Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Q
Transféré par
Mahesh Singh0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
34 vues1 page1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce document1
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
34 vues1 pageQ
Transféré par
Mahesh Singh1
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
Q. Define Following electrical network.
1. Linear and Non Linear Network
2. Bilateral and Unilateral Network
3. Active and Passive Network
4. Lumped and Distributed Network
Ans: The behavior of the entire network depends on the behavior and characteristics of its elements.
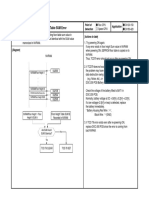
The classification of networks can be shown as,
1. Linear Network : A circuit or network whose parameters i.e. elements like resistances,
inductances and capacitances are always constant irrespective of the change in time, voltage,
temperature etc. is known as linear network. The Ohm's law can be applied to such network. The
mathematical equations of such network can be obtained by using the law of superposition. The
response of the various network elements is linear with respect to the excitation applied to them.
Non Linear Network : A circuit whose parameters change their values with change in time,
temperature, voltage etc. is known as non linear network . The Ohm's law may not be applied to
such network. Such network does not follow the law of superposition. The response of the
various elements is not linear with respect to their excitation. The best example is a circuit
consisting of a diode where diode current docs not vary linearly with the voltage applied to it.
2.Bilateral Network : A circuit whose characteristics, behavior is same irrespective of the direction
of current through various elements of it, is called bilateral network. Network consisting only
resistances is good example of bilateral network.
Unilateral Network : A circuit whose operation, behavior is dependent on the direction of the
current through various elements is called unilateral network. Circuit consisting diodes, which
allows flow of current only in one direction is good example of unilateral circuit.
3. Active Network: A circuit which contains at least one source of energy is called active. An
energy source may be a voltage or current source.
Passive Network: A circuit which contains no energy source is called passive circuit. This is
shown in the Fig.
4. Lumped Network: A network in which all the network elements arc physically separable is
known as lumped network. Most of the electric networks are lumped in nature, which consists
elements like R, L, C, voltage source etc.
5. Distributed Network: A network in which the circuit elements like resistance, inductance etc.
cannot be physically separable for analysis purposes, is called distributed network. The best
example of such a network is a transmission line where resistance, inductance and capacitance
of a transmission line are distributed all along its length and cannot be shown as separate
elements, anywhere in the circuit
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Finals - Attempt ReviewcircuitDocument13 pagesFinals - Attempt ReviewcircuitRony Maea40% (5)
- Tesis RekaciptaDocument56 pagesTesis Rekaciptaatukbelumganyut73% (15)
- Busbar General Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesBusbar General Datasheet PDFRa HermawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Examination Nov 2012Document16 pagesExamination Nov 2012Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Assesment MCTDocument5 pagesFinal Assesment MCTMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Pse - 2012-2013Document23 pagesTutorial Pse - 2012-2013Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Pse 1 5 (7 Marks)Document33 pagesPse 1 5 (7 Marks)Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Quetion PaperDocument4 pagesQuetion PaperMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAudit Lesson PlanMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Pse1 5 (2 Marks)Document3 pagesPse1 5 (2 Marks)Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial PSE 2011-2012Document23 pagesTutorial PSE 2011-2012Mahesh Singh100% (1)
- EXPERIMENT No 2Document2 pagesEXPERIMENT No 2Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Pas CT 2 PaperDocument1 pagePas CT 2 PaperMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- PAS Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPAS Lesson PlanMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- PowerSystem Group Work Assignment Under BOS - FinalDocument2 pagesPowerSystem Group Work Assignment Under BOS - FinalMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- P 2017Document43 pagesP 2017Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Integers 1Document2 pagesIntegers 1Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Poonguzhali 2014Document9 pagesPoonguzhali 2014Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Poonguzhali 2014Document9 pagesPoonguzhali 2014Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document41 pagesChapter 2PandoraSkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate 2016 Question PaperDocument81 pagesGate 2016 Question PaperNitin ChandelPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 02 Ace - 17Document46 pagesEe 02 Ace - 17Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Im 1464694143Document47 pagesIm 1464694143saravananPas encore d'évaluation
- An Innovative Bio Inspired PSO Algorithm To EnhanceDocument3 pagesAn Innovative Bio Inspired PSO Algorithm To EnhanceMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- IMPORTANT QUESTION IN ELECTRICAL ENGG FOR ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAMS OF UPRVUNL, UPPCL, MPPKVVNL, HPPSC, IES, GATE and Other State Psus.Document223 pagesIMPORTANT QUESTION IN ELECTRICAL ENGG FOR ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAMS OF UPRVUNL, UPPCL, MPPKVVNL, HPPSC, IES, GATE and Other State Psus.Rishi Kant Sharma100% (1)
- InDocument1 pageInMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- BE (6th Semester) Examination, April-May, 2018: Printed Pages: 3 Roll NoDocument4 pagesBE (6th Semester) Examination, April-May, 2018: Printed Pages: 3 Roll NoMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 300817Document4 pages300817Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- DRM Application PDFDocument1 pageDRM Application PDFMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of Examination-April-May, 2019: Available DetailsDocument6 pagesName of Examination-April-May, 2019: Available DetailsMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- BE (6 Semester) Examination, Nov.-Dec., 2017: Process ControlDocument4 pagesBE (6 Semester) Examination, Nov.-Dec., 2017: Process ControlMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- M. Tech. (Second Semester) Examination, April-May 2018Document4 pagesM. Tech. (Second Semester) Examination, April-May 2018Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Power and Energy Systems: S.S. Gokhale, V.S. KaleDocument7 pagesElectrical Power and Energy Systems: S.S. Gokhale, V.S. KaleMahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- AC5920 Series: 1550 NM MQW-DFB 2.5Gbps Direct Modulation LaserDocument5 pagesAC5920 Series: 1550 NM MQW-DFB 2.5Gbps Direct Modulation LaserHudson M. CerriPas encore d'évaluation
- Charge-Density-Wave Conductors: Articles You May Be Interested inDocument7 pagesCharge-Density-Wave Conductors: Articles You May Be Interested inMiguel Angel Gonzalez JaimesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ltspice Caveats: "Design Tool Investigation Report" by Hao FuDocument2 pagesLtspice Caveats: "Design Tool Investigation Report" by Hao Fu29377Pas encore d'évaluation
- Product Data Sheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Nsx250B, 25 Ka at 415 Vac, TMD Trip Unit 250 A, 4 Poles 3DDocument3 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Nsx250B, 25 Ka at 415 Vac, TMD Trip Unit 250 A, 4 Poles 3DraghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Four-Position Sectionalizing Loadbreak SwitchesDocument8 pagesFour-Position Sectionalizing Loadbreak SwitchesGustavo PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Low Frequency Dielectric Spectroscopy To EstimateDocument4 pagesApplication of Low Frequency Dielectric Spectroscopy To EstimateAnggiPas encore d'évaluation
- 876-0255-000 - b1 (Install Procedure, Bantam)Document16 pages876-0255-000 - b1 (Install Procedure, Bantam)mglemPas encore d'évaluation
- LSR4328 ManualDocument52 pagesLSR4328 Manualikolev57Pas encore d'évaluation
- Applications: 11-4 ACSRDocument3 pagesApplications: 11-4 ACSRJuan Carlos Vivas GuioPas encore d'évaluation
- 600V PolyradXT TXDocument1 page600V PolyradXT TXLuis LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Lab 8: Jadavpur UniversityDocument11 pagesAnalog Lab 8: Jadavpur UniversityIron PatriotPas encore d'évaluation
- Generation of PWM Using Verilog in FPGA 11Document7 pagesGeneration of PWM Using Verilog in FPGA 11Rajani kant tiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Omron H3CA Timer DatasheetDocument16 pagesOmron H3CA Timer DatasheetpumperNXPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding The How and Why of Electrical Product Safety TestingDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The How and Why of Electrical Product Safety TestingLanstein Joe E PPas encore d'évaluation
- Electroni Project Titles1 (2015-2016) PDFDocument70 pagesElectroni Project Titles1 (2015-2016) PDFmageshwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Microwave Theory and TechniquesDocument599 pagesMicrowave Theory and Techniquesdhanushcm2001Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4x2x18 AWG 600V Individual and Overall Shielded Instrumentation Cable - 8PM3104xxxDocument2 pages4x2x18 AWG 600V Individual and Overall Shielded Instrumentation Cable - 8PM3104xxxJosue MuñozPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 1Document25 pagesSection 1mohamed mPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet: 5535/5545 Accelerometer Signal ConditionerDocument3 pagesDatasheet: 5535/5545 Accelerometer Signal ConditionerAllen BradleyPas encore d'évaluation
- NVRAM Floor Height Table SUM Error: Point of Detection ApplicationDocument1 pageNVRAM Floor Height Table SUM Error: Point of Detection ApplicationDaniel GatdulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module AppliManual2006-2007 PDFDocument173 pagesModule AppliManual2006-2007 PDFJose HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Anly Timer: Multi-Function Analogue TimerDocument2 pagesAnly Timer: Multi-Function Analogue TimerkahandawalaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 To 1 Balun For End Fed AntennaDocument24 pages9 To 1 Balun For End Fed AntennaKlaudio KostaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Dual Nature of LightDocument2 pagesA Dual Nature of LightRoshdy WaheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ava 5546 ExcDocument4 pagesAva 5546 ExcTin Min NaingPas encore d'évaluation
- VANGUARD ct8000Document6 pagesVANGUARD ct8000juan primoPas encore d'évaluation