Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Def 2001
Transféré par
nagesh1986Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Def 2001
Transféré par
nagesh1986Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Study Notes
2014
V1
Auditing & Attestation Index
V1
# of notes Page #
Cover 1
Index 2
Audit Standards & Engagement Planning 60 3
Internal Controls 30 7
Audit Evidence 66 10
Reporting 33 13
Other Services and Reports 23 15
Audit Sampling 40 17
Information Technology (IT) 25 19
Auditing and Assurance (Miscellaneous) 34 21
Total number of notes 311
Total number of pages 23
Topic
http://cpa-exam.weebly.com/index.html
FREE Notes
1. 2 considerations in deciding to accept an audit:
1. auditability of the financial statements
2. management integrity
2. 3 categories of GAAS:
1. General standards
2. Fieldwork standards
3. Reporting standards
3. 10 GAAS standards: TIPPICANOE
GENERAL
1. Training & Proficiency
2. Independence
3. due Professional Care
FIELDWORK
1. Planning & Supervision
2. Internal Controls
3. Corroborative Audit Evidence
REPORTING
1. Accounting Principles in Conformity with GAAP
2. No new Account Principles added - CONSISTENCY
3. Omitted Information Disclosures - None
4. Expression of an Opinion
4. Acceptable DR formula:
Acceptable DR = AR / RMM RMM = (IR x CR)
5. Accounting Principles in conformity with US GAAP
standard: REPORTING STANDARD 1
The report must explicitly state whether the financial statements
are in conformity with US GAAP
6. An auditor gathers info necessary to identify RMM due to
fraud by:
1. Inquiry of management
2. Consideration of fraud risk factors
3. Consideration of results of analytical procedures
4. Consideration of certain other info.
- In addition, discussion among engagement personnel
regarding RMM due to fraud is required.
7. AUD-New Reserch Task Format - types:
1. AU - US Auditing Standards
2. PCAOB - PCAOB Auditing standards
3. AT - Attestation Services
4. AR - Statements on Standards for Accounting and Review
Services
5. ET - Code of Professional Conduct
6. BL - Bylaws
7. VS - Statements on Standards for Valuation Services
8. CS - Statement on Standards for Consulting Services
9. PFP - Personal Financial Planning
10. CPE - Continuing Professional Education
11. QC - Quality Control Standards
8. Auditor's preliminary judgement about materiality:
Entity's annualized interim financial statements.
9. Basic types of audits:
1. Compliance Audits
2. Operational Audits
3. Financial statement Audits (90% of what is tested!)
10. Conditions generally present in all individuals that
commit fraud:
- Incentives
- Opportunities
- Attitudes that rationalize
11. Corroborative audit evidence standard:
FIELDWORK STANDARD 3
(less substantive testing if IC reliance high)
The auditor must obtain sufficient appropriate corroborative
audit evidence by performing audit procedures to afford a
reasonable basis for an opinion regarding the financial
statements under audit.
12. Define audit risk: The risk that the auditor may unknowingly
fail to appropriately modify the opinion on financial statements
that are materially misstated
13. Describe professional skepticism: an attitude that includes
a questioning mind and a critical assessment of audit evidence
14. Difference between CR, IR with DR:
- IR & CR exist independently
- DR relates to the auditor's procedures & can be changes at
his/her discretion.
15. differences between auditing standards and auditing
procedures: standards measure the quality of an auditor's
work and procedures relate to the acts the auditor should take
16. due Professional care standard: GENERAL STANDARD 3
critical review of judgement at every level
skill and care of a prudent CPA
complete workpapers
due diligence
professional skepticism
17. Elements of Quality control: [HEAL ME]
Human Resources (Personnel management)
Ethical Requirements (Independence)
Acceptance and continuance of client relatinoships and specific
engagements
Leadership responsibilities within the firm (tone from the top)
Monitoring
Engagement performance
18. Examples of when auditors are not independent:
- ore than 1 year of audit fees outstanding
- Material loan/lease unless from client in lending business and
fully secured
- Material litigation involving credibility of accountant or
management
- Accepts more than just a token gift
- spouse/sibling employed as client's internal auditor
- Final responsibility for journal entries (don't take role of
management)
Audit Standards & Engagement Planning
M
3
http://cpa-exam.weebly.com/index.html
FREE Notes
19. Expression of an opinion standard:
REPORTING STANDARD 4
The report must contain either an expression of an opinion on
the statements taken as a whole, or an assertion to the effect that
an opinion can't be expressed. There should be a clear cut
indication of the character of the auditor's work and the degree of
responsibility the auditor is taking
20. Fraud risk factors - examples of attitudes /
rationalizations:
1. Relating to board members, management or employees
2. Those with access to assets susceptible to misappropriation
21. Fraud risk factors - examples of incentives / pressures:
1. Threatened financial stability or profitability
2. Excessive pressure on management to meet requirements or
third party expectations
3. Management or directors' financial situation threatened by
4. Excessive pressure to meet financial target set up by directors
or management
5. Personal financial obligations
6. Adverse relationship between company and employees
22. Fraud risk factors - examples of opportunities:
1. Industry provides opportunities for...(bad controls)
2. Ineffective monitoring of management
3. Complex or unstable organizational structure
4. Internal control deficient
5. Characteristics of assets (easy to take or convert to cash)
6. Inadequate internal control
23. Further Audit Procedure:
- Tests of controls and
- Substantive procedures are further audit procedures.
24. GAAS Standards - Fieldwork:
1. Planning & Supervision
2. Internal Controls
3. Corroborative Audit Evidence
25. GAAS Standards - General:
1. Training & Proficiency
2. Independence
3. Due Professional Care
26. GAAS Standards - Reporting:
1. Accounting Principles in Conformity with GAAP
2. No new Account Principles added - CONSISTENCY
3. Omitted Information Disclosures - None
4. Expression of an Opinion
27. Independence should be maintained in...:
both fact and appearance.
No direct financial interest, no MATERIAL indirect financial
interest
28. Independence standard: GENERAL STANDARD 2
In all matters relating to the assignment, an independence in
mental attitude must be maintained by the auditors
- integrity & objectivity
- must be independent for attestation engagements (ERA'S)
---Examinations/Audits
---Reviews
---Agreed-upon procedure engagements
---Special reports
- Independence must be maintained in fact and appearance
- examples of what could compromise independence on another
flash card
29. Information from predecessor auditors: Auditors are
required to talk to previous auditor before accepting engagement.
Successor auditor initiates contact by talking to client who talks
to predecessor auditor. If client refuses, auditor MUST decline the
engagement
30. Internal controls standard: FIELDWORK STANDARD 2
auditor must obtain sufficient understanding of the entity and
environment including internal control to assess the risk of
material misstatement (RMM) whether due to error or fraud and
to design the nature, timing and extent of further audit
procedures
31. Key considerations in developing an audit program:
- Materiality
- Risk of Material Misstatement (RMM)
- Business & Industry
32. No new accounting principles applied - consistency
standard: REPORTING STANDARD 2
The report must identify when principles have not been
consistently observed from current period to last period
33. Omitted informative disclosures - none standard:
REPORTING STANDARD 3
Simple - don't omit any important informative disclosures
34. Planning and supervision standard: FIELDWORK STANDARD 1
auditor must adequately plan the work and must properly
supervise any assistants
35. Prior to commencing fieldwork, An auditor usually
discusses about the general audit strategy with the
client's
management:
1. The arrangements regarding the conduct of the audit
(e.g., timing, client assistance, availability of documents)
2. Involvement of specialists
3. Involvement of a predecessor auditor
4. Fees and billing
5. Any limitation of or other arrangements regarding auditor
liability
6. Conditions under which access to audit documentation may be
granted to others
7. Additional services to be provided relating to regulatory
requirements
8. Other services to be provided in connection with the
engagement (e.g., reviews of interim financial information)
Audit Standards & Engagement Planning
4
http://cpa-exam.weebly.com/index.html
FREE Notes
36. Steps in an audit:
1. Plan audit
2. Obtain understanding of client and its environment including
internal controls
3. Assess risks of misstatement and design further tests
4. Perform tests of controls
5. Perform substantive procedures
6. Complete the audit
7. Issue audit report
37. Steps in consideration of fraud in a financial statement
audit:
1. Understand the nature & characteristics of fraud
2. Discuss risk of fraud with engagement staff
3. Obtain information to identify risks of fraud
4. Identify risks that may result in material misstatement due to
fraud
5. Assess identified risks after considering programs and
controls
6. Respond to the results of the assessment
7. Evaluate the audit evidence obtained from audit tests
performed. (if fraud, must discuss with at least one level of mgmt
above those involved)
8. Communicate about fraud to management & the audit
committee
9. Document the auditor's consideration of fraud
38. Steps in planning an audit (planning procedures):
[BRAIN STOPS]
Basic discussions with the client
Review of audit documentation
Ask about recent developments
Interim financial statements (analyzing variances mandatory)
Non-audit personnel (e.g. tax prep)
Staffing
Timing
Outside assistance (specialists)
Pronouncements
Scheduling with the client
39. The most effective in reducing attestation risk:
Examination of evidence
40. Training & Proficiency Standard: GENERAL STANDARD 1
Audit must be performed by a person having adequate technical
training and proficiency as an auditor
- Proper education in accounting
- Knowledge of industry & business
- Practical experience (CE)
41. Types of assurance and which one needed for audit: -
Absolute assurance
- 100% positive when every single thing is tested
- Reasonable assurance - enough substantive testing performed
that you can be reasonably assure of correctness
42. What are compliance audits testing for?:
- IRS audits - Government audits (laws & regulations)
- CPA to determine compliance with bond/note provisions
43. What are financial statement audits testing for?:
- Done to give objective opinion of the fairness of financial statement
presentation and conformity with GAAP.
- Assess principles & estimates made by MANAGEMENT
44. What are GAAS for?:
Measure the quality of the auditor's performance
45. What are operational audits testing for?:
- Effectiveness / Efficiency / Economy.
- Done by internal auditors, government auditors or CPAs
46. What are the causes of material misstatements:
Errors Fraud
47. What are the components of audit risk?:
Audit risk =Inherent Risk x Control Risk x Detection Risk
AR = (IR x CR) x DR
(IR x CR) = RMM therefore
AR = RMM x DR
48. What are the types of fraud:
- Fraudulent financial reporting - Misappropriation of assets
49. What does GAAS stand for:
Generally Accepted Auditing Standards
50. What engagements do auditors not have to be
independent for?: Compliations
Taxes
Consultations
51. What engagements must auditors be independent for?:
ERA'S
Examinations / Audits
Reviews
Agreed-upon procedure engagements leading to findings
Special Reports
52. What is an Audit Program / Audit Plan and is it
required?: - step by step list of audit procedures
- Required for every GAAS audit
53. What is the difference between Quality Control and
GAAS:
Quality control is for all members of a CPA firm on ALL engagements
GAAS is for each individual engagement
54. What major issues should a successor auditor address
with a predecessor auditor?: [RID-C]
Reasons for change
Integrity of manageemnt
Disagreements during audit
Communication with Audit Committee
55. What matters must be communicated to those charged
with governance?: [DISAPPROVE]
Disagreements with management
Illegal acts
Significant accounting policies
Adjustments
Prior discussions with management
Problems
Responsibilities
Other information
Views of other accountants
Estimates
Audit Standards & Engagement Planning
5
FREE Notes
56. What should be included in an engagement letter?: [FACSIMILE]
Fees
Auditor's responsibility
Confirmation of engagement
Scope & nature of the engagement (intro & scope paragraph)
Internal control - deficiencies therein
Management's responsibility
Irregularities
iLLegal acts
Errors
57. When an engagement is accepted, what is required and what is recommended?:
Written communication required from the management
engagement
letter
recommended
58. Who does the outside auditor report to and what are the requirements of this body?: The auditor reports to the audit
committee of the board of directors. This is a sub-committee of board members who are not officers or employees of the company (must be
independent)
59. Who is charged with corporate governance?:
Board of Directors, Audit Committee (independent) NOT management
60. Who is responsible for the principles and estimates of financial statements?:
Management
Audit Standards & Engagement Planning
6
http://cpa-exam.weebly.com/index.html
FREE Notes
1. 5 Components of internal control: [CRIME]
Control activities (3)
Risk assessment (2)
Information and communication (4)
Monitoring (5)
control Environment (1)
2. 13 management assertions: [U-PERCV]
Understandability & Classification (UC)
Presentation & Disclosure (PD)
Existence or Occurrence (Vouching) (EO or VO)
Rights & Obligations (RO)
Completeness (Tracing) & Cutoff (CC or TC)
Valuation, Allocation & Accuracy (VAA)
3. Assessing risk of Material Misstatement: Different approaches if you can or can't rely on internal controls:
Can't rely = substantive approach
Can rely = combined approach
4. Assume the purchase requisition is an internal document sent by the department in need of supplies to the purchasing
department::
1. purchasing dept determines the proper quantity & vendor for the purchase & prepares a purchase order (PO).
2. one copy of the PO sent to the vendor. another copy sent to the receiving dept to allow the receiving personnel to know that items received
have been ordered.
3. However, the copy of the PO sent to receiving will not mention the quantity of the items on it. so as to encourage personnel to count the
goods when they are received.
4. when the goods are received, a "receiving report" is prepared by the receiving dept & forwarded to the accounting dept.
5. Vendor's bill or (or) Vendor's advice: received by accounting dept from the vendor.
6. when the accounting dept has PO, Receiving report, Vendor's advice & then the payment is approved & recorded in the purchase journal
since evidence exists that the time was ordered, received & billed.
7. A check & remittance advice is subsequently sent to the vendor in accordance with the term of the scale.
8. PO, receiving report & vendor advice are "stamped paid to prevent duplicate payments."
5. Authority to accept incoming goods in receiving should be based on:
Independent verification of a valid order is a pre-requisite to acceptance.
- Approved purchase order provides evidence that the goods are received were ordered.
- Bill of lading = support the amt., received.
6. Components of internal control - Control activities: [PIPS], [ARCCS]
Performance reviews (actual vs. budget, etc)
Information processing (IT)
Physical controls (access to assets)
Segregation of duties***
---Authorization of transactions
---Recording (posting) of transactions
---Custody of Assets
---Comparisons (reconciliations)
---Segregate all the above jobs to different employees
7. Components of internal control - control Environment: [CHOPPER]
Commitment to competence
Human resource policies and practices
Organizational structure
Participation of those charged with governance
Philosophy of management & operating style
Ethical values & integrity
Responsibility assignment
- It sets the tone of the organization.
- It influencing the ctrl consciousness of the people.
Internal Controls
-
8. Control environment inherent limitations: [COCO]
Collusion - fraud
Override by management - fraud
Competence - error
Obsolescence - error
7
http://cpa-exam.weebly.com/index.html
FREE Notes
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- 1 2 3 4 Mishir Sen English Channel Radhey Radhey Dangerous Five Point Someone Aarti Saha Kirat Karam K BichdeDocument1 page1 2 3 4 Mishir Sen English Channel Radhey Radhey Dangerous Five Point Someone Aarti Saha Kirat Karam K Bichdenagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Mishir Sen English Channel Radhey Radhey Dangerous Five Point Someone Aarti SahaDocument1 pageMishir Sen English Channel Radhey Radhey Dangerous Five Point Someone Aarti Sahanagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- 5 6 7 8 Mishir Sen English Channel Radhey Radhey Dangerous Five Point Someone Aarti Saha Kirat Karam K BichdeDocument1 page5 6 7 8 Mishir Sen English Channel Radhey Radhey Dangerous Five Point Someone Aarti Saha Kirat Karam K Bichdenagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Kids R Michieveous They R Naughty NDTV India Fdo CryimyDocument1 pageKids R Michieveous They R Naughty NDTV India Fdo Cryimynagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Summers Are Hot and Humid NDTV India Fdo CryimyDocument1 pageSummers Are Hot and Humid NDTV India Fdo Cryimynagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Ran Ran Go Away Sharavan NDTV India Fdo CryimyDocument1 pageRan Ran Go Away Sharavan NDTV India Fdo Cryimynagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Sharna Sharavan NDTV India Fdo CryimyDocument1 pageSharna Sharavan NDTV India Fdo Cryimynagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Harankand Harankand NDTV India Fdo AaDocument1 pageHarankand Harankand NDTV India Fdo Aanagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- Garahankand Garahankand NDTV Dadl Fdo AaDocument1 pageGarahankand Garahankand NDTV Dadl Fdo Aanagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Booking ID: WNHH6NL Your TPIN No./Kiosk Pick-Up Code: WNHH6NLDocument2 pagesBooking ID: WNHH6NL Your TPIN No./Kiosk Pick-Up Code: WNHH6NLnagesh1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
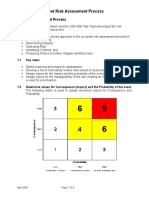
- 4 Fleet Risk Assessment ProcessDocument4 pages4 Fleet Risk Assessment ProcessHaymanAHMEDPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Apr Form No. 02Document4 pagesApr Form No. 02Francis Gavin Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- JG SUMMIT HOLDINGS, INC. vs. CA G.R. 124293 Sept. 24, 2003 - DigestDocument1 pageJG SUMMIT HOLDINGS, INC. vs. CA G.R. 124293 Sept. 24, 2003 - DigestMichelle LimPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- May 2017Document7 pagesMay 2017Patrick Arazo0% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- OA Frame Work Students GuideDocument545 pagesOA Frame Work Students GuideutphalrainaPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Dear SirDocument2 pagesDear SircaressaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Briefs On Comparative Company Law (US, UK and Germany)Document13 pagesCase Briefs On Comparative Company Law (US, UK and Germany)Zokirjon AbdusattarovPas encore d'évaluation
- Amtrak Dining RFPDocument54 pagesAmtrak Dining RFPdgabbard2Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Policy Guidelines On Issuance and Operation of Prepayment Instruments in IndiaDocument10 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Issuance and Operation of Prepayment Instruments in IndiaPreethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Plan On PepsicoDocument24 pagesMarketing Plan On PepsicoWaqar AfzaalPas encore d'évaluation
- MECO 121-Principles of Macroeconomics-Daud A DardDocument5 pagesMECO 121-Principles of Macroeconomics-Daud A DardHaris AliPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sugar Cube ProjectDocument24 pagesThe Sugar Cube ProjectMuhammad Ali MukhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Saudi Aramco Test Report: 30.apr.13 Inst SATR-J-6501 Instrument Loop - Inputs - Transmitter Circuit TestDocument4 pagesSaudi Aramco Test Report: 30.apr.13 Inst SATR-J-6501 Instrument Loop - Inputs - Transmitter Circuit TestRashid Arshad100% (1)
- Interoffice Legal MemoDocument8 pagesInteroffice Legal MemoArvin Antonio Ortiz100% (1)
- Interesting Cases HbsDocument12 pagesInteresting Cases Hbshus2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- United States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitDocument10 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitScribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- MCQ On Marketing ManagementDocument39 pagesMCQ On Marketing ManagementtusharPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital One's Letter To The Federal ReserveDocument15 pagesCapital One's Letter To The Federal ReserveDealBookPas encore d'évaluation
- The Plus T Hat Gives You More: Dräger Fabius PlusDocument8 pagesThe Plus T Hat Gives You More: Dräger Fabius PlusSico LabenPas encore d'évaluation
- RC SCM310 ProductionOrdersDocument327 pagesRC SCM310 ProductionOrdersRRROMANCAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document15 pagesChapter 1Yap Chee HuaPas encore d'évaluation
- AccountingDocument7 pagesAccountingHà PhươngPas encore d'évaluation
- Bills of Material: Rev. Date Description by CHK'D Reviewed ClientDocument5 pagesBills of Material: Rev. Date Description by CHK'D Reviewed ClientChaitanya Sai TPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Form Mcom Sem 1 PDFDocument1 pageExam Form Mcom Sem 1 PDFTANMAYA GUPTAPas encore d'évaluation
- 120 OcmugDocument176 pages120 Ocmugatiwari_45Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2 Ent530 - Social Media PortfolioDocument25 pagesAssignment 2 Ent530 - Social Media PortfolioNUR AININ SOFIA MOHD OMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Four Fold TestDocument19 pagesFour Fold TestNeil John CallanganPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of WorkDocument45 pagesScheme of WorkZubair BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Chart of AccountzsDocument22 pagesChart of AccountzsMuddser ShahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Consultants Registered With Dda Sl. No. Name & Address of The Agency ValidityDocument4 pagesStructural Consultants Registered With Dda Sl. No. Name & Address of The Agency ValidityRupali ChadhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)