Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Backtracking - Pass & Phase of Compiler
Transféré par
JoinKingCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Backtracking - Pass & Phase of Compiler
Transféré par
JoinKingDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
BACKTRACKING
Backtracking is a general algorithm for finding all (or some) solutions to some computational
problem, that incrementally builds candidates to the solutions, and abandons each partial candidate c
("backtracks") as soon as it determines that c cannot possibly be completed to a valid solution.
WHAT IS A PASS IN A COMPILER?
A standard way to classify compilers is by the number of passes. Usually, compiling is a relatively
resource intensive process and initially computers did not have enough memory to hold such a program
that did the complete job. Due to this limitation of hardware resources in early computers, compilers
were broken down in to smaller sub programs that did its partial job by going over the source code
(made a pass over the source or some other form of it) and performed analysis, transformations and
translation tasks separately. So, depending on this classification, compilers are indentified as one-pass or
multi-pass compilers.
As the name suggests, one-pass compilers compiles in a single pass. It is easier to write a one-pass
compiler and also they perform faster than multi-pass compilers. Therefore, even at the time when you
had resource limitations, languages were designed so that they could be compiled in a one-pass (e.g.
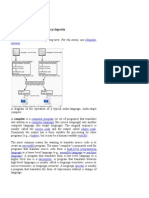
Pascal). On the other hand, a typical multi-pass compiler is made up of several main stages. The first
stage is the scanner (also known as the lexical analyzer). Scanner reads the program and converts it to a
string of tokens. The second stage is the parser. It converts the string of tokens in to a parse tree (or an
abstract syntax tree), which captures the syntactic structure of the program. Next stage is the that
interpret the semantics of the syntactic structure. The code optimizations stages and final code
generation stage follow this.
WHAT IS A PHASE IN A COMPILER?
The term phase often comes up when you talk about compiler construction. Initially, compilers were
every simple pieces of single, monolithic software written by one person for the compilation of a simple
language. But when the source code of the language to be translated becomes complex and large, the
compiler was broken down in to multiple (relatively independent) phases. The advantage of having
different phases is that the development of the compiler can be distributed among a team of
developers. Furthermore, it improves the modularity and reuse by allowing phases to be replaced by
improved ones or additional phases (such as further optimizations) to be added to the compiler. The
process of dividing the compilation to phases was introduced by the PQCC (Production Quality Compiler-
Compiler Project) at Carnegie Melon University. They introduced the terms front end, middle end and
back end. Most compilers have at least two phases. But usually, back end and front end encapsulate
these phases.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PHASE AND PASS IN COMPILER?
Phase and Pass are two terms used in the area of compilers. A pass is a single time the compiler passes
over (goes through) the sources code or some other representation of it. Typically, most compilers have
at least two phases called front end and back end, while they could be either one-pass or multi-pass.
Phase is used to classify compilers according to the construction, while pass is used to classify compilers
according to how they operate.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pass and Phase DifferenceDocument1 pagePass and Phase DifferenceJoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- A Compiler Is A Computer ProgramDocument6 pagesA Compiler Is A Computer Programapi-26190816Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wikipedia One-Pass Versus Multi-Pass CompilersDocument2 pagesWikipedia One-Pass Versus Multi-Pass CompilersBeigh Umair ZahoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Design IntroductionDocument4 pagesCompiler Design IntroductionSudeshna KunduPas encore d'évaluation
- Lovely Professional: Submitted To: - Submitted By:-Neha Malhotra Satnam SinghDocument15 pagesLovely Professional: Submitted To: - Submitted By:-Neha Malhotra Satnam SinghSatnam Singh MehrokPas encore d'évaluation
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentaniketkumar184415Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture # 1Document21 pagesLecture # 1mohammad ikhlasPas encore d'évaluation
- The Curse of Compiler ConstructionDocument50 pagesThe Curse of Compiler ConstructionRohit100% (1)
- The Curse of Compiler ConstructionDocument50 pagesThe Curse of Compiler Constructioni1958239Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument19 pagesCompiler: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediamanoj kumar rout100% (2)
- Compiler Design NotesDocument130 pagesCompiler Design NotesDivya RaghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler DesignDocument94 pagesCompiler DesignPradeepkumar PradeepkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler 2021 Module 1Document15 pagesCompiler 2021 Module 1ZealPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler ConstructionDocument5 pagesCompiler ConstructionEman noorPas encore d'évaluation
- Purpose of Translator Different Types of Translators: CompilerDocument32 pagesPurpose of Translator Different Types of Translators: CompilerReal SuperstarsPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Design Unit-1 - 3Document4 pagesCompiler Design Unit-1 - 3sreethu7856Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler DesignDocument34 pagesCompiler DesignAK CollectionPas encore d'évaluation
- Language Translation: Programming ToolsDocument7 pagesLanguage Translation: Programming ToolsToni-Ann WillisPas encore d'évaluation
- CC1Document6 pagesCC1Sushant ThitePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Compiler Design: Submitted To:Ms. Shweta Submitted By:Rajan Arora Branch:CSE Sec:B1 Roll No:071076Document14 pagesAssignment Compiler Design: Submitted To:Ms. Shweta Submitted By:Rajan Arora Branch:CSE Sec:B1 Roll No:071076Shivani AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Design - Quick Guide: Language Processing SystemDocument51 pagesCompiler Design - Quick Guide: Language Processing SystemKassiePas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 NotesDocument27 pagesModule 3 NotesmPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Design Unit-1 - 2Document3 pagesCompiler Design Unit-1 - 2sreethu7856Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler: This Piece of Writing Is About The Compilation Process.Document6 pagesCompiler: This Piece of Writing Is About The Compilation Process.Muhammad Adeel KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- MCSE 204: Adina Institute of Science & TechnologyDocument16 pagesMCSE 204: Adina Institute of Science & Technologyrajneesh pachouriPas encore d'évaluation
- CD Unit - 1 Lms NotesDocument58 pagesCD Unit - 1 Lms Notesashok koppoluPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Compiler DesignDocument70 pagesUnit 1 Compiler DesignNoidaTut E-LearnPas encore d'évaluation
- Module - I: Introduction To Compiling: 1.1 Introduction of Language Processing SystemDocument7 pagesModule - I: Introduction To Compiling: 1.1 Introduction of Language Processing SystemSHIVANI KOTHARIPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler DesignDocument118 pagesCompiler DesignMohamed SelmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Code Beneath the Surface: Mastering Assembly ProgrammingD'EverandCode Beneath the Surface: Mastering Assembly ProgrammingPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler ConstructionDocument63 pagesCompiler ConstructionMSMWOLFPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler DesignDocument47 pagesCompiler DesignLearn UpPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Design Concepts Worked Out Examples and MDocument100 pagesCompiler Design Concepts Worked Out Examples and MLalit Kumar100% (1)
- Compiler Design Short NotesDocument133 pagesCompiler Design Short NotesSaroswat RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes Compile CompleteDocument117 pagesNotes Compile Completenewb53223Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Construction ToolsDocument2 pagesCompiler Construction Toolsbijay khadka100% (1)
- Compiler Design: ObjectivesDocument45 pagesCompiler Design: Objectivesminujose111_20572463Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 Com 414 (Compiler Construction)Document79 pages2018 Com 414 (Compiler Construction)Afolabi Oluwatobi Benjamin100% (2)
- Compiler WikibookDocument498 pagesCompiler WikibookSumanta DattaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Compiler DesignDocument63 pagesIntroduction of Compiler DesignSayli GawdePas encore d'évaluation
- Practical 2 HPCDocument5 pagesPractical 2 HPCanjaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 08 Language Translation PDFDocument11 pagesLecture 08 Language Translation PDFJONATHAN WABWIREPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Design Lecture Notes (10CS63) : D C S & EDocument96 pagesCompiler Design Lecture Notes (10CS63) : D C S & EAkshayPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Design - Quick GuideDocument38 pagesCompiler Design - Quick GuideThanga DuraiPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-1 1.1. Introduction of Language ProcessingsystemDocument14 pagesUNIT-1 1.1. Introduction of Language ProcessingsystemRahul JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document8 pagesAssignment 2Sarp MPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Compiler Design NotesDocument31 pages2 Compiler Design NotesPadmavathi BPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Design-Short NotesDocument61 pagesCompiler Design-Short Notesambachew tarekegnPas encore d'évaluation
- System Programming (BTCS-405A) Session:jan-May, 2018: ContentsDocument10 pagesSystem Programming (BTCS-405A) Session:jan-May, 2018: Contentshimanshu patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 1Document43 pagesUnit - 1slcascs2022Pas encore d'évaluation
- 13 CD - Runtime Env 3Document38 pages13 CD - Runtime Env 3singamsettysanjana04Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Study of Research Paper On Phases ofDocument7 pagesA Study of Research Paper On Phases ofDivyank ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 01: Questions: A) Explain Following Terms and Relation Between ThemDocument7 pagesExperiment 01: Questions: A) Explain Following Terms and Relation Between ThemHarshilPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1 IntroductiontoCompilerpdf 2023 12 18 08 57 18Document71 pagesCh1 IntroductiontoCompilerpdf 2023 12 18 08 57 18nagabe8303Pas encore d'évaluation
- CompilersDocument7 pagesCompilersjafameg801Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Monica SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CD KCS502 Unit 1 ADocument8 pagesCD KCS502 Unit 1 Ashivendrasingh43613Pas encore d'évaluation
- History: History of Compiler ConstructionDocument4 pagesHistory: History of Compiler ConstructionShyamSunderDadhichPas encore d'évaluation
- AT&FL Lab 11Document6 pagesAT&FL Lab 11paloPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR KIDS: An Easy Step-by-Step Guide For Young Programmers To Learn Coding Skills (2022 Crash Course for Newbies)D'EverandCOMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR KIDS: An Easy Step-by-Step Guide For Young Programmers To Learn Coding Skills (2022 Crash Course for Newbies)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thatquiz Org TQ Teacher HTMLDocument1 pageThatquiz Org TQ Teacher HTMLJoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE R15 Syllabus-UGDocument204 pagesCSE R15 Syllabus-UGJoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE R15 Syllabus-UGDocument204 pagesCSE R15 Syllabus-UGJoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Message Digest FunctionsDocument3 pagesMessage Digest FunctionsJoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction: What Is UNIX ?Document1 pageIntroduction: What Is UNIX ?JoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Unix Programming Lab ManualDocument8 pagesUnix Programming Lab ManualJoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To Webinar Session About "Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network"Document7 pagesWelcome To Webinar Session About "Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network"JoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Usp Lab ProgramsDocument3 pagesUsp Lab ProgramsJoinKing100% (1)
- Unix Lab SyllabusDocument2 pagesUnix Lab SyllabusJoinKing100% (1)
- Documents - 51 - Computer Science EnggDocument2 pagesDocuments - 51 - Computer Science EnggJoinKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperconverged Infrastructure For Dummies 2019 Edition PDFDocument65 pagesHyperconverged Infrastructure For Dummies 2019 Edition PDFAlex Irmel Oviedo Solis100% (1)
- Configuracion Basica Switch y RouterDocument4 pagesConfiguracion Basica Switch y RouterPaul Andres Heredia FerrufinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Embedded MB QRG Mzglkai e 10Document2 pagesEmbedded MB QRG Mzglkai e 10invaderPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 4 - ITMDocument30 pagesSession 4 - ITMSubhranil MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Website and SMO ProposalDocument3 pagesWebsite and SMO Proposalamitm4uPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Year Project SRSDocument25 pagesFinal Year Project SRSNikhil YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.slide - Globalzation and InternetDocument20 pages11.slide - Globalzation and Internetbams_febPas encore d'évaluation
- CloudBerry Backup For MS SQLDocument13 pagesCloudBerry Backup For MS SQLTharindu NirushanPas encore d'évaluation
- ANPD Project DocumentationDocument49 pagesANPD Project DocumentationB. SRUTHILAYAPas encore d'évaluation
- XXXX Courier WitoutscreensDocument53 pagesXXXX Courier WitoutscreensgovindarajnPas encore d'évaluation
- DxdiagDocument15 pagesDxdiagkikihandlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Siliconsmartuserguide PDFDocument1 350 pagesSiliconsmartuserguide PDFChristian Cao50% (2)
- Pentration Testing Report ShivDocument11 pagesPentration Testing Report ShivMAJ. VIKAS TYAGI DGR Batch 08Pas encore d'évaluation
- DP Sound CMedia 15036 DriverssDocument320 pagesDP Sound CMedia 15036 DriverssRajesh1146Pas encore d'évaluation
- Latex Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesLatex Cheat SheetTadeu FelixPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Media Community Using Optimized Clustering Algorithm Data Mining ProjectDocument2 pagesSocial Media Community Using Optimized Clustering Algorithm Data Mining ProjectSanket GhattePas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting SystemDocument56 pagesOnline Voting Systemajay_anavPas encore d'évaluation
- LI-MAT Soft Solutions PVT LTDDocument7 pagesLI-MAT Soft Solutions PVT LTDamisha singhPas encore d'évaluation
- M&A Research ReportDocument19 pagesM&A Research ReportoliverPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexi Remote Radio Head 2TX 900Document5 pagesFlexi Remote Radio Head 2TX 900Reza BordbarPas encore d'évaluation
- M32 Edit Releasenote - 4.3Document1 pageM32 Edit Releasenote - 4.3bg audioPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimas: Alif RahmatdanaDocument1 pageDimas: Alif RahmatdanaEva MariaPas encore d'évaluation
- In-Band Communication: - Vaibhav Sonewane Potp - FpgaDocument17 pagesIn-Band Communication: - Vaibhav Sonewane Potp - Fpgavaibhav sonewanePas encore d'évaluation
- Sap Basis With Hana Consultant Ramana Reddy. M Gmail: Mobile: +91-8970335642Document3 pagesSap Basis With Hana Consultant Ramana Reddy. M Gmail: Mobile: +91-8970335642chinna chinnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Webinar Computer PetladDocument1 pageWebinar Computer PetladXyzPas encore d'évaluation
- Getting StartedDocument70 pagesGetting StartedFernando DuartePas encore d'évaluation
- Database Programming With SQL FINAL Part 2Document11 pagesDatabase Programming With SQL FINAL Part 2José Obeniel LópezPas encore d'évaluation
- Compress - Document (1) - 1 - 20230510213530 PDFDocument3 pagesCompress - Document (1) - 1 - 20230510213530 PDFAllen McintoshPas encore d'évaluation
- OGG Support Type ObjectDocument4 pagesOGG Support Type Objectrdba2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Operate A Spreadsheet ApplicationDocument8 pagesOperate A Spreadsheet ApplicationAnonymous PcPkRpAKD5Pas encore d'évaluation