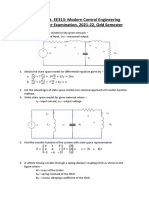
4. For the system shown in figure 4, obtain the state space representation, if the input is Q
in
and the outputs
of interest are Q
out
, H
1
and H
2
. Indicate the A, B, C and D matrices.
5. The figure 5 illustrates two masses (carts) connected via spring, moving at a surface with no friction.
Derive a state space model for this system, assuming that the force F is considered as input, and the
position
1
x is considered as output.
Fig 4
Fig 5
Fig 3
B
2
M
K
1
K
2
X
1 X
2
F(t)
Fig 1(b)
Fig 1(a)
Fig 2
Q
out
L L
H
1
H
2
a
represents
fluid
resistance
Density
A
1
A
2
Q
in
a
L
R
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ejercicios Modeling of Dynamic Systems1Document6 pagesEjercicios Modeling of Dynamic Systems1J Jick PerSeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistemas DinamicosDocument14 pagesSistemas DinamicosAmilcar SánchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 ADVANCED CONTROL 48580-Spring 2010Document9 pagesAssignment 1 ADVANCED CONTROL 48580-Spring 2010auuser2011Pas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Assignment 1Document4 pagesControl System Assignment 1atharvaPas encore d'évaluation
- ExercisesDocument58 pagesExercisesmjdaleneziPas encore d'évaluation
- X X X A T: MECH 364 Assignment 2Document9 pagesX X X A T: MECH 364 Assignment 2Chandra SekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sequential Circuits IIIDocument7 pagesSequential Circuits IIISwarnadip SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial I Basics of State Variable ModelingDocument11 pagesTutorial I Basics of State Variable ModelingRebecca GrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Acs 2018s2 Assn1Document4 pagesAcs 2018s2 Assn1MiraelPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Control II - Assignment 1 Rev3Document4 pagesAutomatic Control II - Assignment 1 Rev3ehsanzkr_499329029Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid VehicleDocument13 pagesHybrid VehicleLawrence BognotPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Control ExerciseDocument140 pagesAutomatic Control Exercisetaile1995Pas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm 04 PDFDocument3 pagesMidterm 04 PDFOlga Joy Labajo GerastaPas encore d'évaluation
- EXP (5) - State Variable Feedback DesignDocument7 pagesEXP (5) - State Variable Feedback Designبدون اسمPas encore d'évaluation
- DSC Exercises PDFDocument37 pagesDSC Exercises PDFsamielmadssiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acs 2019s1 Assn1Document5 pagesAcs 2019s1 Assn1MiraelPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Ec 2003Document26 pagesGate Ec 2003Ganesh RadharamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios DSCDocument39 pagesEjercicios DSCFreyley LeyvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument6 pagesMiddle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering DepartmentSwati PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- EE380: Quiz - 2 SolutionsDocument4 pagesEE380: Quiz - 2 SolutionsSamurai GamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Electrical Engineering EE361L: Control Systems LabDocument16 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering EE361L: Control Systems Labshryr.scorpioPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm 05 PDFDocument5 pagesMidterm 05 PDFOlga Joy Labajo GerastaPas encore d'évaluation
- Es386 2018Document6 pagesEs386 2018Luke HoganPas encore d'évaluation
- R5310206 Linear & Discrete Systems AnalysisDocument2 pagesR5310206 Linear & Discrete Systems AnalysissivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 1Document2 pagesHW 1Ahmad ZakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee1354 Modern Control Systems - FinalDocument23 pagesEe1354 Modern Control Systems - FinalSamatha Rao KPas encore d'évaluation
- FE - Sample 1Document11 pagesFE - Sample 1tghafiyzafryPas encore d'évaluation
- HW CH3Document3 pagesHW CH3DODI0% (1)
- V Semester E&E (A, B & C Sections) Linear Control Theory: Assignment - I (19-08-2016)Document2 pagesV Semester E&E (A, B & C Sections) Linear Control Theory: Assignment - I (19-08-2016)deepanshuPas encore d'évaluation
- Control SystemsDocument3 pagesControl SystemsselvajothiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Systems 334 (308814 v1) End of Semester 1 Examinations, June 2007Document12 pagesDynamic Systems 334 (308814 v1) End of Semester 1 Examinations, June 2007Jill Dagreat100% (1)
- Semester 1 Assessment 2009 436-431 Mechanics 4 Unit2 DynamicsDocument4 pagesSemester 1 Assessment 2009 436-431 Mechanics 4 Unit2 DynamicsSon TranPas encore d'évaluation
- QuestionsDocument21 pagesQuestionsShreyan SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Supreet P APas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No.03: Mathematical Modeling of Physical System: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No.03: Mathematical Modeling of Physical System: ObjectiveSao SavathPas encore d'évaluation
- T. Also Find The Limiting Value of F(S) As A Approaches ZeroDocument2 pagesT. Also Find The Limiting Value of F(S) As A Approaches Zerotushar kshirsagarPas encore d'évaluation
- RegelTechniek1 2014Document3 pagesRegelTechniek1 2014John AppleseedPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 1Document3 pagesWorksheet 1million shiferawPas encore d'évaluation
- State Space ModellingDocument19 pagesState Space Modellingindula123Pas encore d'évaluation
- RT Exercises and Solutions Med TentatalDocument264 pagesRT Exercises and Solutions Med TentatalSANA100% (1)
- EE1354 MODERN CONTROL SYSTEMS - FinalDocument23 pagesEE1354 MODERN CONTROL SYSTEMS - FinalMebrePas encore d'évaluation
- 9A19401 Contol SystemsDocument7 pages9A19401 Contol SystemssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Services - Electrical Main Paper I & II - 1992-2012 - 7.6MBDocument253 pagesCivil Services - Electrical Main Paper I & II - 1992-2012 - 7.6MBAnika DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- 3cs EceDocument3 pages3cs Ecekirankumar412Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2 MSDDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 MSDHemkeshPas encore d'évaluation
- EM Tutorial Sheet 1bDocument3 pagesEM Tutorial Sheet 1bAditya singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet State SpaceDocument7 pagesSheet State SpaceMahmoud A. AboulhasanPas encore d'évaluation
- EE3301Document3 pagesEE3301Charandeep TirkeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 360 Armature DC Motor Transfer FunctionDocument2 pagesMe 360 Armature DC Motor Transfer FunctionArun SukumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Q. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3Document16 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3rubensPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment BONUS MENG 375-3705 Spring 2014Document3 pagesAssignment BONUS MENG 375-3705 Spring 2014Yehia RaefPas encore d'évaluation
- 02Document43 pages02Vitelio PinzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Exo StudentDocument3 pagesExo StudentHassanPas encore d'évaluation
- QUESTIONDocument15 pagesQUESTIONHammad SargurohPas encore d'évaluation
- X Y Ei Y Y Ei Y Y X Ei Y Y: Smart Mater. Struct. 18 (2009) 115012 YchenetalDocument1 pageX Y Ei Y Y Ei Y Y X Ei Y Y: Smart Mater. Struct. 18 (2009) 115012 YchenetalelishirinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cpe08 Midterm Exam Part 1and 2Document4 pagesCpe08 Midterm Exam Part 1and 2Elle EllePas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Accounting TermsDocument1 pageFinancial Accounting TermsDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Helical GearDocument7 pagesHelical GearDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Inspection SheetDocument10 pagesTechnical Inspection SheetDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Wheel VehiclesDocument38 pages3 Wheel VehiclesDeepak Agrawal100% (1)
- Fine Micro ExtrusionDocument20 pagesFine Micro ExtrusionDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Flood Monitoring and Control SystemDocument16 pagesAutomatic Flood Monitoring and Control SystemDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - Automatic Traction Control (ATC)Document1 page3 - Automatic Traction Control (ATC)Deepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Influence of Ultrasonic Vibration On Micro-ExtrusionDocument2 pagesInfluence of Ultrasonic Vibration On Micro-ExtrusionDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro-Extrusion of Ultra-Fine Grained Aluminium: Original ArticleDocument10 pagesMicro-Extrusion of Ultra-Fine Grained Aluminium: Original ArticleDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Control (ME503) : Mechanical Engineering Department Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology AllahabadDocument6 pagesAutomatic Control (ME503) : Mechanical Engineering Department Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology AllahabadDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Sastra-Baja Event ReportDocument10 pagesSastra-Baja Event ReportDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Point SomeoneDocument126 pagesFive Point SomeoneDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Control (ME503) : Mechanical Engineering Department Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology AllahabadDocument2 pagesAutomatic Control (ME503) : Mechanical Engineering Department Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology AllahabadDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Control (ME503) : Mechanical Engineering Department Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology AllahabadDocument3 pagesAutomatic Control (ME503) : Mechanical Engineering Department Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology AllahabadDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Amir Power Grid Joining LetterDocument1 pageAmir Power Grid Joining LetterDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Amir Gate 2010 EE ResultDocument1 pageAmir Gate 2010 EE ResultDeepak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Na NakakamatayDocument23 pagesPhysics Na NakakamatayDaniel Monclear CatiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Arcs & NGRDocument6 pagesSecondary Arcs & NGRSaadAbdulBasitPas encore d'évaluation
- Abe ReviewerDocument82 pagesAbe ReviewerJohn Vincent Nate100% (3)
- Analogue Control Systems: For Diesel & Gas Engines, Gensets, Combined Heat & Power, Pump DrivesDocument12 pagesAnalogue Control Systems: For Diesel & Gas Engines, Gensets, Combined Heat & Power, Pump Driveslethanhtu0105Pas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsabvincenzo78sPas encore d'évaluation
- Olp Gce Mech & Heat CT 5Document20 pagesOlp Gce Mech & Heat CT 5Shabbir H. KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics - Unit 2 - Week 1 - INTRODUCTION PDFDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics - Unit 2 - Week 1 - INTRODUCTION PDFAkhilesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Che323 Note Cooling Tower 3Document130 pagesChe323 Note Cooling Tower 3ifiokPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System ProtectionDocument16 pagesPower System ProtectionIsmat Jahan NabilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept of Pn-Junction Diode: A.Mounika, Assistant Professor ECE-Department A.I.T.S-TirupatiDocument21 pagesConcept of Pn-Junction Diode: A.Mounika, Assistant Professor ECE-Department A.I.T.S-TirupatimounikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage Stability Improvement Using FACTS Devices: Prepared By: Supervised byDocument28 pagesVoltage Stability Improvement Using FACTS Devices: Prepared By: Supervised byAditya Tiwari100% (1)
- Mechanical - Engineering - Mechanical Vibrations - Vibrations of Two Degree of Freedom Systems - NotesDocument28 pagesMechanical - Engineering - Mechanical Vibrations - Vibrations of Two Degree of Freedom Systems - NotesSahrish RaeesPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problems Electrostatics PDFDocument47 pagesSolved Problems Electrostatics PDFPraneetha InumarthiPas encore d'évaluation
- EMT10 NewDocument12 pagesEMT10 NewzcaptPas encore d'évaluation
- Pile Foundations in Engineering Practice by S.Prakash and Hari D Sharma PDFDocument784 pagesPile Foundations in Engineering Practice by S.Prakash and Hari D Sharma PDFHayro Copacalle50% (4)
- Model of Pulsed Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) Using RL CircuitDocument9 pagesModel of Pulsed Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) Using RL CircuitAhmed ShadeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ScienceDocument10 pagesProject ScienceJD MaestrePas encore d'évaluation
- Master SheetDocument304 pagesMaster SheetasimtkPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Llave Eckel 7-5-8Document67 pagesManual Llave Eckel 7-5-8Edgar ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Diep - Io ClassessDocument4 pagesDiep - Io ClassessIvanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2022 Maharashtra State Board Important QuestionDocument17 pages2022 Maharashtra State Board Important Questionjayesh pandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Review On Solar RefrigeratorDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Solar Refrigeratordazelasif100% (1)
- Energy and Buildings: Hao Tian, Zhiguang He, Zhen LiDocument12 pagesEnergy and Buildings: Hao Tian, Zhiguang He, Zhen LiKanishk GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Science Notes 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 1 HindiDocument11 pages10 Science Notes 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 1 HindiNeelesh Baghel100% (6)
- Power ElectronicsDocument20 pagesPower Electronicsr.anushyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Podkletnov 2001 Paper With Giovanni ModaneseDocument39 pagesPodkletnov 2001 Paper With Giovanni ModaneseNullpunktsenergiePas encore d'évaluation
- MM326 SYSTEM DYNAMICS - hw1 - Sol PDFDocument9 pagesMM326 SYSTEM DYNAMICS - hw1 - Sol PDFdragons123x100% (1)
- Diode Test and Familiarization: Table1 1Document3 pagesDiode Test and Familiarization: Table1 1cent carinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lexmar Hyberbaric SystemDocument2 pagesLexmar Hyberbaric SystemBart Kemper, P.E.Pas encore d'évaluation