Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Radioactivity Theory E
Transféré par
thinkiitCopyright
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Radioactivity Theory E
Transféré par
thinkiitDroits d'auteur :
"manishkumarphysics.
in"
1
CHEMISTRY
Radioactivity
Spontaneous disintegration of nuclei due to emission of radiations like o, |, is called radioactivity.
Radioactivity is a nuclei phenomenon.
Radioactivity is not depend on external conditions like temperature, pressure etc.
Radioactivity of a substance is independent to its physical state.
x(s), x(l), x(g), (x)
+
(g), (x)
(g) in all form, x is radioactive.
14
CO
2
,
14
6
C(s),
14
6
C(g) is radioactive.
* All radioactive disintegration followI
st
order kinetics.
A B + C
Int. nuclie N
0
At time t. N
Activity : Rate of decay or disintegration of radioactive element.
Specific activity : Activity of unit mass (or 1 g) of radioactive element / sample.
N . A =
Unit of activity :
* curie (C
i
) = 3.7 10
10
dps
millicurie (mC
i
) = 3.7 10
7
dps
microcurie (C
i
) = 3.7 10
4
dps
* Rutherford (1 Rd) = 1 10
6
dps
S.I. unit of activity = Becquerel (Bq)
* 1 Bq = 1 disintegration per second (dps)
N =
M
W
N
A
W = weight of substance
M = Molar mass
N
A
= 6.022 10
23
A
N
M
w
. A =
* = Not dependent on temperature.
dt
dN
= N
}
N
dN
=
}
dt
t
0
e N N
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
N
N
ln
t
1
0
w
w
n
n
N
N
A
A
0 0 0 0
= = =
n
0
= initial moles
w
0
= initial weight
"manishkumarphysics.in"
2
CHEMISTRY
=
t
1
ln
|
.
|
\
|
w
w
0
(w = weight of Aremaining after time t)
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
x w
w
ln
t
1
0
0
Half life :
t = t
1/2
; N =
2
N
0
=
2 / 1
t
1
ln
|
|
.
|
\
|
2 / N
N
0
0
=
2 / 1
t
2 ln
=
693 . 0 2 ln
t
2 / 1
Average life :
2 / 1 . avg
t 44 . 1
1
T =
=
T
avg.
=
0
0
N
t . dN
}
=
1
(
dt
dN
= N and N = N
0
e
t
, dN = N
0
e
t
dt)
Application of radioactivity :
1. Carbon dating : (used for wooden object)
In living matter existing in nature :
6
C
14
:
6
C
12
= 1 : 10
12
(radio active) (stable)
In upper atmosphere :
7
N
14
+
0
n
1
6
C
14
+
1
p
1
Ratio of radioactive carbon in dead animals / trees decreases with respect to time.
t =
1
ln
|
.
|
\
|
A
A
0
Half life of
6
C
14
= 5770 yrs.
A = activity of old wood piece.
A
0
= activity of fresh wood piece.
Age of wooden piece should be nearly t
1/2
or (2 to 3 times of t
1/2
).
2. Age of rocks or minerals
92
U
238
x
82
Pb
206
(radioactive) (stable)
Assumption:
Rock did not contain any lead or all lead is formed due to disintegration of uranium.
92
U
238
82
Pb
206
+ x
2
He
4
+ y
1
e
0
z
X
A
z 2
X
A 4
+
2
He
4
z
Y
A
z + 1
Y
A
+
1
e
0
Number of o-particles =
4
. no mass of difference
=
4
206 238
= 8
"manishkumarphysics.in"
3
CHEMISTRY
238 = 206 + 4x + 0 .....(1)
92 = 82 + 2x y .....(2)
On solving (1) and (2),
x = 8
y = 6
92
U
238
82
Pb
206
+ 8(
2
He
4
) + 6(
1
e
0
)
At time t w g y g
t =
1
ln
|
.
|
\
|
w
w
0
t =
1
ln
|
|
.
|
\
|
x w
w
0
0
w = w
0
x
w
0
= w + x
1 mole or 238 g U provide 206 g of Pb
206
238
g U provide 1 g Pb
206
238
y g U provide y g Pb
x =
206
238
y
w
0
= w +
206
238
y
92
U
238
82
Pb
206
+ 8
2
He
4
+ 6
1
e
V(in mL) collected
n
He
=
RT
PV
........ (1)
t =
1
ln
|
.
|
\
|
n
n
0
n =
238
w
........ (2)
n
0
= n +
8
n
He
Radiations :
o :
2
He
4
(
2
4
He
2+
) (nucleus of He-atom)
| or |
:
1
e
0
(fast moving electron emitted fromnucleus)
:
0
0
(electromagnetic radiation (waves) of high frequency)
speed : > | > o
penetrating power : > | > o
ionisation power : o > | >
"manishkumarphysics.in"
4
CHEMISTRY
Emission of rays Usual condition Effect Process representation / example
1. o Z > 83
p
n
ratio increases
Z
X
A
Z 2
X
A 4
+
2
He
4
92
U
238
90
Th
234
+
2
He
4
2. | If
p
n
ratio is high.
p
n
ratio decreases
Z
Y
A
Z+ 1
Y
A 4
+
1
e
0
eg.
6
C
12
(stable)
p
n
=
6
6
6
C
14
7
N
14
+
1
e
0
6
C
14
(radioactive)
p
n
=
6
8
(high)
p
n
=
6
8
p
n
=
7
7
eg.
11
Na
24
(radioactive)
p
n
=
11
13
(high)
0
n
1
1
p
1
+
1
e
0
(from nucleus)
11
Na
23
(stable)
p
n
=
11
12
11
Na
22
p
n
=
11
11
(
p
n
ratio low)
3. If nucleus energy nucleus energy
43
Tc
99
43
Tc
99
+
level is high level decreases high low
nucleus nucleus
energy energy
(metastable)
4. (a) Positron emission If
p
n
ratio is low
p
n
ratio increases
Z
Y
A
Z 1
Y
A
+
+1
e
0
(
+1
e
0
)
11
Na
22
10
Ne
22
+
+1
e
0
1
p
1
0
n
1
+
+1
e
0
(from nucleus)
(b) Electron capture If
p
n
ratio is low
p
n
ratio increases
Z
X
A
+
shell K
0
1
e
Z 1
X
A
(EC) or K-shell
80
Hg
197
+
1
e
0
79
Au
197
electron capture
) shell K (
1
0
0
1
1
1
x e p
+
Nuclear stability belt :
"manishkumarphysics.in"
5
CHEMISTRY
-emission
0
n
1
1
p
1
+
1
e
0
* Z upto 20 : nuclei stable with n/p ratio nearly 1 : 1
* Z > 20 : n/p ratio increases will Z in stable nuclie region.
* More number of neutrons are required to reduce repulsion between protons.
*
83
Bi
209
: Stable with largest n/p ratio
p
n
=
1
52 . 1
Even - odd rule : (Out of syllabus)
no. of n no. of p no. of stablenuclic
even even 155 (max)
even odd 55
odd even 50
odd odd 5 (min)
* Expected pairing of nucleus
Magic Numbers :
Nuclei in which nucleons have magic no. (2, 8, 20, 28, 50 ....) are more stable.
e.g.
2
He
4
,
8
O
16
* Expected closing of nucleus energy shell.
Group displacement law : (Given by Soddy and Fajan)
* When 1o emission takes place from a nuclie, new formed nuclie occupy two position left in periodic table.
* When 1| emission takes place from a nuclie, newformed nuclie occupy one position right in periodic table.
Due to emission of 1| particle; isobars are formed.
Due to emission of 1oparticle; isodiaphers are formed.
Due to emission of 1o and 2| ; isotopes are formed.
Isotopes: same number of proton eg.
6
C
14
and
6
C
12
Isobars : same mass number eg.
6
C
14
and
7
N
14
Isotones: same number of neutron eg.
2
He
4
and
1
H
3
Isodiaphers : Same (n p) difference
e.g.
9
F
19
and
19
K
39
; (n p) = 10
"manishkumarphysics.in"
6
CHEMISTRY
Isosters : Same number of atoms and electrons
e.g. N
2
and CO
N
2
O and CO
2
Artifical nuclear reaction :
* specific nuclei + stricking particle New nuclei + emitted particle
eg. 1. (o, p type)
7
N
14
+
2
He
4
8
O
17
+
1
p
1
(or
1
H
1
)
(s.p.) (e.p.)
2. (n, type)
11
N
23
+
1
n
0
11
Na
24
+
3. (D, p type)
13
Al
27
+
1
H
2
13
Al
28
+
1
H
1
4. (p, o type)
3
Li
7
+
1
H
1
2
He
4
+
2
He
4
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion :
In both processes, large amount of heat evolved due to conversion of some mass into energy.
Nuclear fission : Is a process where heavy nuclei splits into large nuclei.
92
U
235
+
0
n
1
92
U*
236
eg. atom bomb is based on fission.
Nuclear fusion :
Is a process where light nuclei fused together to form heavy nuclei.
1
H
2
+
1
H
3
2
He
4
+
0
n
1
1
H
2
+
1
H
2
2
He
4
Hydrogen bomb is based on fusion. Very high temperature is required in this process.
For objective questions :
Total time (T) = no. of halves (n) Half life (t
1/2
)
2 / 1
t n T =
No. of half life Int. wt. Final weight
1 w w/2
2 w/2 w/4 = w/2
2
3 w/4 w/8 = w/2
3
Amount of substance left in n halves (wt / mole) =
n
2
) mole / wt ( amount Initial
"manishkumarphysics.in"
7
CHEMISTRY
Radioactive Disintegration Series :
Aseries of continued disintegrations starting from an unstable nucleus (radioactive elements) and ending at
a stable nucleus, is known as radioactive disintegration series.
Mainly radioactive disintegration series are four type -
(1) Thoriumseries (4n series) :
Th
2 23
90
(Starting element)
| o 4 , 6
Pb
8 20
82
(last element)
(2) Neptunium series (4n + 1 series):
Np
237
93
(Starting element)
| o 4 , 7
Bi
209
3 8
(last element)
(3) Uranium Series (4n + 2 series) :
U
8 23
92
(Starting element)
| o 6 , 8
Pb
206
82
(last element)
(4) Actinium Series (4n + 3 series) :
U
5 23
2 9
(Starting element)
| o 4 , 7
Pb
7 20
82
(last element)
* Thorium series (4n series), Uranium Series (4n + 2 series), Actinium Series (4n + 3 series) are naturally
series. But Neptunium series (4n + 1 series) is artificial series because Neptunium237 is perpared artificial
and the only member of this series found in nature is the stable end product Bi209.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 - RadioactivityDocument35 pagesChapter 14 - RadioactivitySherena Peter Govind100% (1)
- Chapter20a Nuclear ChemistryDocument14 pagesChapter20a Nuclear ChemistryAmith KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Chemistry: Atomic Structure HWT - 1Document3 pagesSolutions To Home Work Test/Chemistry: Atomic Structure HWT - 1varunkohliinPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 08 NuclearDocument32 pagesPhysics 08 NuclearPiotr NowakPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Nuclear Chemistry PDFDocument51 pages1 - Nuclear Chemistry PDFSangga Buana Komara100% (1)
- Unit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsDocument16 pagesUnit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsPankaj Kumar50% (4)
- Unit-3 US02CPHY02 Nuclear Physics For F Y B SCDocument62 pagesUnit-3 US02CPHY02 Nuclear Physics For F Y B SCsanjay sPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 - Radioactivity and Nuclear Transformation - Page No. 167Document6 pages03 - Radioactivity and Nuclear Transformation - Page No. 167Arvind TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Radioactive Decay: © 2006, K.E. Holbert Page 1 of 9Document9 pagesRadioactive Decay: © 2006, K.E. Holbert Page 1 of 9ucing_33Pas encore d'évaluation
- RadioactivityDocument48 pagesRadioactivityAhmedAmer1Pas encore d'évaluation
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistrySankar SasmalPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of AtomDocument20 pagesStructure of AtomSachin KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Radio ActivityDocument7 pages15 Radio ActivityHasmukh ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics of Nuclear MedicineDocument33 pagesPhysics of Nuclear MedicineEssa AliPas encore d'évaluation
- International Chemistry Olympiad 2014 (Problems)Document80 pagesInternational Chemistry Olympiad 2014 (Problems)Science Olympiad Blog100% (7)
- CHM031L - Nuclear ChemistryDocument42 pagesCHM031L - Nuclear ChemistryKath CarmonaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1B23 Modern Physics, Astronomy, and Cosmology: Partial Notes, Astronomy Set 1 - Stars Luminosity and TemperatureDocument10 pages1B23 Modern Physics, Astronomy, and Cosmology: Partial Notes, Astronomy Set 1 - Stars Luminosity and TemperatureRoy VeseyPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Dates: There Will Be No Make-Up: Tests or Exams!Document35 pagesTest Dates: There Will Be No Make-Up: Tests or Exams!dead_knightPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic StructureDocument41 pagesAtomic StructuresavisuPas encore d'évaluation
- ZChapter18 Nuclear ChemistryDocument15 pagesZChapter18 Nuclear ChemistryViha AncilliaPas encore d'évaluation
- AIEEE Paper 2002 AnswersDocument14 pagesAIEEE Paper 2002 AnswersKunwar Achint SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect 5-Atomic StructureDocument36 pagesLect 5-Atomic Structurehafizuddinbahri97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Olved Xamples: Chapter # 46 The NucleusDocument18 pagesOlved Xamples: Chapter # 46 The NucleusthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- MM FormulaeDocument2 pagesMM FormulaeReddyvari VenugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- NEET UG Physics Atom and Nucleus MCQsDocument36 pagesNEET UG Physics Atom and Nucleus MCQsKapila KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics of Nuclear Medicine PDFDocument34 pagesPhysics of Nuclear Medicine PDFHunter X HunterPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Chemistry: Symbol or Symbol - Mass #Document18 pagesNuclear Chemistry: Symbol or Symbol - Mass #simpanan hitamPas encore d'évaluation
- Radioacitvity PDFDocument14 pagesRadioacitvity PDFArjun RavalPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Nuclear Chemistry (Type of Radioactive Decay)Document15 pages4 Nuclear Chemistry (Type of Radioactive Decay)Fatin IziantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic NucleusDocument15 pagesAtomic Nucleussreenivas1990100% (1)
- An Approach: Proton-SecondsDocument60 pagesAn Approach: Proton-SecondsIan BeardsleyPas encore d'évaluation
- CHME2201 Chapter-6Document10 pagesCHME2201 Chapter-6Muma DenisPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Physics: 1. NucleusDocument13 pagesNuclear Physics: 1. NucleusAditya BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of First-Order Differential Equations to Real World Systems ChapterDocument40 pagesApplications of First-Order Differential Equations to Real World Systems ChapterJasperJohnGarcia0% (1)
- RadioisotopesDocument28 pagesRadioisotopessivagurunathan.P100% (3)
- Review Questions - Solutions: Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesReview Questions - Solutions: Multiple ChoiceMarikPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAP 4 Periodic TablebDocument73 pagesCHAP 4 Periodic TablebLily MardyanaPas encore d'évaluation
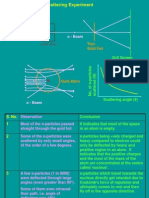
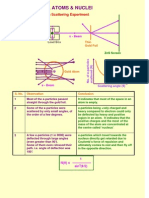
- Atoms & Nuclei: Rutherford's Alpha Scattering ExperimentDocument9 pagesAtoms & Nuclei: Rutherford's Alpha Scattering ExperimentNathanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch9 HatomDocument30 pagesCh9 HatomgvarisPas encore d'évaluation
- HDocument87 pagesHSumit GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- General Inorganic Chemistry - Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesGeneral Inorganic Chemistry - Lecture NotesLorenz100% (2)
- Dulong Einstein DebyeDocument35 pagesDulong Einstein DebyeamenzouPas encore d'évaluation
- Break-Up of Questions: Mechanics Sound Heat Electromagnetism Optics Modern Physics 6 2 2 5 2 3Document12 pagesBreak-Up of Questions: Mechanics Sound Heat Electromagnetism Optics Modern Physics 6 2 2 5 2 3Jasbir MaanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Method of Proton SecondsDocument30 pagesThe Method of Proton SecondsIan BeardsleyPas encore d'évaluation
- RadioisotopesDocument49 pagesRadioisotopesSeon KimPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 3 Nuclear ChemistryDocument28 pagesMODULE 3 Nuclear ChemistryILIVEFOR MONSTA7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Answers: TEST - 2 (Paper-I)Document12 pagesAnswers: TEST - 2 (Paper-I)ABHIJEET SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chart of The NuclidesDocument9 pagesChart of The NuclidesEmmy1706Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure Type 1Document28 pagesAtomic Structure Type 1kaushik247Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear ReactionDocument40 pagesNuclear ReactionJeffrey Teh50% (2)
- Thermodynamics and Electrochemistry ReviewDocument6 pagesThermodynamics and Electrochemistry ReviewStephenPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Chemistry Lesson OutlineDocument12 pagesNuclear Chemistry Lesson OutlineKate ComonicalPas encore d'évaluation
- NuclearDocument5 pagesNuclearmargaretwambui294Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture # 2: U+ N Ba+ KR +3 N+200MevDocument7 pagesLecture # 2: U+ N Ba+ KR +3 N+200MevSàrvêsh Kümår YaduvanshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Five Phonons II. Thermal PropertiesDocument39 pagesChapter Five Phonons II. Thermal PropertiesPenny YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary Particles: The Commonwealth and International LibraryD'EverandElementary Particles: The Commonwealth and International LibraryPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Nitrogen: Physical Chemistry: A Series of MonographsD'EverandActive Nitrogen: Physical Chemistry: A Series of MonographsPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 - Linear Programming PDFDocument13 pages14 - Linear Programming PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 - Chemistry in Everyday Life (New) PDFDocument17 pages18 - Chemistry in Everyday Life (New) PDFthinkiit60% (10)
- 13 - Alcohol, Phynol, Ether (New) PDFDocument37 pages13 - Alcohol, Phynol, Ether (New) PDFthinkiit100% (2)
- 15 Probability PDFDocument16 pages15 Probability PDFthinkiit100% (2)
- 17 - Polymers (New) PDFDocument17 pages17 - Polymers (New) PDFthinkiit100% (3)
- 7 - Continuity and Differentiability PDFDocument16 pages7 - Continuity and Differentiability PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - Differential Equations PDFDocument9 pages11 - Differential Equations PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 - Three-Dimensional Geometry PDFDocument20 pages13 - Three-Dimensional Geometry PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Vectors PDFDocument14 pages12 Vectors PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Determinants PDFDocument11 pages6 Determinants PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Integrals PDFDocument19 pages9 Integrals PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 - Biomolecules (New) PDFDocument16 pages16 - Biomolecules (New) PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Areas of Bounded Regions PDFDocument8 pages10 - Areas of Bounded Regions PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Applications of Derivatives PDFDocument15 pages8 - Applications of Derivatives PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Matrices PDFDocument14 pages5 Matrices PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Inverse Trigonometic FunctionsDocument19 pages2 - Inverse Trigonometic FunctionsHarsh RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - Co - Ordination Compounds PDFDocument24 pages11 - Co - Ordination Compounds PDFthinkiit100% (1)
- 3 - Relations and Functions PDFDocument21 pages3 - Relations and Functions PDFthinkiit100% (1)
- 9 - P-Block Elements PDFDocument27 pages9 - P-Block Elements PDFthinkiit86% (7)
- 10 - D - and F - Block Elements PDFDocument18 pages10 - D - and F - Block Elements PDFthinkiit100% (19)
- 14 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids (New) PDFDocument33 pages14 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids (New) PDFthinkiit67% (3)
- 15 - Amines (New) PDFDocument25 pages15 - Amines (New) PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 - Haloareans and Halo Alkanes (New) PDFDocument14 pages12 - Haloareans and Halo Alkanes (New) PDFthinkiit100% (1)
- 8 - General Principles & Processes of Elements PDFDocument12 pages8 - General Principles & Processes of Elements PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 - Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument16 pages6 - Chemical Kinetics PDFthinkiit100% (1)
- Surface ChemistryDocument12 pagesSurface ChemistryMecho HillPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Electrochemistry PDFDocument15 pages5 - Electrochemistry PDFthinkiit100% (1)
- 3 - Solid State PDFDocument15 pages3 - Solid State PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Solution PDFDocument14 pages4 Solution PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Communication Systems PDFDocument12 pages10 - Communication Systems PDFthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- Analize de Aciditate Si Isocianat La Fabricarea - The Plastics PDFDocument6 pagesAnalize de Aciditate Si Isocianat La Fabricarea - The Plastics PDFCorina StanculescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics Reviewer 3 (FINAL)Document28 pagesElectronics Reviewer 3 (FINAL)ljoyü100% (1)
- Accuracy and Stability in Incompressible SPH (ISPH) Based PDFDocument23 pagesAccuracy and Stability in Incompressible SPH (ISPH) Based PDFAlejandro GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of The Optical Properties of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) Doped With A New Diarylethen CompoundDocument10 pagesStudy of The Optical Properties of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) Doped With A New Diarylethen CompoundHuỳnh Minh KhôiPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 2. AbstractDocument5 pagesExp 2. AbstractBrev Candare50% (2)
- Online Quiz Answers I A 1Document115 pagesOnline Quiz Answers I A 1ShawnJerryNemoPas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics 1 - 12 - Q1 Module 2 Week 3Document4 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - 12 - Q1 Module 2 Week 3Lawrence Sean MotinPas encore d'évaluation
- Brayton Cycle PDFDocument43 pagesBrayton Cycle PDFAdly_arkim100% (2)
- Experiment 3.Document6 pagesExperiment 3.tracyymendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- FR4 3Document3 pagesFR4 3Elyse Fawohodie Kwadwo100% (5)
- Spacetime Singularity & Poincare's Balayage: Mathematical Renormalization of Newtonian Potentials Using Nonlinear Singular Elliptic and Parabolic Equations. Carlos C. ArandaDocument13 pagesSpacetime Singularity & Poincare's Balayage: Mathematical Renormalization of Newtonian Potentials Using Nonlinear Singular Elliptic and Parabolic Equations. Carlos C. ArandaCarlos Cesar ArandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lit Review of Speed Control of High-Performance Brushless DC Motor Drives by Load Torque EstimationDocument2 pagesLit Review of Speed Control of High-Performance Brushless DC Motor Drives by Load Torque EstimationKobeed DhakalPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Particle Testing - 1Document128 pagesMagnetic Particle Testing - 1Shankara100% (1)
- Column Interaction ChartDocument3 pagesColumn Interaction ChartManikandan ThayumanavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Front Horn Theory - Design of A Front Loaded Exponential HornDocument26 pagesFront Horn Theory - Design of A Front Loaded Exponential HornSean_Middleton100% (3)
- Buckling of Struts Lab GuideDocument6 pagesBuckling of Struts Lab GuideMohamed Zamri0% (1)
- Hydrodynamic Stability - Matt TurnerDocument101 pagesHydrodynamic Stability - Matt TurnerAnonymous uzyb8bBqN9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity and Magnetism For Mathematicians GarrityDocument75 pagesElectricity and Magnetism For Mathematicians GarrityChristian Gonzalez43% (7)
- Dispersion On A Sphere: Received23 December 1952)Document11 pagesDispersion On A Sphere: Received23 December 1952)Jenny Astrid Baron MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- WellheadNodalGas SonicFlowDocument7 pagesWellheadNodalGas SonicFlowthe_soldier_15_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engg Mech and Strength of MaterialsDocument73 pagesEngg Mech and Strength of MaterialsClaire NecesitoPas encore d'évaluation
- EDC Formula Notes - PDF 65Document8 pagesEDC Formula Notes - PDF 65VenkatGollaPas encore d'évaluation
- PJC H2 PHY 9646 Mid-Year Paper 2012Document22 pagesPJC H2 PHY 9646 Mid-Year Paper 2012Ng Jia ChengPas encore d'évaluation
- Camless Engine PresentationDocument20 pagesCamless Engine PresentationRavi Bhadani80% (10)
- Kementerian Pendidikan, Kebudayaan, Riset, Dan Teknologi Universitas Negeri Semarang (Unnes)Document5 pagesKementerian Pendidikan, Kebudayaan, Riset, Dan Teknologi Universitas Negeri Semarang (Unnes)Aflah Agus RizkikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Unit - UbDDocument3 pagesEnergy Unit - UbDKarl McBurnettPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics (A Summary of Its Definition)Document6 pagesPhysics (A Summary of Its Definition)biltspovertyPas encore d'évaluation
- NMAT Mock Exam For ChemDocument16 pagesNMAT Mock Exam For ChemMDreamer100% (2)
- DFT Review for Transition Metal ChemistryDocument60 pagesDFT Review for Transition Metal ChemistryGiliandroFariasPas encore d'évaluation
- Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology: ArticleinfoDocument19 pagesTunnelling and Underground Space Technology: ArticleinfoADAMPas encore d'évaluation