Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Annual: Appears in These Related Concepts
Transféré par
GenevieveScarlett0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
11 vues4 pagesAnnual a plant which naturally germinates, flowers, and dies in one year. Apical meristem the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells. Elongation the addition of nucleotides to the 3'-end of a growing RNA chain during transcription.
Description originale:
Titre original
Meaning of Words
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAnnual a plant which naturally germinates, flowers, and dies in one year. Apical meristem the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells. Elongation the addition of nucleotides to the 3'-end of a growing RNA chain during transcription.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
11 vues4 pagesAnnual: Appears in These Related Concepts
Transféré par
GenevieveScarlettAnnual a plant which naturally germinates, flowers, and dies in one year. Apical meristem the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells. Elongation the addition of nucleotides to the 3'-end of a growing RNA chain during transcription.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
annual
a plant which naturally germinates, flowers, and dies in one year
Appears in these related concepts:
Plant Life Spans
Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Mental Illnesses
Higher Processing
apical
situated at the growing tip of the plant or its roots, in comparison with
intercalary growth situated between zones of permanent tissue
Appears in these related concepts:
Chromalveolata: Alveolates
Mosses
Blue Light Response
apical meristem
the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells),
found in zones of the plant where growth can take place at the tip of a root or
shoot.
Appears in these related concepts:
Abscisic Acid, Ethylene, and Nontraditional Hormones
Genetic control of flowers
axillary bud
embryonic shoot that lies at the junction of the stem and petiole that gives rise
to a branch or flower
Appears in these related concepts:
Stems
Stem Modifications
cell
The basic unit of a living organism, consisting of a quantity of protoplasm
surrounded by a cell membrane, which is able to synthesize proteins and
replicate itself.
Appears in these related concepts:
The Science of Biology
Two Types of Science: Basic Science and Applied Science
Studying Cells
cortex
the tissue of a stem or root that lies inward from the epidermis, but exterior to
the vascular tissue
Appears in these related concepts:
Characteristics of Mammals
Neurons and Glial Cells
The Nervous System
cutting
placing part of a stem containing nodes or internodes in water or moist soil in
order to produce new plants
Appears in these related concepts:
Extremophiles and Biofilms
Auxins, Cytokinins, and Gibberellins
Natural and Artificial Methods of Asexual Reproduction
dicot
a plant whose seedlings have two cotyledons; a dicotyledon
Appears in these related concepts:
Roots and Leaves
Diversity of Angiosperms
Stem Anatomy
elongation
the addition of nucleotides to the 3'-end of a growing RNA chain during
transcription
Appears in these related concepts:
DNA Sequencing Techniques
Elongation and Termination in Prokaryotes
Initiation of Transcription in Eukaryotes
lignin
a complex, non-carbohydrate, aromatic polymer present in all wood
Appears in these related concepts:
Other Topics in Genomics
Cell Structure and Function
Plant Adaptations to Life on Land
meristem
the plant tissue composed of totipotent cells that allows plant growth
Appears in these related concepts:
Additional Land Plant Adaptations
Types of Root Systems
Meristems
monocot
one of two major groups of flowering plants (or angiosperms) that are
traditionally recognized; seedlings typically have one cotyledon (seed-leaf)
Appears in these related concepts:
Evolution of Angiosperms
The Life Cycle of an Angiosperm
The Importance of Seed Plants in Human Life
phloem
a vascular tissue in land plants primarily responsible for the distribution of
sugars and nutrients manufactured in the shoot
Appears in these related concepts:
The Major Divisions of Land Plants
Vascular Tissue: Xylem and Phloem
Plant Tissues and Organ Systems
tracheid
elongated cells in the xylem of vascular plants that serve in the transport of
water and mineral salts
Appears in these related concepts:
Leaf Structure, Function, and Adaptation
Movement of Water and Minerals in the Xylem
Bryophytes
xylem
a vascular tissue in land plants primarily responsible for the distribution of
water and minerals taken up by the roots; also the primary component of
wood
Appears in these related concepts:
Gymnosperms
Diversity of Gymnosperms
The Chemical Composition of Plants
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Life Science Basics For The GEDDocument6 pagesLife Science Basics For The GEDPinn phaPas encore d'évaluation
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyAnna MontiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Science NotesDocument43 pagesGrade 10 Science NotesIoana Burtea89% (27)
- Bio NeetDocument403 pagesBio NeetSona Jithin100% (1)
- Plant Cell 2Document12 pagesPlant Cell 2Icy MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report Plant PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLab Report Plant Physiologysarahyahaya100% (1)
- 8384 ST PDFDocument20 pages8384 ST PDFJohn Dave Francisco100% (1)
- Week 9 10 Patterns of Descent With ModificationDocument13 pagesWeek 9 10 Patterns of Descent With ModificationKiel Tj Evangelista100% (1)
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersD'EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Igcse SummaryDocument86 pagesBiology Igcse SummaryTarun PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Botany MidtermDocument4 pagesBotany MidtermMatthew PerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Crop Plant Parts and FunctionsDocument11 pagesCrop Plant Parts and FunctionsJetro Neil GapasinPas encore d'évaluation
- Dictionary ScienceDocument19 pagesDictionary ScienceVALERIE RODRÍGUEZPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Tissue Culture: Benefits, Structure, Types and TechniquesDocument20 pagesPlant Tissue Culture: Benefits, Structure, Types and TechniquesShantu ShirurmathPas encore d'évaluation
- Sinh Li Thuc VatDocument83 pagesSinh Li Thuc VatNguyễn HiếuPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Biology Guide on Organ Systems, Tissues, and StructuresDocument27 pagesPlant Biology Guide on Organ Systems, Tissues, and Structuresashok parmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Raven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionDocument32 pagesRaven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionMoath EnnabPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio English 2022 Manohar SirDocument136 pagesBio English 2022 Manohar SirAB Singh CharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 Part 2 Introduction To Plant BiologyDocument60 pagesWeek 1 Part 2 Introduction To Plant BiologymarkvincentmahutocPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure and Functions of Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesStructure and Functions of Plant Tissuesdina aribahPas encore d'évaluation
- 2ND PERIODICAL EXAM OUTLINE COVERS LIFE SCIENCE TOPICSDocument4 pages2ND PERIODICAL EXAM OUTLINE COVERS LIFE SCIENCE TOPICSCristina MaquintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Notes SummaryDocument12 pagesBiology Notes Summaryrobin.kipchumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Tissue SystemsDocument2 pagesPlant Tissue SystemsJohn0% (1)
- Plant Form and Function Gen Bio IIDocument42 pagesPlant Form and Function Gen Bio IIPalad , John Carlo BernabePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy.. Paper ADocument6 pagesAnatomy.. Paper ASoha Ch100% (1)
- कोशिका (CELL) : जीव ववज्ञान (BIOLOGY)Document13 pagesकोशिका (CELL) : जीव ववज्ञान (BIOLOGY)DHRUP KUMAR THAKURPas encore d'évaluation
- General-Biology-2-Plant-Cells 2Document10 pagesGeneral-Biology-2-Plant-Cells 2villasencio.shaneePas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Structure + Growth QuestionsDocument11 pagesPlant Structure + Growth Questionsante890% (1)
- Lection 1 and 2Document2 pagesLection 1 and 2MariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plants Cell: BY Ayaa Anthony. 2Nd Semester-Cpha I 2021/2022 Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesPlants Cell: BY Ayaa Anthony. 2Nd Semester-Cpha I 2021/2022 Department of PharmacyAyaa AnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Cells Vs Animal CellsDocument51 pagesPlant Cells Vs Animal CellsDivyakumar PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Campbell Biology 12th Edition SummaryDocument6 pagesCampbell Biology 12th Edition Summaryprincesje05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Test Reviewer C D E G K LDocument15 pagesSummative Test Reviewer C D E G K LGabriel John JuelePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQDocument10 pagesLecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQUmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Kingdom: Cell Walls Central VacuoleDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom: Cell Walls Central VacuoleRishel Reign GasparPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ TITLEDocument10 pagesMCQ TITLEPasipanodya MuzendaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument19 pages1-Characteristics of Living OrganismsLulwa KhaskiehPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen BioDocument3 pagesGen BioAlly OcbianPas encore d'évaluation
- The Plant KingdomDocument19 pagesThe Plant KingdomManasa KolisettiPas encore d'évaluation
- An Adaptation Is A Trait That Allows Individuals To Produce More Offspring in A Particular Environment Than Individuals Without The TraitDocument3 pagesAn Adaptation Is A Trait That Allows Individuals To Produce More Offspring in A Particular Environment Than Individuals Without The TraitDianna Ipray GriffithsPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 4 Roots and StemDocument3 pagesQuiz 4 Roots and Stemangelica valenzonaPas encore d'évaluation
- BotanyDocument316 pagesBotanyorionbotanicalfarmPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Theory: Functions of LifeDocument12 pagesCell Theory: Functions of LifeSeila MoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts and Functions of PlantsDocument21 pagesParts and Functions of PlantsRaz QuipedPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8Document11 pagesChapter 8sheisbonjing PHPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant and Animal BiologyDocument106 pagesPlant and Animal BiologyJesse LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Cluster Biology of PlantsDocument48 pagesCluster Biology of Plantsapi-452104023100% (1)
- Biology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)Document22 pagesBiology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)AbdoPas encore d'évaluation
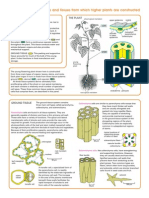
- The main cell types and tissues that make up higher plantsDocument2 pagesThe main cell types and tissues that make up higher plantsJinyuanLowPas encore d'évaluation
- Handouts-Lect. 29 - Introduction To Kingdom Plantae PDFDocument6 pagesHandouts-Lect. 29 - Introduction To Kingdom Plantae PDFRizwan BalochPas encore d'évaluation
- PlantsDocument14 pagesPlantsGlormina Asprec AvenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition and Overview of A Plant CellDocument19 pagesDefinition and Overview of A Plant CellRica NorcioPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Waec Revision: The 10 Key Topics in Biology That WAEC Set Every YearDocument8 pagesBiology Waec Revision: The 10 Key Topics in Biology That WAEC Set Every YearOyasor Ikhapo AnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Green Modern Ecology Ecosystem Presentation TemplateDocument22 pagesGreen Modern Ecology Ecosystem Presentation Templatelyka garcia100% (1)
- Earth & Life ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth & Life ScienceYhazmeen Lily LibrodoPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyDocument4 pagesPlant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Introduction To Plant DevelopmentDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Plant DevelopmentLuke Jovanni TAOCPas encore d'évaluation
- Extended Only: CHP 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms: BasicsDocument21 pagesExtended Only: CHP 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms: BasicsX GamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Tissues: Epidermis Ground Tissue Vascular Tissue Biomass Leaves Xylem Phloem Differentiated PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesPlant Tissues: Epidermis Ground Tissue Vascular Tissue Biomass Leaves Xylem Phloem Differentiated Photosynthesismurari_sahu100% (1)
- AP Kingdom PlantaeDocument79 pagesAP Kingdom PlantaeDaniel LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2Document22 pagesUnit 2NAVEENPas encore d'évaluation
- (PDF) Seedless Land Plants, Evolution and Diversification ofDocument11 pages(PDF) Seedless Land Plants, Evolution and Diversification ofAbdullahi MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant KingdomDocument8 pagesPlant KingdomGirish GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocky Mountain Mosses - A Moss Primer For AmateursDocument35 pagesRocky Mountain Mosses - A Moss Primer For AmateursColorado Native Plant Society100% (1)
- 2017 SAT Questions Reading With Answers Science 2 1 1Document6 pages2017 SAT Questions Reading With Answers Science 2 1 1Andrew NamPas encore d'évaluation
- Plants and The Colonization of LandDocument38 pagesPlants and The Colonization of LandNacorPas encore d'évaluation
- GurgelLopez-Bautista.2007.Red Algae A335Document6 pagesGurgelLopez-Bautista.2007.Red Algae A335Tiya Aliani LestariPas encore d'évaluation
- De Vries - Archibald - 2018 - Plant Evolution - Landmarks On The Path To Terrestrial LifeDocument7 pagesDe Vries - Archibald - 2018 - Plant Evolution - Landmarks On The Path To Terrestrial LifeFernando AndradePas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 From Algae To Terrestrial Plants-Student SheetDocument2 pages3.1 From Algae To Terrestrial Plants-Student Sheeteshaaljamal27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bryophytes of Central Province Sri LankaDocument6 pagesBryophytes of Central Province Sri LankaAshen NirodyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amerita Lab 4Document7 pagesAmerita Lab 4matthiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 11Document64 pagesUnit 11Lighto RyusakiPas encore d'évaluation
- PBB 213 - Bryology and Pteridology at Edo University IyamhoDocument17 pagesPBB 213 - Bryology and Pteridology at Edo University IyamhoKhan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Plant Systematics: Michael G. SimpsonDocument76 pagesFundamentals of Plant Systematics: Michael G. SimpsonDimo PratannaPas encore d'évaluation
- PP9 Biodiversity of Plants 1453879364Document93 pagesPP9 Biodiversity of Plants 1453879364khijogpPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylogeny and Diversification of BryophytesDocument26 pagesPhylogeny and Diversification of BryophytesHamengku AgengPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution of PlantsDocument5 pagesEvolution of PlantsChristine ShellyPas encore d'évaluation
- QiuEtAl 2006 Antóceros Como Irmãos de TraqueófitasDocument6 pagesQiuEtAl 2006 Antóceros Como Irmãos de TraqueófitasGeorge SidneyPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO192 GENERAL BIOLOGY PRACTICAL II SUMMARY 08024665051Document45 pagesBIO192 GENERAL BIOLOGY PRACTICAL II SUMMARY 08024665051Brian CopperPas encore d'évaluation
- BotanyDocument10 pagesBotanyYekitaSPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio CH 20 Plant DiversityDocument26 pagesBio CH 20 Plant DiversityHasan AlzaghalPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Diversity Module Content FinalDocument9 pagesPlant Diversity Module Content FinalBlessing Patrick BanganiPas encore d'évaluation
- L Plant Fossils. Cleal, Christopher PDFDocument224 pagesL Plant Fossils. Cleal, Christopher PDFOstrac NapicPas encore d'évaluation
- Pteridophytes PDFDocument80 pagesPteridophytes PDFJBPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Jonathan Shaw, P É Ter SZ Ö V É Nyi, and Blanka ShawDocument18 pagesA. Jonathan Shaw, P É Ter SZ Ö V É Nyi, and Blanka ShawRaúl Hernández100% (1)
- Botany Assignment on BryophytesDocument22 pagesBotany Assignment on BryophytesUmair DogarPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Questions: Osmunda Is An Intermediate Between Leptosporangiate and Eusporangiate FernDocument4 pagesLong Questions: Osmunda Is An Intermediate Between Leptosporangiate and Eusporangiate FernCDB 1st Semester 2077Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shaw, J. & K. Renzaglia. (2004) - Phylogeny and Diversification of Bryophytes. American PDFDocument26 pagesShaw, J. & K. Renzaglia. (2004) - Phylogeny and Diversification of Bryophytes. American PDFDiego Andres Moreno GaonaPas encore d'évaluation