Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Design of Passengers Vehicle Body On Fire Accidents
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Design of Passengers Vehicle Body On Fire Accidents
Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 11 | NCAMESHE - 2014 | Jun-2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 192
DESIGN OF PASSENGERS VEHICLE BODY ON FIRE ACCIDENTS
K.Somasundaram
1
, S.Gopal
2
, K.Vignesh
3
, N.Nagarajan
4
, K.Visagavel
5
1
Student, Mechanical Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Tamilnadu, India
2
Student, Mechanical Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Tamilnadu, India
3
Student, Mechanical Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Tamilnadu, India
4
Asst.Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Tamilnadu, India
5
Professor&Head, Mechanical Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Tamilnadu, India
Abstract
Generally Fire Accidents in Heavy Vehicles occur due to many reasons like Short Circuit of Electrical Connections, Bringing
Flammable Materials and Indiscipline activities of People. So Passengers die in a large number including Children. It is mainly
focused to safeguard the Passengers in Buses and Trains. During Fire Accidents, They have only two ways to escape, one is the
Main Way and another is the Emergency Exit, so they cannot escape quickly and easily. By changing the Design of the body of the
Vehicle, They can escape easily. By using the slider mechanism.
Keywords: Fire, Body of the Vehicle, Emergency Exit
--------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------
1. INTRODUCTION
Body is the super structure for all vehicles. It may either be
constructed separately and bolted to the chassis or
manufactured integral with chassis (i.e. Frameless
construction). The chassis and body make the complete
vehicle.
A body consists of windows and doors, engine cover, roof,
luggage cover etc. The electrical system in the body is
connected to the chassis electrical units so that the battery
and the generator can furnish the required electrical energy
to the system.
2. OVERVIEW OF THE PROJECT
The main objective of our project is to protect passenger
from fire accidents. Fire Accidents in heavy vehicles is a
major issue. It occurs due to many reasons like Short Circuit
of Electrical Connections, Bringing Flammable Materials
and Indiscipline activities of People. Due to this, there is
more human loss. During Fire Accidents, Passengers have
only two ways to escape in vehicle, one is the Main way and
another is the Emergency Exit. They cannot move easily and
quickly.
In this system, the external sides of the body are designed as
a slider which slides when the signal is received from
sensor. During occurrence of fire, the temperature sensors
sense the temperature and send signal to the Motor, which
results in movement of slider and also manual operating
system with glass guard provided with driver. So people can
escape easily and quickly.
3. TYPES OF VEHICLEBODY
For different types of automobile vehicle, passenger space
and overall dimensions vary. Various types of bodies for
different vehicle can be listed as
i. Buses
ii. Car
iii. Tanker
iv. Jeep
v. Tractor
vi. Straight truck
vii. Delivery van
viii. Three wheeler (i.e. auto)
4. WORKING OF THE SYSTEM
4.1 General Working
Initially, during occurrence of fire, there is a temperature
sensor which senses the temperature of the body and gives a
signal. By this signal the slider movement takes place. The
Slider movement is controlled by a motor. As the signal
reaches, the motor starts to operate and the Slider moves.
The Power is transmitted from the Motor to slider by Chain.
Now as the slider moves to an end, there will be a free space
where it will be easy for the passengers to escape.
IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 11 | NCAMESHE - 2014 | Jun-2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 193
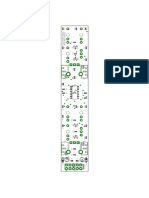
Schematic diagram of working
4.2 Static Condition
Initially, during occurrence of fire, there is a temperature
sensor named LM35, which senses the temperature of the
body and gives a signal. By this signal the slider movement
takes place. The Slider movement is controlled by a Stepper
DC motor. The drive and control of Motor is done by
Microcontroller AT89652. As the signal reaches, the motor
starts to operate and the Slider moves. The Power is
transmitted from the Motor to slider by Chain. Now as the
slider moves to an end, there will be a free space where it
will be easy for the passengers to escape.
4.3 Dynamic Condition
In some cases, the vehicle may be in motion and Passenger
may unable to get out of the vehicle during Fire. For certain
conditions, the temperature sensor senses the temperature of
the body and then it makes a signal. By this signal the fuel
gets cut off by the Throttle Sensor and there will be no fuel
going to the engine. Due to this the vehicle will remain in
rest condition. Then the Microcontroller again controls and
drives the motor. It will operate and make the slider to
move, the movement is by Chain. By this passengers can
escape easily and quickly.
5. COMPONENTS
The major components involved in this project for effective
use of passenger vehicle body are as follows:
Bus Body Attachment Components
i. Temperature SensorLM35
ii. Slider
iii. Throttle Position Sensor
iv. Stepper Motor
Let us study about the functions and features in detail of the
above components one by one which are as follows.
5.1 Temperature SensorLM35
The Temperature sensor is fixed in the vehicle, which can
sense the temperature of the Vehicle. The LM35 series are
precision integrated-circuit temperature sensors, with an
output voltage linearly proportional to the Centigrade
temperature. Thus the LM35 has an advantage over linear
temperature sensors calibrated in Kelvin, as the user is not
required to subtract a large constant voltage from the output
to obtain convenient Centigrade scaling. The LM35 does not
require any external calibration or trimming to provide
typical accuracies of C at room temperature and C
over a full 55C to +150C temperature range. Low cost is
assured by trimming and calibration at the wafer level. The
low output impedance, linear output, and precise inherent
calibration of the LM35 make interfacing to readout or
control circuitry especially easy. The device is used with
single power supplies, or with plus and minus supplies. As
the LM35 draws only 60 A from the supply, it has very
low self-heating of less than 0.1C in still air. The LM35 is
rated to operate over a 55C to +150C temperature range,
while the LM35C is rated for a 40C to +110C range
(10 with improved accuracy). The LM35 series is
available packaged in hermetic TO transistor packages,
while the LM35C, LM35CA, and LM35D are also available
in the plastic TO-92 transistor package. The LM35D is also
available in an 8-lead surface-mount small outline package
and a plastic TO-220 package.
Features
Calibrated Directly in Celsius (Centigrade)
Linear + 10 mV/C Scale Factor
0.5C Ensured Accuracy (at +25C)
Rated for Full 55C to +150C Range
Suitable for Remote Applications
Low Cost Due to Wafer-Level Trimming
Operates from 4 to 30 V
Less than 60-A Current Drain
Low Self-Heating, 0.08C in Still Air
Nonlinearity Only C Typical
Low Impedance Output, 0.1 for 1 mA Load
IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 11 | NCAMESHE - 2014 | Jun-2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 194
5.2 Slider
In this system, we are making the external sides of the body
as a slider. Slider is nothing but a moving member, which
slides when the signal is received. The slider also includes
the window part of the vehicle. The slider is operated by a
Stepper DC Motor. The Power is transmitted by the Stepper
Motor to Slider by a Chain.
5.3 Throttle Position Sensor
A throttle position sensor (TPS) is a sensor used to monitor
the position of the throttle in an internal combustion engine.
The sensor is usually located on the butterfly spindle/shaft
so that it can directly monitor the position of the throttle.
More advanced forms of the sensor are also used, for
example an extra closed throttle position sensor (CTPS) may
be employed to indicate that the throttle is completely
closed. Some engine control units (ECUs) also control the
throttle position electronic throttle control or "drive by wire"
systems and if that is done the position sensor is used in a
feedback loop to enable that control.
5.4 Stepper Motor
The stepper motor is an electromagnetic device that converts
digital pulses into mechanical shaft rotation. The Typical
Use of DC Stepper Motor is Position Control (Relative
Position without Feedback). This type of stepper motor is
good holding Torque.
6. CONCLUSIONS
Hence, by implementing this system large amount of Human
Life can be saved. It can be implemented in AC coach
buses, where more fire Accidents occur. Then we have
better advantage to save the people.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Department of mechanical
Engineering in Knowledge institute of technology. We are
extremely grateful to thank our principal Dr.PSS.Srinivasan
for providing all facilities to complete this project. The
authors appreciate the support of Dr.K.Visagavel, Professor
& Head- Department of Mechanical Engineering and
Mr.N.Nagarajan, Asst. Professor, Mech.
REFERENCES
[1]. Rompe and Krger, (1985). Research On Emergency
Exit System for bus safety. technical report.
[2]. Shiosaka and Kuboike, (1996). Research on emergency
exit system for school bus safety. Technical report
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Port ClearanceDocument98 pagesPort Clearanceduckerz28Pas encore d'évaluation
- 18SP546 (Search-Manual-Online - Com) PDFDocument8 pages18SP546 (Search-Manual-Online - Com) PDFJesus Vega HummerPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Alterations and Works London Underground Tenanted PremisesDocument34 pagesGuide To Alterations and Works London Underground Tenanted PremisesTan ChingPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Leader VocabularyDocument36 pagesMarket Leader VocabularyBalan Claudiu100% (1)
- ToxicokineticsDocument31 pagesToxicokineticsabdiukon100% (1)
- Zenith Aviation - Air RegulationsDocument100 pagesZenith Aviation - Air RegulationsParas Aggarwal75% (4)
- TTM Single Aisle Line & Base Ata 28Document354 pagesTTM Single Aisle Line & Base Ata 28林至伟Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aasho Road TestDocument12 pagesAasho Road TestRogero Mar CPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Trends in Bumper Design For Pedestrian ImpactDocument16 pagesCurrent Trends in Bumper Design For Pedestrian ImpactVikas VPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahir Dar University LSCMDocument34 pagesBahir Dar University LSCMAnonymous MrEL6JPPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts Manual Di1611 Konica 7216Document53 pagesParts Manual Di1611 Konica 7216vagmixPas encore d'évaluation
- CV of Ramoni Saidi A. Piping EngrDocument8 pagesCV of Ramoni Saidi A. Piping EngrAnonymous qaI31HPas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Name Employee No. Vehicle No Test Date Exp. Date Emission Report (Yes/ No)Document3 pagesEmployee Name Employee No. Vehicle No Test Date Exp. Date Emission Report (Yes/ No)prashanthPas encore d'évaluation
- DN-PT022 - 2023 - INDO PT Mandala Putera PrimaDocument1 pageDN-PT022 - 2023 - INDO PT Mandala Putera PrimaFirmansudiyoPas encore d'évaluation
- BGP SE Asia Pre Startup Inspection Checklist 2 - 2011Document31 pagesBGP SE Asia Pre Startup Inspection Checklist 2 - 2011Dale WearpackPas encore d'évaluation
- "Joining Time": A. Cases in Which Joining Time Is AdmissibleDocument24 pages"Joining Time": A. Cases in Which Joining Time Is Admissiblevijaygarge59100% (1)
- Pedido LFDocument81 pagesPedido LFgonzalo rodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To DeKalb: 2018 Newcomers Guide by Champion NewspaperDocument48 pagesWelcome To DeKalb: 2018 Newcomers Guide by Champion NewspaperDonna S. Seay100% (1)
- Updated FC Road User Permit - FEU To Festival MallDocument1 pageUpdated FC Road User Permit - FEU To Festival MallWild Flower Bhiebe67% (6)
- DNV-OS-C301 (Stability & Watertight Integrity)Document27 pagesDNV-OS-C301 (Stability & Watertight Integrity)tidus00_3Pas encore d'évaluation
- DVCA - 18022017 - Ver01.1 BOTTOMDocument1 pageDVCA - 18022017 - Ver01.1 BOTTOMcesvenegasPas encore d'évaluation
- TML Ir Ar 2018 19 PDFDocument406 pagesTML Ir Ar 2018 19 PDFHarsh TimbadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifi'" 31fil I UiDocument10 pagesLifi'" 31fil I UiMy NamePas encore d'évaluation
- New Verna Owner's Manual - Full Version PDFDocument411 pagesNew Verna Owner's Manual - Full Version PDFArnab GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture-5 Street Lighting: Md. Manik Mia Lecturer Sonargaon UniversityDocument14 pagesLecture-5 Street Lighting: Md. Manik Mia Lecturer Sonargaon UniversityManik MiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ergolet - LAMBDA 175Document2 pagesErgolet - LAMBDA 175Евгений ЧеглаковPas encore d'évaluation
- Traffic Survey Manual and User GuideDocument37 pagesTraffic Survey Manual and User Guidephanna0% (1)
- Mazda & China Parts List (Market) 01-05-2023Document1 pageMazda & China Parts List (Market) 01-05-2023m h habib m h kassamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - TrafficDocument10 pagesChapter 5 - TrafficMercy Temblor LibrePas encore d'évaluation
- CLC Protocol 92 and R.A. 9483Document2 pagesCLC Protocol 92 and R.A. 9483MrAlbusPas encore d'évaluation