Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Patho Diagram
Transféré par
NielArmstrongCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Patho Diagram
Transféré par
NielArmstrongDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
B.
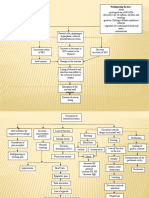
Diagram of Pathophysiology
Precipitating Factors:
- Smoking
- Drinking Alcohol
- Taking NSAIDs
Predisposing Factors:
- Genetics
- Helicobacter pylori
- Hypersecretory Condition
Normal antireflux barrier is
impaired
Tissue cannot withstand
the digestive action of
gastric acid HCL and
Pepsin
Increased concentration or
activity of acid-pepsin
Ulcer induced by NSAIDs
Topical irritation of the
gastric epithelial cells and
reduced protective
prostaglandin synthesis
Pharmacologic properties
Altered mucosal gel layer
Decrease resistance of
the Mucosa
Erosion to the mucosa
Damage mucosa cannot
secrete enough mucous
Act as a barrier to HCL
Decrease Resistant to
bacteria
Helicobacter bacteria
occur
Signs and Symptoms:
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Pain after eating
- vomiting
- Weakness due to
vomiting, loss of
appetite and pain
- Heartburn or
Bleeding
perforation from
the ulcer
- Gastric outlet
obstruction
Normal flora of mucosal
layer which coats the lining
of the human stomach and
doudenum
inflammation
Host immune system
reponse
Damage mucosal defense
system
Diminished blood flow
The bacteria that remained present in the system
of the host pauses and continuous to multiply
which makes the host as carrier for a long time.
The bacteria that does not
re- infect the host is shed
into the stool
Medical Management
- IV fluids and electrolytes
- Bed rest
- Avoid NSAIDs
- Histamine-2 (H2) receptor antagonist
Surgical Movement
- Vagotomy may be performed to reduce
gastric acid secretion
Nursing Management
- Advice to avoid spicy and acidic food and dairy products and
caffeinated drinks; alcohol and smoking cigarettes.
- Advice to take small frequent meals
- Any bleeding from the rectum, blood in stools sudden acute
abdominal pain restlessness, falling of temperature should be
reported at once to the physician or the patient should be brought at
once to the hospital.
- Take vital signs and teach patient family member how to take and
record same.
- Provide light clothing or linens.
- Modify the environment through cooling by turning on the air
conditioner or fan.
- Instruct to increase oral fluid intake
- Regulate IV fluid.
- Administer medications as ordered.
- Teach members of the family how to report all symptoms to the
attending physician especially when patient is being cared for at
home.
- Teach, guide and supervise members of the family on nursing
techniques which will contribute to the patients recovery.
- Interpret to family the nature of disease and need for practicing
preventive and control measures.
If treated If not treated
Good Prognosis
- internal bleeding in
the digestive system
- splitting (perforation)
of a section of the
digestive system or
bowel, which
spreads the infection
to nearby tissue
- High possibility of
getting Gastric
cancer
Death
Bad Prognosis
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Oxford Handbook of Acute Medicine 4th (2019) PDFDocument971 pagesOxford Handbook of Acute Medicine 4th (2019) PDFabinaya100% (9)
- Medical TerminologyDocument627 pagesMedical TerminologyMais Mohammed100% (8)
- Case ScenarioDocument2 pagesCase ScenarioMARIA ANGELIKA DEL ROSARIOPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP EsrdDocument2 pagesNCP EsrdAziil LiizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Ab ActivitiesDocument7 pagesCell Ab ActivitiesJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Ppe4 Reflection AssignmentDocument11 pagesPpe4 Reflection Assignmentapi-318846856100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of DMShelly_Ann_Del_9959Pas encore d'évaluation
- Father Saturnino Urios University Butuan City, PhilippinesDocument15 pagesFather Saturnino Urios University Butuan City, PhilippinesKathleen JosolPas encore d'évaluation
- SOAPIEDocument4 pagesSOAPIEdhianne_garcia2001Pas encore d'évaluation
- DOH Control of Diarrheal DiseasesDocument16 pagesDOH Control of Diarrheal DiseasesNielArmstrongPas encore d'évaluation
- The 1932 Cancer Cure - by Joseph GallgherDocument9 pagesThe 1932 Cancer Cure - by Joseph GallgherJoseph Gallagher100% (3)
- 50 Item Pharmacology ExamDocument10 pages50 Item Pharmacology Examshark_tale04100% (1)
- Personal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesDocument15 pagesPersonal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesteuuuuPas encore d'évaluation
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument2 pagesTheoretical FrameworkLisette CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions: 1 US A Te CareDocument2 pagesSolutions: 1 US A Te CareelonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Source (Level 1) (Bacalla) : Criteria Score Weight Computation Actual Score JustificationDocument2 pagesWater Source (Level 1) (Bacalla) : Criteria Score Weight Computation Actual Score JustificationlovlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Pressure Measurement Is An Important Part of The Patient's Data Base. It Is Considered To BeDocument1 pageBlood Pressure Measurement Is An Important Part of The Patient's Data Base. It Is Considered To BeMir MirPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study FormatDocument5 pagesCase Study FormatEden OlasabPas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking UpstreamDocument1 pageThinking UpstreamDONITA DALUMPINESPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 114 Gerontology - WeeK 1Document38 pagesNCM 114 Gerontology - WeeK 1Jmarie Brillantes Popioco0% (1)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPapi-3728995Pas encore d'évaluation
- FNCPDocument17 pagesFNCPRaquel M. MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Intensive Nursing Practicum: Rle LCP Module Rle LCP Unit WeekDocument8 pagesBachelor of Science in Nursing: Intensive Nursing Practicum: Rle LCP Module Rle LCP Unit WeekMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallarePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study of FractureDocument3 pagesDrug Study of FractureMarijune Caban ViloriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Percutaneous Endoscopic GastrostomyDocument27 pagesPercutaneous Endoscopic GastrostomyDoha EbedPas encore d'évaluation
- Pscy PrelimDocument20 pagesPscy PrelimAinah Batua-anPas encore d'évaluation
- Transcultural Perspective in The Nursing Care of Adults Physiologic Development During AdulthoodDocument5 pagesTranscultural Perspective in The Nursing Care of Adults Physiologic Development During AdulthoodeuLa-mayzellPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 109 2023 F-ACAD-29 - Syllabus Template (Rev 6)Document63 pagesNCM 109 2023 F-ACAD-29 - Syllabus Template (Rev 6)Joyce EricaPas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument9 pagesPathophysiologySuzette PipoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture NCM 109Document11 pagesLecture NCM 109Evangeline Anne MacanasPas encore d'évaluation
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionPas encore d'évaluation
- ROLES RESPONSIBILITIES OF A MC NURSE IN CHALENGEING SITUATIONS Merged Compressed Merged MergedDocument53 pagesROLES RESPONSIBILITIES OF A MC NURSE IN CHALENGEING SITUATIONS Merged Compressed Merged MergedYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cord ProlapseDocument2 pagesCord ProlapseUsman Ali AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care of Uremic SyndromeDocument11 pagesNursing Care of Uremic Syndromeyoedha_banditozz50% (2)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinjhinPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastritis: Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesGastritis: Signs and SymptomsSher KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- D. Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesD. Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaBill Clinton Lamira BabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 3 NCM 112Document4 pagesTopic 3 NCM 112Marielle ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection - Bill of RightDocument1 pageReflection - Bill of RightJesse Israel TadenaPas encore d'évaluation
- FNCPDocument14 pagesFNCPhelloaPas encore d'évaluation
- H MoleDocument2 pagesH MoleJoanna Marie Datahan EstomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Roles of NursesDocument3 pagesRoles of NursesRI NAPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJames Lavarias SuñgaPas encore d'évaluation
- COPAR Tally SheetDocument3 pagesCOPAR Tally SheetAnna SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurses Notes Soapie Day 2Document3 pagesNurses Notes Soapie Day 2Sunny Al asadiPas encore d'évaluation
- MeaslesDocument7 pagesMeaslesKarl FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument52 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanSherinne Jane CariazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine Myoma Case Study Group A FinalDocument88 pagesUterine Myoma Case Study Group A Finallowell cerezoPas encore d'évaluation
- Logic101 Exercise No.6Document3 pagesLogic101 Exercise No.6Juliana Sophia DelanPas encore d'évaluation
- PRC Form (Minor Operation)Document1 pagePRC Form (Minor Operation)mawelPas encore d'évaluation
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bpud, PathoDocument2 pagesBpud, PathoSheng GosepPas encore d'évaluation
- German MeaslesDocument8 pagesGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geriatric NursingDocument6 pagesGeriatric NursingMadelaine Mary Rose GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Identification and DiagnosisDocument22 pagesCommunity Identification and Diagnosiskuruvagadda sagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument5 pagesChronic PyelonephritisIsak ShatikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Garantisadong PambataDocument4 pagesGarantisadong PambataAmiel Francisco ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Involuntarily Blinking Pink ConjunctivaJulianne B. Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument1 pageSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: IndependentVanetPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperchloremia: Group 11 Singh, Joshua Silverio, Silver John Tabarnilla, Michiko Unico, Paula Villa, JustinaDocument15 pagesHyperchloremia: Group 11 Singh, Joshua Silverio, Silver John Tabarnilla, Michiko Unico, Paula Villa, JustinaKyle De Sagun OtedaPas encore d'évaluation
- SEMINAR On New FilariaDocument50 pagesSEMINAR On New FilariaArun JvPas encore d'évaluation
- D."Parang Giniginaw Man Ako" As Verbalized, Patient CoversDocument1 pageD."Parang Giniginaw Man Ako" As Verbalized, Patient CoversSherena NicolasPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurses Assigned in Rural ServicesDocument3 pagesNurses Assigned in Rural ServicescubezeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Tannenbaum and Schmidt ContinuumDocument13 pagesTannenbaum and Schmidt ContinuumNielArmstrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy Risk Category C: Alert: AmoxicillinDocument5 pagesPregnancy Risk Category C: Alert: AmoxicillinNielArmstrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Myasthenia Gravis, Alzheimers Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Bell PalsyDocument9 pagesMyasthenia Gravis, Alzheimers Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Bell PalsyNielArmstrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Myasthenia GravisDocument21 pagesPathophysiology of Myasthenia GravisNielArmstrong100% (2)
- Doh - (Imci)Document25 pagesDoh - (Imci)NielArmstrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Undescended TestisDocument2 pagesUndescended TestisdyarraPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Park in Son Case For StudentsDocument4 pagesAnti Park in Son Case For StudentstaryndavidsPas encore d'évaluation
- Case History Final PDFDocument16 pagesCase History Final PDFRameshPas encore d'évaluation
- LDN (Low Dose Naltrexone) VariousPatentsandPatentApplicationsDocument47 pagesLDN (Low Dose Naltrexone) VariousPatentsandPatentApplicationsLynn Allison NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- IHC DR Rajiv Kumar PDFDocument118 pagesIHC DR Rajiv Kumar PDFJeetPas encore d'évaluation
- Routine Checkups: English For NursingDocument5 pagesRoutine Checkups: English For Nursingnadya sharifeaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Krok 1 2008 by ModulsDocument12 pagesKrok 1 2008 by Modulsa_friend_in_neeedPas encore d'évaluation
- 24-Sequelae of Wearing Complete Dentures - Rajat DangDocument19 pages24-Sequelae of Wearing Complete Dentures - Rajat DangNaunit Vaid100% (1)
- Costing Ranap Jan-JunDocument32 pagesCosting Ranap Jan-Jungalih wicaksonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Should Smoking Cigarette Be BannedDocument4 pagesShould Smoking Cigarette Be BannedHusna SallehPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Report MielopatiDocument37 pagesCase Report MielopatiAnnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Can Postoperative Nutrition Be Favourably Maintained by Oral Diet in Patients With Emergency Temporary Ileostomy? A Tertiary Hospital Based StudyDocument5 pagesCan Postoperative Nutrition Be Favourably Maintained by Oral Diet in Patients With Emergency Temporary Ileostomy? A Tertiary Hospital Based StudydwirizqillahPas encore d'évaluation
- Kaplan Peds ConceptsDocument8 pagesKaplan Peds ConceptsnanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Approachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02Document63 pagesApproachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02adnansirajPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing and Healthcare 2019 ConferenceDocument8 pagesNursing and Healthcare 2019 ConferenceNursing CongressPas encore d'évaluation
- Potential Long-Term Side Effects of Exposure To ChemoDocument21 pagesPotential Long-Term Side Effects of Exposure To ChemoMichael BublePas encore d'évaluation
- Pulp Therapy For Primary Molars-UK GuidelinesDocument9 pagesPulp Therapy For Primary Molars-UK GuidelinesRania AghaPas encore d'évaluation
- AIChE Journal Vol (1) - 51 No. 12 December 2005Document229 pagesAIChE Journal Vol (1) - 51 No. 12 December 2005naraNJORPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry For Medics WWW - Namrata.coDocument48 pagesBiochemistry For Medics WWW - Namrata.coOsteo FerdianPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study I - Cigarette Smoking in Lung CancerDocument12 pagesCase Study I - Cigarette Smoking in Lung CancerDavid AcuñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grand Rounds 11-12Document10 pagesGrand Rounds 11-12mforbush130Pas encore d'évaluation
- ESR Educational DocumentDocument2 pagesESR Educational DocumentTanveerPas encore d'évaluation
- Effectiveness of A Topical Formulation Containing Metronidazole For Wound Odor and Exudate ControlDocument11 pagesEffectiveness of A Topical Formulation Containing Metronidazole For Wound Odor and Exudate ControlAnita KusumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteosarcoma CaseDocument28 pagesOsteosarcoma CaseChristine Karen Ang SuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical MnemonicsDocument27 pagesClinical MnemonicswilliamscottonPas encore d'évaluation