Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Secret Pharmacology Step 1 Study Guide: Pharm"
Transféré par
Fahd Abdullah Al-refaiDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Secret Pharmacology Step 1 Study Guide: Pharm"
Transféré par
Fahd Abdullah Al-refaiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Secret Pharmacology
Step 1 Study
Guide
All you need for Step 1
Pharm
Abciximab
Antiplatelet: monoclonal antibody to brin
receptor (glycoprotein IIb/IIIa) on PLTs. Used
to prevent clotting after coronary
angioplasty
Acarbose
Oral hypoglycemic: !-glucosidase inhibitor.
Prevents oligosaccharide hydrolysis leading
to less postprandial hyperglycemia. Tox: GI
disturbances
Acetaminophen
Antipyretic analgesic: CNS-active antipyretic,
analgesic. Less toxic than aspirin but more
dangerous in overdose (causes hepatic
necrosis-antidote: acetylcysteine)
Acetazolamide, dorzolamide
Diuretic: carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Causes
NaHCO3 diuresis and bicarbonate depletion at
proximal tubule. Used in alkalosis, alkalinizing urine,
glaucoma. Tox: metabolic acidosis. and therefore
has self-limited action. Dorzolamide is a topical for
glaucoma (decreases aqueous humor production)
Acyclovir, valacyclovir penciclovir,
famciclovir
Antiviral: converted to dNTP analogs, inhibit
DNA polymerase in HSV, VZV, EBV. Activated
by viral thymidine kinase. Tox: tremor,
delirium, crystallization in urinary tract
Adenosine
Antiarrhythmic: "Class V". IV only.
Hyperpolarizes AV node, blocking
conduction for 10-15 sec. Used to dx,
abolish nodal reentry arrhythmias.
Albendazole, mebendazole
Antihelminth: inhibit microtubule synthesis.
Used for all roundworm infections.
Allopurinol
Antigout: inhibitor of xanthine oxidase;
prevents attacks during chronic gout and
during chemotherapy for leukemia/
lymphoma
Albuterol, terbutaline
"2-agonists for asthma. Acute attacks only.
Tox: tremor, arrhythmia.
Alprazolam, lorazepam
Benzodiazepine: intermediate duration of
action. Used in anxiety states, selectivity for
panic attacks and phobias. Tox: psychologic
and physical dependence, additive e#ects
with other CNS depressants
Amantadine, rimantadine
Antiviral: prevents uncoating of inuenza A
inside host cells. Reduces duration of u
symptoms. Amantadine also causes release
of dopamine for Parkinsons. Tox: ataxia,
dysphasia.
Amiodarone
Antiarrhythmic: action in all 4 Classes. Used
for life-threatening atrial and ventricular
arrhythmias. Tox: pulmonary brosis,
hepatoxicity, thyroid dysfunction
Amitriptyline, nortriptyline, desipramine,
imipramine
TCA: blocks reuptake of NE and 5-HT. Tox:
antimuscarinic (atropine-like), anti-! (orthostatic
hypotension), sedation, overdose (seizures, coma,
QRS widening). Additive e#ects with other CNS
depressants. Use bicarb in toxicity.
Amoxicillin, ampicillin
Penicillin (beta-lactam): better coverage than
PCN. Amoxicillin is oral pills. Can be used
for almost all mild infections. Penicillinase-
susceptible unless given w/ inhibitor. Tox:
penicillin allergy
Amphetamine
Indirect sympathomimetic: releases
catecholamine store. CNS stimulant action.
Used for narcolepsy, obesity, ADHD. Tox:
psychosis, HTN, MI, seizures
Amphotericin B
Antifungal: 1st line for most systemic mycoses.
Emulsies fungal cell membrane by binding
ergosterol. Tox: shake and bake, nephrotoxicity.
Must be given intrathecally for meningitis. Nystatin
is similar and used topically. Flucytosine is used
w/ amphotericin to inhibit DNA/RNA synthesis.
Anistreplase (APSAC)
Thrombolytic: longer acting in body than
other thrombolytics (rt-PA, streptokinase,
urokinase). Tox: bleeding, allergy to
streptococcal protein
Aspirin
NSAID prototype: inhibits cyclooxygenase
(COX) I and II irreversibly. Potent antiplatelet
agent as well as antipyretic analgesic anti-
inammatory drug. In overdose, alkalinize
urine and dialyze
Atenolol
"1-selective blocker: low lipid solubility, less
CNS e#ect; used for HTN. Mnemonic for "1-
selective blockers: their names start with A
through M. (except labetalol)
Atropine
Antimuscarinic: lipid soluble, CNS e#ects. Tox:
blind as a bat, dry as a bone, hot as a hare, mad
as a hatter, red as a beet," urinary retention,
mydriasis. Use physostigmine in toxicity. Blocks
SLUD: salivation, lacrimation, urination,
defecation
Azathioprine
Immunosuppressant: similar to 6-MP but for
kidney transplant. Tox: myelosuppression,
xanthine oxidase-dependent
Aztreonam
Monocyclic "-lactam. Penicillinase-resistant.
Used only against GN bugs, especially nasty
GNRs. Not a cross-allergen w/ PCN, can be
used in CKD patients (unlike
aminoglycosides)
Baclofen
GABA-analog spasmolytic: activates GABAB
receptors in the spinal cord.
Beclomethasone Inhaled corticosteroid for chronic asthma.
Benztropine
Central antimuscarinic for Parkinsonian
tremor/rigidity
Bethanechol
Muscarinic agonist: choline ester with good
resistance to cholinesterase. Used for postop
or neurogenic ileus or urinary retention.
Bismuth, sucralfate
Antiulcer: protect ulcer base and hasten
recovery.
Bleomycin
Antineoplastic: causes free radical DNA
damage. Used in testicular ca, lymphomas
(ABVD). Tox: pulmonary brosis.
Bromocriptine, pramipexole,ropinirole
Ergot alkaloid: dopamine agonist in CNS;
inhibits prolactin. Used in Parkinsons
hyperprolactinemia. Tox: CNS, dyskinesias,
hypotension
Bupivacaine, lidocaine, tetracaine, procaine,
cocaine
Local anesthetics: block Na+ channels. 2 Is in
name: amide. 1 I in name: ester. Does not
penetrate infected tissue well. Causes loss of
sensation in this order: pain, temperature, touch,
pressure. Tox: CNS excitation, severe myocardial
toxicity (bupivicaine), arrhythmia (cocaine).
Bupropion
Heterocyclic antidepressant: MOA unknown.
Also used for smoking cessation. Tox:
stimulant-like, seizure in bulimics.
Buspirone
Anxiolytic: atypical drug that interacts with
5HT1A receptors; slow onset. Minimal
potentiation of CNS depressants including
ethanol; negligible abuse liability
Busulfan
Antineoplastic: DNA alkylator. Used in CML.
Tox: pulmonary brosis.
Captopril
ACE inhibitor: used in HTN, diabetic renal disease,
and CHF. Tox: cough, angioedema (both due to
increased bradykinin) proteinuria, teratogen to
fetal kidneys, hyperkalemia. In CKD, the action of
A-II may be all that is preserving GFR.
Carbachol, pilocarpine
Nonselective muscarinic and nicotinic
agonist: choline ester with good resistance
to cholinesterase; used for glaucoma (not
1st-line)
Carbamazepine
Anticonvulsant: 1st line for tonic-clonic and
trigeminal neuralgia, also used ( phenytoin,
valproate) for partial seizures. Same MOA as
phenytoin (Na+ channel blocker). Tox: diplopia,
ataxia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia,
hepatotoxicity, teratogen, induces P450
Caspofungin
Antifungal: disrupts fungal cell wall
synthesis.
Cefazolin, cephalexin
1st-gen cephalosporin: bactericidal "-
lactamase-resistant "-lactams. Used for
GPCs, weak activity against GNRs. Tox:
potential allergy
Cefuroxime, cefoxitin, cefotetan
2nd-gen cephalosporin. Used for GPCs, H.
u, Klebsiella, in sinusitis or otitis.
Ceftriaxone, ceftaz, ceftiz
3rd-gen cephalosporin. Used in nasty GN
sepsis and meningitis (also covers
Pneumococcus).
Cefepime
4th-gen cephalosporin: developed to treat
Pseudomonas.
Celecoxib, rofecoxib
First COX-II-selective NSAIDs. Reduced GI
toxicity, increased thrombosis
Chloramphenicol
Antibiotic: inhibits peptidyl transferase at 50S
subunit. Can be used for almost any bugs, but is
rarely used due to side e#ects. Tox: reversible
myelosuppression, aplastic anemia, gray baby
syndrome due to inhibition of UDP-glucuronyl
transferase
Chloroquine, meoquineprimaquine
Antimalarial: kill blood forms of
Plasmodium. Chloroquine resistance is
widespread. Primaquine is active against
liver forms. Tox: GI distress, rash, G6PD
oxidant e#ect
Cholestyramine, colestipol
Antilipemic: bind bile acids to prevent
reabsorption; body converts more
cholesterol to bile salts to compensate. Tox:
constipation, bloating, terrible taste
Cimetidine
H2 blocker prototype: used in GERD, ulcers.
Tox: inhibits hepatic drug metabolism;
antiandrogen e#ects. Analogs w/ neither
toxicity:: ranitidine, famotidine, etc
Ciprooxacin, -oxacins
Fluoroquinolone: bactericidal inhibitor of
topoisomerase. Used against most GNRs in UTIs,
bacterial diarrhea. Tox: GI distress, cartilage
damage in tendons causing tendonitis, tendon
rupture. Avoid in children and pregnant women.
Cisplatin
Antineoplastic: DNA alkylator. Used for
testicular, bladder ca. Tox: kidney, acoustic
nerve. Carboplatin is similar.
Clindamycin
Antibiotic: bacteriostatic, inhibits formation
of initiation complex at the 50S subunit. Used
against anaerobic pneumonia and GPCs. Tox:
GI distress, pseudomembranous colitis.
Linezolid is similar but used for MRSA, VRE.
Clomiphene
Estrogen partial agonist at pituitary: causes
release of FSH and LH, inducing ovulation.
Used to treat infertility. Tox: hot ashes,
ovary-megaly, twins or triplets.
Clonidine
!2 agonist: acts centrally to reduce SNS
outow, lowers BP. Tox: rebound HTN,
sedation, dry mouth. Methyldopa is similar
but causes positive Coombs.
Clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone
Atypical antipsychotic: low a$nity for dopamine D2
receptors, higher for D4 and 5-HT2A receptors.
Used for schizophrenia; olanzapine used for OCD,
anxiety, etc. Tox: less EPS, anticholinergic e#ects
than neuroleptics. Clozapine requires weekly WBC
for r/o agranulocytosis, causes weight gain
Cocaine
Indirect sympathomimetic: blocks
catecholamine reuptake. Local anesthetic (ester
type). Used for nasal surgery. Marked CNS
stimulation, euphoria; high abuse liability. Tox:
stroke, psychosis, arrhythmias, seizures
Colchicine
Microtubule assembly inhibitor: freezes
WBCs in gouty joints. Tox: GI, hepatic, renal
Cromolyn
Anti-asthma: mast cell stabilizer. 3rd line
agent for prophylaxis.
Cyanide
Toxin: poisons oxidative phosphorylation
and creates metHb. Use nitrites in toxicity
Cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide
Antineoplastic, immunosuppressive: DNA
alkylating agent. Used in HL, breast ca. Tox:
Hemorrhagic cystitis (prevent w/ mesna),
myelosuppression
Cyclosporine
Immunosuppressant: inhibits calcineurin,
and thereby IL-2. Used in transplant
immunosuppression. Tox: nephrotoxicity
(dose-limiting), infections. Tacrolimus is
nearly identical
Cytarabine
Antineoplastic: DNA polymerase inhibitor.
Used in AML. Tox: leukopenia.
Cytokines
EPO: renal-failure anemia. G-CSF/GM-CSF:
recover bone marrow. IFN-!: HBV or HCV,
HHV-8. IFN-": MS. IFN-%: CGD.
Dactinomycin
Antineoplastic: intercalates in DNA. Used in
Wilms, Ewings, rhabdomyosarcoma (kids
tumors)
Dantrolene
Blocker of Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic
reticulum of skeletal muscle. Used for
malignant hyperthermia, muscle spasm,
malignant neuroleptic syndrome, and
serotonin syndrome.
Daunorubicin Like doxorubicin but only used for AML
Deferoxamine
Chelator: chelates Fe very avidly, aluminum
less so
Desmopressin
ADH analog: synthetic peptide used for
pituitary diabetes insipidus, vWD.
Dexamethasone
Glucocorticoid: very potent, long-acting; no
mineralocorticoid activity
Diazepam
Benzodiazepine: binds to BDZ receptors at the
GABAA receptor, increasing frequency of channel
opening. Uses: anxiety, EtOH detox, muscle
spasms, status epilepticus. Tox: psychologic and
physical dependence, additive e#ects with other
CNS depressants
Digoxin
Cardiac glycoside prototype: positive inotropic drug
for CHF. Used in CHF, a-b (decreases AV nodal
conduction). Half-life 40h. Renal excretion. Can cause
long PR, short QT, ST scooping, inverted T. Tox: N/V,
diarrhea. Toxicity exacerbated by hypokalemia, renal
failure, quinidine. Anti-dig Fab available.
Dimercaprol
Chelator (British AntiLewisite): used for As,
Pb, Hg poisoning. 1st line for Pb
Diphenhydramine, chlorpheniramine
Antihistamine H1 blocker prototype: used in
hayfever, motion sickness, sleep aid. Tox:
antimuscarinic, anti-!, sedative
Dobutamine "1 agonist: pure inotrope for ICU care.
Donepezil, tacrine
Antialzheimer: centrally-active
cholinesterase inhibitor to slow progression
of symptoms
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter and agonist drug at
dopamine receptors: pressor for shock and
to increase renal blood ow
Doxorubicin
Antineoplastic: anthracycline drug (cell cycle-
nonspecic); intercalates between base pairs to
disrupt DNA functions and forms cytotoxic free
radicals. Used in breast, most solid tumors, HL
(ABVD regimen) Tox: cardiotoxicity,
myelosuppression
Edetate (EDTA)
Chelating agent: 1st line for Pb poisoning.
Tox: renal tubular necrosis
Ephedrine
Indirect sympathomimetic: like amphetamine
but less CNS stimulation. Used for nasal
decongestion, urinary incontinence
Epinephrine
Agonist at all ! and " receptors. Used in
anaphylaxis, asthma, ICU hypotension,
vasoconstriction w/ local anesthesia.
Erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin
Macrolide: bacteriostatic, inhibits translocation at
the 50S subunit. Used mostly for atypical
pneumonias and Chlamydia UTI. Tox: cholestatic
hepatitis, erythromycin inhibits P450 to increase
warfarin, theophylline, cyclosporine
concentrations.
Etanercept Soluble TNF receptor: used in RA, psoriasis.
Ethacrynic acid
Loop diuretic: same as furosemide in action
and toxicity w/o gout or allergy.
Ethanol
Sedative-hypnotic: increases ow through GABAA
channels. Metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to
acetaldehyde, then by aldehyde dehydrogenase to
acetate. Disulram inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase,
causing accumulation of acetaldehyde. Consumes NAD
+ and produces NADH. Zero-order elimination
kinetics, chronically induces its own metabolism.
Ethosuximide
Anticonvulsant: 1st line for absence. Blocks
thalamic T-type Ca2+ channels. Tox: GI
distress, lethargy, Stevens-Johnson
Etidronate, pamidronate, alendronate
Bisphosphonates: reduce resorption of bone
by inserting into hydroxyapatite. Used in
Pagets disease, osteoporosis, PTH-rP
secretion. Tox: severe esophageal ulceration
Etoposide
Antineoplastic: inhibits topoisomerase only
during G2. Used in small cell carcinomas.
Tox: myelosuppression
Fexofenadine, loratadine, desloratadine
2nd generation antihistamine; does not
enter CNS, little or no sedation
Finasteride
Steroid inhibitor of 5!-reductase: inhibits
synthesis of DHT, the active androgen in
prostate. Used in BPH.
Flecainide, encainide,
Class IC antiarrhythmics. Used for severe,
refractory ventricular arrhythmias. Tox:
propafenone arrhythmogenic,
contraindicated post-MI
Fluconazole, itraconazole
Antifungal: inhibits fungal and host P450.
Used for more severe infxns than
ketoconazole: Cryptococcal meningitis,
Candida sepsis. No antiandrogenic e#ects.
Fludrocortisone
Synthetic corticosteroid: high
mineralocorticoid and moderate
glucocorticoid activity; long duration of
action
Flumazenil
Benzodiazepine antagonist: used to reverse
CNS depressant e#ects of benzos in
overdose or in anesthesia
5-Fluorouracil
Antineoplastic: pyrimidine antimetabolite (S
phase) that decreases dTMP. Used mainly for
colon ca or supercial tumors. Tox:
myelosuppression not rescuable w/
leucovorin
Fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, citalopram
SSRI antidepressant. Also used for OCD. Takes
e#ect in 2-3 weeks. Tox: less antimuscarinic,
cardiotoxic; more GI distress and sexual
dysfunction. Causes serotonin syndrome if
used w/ MAOI. Fluoxetine inhibits P450.
Flutamide
Androgen receptor antagonist: nonsteroid
that blocks DHT. Used in prostate ca.
Furosemide
Loop diuretic: blocks Na+/K+/2Cl- transporter,
preventing urine concentration. Used for edema
states, hypercalcemia. Can be used in severe
renal disease. Tox: hypokalemia, allergy to sulfa,
ototoxicity, hypovolemia, gout, hypocalcemia.
Gabapentin
Anticonvulsant and analgesic: increases CNS
GABA. Used for general and partial seizures
and peripheral neuropathy. Tox: sedation,
ataxia.
Ganciclovir, foscarnet
Antiviral: GTP analog that requires activation
by thymidine kinase. Used for CMV. Tox:
neutropenia. Foscarnet does not require
activation.
Gembrozil, clobrate
Antilipemics: stimulate lipoprotein lipase to
convert TGs to FAs. Used in
hypertriglyceridemias and mixed
triglyceridemia/hypercholesterolemia. Tox:
liver (increased LFTs), myositis
Gentamicin, tobramycin, streptomycin
Aminoglycoside: bactericidal, inhibits formation
of initiation complex at the 30S subunit. Used
against all aerobic GNRs as in sepsis, and will
clear out bowels if given chronically or so
intended. Tox: nephrotoxicity (major cause of
acute tubular necrosis), ototoxicity, teratogenic.
Glipizide, glyburide
Oral hypoglycemics: 2nd generation. Close K
+ channels on " cells, depolarize cell, cause
fusion of insulin vesicles w/ membrane. Tox:
hypoglycemia
Griseofulvin
Antifungal: interferes w/ microtubules in
keratinized tissues. Used in topical
dermatophytic infxns.
Guanethidine
Postganglionic sympathetic neuron blocker:
depletes monoamine stores. Ee#ect reversed
by TCAs, cocaine. Tox: severe orthostatic
hypotension, sexual dysfunction
Haloperidol, uphenazine, thioridazine,
chlorpromazine
Antipsychotic: blocks central dopamine D2 receptors.
Used in schizophrenia, psychosis. Tox: EPS e#ects
(acute dystonia, akinesia, akithisia, tardive
dyskinesia), hyperprolactinemia, antimuscarinic, anti-
!. Less ANS adverse e#ects than phenothiazines.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. (neuroleptics)
Halothane, isourane, enurane,
methoxyurane
General anesthetic: inhaled halogenated
hydrocarbon, MOA unknown. Cause myocardial
depression, respiratory depression, increased ICP.
Halothane is hepatotoxic, enurane is
proconvulsant. All can cause malignant
hyperthermia, particularly w/ succinylcholine.
Heparin
Anticoagulant: large polymeric molecule with
antithrombin, and anti-factor X activity.
Rapid onset. Tox: bleeding, HIT, use
protamine as antidote. LMW-heparins target
Xa w/o PTT monitoring.
Hexamethonium
SNS-plegic: nAChR antagonist. Used in HTN.
Tox: orthostatic hypotension, blurred vision
Hydralazine
Antihypertensive: increases cGMP to dilate
arterioles, reduce afterload. Used in HTN,
CHF. Tox: tachycardia, volume retention,
SLE-like
Hydrochlorothiazide
Thiazide diuretic prototype: blocks Na+/Cl-
symporter in distal tubule; Ca2+ is
reabsorbed instead. Used in HTN, CHF,
chronic calcium stones. Tox: hypokalemia,
retention of urate, glucose, lipids, calcium
Ibuprofen
NSAID prototype: short duration. Inhibits
cyclooxygenase (both I and II) reversibly.
Used in arthritis, dysmenorrhea, muscle
inammation. Tox: peptic ulcer, renal
damage
Imipenem, meropenem
Antibiotic: broad-spectrum carbapenem "-
lactam. Penicillinase-resistant. Used for almost
all infections except VRE and MRSA. Imipenem is
given w/ cilastatin to inhibit renal metabolism.
Tox: PCN allergy, seizures in overdose
Indinavir, saquinivir, others
Antiviral: HIV protease inhibitor. Prevents
cleavage of polyprotein to produce
functional viral enzymes. Tox: bu#alo hump
or truncal obesity, hyperlipidemia. Ritonavir
inhibits P450.
Indomethacin
NSAID prototype: highly potent and acute
(gout). Closes PDA. Tox: ulcers, renal
damage
Iniximab Anti-TF Ab: used in Crohns, RA.
Ipratropium
Antimuscarinic agent: aerosol for asthma,
COPD. Good bronchodilator in 20-30% of
patients. 2nd line choice.
Isoniazid
Antimycobacterial: inhibits synthesis of mycolic
acid. Used as part of treatment regimen or for
single prophylaxis of contacts or positive PPD. Fast
or slow metabolism by N-acetyltransferase (genetic
variability). Tox: peripheral neuropathy (reversed by
pyridoxine), G6PD hemolysis, SLE-like, hepatitis
Isoproterenol
"1, "2 agonist: bronchodilator, cardiac
stimulant. Always causes tachycardia
because both direct and reex actions
increase HR. Tox: AV block (rare), angina
Ivermectin
Antihelminth: activates worms GABA
receptor. Used in onchocerciasis (river
blindness)
Ketamine
Dissociative anesthetic: acts at NMDA
glutamate receptor. Stimulates myocardium,
excellent analgesic. Tox: hallucination,
disorientation, nightmares.
Ketoconazole, clotrimazole
Antifungal azole: inhibits fungal P450 to decrease
ergosterol synthesis. Used for Candida,
dermatophytes and weak systemic mycoses. Used
in PCOS to prevent hirsutism (is antiandrogenic).
Tox: hepatic dysfunction, inhibits steroid
synthesis and P450. Clotrimazole is topical.
Labetalol
!- and "-blocker: used in HTN. Tox: AV
block, hypotension
Lamotrigine
Anticonvulsant: blocks voltage-gated Na+
channels. Used in partial and general
seizures. Tox: Stevens-Johnson.
Leuprolide
GnRH analog: agonist when pulsatile,
antagonist when continuous. Used for
infertility (pulsatile), prostate ca or
leiomyoma (continuous). Tox: antiandrogen,
N/V.
Levodopa/carbidopa
Dopamine precursor. Used in parkinsonism.
Tox: arrhythmia, dyskinesia, resumption of
Parkinson symptoms between doses (on-
o# phenomena)
Lidocaine, mexetiline, tocainide
Class IB antiarrhythmics. Medium duration
amide anesthetic (lido). Shorten AP duration.
Used in ventricular arrhythmias (v-b,
v-tach), as seen post-MI. Tox: CNS
excitation, CV depression
Lithium
Antimanic prototype: drug of choice in mania and
bipolar a#ective disorders; blocks phosphatidyl
inositol system. Tox: tremor, hypothyroidism,
nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, narrow
therapeutic index, seizures (in overdose),
teratogen (Ebsteins malformations)
Losartan
Angiotensin II receptor blocker. Tox:
hyperkalemia, teratogen (fetal kidneys).
Lovastatin, other -statins
Antilipemic: inhibit HMG-CoA reductase to
decrease LDL and increase HDL. Tox: liver
damage (elevated LFTs), myositis
Mannitol
Diuretic: osmotic action creates large volume
of urine. Used in ARF, shock, or to decrease
ICP
Maprotiline
Heterocyclic antidepressant: NE reuptake
inhibitor. Tox: sedation, orthostatic
hypotension
Meperidine
Opioid analgesic: synthetic and taken orally.
Strong agonist at mu opioid receptors, is
anti-muscarinic receptors, so it is the drug
of choice for cholecystectomy analgesia b/c
it prevents sphincter of Oddi spasm.
6-Mercaptopurine
Antineoplastic: blocks purine synthesis. Used
in leukemias & NHL. Myelosuppression
increases with allopurinol (metabolized by
xanthine oxidase).
Metformin
Oral biguanide hypoglycemic: MOA
unknown, may inhibit gluconeogenesis. Can
be used in DM1. Tox: lactic acidosis
Methotrexate
Antineoplastic, immunosuppressant: S-phase
specic drug, inhibits dihydrofolate reductase,
decreasing dTMP. Tox: Myelosuppression.
Leucovorin (folinic acid) rescue used to reduce
toxicity after very high doses
Metoprolol
"1-selective blocker: used in HTN, CHF, and
for prevention of post-MI sudden death,
arrhythmias. Tox: bradycardia, AV block,
impotence
Metronidazole
Antiprotozoal antibiotic: damages bugs by
oxidizing DNA. Used in anaerobic bacterial
infections and Giardia, Entamoeba, Trichomonas,
Gardnerella. Tox: GI distress, disulram-like
reaction to alcohol. Subject to P450 inhibition or
induction
Mifepristone (RU 486)
Progesterone and glucocorticoid inhibitor:
abortifacient (implantation requires
progesterone). Tox: bleeding, GI
disturbances
Milrinone, amrinone
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: increase
contractility by increasing cAMP. Used in
acute heart failure (as in ICU) only.
Mirtazapine
Heterocyclic antidepressant: antagonist of
!2, central 5-HT receptors. Tox: sedation,
weight gain
Misoprostol
PGE1 derivative: increases mucus barrier and
decreases acid in stomach. Prevents ulcers
due to NSAIDs, maintains PDA, induces
labor. Tox: diarrhea, abortion.
Morphine
Opioid analgesic: strong mu receptor agonist. Poor
oral bioavailability. E#ects include analgesia,
constipation, emesis, sedation, respiratory depression,
miosis, and urinary retention. Tolerance may be
marked; high potential for psychologic and physical
dependence. Additive e#ects with other CNS
depressants. Codeine is a morphine prodrug.
Nafcillin, -oxacillins
Penicillinase-resistant penicillin. Used for
Staph. Tox: allergy, methicillin is no longer
used but caused interstitial nephritis
Naloxone
Opioid mu receptor antagonist: used to
reverse CNS depressant e#ects of opioid
analgesics (overdose or when used in
anesthesia)
Neostigmine, physostigmine
Cholinesterase inhibitors. -stigmines are carbamates that inhibit
cholinesterase by pyridostigmine, edrophonium carbamylation.
Neostigmine: used for postop ileus or neuromuscular blockade
reversal, treatment of myasthenia gravis. Physostigmine: used for
glaucoma (crosses BBB) or atropine overdose. Pyridostigmine: long-
acting, used for treatment of myasthenia gravis. Edrophonium:
short-acting, used to dx myasthenia gravis.
Nevirapine
Nonnucleoside HIV-RT inhibitor: allosteric
inhibition. Others: efavirenz, delavirdine.
Tox: Stevens-Johnson, induction of P450,
insomnia/nightmares
Niacin
Antilipemic: reduces VLDL secretion from
hepatocytes. Tox: ushing (reduces w/ use)
Nifedipine
Calcium channel blocker prototype:
vasoselective. Used in angina, HTN. Tox:
edema, ushing, (no arrhythmias b/c not
cardioactive)
Nitroglycerin, nitroprusside
Antianginal vasodilator prototype: releases NO in
veins >> arteries. Reduces preload. Used for
stable, Prinzmetal angina. Tox: tachycardia,
hypotension, headache. Isosorbide nitrate is long-
acting version. Nitroprusside has di#erent but
similar mechanism, can lead to cyanide toxicity.
Nitrosoureas (-mustines)
Antineoplastic: DNA alkylator. Cross BBB, so
used in GBM, other brain ca. Tox: CNS.
Norepinephrine
Agonist at all ! and at "1 adrenoceptors.
Used as ICU pressor but sacrices renal
blood perfusion. Causes reex bradycardia.
Tox: renal ischemia, HTN
Octreotide
Somatostatin analog. Used in acromegaly,
carcinoid, gastrinoma, glucagonoma, VIP-
oma, varices
Omeprazole
Antiulcer: irreversible blocker of H+/K+
ATPase proton pump in parietal cells of
stomach. Used in ZE, GERD, ulcers. Tox:
none
Ondansetron, granisetron,
Antiemetics. -setrons are 5-HT3 receptor
blockers used for cancer chemotherapy and
Metoclopramide for postop N/V.
Metoclopramide is a dopamine antagonist at
the area postrema.
Orlistat
Antiobesity: inhibits pancreatic lipase. Tox:
steatorrhea, bloating, fat-soluble vitamin
deciency
Oxybutin, glycopyrrolate
Antimuscarinic: target GU system to prevent
incontinence in quadriplegics
Oxytocin
Stimulates labor, uterine contractions, milk
letdown.
Paclitaxel (-axels)
Antineoplastic: prevents anaphase by
freezing spindle. Used in female cancers.
Tox: myelosuppression.
Parathion, malathion, Echothiophate
Organophosphate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor:
used as insecticide, are poisons. Other
organophosphates: DFP, soman, tabun, Causes
DUMBBLSS: diarrhea, urination, miosis,
bronchospasm, bradycardia, lacrimation,
sweating, salivation.
Penicillamine
Chelator, immunomodulator: Cu poisoning
and sometimes Pb, Hg, As. Used in Wilsons
disease and rheumatoid arthritis
Penicillin G
Penicillin. Used against all GP bugs, GNCs.
Penicillinase-susceptible. Tox: penicillin
allergy, Coombs-positive hemolytic anemia.
Phenelzine, trancylcypromine isocarboxazid
MAOI antidepressant: increase levels of all
monoamines. Only used for psychotic
depression due to side e#ects. Tox: hypertensive
crisis with tyramine or meperidine intake,
serotonin syndrome with tryptophan ingestion
Phenobarbital, thiopental
Barbiturate. Used for sedation, most seizures.
Increases duration of GABAA channel opening.
Nonteratogenic: 1st line anticonvulsant in pregnancy.
Tox: dependence, CNS/respiratory depression
(additive), induces P450, induces ALA synthase (cannot
be used in porphyrics). Thiopental used for induction
of general anesthesia
Phenoxybenzamine, phentolamine
!-blocker. Phenoxybenzamine is
irreversible, phentolamine is reversible. Used
in pheochromocytoma. Tox: orthostatic
hypotension
Phenylephrine !1 agonist: pure pressor for ICU shock.
Phenytoin (carbamazepine, valproate)
Anticonvulsant: blocks neuronal Na+ channels, inhibiting glutamate
release from presynaptic excitatory neuron. 1st line for tonic-clonic
tx, status epilepticus prophylaxis. Serum levels variable due to rst-
pass metabolism and dose-dependent nonlinear elimination kinetics.
Tox: nystagmus, ataxia, diplopia, sedation, SLE-like, P450 induction
drug-binding interactions. Chronic: gingival hyperplasia in kids,
peripheral neuropathy, hirsutism, B12 depletion. Teratogen.
Pilocarpine
Muscarinic agonist: used as eyedrops for
narrow or wide-angle glaucoma. Tox:
sweating, salivation
Pioglitazone, -glitazones
Oral hypoglycemic: increases insulin
sensitivity. Used alone or in combination.
Tox: weight gain.
Piperacillin, ticarcillin, carbenicillin
GN-active penicillin. Penicillinase-
susceptible; given w/ inhibitor. Used for
Pseudomonas or other GNRs. Tox: allergy.
Takes Care of Pseudomonas
Pirenzipine, propantheline
Antiulcer: antimuscarinics active on parietal,
ECL cells. Tox: tachycardia, dry mouth,
diplopia.
Piroxicam
NSAID with longest duration of action (t1/2
about 40 h)
Pralidoxime
Acetylcholinesterase regenerator: binds
phosphorus in organophosphates toxicity
Praziquantel
Antihelminth: causes parasite paralysis by
calcium-inux pathway. Used in all uke and
tapeworm infections.
Prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin
!1-selective blockers: used in HTN. Tox:
rst-dose orthostatic hypotension
Prednisone
Glucocorticoid prototype: potent, short-acting;
much less mineralocorticoid activity than cortisol
but more than dexamethasone or triamcinolone.
Common in chemotherapy, immunosuppression.
May cause apoptosis or inhibit division. Tox:
Cushings
Probenecid
Uricosuric: inhibitor of renal weak acid
secretion and reabsorption in S2 segment of
proximal tubule; prolongs half-life of
penicillin, inhibits reabsorption of uric acid.
Probucol
Antilipemic: MOA unknown. Withdrawn but
may be e#ective in preventing restenosis of
coronaries after angioplasty. Tox:
arrhythmias, decreased HDL
Propranolol
Nonselective "-blocker prototype. All "-
blockers are also Class II antiarrhythmics,
which slow conduction through AV node.
Tox: see metoprolol.
Propylthiouracil, methimazole
Antithyroid: reduces iodination of tyrosine,
MIT/DIT coupling, peripheral T4-to-T3
conversion (T4 is majority but T3 is more
active). Tox: rash, agranulocytosis (rare),
aplastic anemia.
Prostacyclin
PGI2: vasodilator, inhibitor of platelet
aggregation.
Quinidine, amiodarone, procainamide,
disopyramide
Class IA antiarrhythmics and local anesthetics.
Slow Phase 0 and increase ring threshold,
increasing AP duration, refractory period. Used
for a-b, a-utter, v-tach. Tox: cinchonism,
torsade (quinidine), SLE-like (procainamide).
Amiodarone is primarily Class III.
Quinine, quinidine
Antimalarial: kill blood forms, no e#ect on
liver stages. Tox: cinchonism, positive
Coombs test
Reserpine
Antihypertensive: depletes monoamine
stores. Used in HTN. Tox: sedation,
depression
Ribavirin
Antiviral: inhibits viral RNA polymerase.
Guanosine analog. Used for RSV, inuenza,
HCV. Tox: hemolytic anemia, teratogen.
Rifampin
Antimicrobial: inhibits bacterial RNA
polymerase. Used in TB, leprosy, and for
contacts of those with meningococcal or
H.u infxn. Tox: orange urine, hepatitis,
induces P450.
Salmeterol
"2 agonist: inhaled, long-acting for chronic
asthma. Tox: arrhythmia, tremor.
Scopolamine
Antimuscarinic: centrally-active drug for
motion sickness
Selegiline, entacapone,
Dopamine breakdown inhibitors. Selegiline is
selective for MAO-B, -capones inhibit
tolcapone COMT
Sibutramine
Antiobesity: inhibitor of NE, 5-HT uptake.
Tox: HTN, tachycardia.
Sildenal
Boner pill: phosphodiesterase inhibitor,
causes increased cGMP, relaxation of smooth
muscle. Tox: headache, blue/green vision,
hypotensive crisis w/ nitrates
Somatotropin GH analog. Used in GH deciency, Turners
Sotalol, bretylium, ibutilide
Class III antiarrhythmics. Increase AP
duration, refractory period. 2nd line agents
for atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Tox:
Sotaloltorsades. IbutilideTorsades.
Bretyliumarrhythmogenic.
Spironolactone, amiloride, triamterene
Diuretics: non-K+-wasting. Spironolactone
antagonizes aldosterone activity in collecting tubule.
Other 2 block ENaC mobilization by another
mechanism. Used in K+-wasting diuresis,
hyperaldosteronism, CHF. Spironolactone has
antiandrogenic e#ects (gynecomastia) and can be used
in PCOS to prevent hirsutism.
Streptokinase
Thrombolytic: accelerates plasminogen-to-
plasmin conversion. Tox: bleeding, allergy
Succimer (DMSA)
Chelator: dimercaptosuccinic acid; used to
chelate Pb and As
Succinylcholine
Depolarizing paralytic: nAChR antagonist
selective for motor receptor. Short duration (5
min). No antidote for Phase 1 (depolarized) block,
use neostigmine to reverse Phase 2 (repolarized)
block. Contraindicated in any hyperkalemic
condition.
Sulfasalazine
Immunosuppressant: sulfa drug + ASA
derivative, activated in gut. Used in
ulcerative colitis, Crohns.
Sumatriptan,
5-HT1D receptor agonists. Vasocontrict,
short half-life. Used to abort migraine
attacks. other "-triptans" Tox: Prinzmetal-
like vasospasm, contraindicated in coronary
artery dz
Tamoxifen, raloxifen
Estrogen partial agonists ("SERMs"). Used in
breast ca, osteoporosis prevention.
Tamoxifen increases uterine ca risk.
Tetracycline, doxycycline
Antibiotic: blocks amino-acyl tRNA at 30S
subunit. Used for zoonoses, Chlamydia UTI,
atypical pneumonia. Doxycycline is excreted in
feces; can use in CKD patients. Tox: bone
deformity and dental discoloration in kids,
Fanconis syndrome, photosensitivity
Thalidomide
Antiinammatory: decreases TNF production
to improve leprosy skin symptoms. Tox:
teratogen (causes ipper limbs)
Theophylline
Anti-asthma: phosphodiesterase inhibitor
favors bronchodilation. Lower therapeutic
index. 3rd line agent.
Ticlopidine, clopidogrel
Antiplatelet: blocks ADP receptor to prevent
aggregation. Prevents strokes, occlusion
after angioplasty
Tolbutamide, chlorpropamide
Oral hypoglycemics: older sulfonylurea
group. Tox: hypoglycemia, disulram-like
e#ect
Topiramate
Anticonvulsant: Blocks Na+ channels,
increases GABA. Used for general and partial
seizures. Tox: sedation, mental dulling,
kidney stones, weight loss
t-PA
Thrombolytic: tissue plasminogen activator.
Used in acute MI to recanalize the occluded
coronary. Occasionally used in pulmonary
embolism, stroke. Tox: bleeding. Antidote is
aminocaproic acid
Trastuzumab
Antineoplastic: monoclonal Ab against Her2/
neu. Tox: cardiotoxicity.
Trazodone
Heterocyclic antidepressant: 5-HT reuptake
inhibitor. Tox: sedation, nausea, priapism
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Antibiotics: cause blockade at dihydrofolate
reductase and dihydropteroate synthase. Used for
PCP prophylaxis/treatment, Salmonella, pneumonia,
chronic UTI. Tox: sulfa reaction including Stevens-
Johnson and hemolytic anemia, kernicterus in
neonates, may require leucovorin rescue
Tropicamide, topical atropine
Antimuscarinic: eyedrops for ophthalmologic
mydriasis
Tubocurarine
Nondepolarizing paralytic: competitive
nAChR antagonist. -curiums and -
curoniums have di#erent structures. Tox:
histamine release, hypotension. Reverse
blockade w/ cholinesterase inhibitor.
Valproate (carbamazepine, phenytoin)
Anticonvulsant: 1st line for tonic-clonic.
Also used for absence, myoclonic seizures.
Blocks Na+ channels, increases GABA. Tox:
GI distress, hepatic necrosis (rare),
teratogenic (spina bida)
Vancomycin
Antibiotic: bactericidal glycopeptide inhibitor
of cell wall synthesis. Binds D-ala residues.
Used only against GP bugs, especially MRSA
and C. di#. Tox: red man syndrome w/ fast
infusion, ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity
Venlafaxine
Heterocyclic antidepressant: monoamine
reuptake inhibitor. Also used for anxiety.
Verapamil, diltiazem
Calcium channel (L-type) blocker prototype: has
more depressant e#ect on heart than
dihydropyridines (eg, nifedipine). Class IV
antiarrhythmics: slow AV nodal conduction for
SVT. Tox: AV block, CHF, edema, constipation.
The cardiac-specialized CCBs
Vinblastine, vincristine
Antineoplastic: alkaloid that blocks
microtubule polymerization during M phase.
Used in lymphoma, Wilms. Tox:
myelosuppression. Vincristine peripheral
neuropathy
Warfarin
Oral anticoagulant prototype: prevents %-
carboxylation of vitamin K-dependent factors (2,
7, 9, 10), making them useless. Tox: bleeding,
teratogenic, drug-drug interactions. Antidote:
vitamin K, fresh plasma. Monitor PT or INR.
Zarlukast, montelukast
Anti-asthma: block leukotriene receptors.
3rd line agent.
Zanamivir, oseltamivir
Antiviral: prevents release of inuenza A and
B particles from host cells. Used to treat and
prophylax both inuenzae.
Zidovudine (AZT), Didanosine (DDI)
Antiviral: nucleoside inhibitor of HIV RT. Inhibit RT and
when incorporated cause production of a defective
virion. Tox: megaloblastic anemia (AZT), pancreatitis
(DDI), peripheral neurpathy (DDI). Can be used during
pregnancy to reduce transplacental transmission.
Others: lamivudine, stavudine, zalcitabine.
Zileuton
Anti-asthma: 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. 3rd
line agent.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicDocument13 pagesPharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicSherlock HolmesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationDocument5 pagesCancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationOndari gisemba OSINDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Drugs AntidotesDocument3 pagesCommon Drugs AntidotesJhix JadraquePas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 pagesRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti FungalsDocument5 pagesAnti FungalskakuPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmayield: Must Know Pharmacology NotesDocument2 pagesPharmayield: Must Know Pharmacology NotesBianca Desiree VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Impactednurse Nurses Reference PackDocument2 pagesImpactednurse Nurses Reference PackRaenell CurryPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsDocument22 pagesPediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsMuhammad ArifPas encore d'évaluation
- Conflict PresentationDocument19 pagesConflict Presentationapi-231905851Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of ActionDocument3 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of Actionyanks1120Pas encore d'évaluation
- Actinic KeratosisDocument19 pagesActinic Keratosisattydoc1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDocument2 pagesPharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testPas encore d'évaluation
- SketchyPath ChecklistDocument1 pageSketchyPath ChecklistFajar Raza100% (1)
- Laboratory Reference RangesDocument12 pagesLaboratory Reference RangesPrashanth Raju100% (1)
- Pharmacology Examination Test Questions For 3rd Year 6th SemesterDocument6 pagesPharmacology Examination Test Questions For 3rd Year 6th SemesterVishnu KrshPas encore d'évaluation
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs of ChoiceDocument3 pagesDrugs of ChoiceReeti R. Bhat100% (1)
- UWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)Document47 pagesUWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)uowhywxuuiragjadchPas encore d'évaluation
- Kathynotes PDFDocument103 pagesKathynotes PDFvarrakeshPas encore d'évaluation
- AntimicrobialsDocument1 pageAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Common Unit Conversion GuideDocument28 pagesCommon Unit Conversion GuideRazrin RazakPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Body Receptors PDFDocument1 pageDifferent Body Receptors PDFSantosh patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Profiles: CyclophosphamideDocument12 pagesDrugs Profiles: Cyclophosphamidejhk0428Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prefix, Suffix of DrugsDocument6 pagesPrefix, Suffix of DrugsBriel Jake CabusasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultimate Pharm GuideDocument41 pagesUltimate Pharm GuideeanguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical correlations by Dr. Irfan MirDocument55 pagesClinical correlations by Dr. Irfan MirsammieahemdPas encore d'évaluation
- Lang 10 EditionDocument235 pagesLang 10 Editionraju niraulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Class Intoxication Withdrawal: AlcoholDocument5 pagesDrug Class Intoxication Withdrawal: AlcoholLauren LevyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharm Drugs + Classes (All)Document28 pagesPharm Drugs + Classes (All)Tom WuPas encore d'évaluation
- Uworld JournalDocument3 pagesUworld JournalJayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatrics - Neonatal Jaundice PDFDocument2 pagesPediatrics - Neonatal Jaundice PDFJasmine KangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chart - WBC DisordersDocument1 pageChart - WBC DisordersSamuel RothschildPas encore d'évaluation
- Common MedicationsDocument4 pagesCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuby Immunology TransplantationDocument21 pagesKuby Immunology TransplantationMalki kawtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartDocument3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- Internal Medicine #1Document167 pagesInternal Medicine #1Nikhil RayarakulaPas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE Step 1 DrugsDocument36 pagesUSMLE Step 1 DrugscougardiverPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Document2 pagesAntiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Linlin100% (1)
- # Diseases of ConjunctivaDocument4 pages# Diseases of Conjunctivaameerabest100% (1)
- Immunosuppressant Drugs Drug Name Class Function Method/Receptor UseDocument3 pagesImmunosuppressant Drugs Drug Name Class Function Method/Receptor UseKristin DouglasPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsDocument9 pagesImmunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsCas BuPas encore d'évaluation
- 1a..antimicrobials IntroductionDocument84 pages1a..antimicrobials IntroductionAnonymous RlDDdTAsKJPas encore d'évaluation
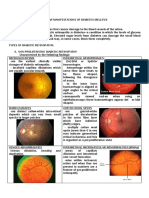
- OPTOMED-HW2-Diabetic Retinopathy PDFDocument3 pagesOPTOMED-HW2-Diabetic Retinopathy PDFDanalie SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Examinations Crib Sheet v7Document36 pagesClinical Examinations Crib Sheet v7aparish10100% (1)
- Bipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesBipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomshumdingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summaryshenric16Pas encore d'évaluation
- MedLinks drug chart overviewDocument7 pagesMedLinks drug chart overviewahsaanahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease Pathognomonic Sign: Muddy Brown CastsDocument1 pageDisease Pathognomonic Sign: Muddy Brown CastsRafey AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Drug ChartDocument50 pagesPharmacology Drug ChartEssentialForLivingPas encore d'évaluation
- Brenner and Stevens, Pharmacology 3 © 2010Document5 pagesBrenner and Stevens, Pharmacology 3 © 2010PharAwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 pagesPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- Step 1 DrugsDocument46 pagesStep 1 DrugsZebram ZeePas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular History: Chest PainDocument5 pagesCardiovascular History: Chest PainTom MallinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Usmle World Step 1 Pharmacology: Question ListDocument73 pagesUsmle World Step 1 Pharmacology: Question ListAnonymous 4txA8N8etPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology KatzDocument13 pagesPharmacology KatzFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs FinalDocument5 pagesDrugs FinalmekeeePas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Most Important DrugsDocument13 pages100 Most Important Drugsngopya djiki67% (3)
- All DrugsDocument482 pagesAll DrugsJessica IbañezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1619 - MJ-Decidua, Chorion, Placenta, Umbilical CordDocument14 pages1619 - MJ-Decidua, Chorion, Placenta, Umbilical CordFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- German QuicklyDocument453 pagesGerman Quicklygaotao100% (2)
- Pharmacology KatzDocument13 pagesPharmacology KatzFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology SkinDocument5 pagesHistology SkinFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- High Yield Internal Medicine Shelf Exam ReviewDocument100 pagesHigh Yield Internal Medicine Shelf Exam ReviewAhsan X Baig100% (5)
- Normal kidney histology and pathology overviewDocument4 pagesNormal kidney histology and pathology overviewFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- German to English Flashcard ListDocument13 pagesGerman to English Flashcard ListFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Verben Klasse 7Document2 pagesVerben Klasse 7Fahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lipid Profiles ExplainedDocument5 pagesLipid Profiles ExplainedFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Graded German Reader - Auf Dem Dorfe - Learn German 1949Document89 pagesGraded German Reader - Auf Dem Dorfe - Learn German 1949Luigi Torval100% (2)
- Histology Muscular TissueDocument12 pagesHistology Muscular TissueFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
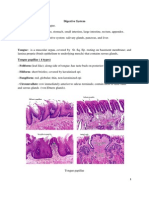
- Digestive HistologyDocument11 pagesDigestive HistologyFahd Abdullah Al-refai100% (1)
- Biliary Pathology GuideDocument45 pagesBiliary Pathology GuideFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined SignificanceDocument4 pagesMonoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined SignificanceFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument38 pagesGastrointestinal BleedingCarmelita Ramos de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument38 pagesGastrointestinal BleedingCarmelita Ramos de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute UGI Bleeding: Stephen Matarazzo MDDocument20 pagesAcute UGI Bleeding: Stephen Matarazzo MDMohamed El-sayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis PresentationDocument21 pagesCholecystitis Cholelithiasis PresentationPrincess Meinny JeanPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 PancreatitisDocument39 pages10 PancreatitisFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- IleusDocument54 pagesIleusselvie87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention Philip Keith March 26, 2008Document24 pagesPulmonary Embolism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention Philip Keith March 26, 2008Fahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Mesenteric IschemiaDocument39 pages5 Mesenteric IschemiaFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Histo of EsophagousDocument2 pagesHisto of EsophagousFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 PeDocument67 pages4 PeFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1DVTDocument67 pages1DVTFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide 86-Human Upper EsophagusDocument5 pagesSlide 86-Human Upper EsophagusFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument46 pagesPulmonary EmbolismThevashini Shridaran100% (1)
- 1 - Introduction and StainingDocument5 pages1 - Introduction and StainingFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- CD Markers For B-Cell LymphomaDocument1 pageCD Markers For B-Cell LymphomaFahd Abdullah Al-refaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Top 100 Over-the-Counter MedicinesDocument4 pagesTop 100 Over-the-Counter MedicinesMayha Gyu1803Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lplpo Poned Oktober 2021Document260 pagesLplpo Poned Oktober 2021Dwi AndraPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Harga Novapharin 2023Document3 pagesDaftar Harga Novapharin 2023Jaya Farma100% (1)
- Pediatric Oral Drug DoseDocument17 pagesPediatric Oral Drug DoseTan 57Pas encore d'évaluation
- Link e CatalogDocument14 pagesLink e CatalogwitarmayanaPas encore d'évaluation
- AntibioticsDocument10 pagesAntibioticsStevhenson PortacioPas encore d'évaluation
- PATIENT SAFETYDocument9 pagesPATIENT SAFETYKok Hui DiongPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Formularium Obat Klinik Pratama Kartika 10 PekalonganDocument2 pagesDaftar Formularium Obat Klinik Pratama Kartika 10 Pekalonganrahma nitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan DiraDocument34 pagesLaporan DiraDEWIPas encore d'évaluation
- IP3 Timur 12 FEBRUARI 2023Document3 pagesIP3 Timur 12 FEBRUARI 2023Roberto SoehartonoPas encore d'évaluation
- ABC FarmasiDocument34 pagesABC FarmasiOngko PriyantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Detail 2 Juli 2021Document16 pagesDetail 2 Juli 2021Fitri Eka JayantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Harga 2019-2Document87 pagesDaftar Harga 2019-2Niken Claudya EcfrencyliePas encore d'évaluation
- Warfarin Interaction2 PDFDocument4 pagesWarfarin Interaction2 PDFannyss ellePas encore d'évaluation
- CALABANGA MONITORING - OdsDocument10 pagesCALABANGA MONITORING - Odsglecy malatePas encore d'évaluation
- Sirkulasi 2021 SD 5-11-2021Document244 pagesSirkulasi 2021 SD 5-11-2021GUDANG FARMASIPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Harga HD Juni 2020Document34 pagesDaftar Harga HD Juni 2020Kean KhamidaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Farmakologi Jilid 2Document158 pagesFarmakologi Jilid 2TeguhsadjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Dafa FarmaDocument44 pagesDafa FarmaboychekaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Inpatient Drug Usage Report MarchDocument22 pagesHospital Inpatient Drug Usage Report MarchWinda NingsihPas encore d'évaluation
- Vademecum Valesalud 201401Document42 pagesVademecum Valesalud 201401petacosPas encore d'évaluation
- Obat Tak TerlayaniDocument33 pagesObat Tak TerlayanianditriaikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Odisha Rate Contract For MedicinesDocument66 pagesOdisha Rate Contract For MedicinesSahil KargwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Parenteral Drugs: Compatibilit Y: Yosefa Asteria, S.Farm.,Apt Rs Suaka Insan BanjarmasinDocument42 pagesParenteral Drugs: Compatibilit Y: Yosefa Asteria, S.Farm.,Apt Rs Suaka Insan Banjarmasinfarida nur ainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotic Cross-Sensitivity ChartDocument1 pageAntibiotic Cross-Sensitivity Chartsuper0113Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paediatric Critical Care Infusions Intubation DrugsDocument2 pagesPaediatric Critical Care Infusions Intubation DrugsА. Сосорбарам100% (1)
- TemplateDocument15 pagesTemplateSelvi Diah MutiaraPas encore d'évaluation
- ETAT Imp Commande Fournisseur ModifDocument3 pagesETAT Imp Commande Fournisseur ModifLoulas RolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Formulary For Primates and Primate SanctuariesDocument20 pagesDrug Formulary For Primates and Primate SanctuariesMel Cid IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Stok 020120Document81 pagesStok 020120diniaiiu26Pas encore d'évaluation