Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Saravanan Paper
Transféré par
Sudhanshu Shekhar0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues4 pagesDYNAMICS OF NEUROSTEROIDS IN THE BRAIN: SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STEROIDOGENIC
ENZYME 3-HSD GENE EXPRESSION IN THE BRAIN OF AN INDIAN MAJOR CARP (LABIO ROHITA)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDYNAMICS OF NEUROSTEROIDS IN THE BRAIN: SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STEROIDOGENIC
ENZYME 3-HSD GENE EXPRESSION IN THE BRAIN OF AN INDIAN MAJOR CARP (LABIO ROHITA)
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues4 pagesSaravanan Paper
Transféré par
Sudhanshu ShekharDYNAMICS OF NEUROSTEROIDS IN THE BRAIN: SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STEROIDOGENIC
ENZYME 3-HSD GENE EXPRESSION IN THE BRAIN OF AN INDIAN MAJOR CARP (LABIO ROHITA)
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
DYNAMICS OF NEUROSTEROIDS IN THE BRAIN: SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STEROIDOGENIC
ENZYME 3-HSD GENE EXPRESSION IN THE BRAIN OF AN INDIAN MAJOR
1
*Saravanan
1
Department of Zoology, Madras Christian College, Tambaram,
2
Department of Zoology, Pachaiyappas College for Women, Kanchipuram
ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT
3-Hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase (3
enzyme is used in the synthesis of neuroactive steroids in steroidogenesis. The 3
conversion of 5
tetrahydroxyprogesterone (3
respectively. The progesterone metabolite of neuroactive steroid, 3
different regions of brain. In the present study, the gene expression of 3
rohita
showed has formed a basis for futu
the fishes.
Copyright Saravanan, N. and Moses Inbaraj, R. This
unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
INTRODUCTION
The steroids synthesised in the brain tissues or neural tissues
are generally called as neurosteroids. Pregnenolone
and progesterone (PROG) can be synthesized in the nervous
system. A crucial biochemical reaction in vertebrates is the
progesterone conversion into neuroactive metabolites such as
5-dihydroprogesterone (5-DHP) and 3
progesterone (3,5-THPROG), which regulate several
neurobiological processes, including stress, depression,
neuroprotection, and analgesia. 3,5-THPROG is a potent
stimulator of type A receptors of -amino butyric acid
(GABA), the main inhibitory neurotransmitter
Herd, 2003; Belelli and Lambert, 2005; Pinna
Belyaeva, et al., 2007). GABAergic neurons of the reticular
thalamic nucleus express high levels of 5
and their nerve endings may secrete allopregnanolone
release GABA in the proximity of postsynaptic GABA
receptors located on the dendrites and somata of glutamatergic
thalamocortical output neurons (Pinault,
considerations are also expected for allopregnanolone
synthesized by medium spiny GABAergic neurons in the
caudate or putamen and also very likely by Purkinje cells that
modulate GABAA receptors expressed postsynaptically on cell
bodies or dendrites of deep cerebellar nuclei neurons
Balboa et al.,2006). The aldo-keto reductase
involved in the metabolism of endogenous substrate, such as
*Corresponding author: Saravanan, N. Department of Zoology, Madras
Christian College, Tambaram, Chennai-600 059, India.
ISSN: 0975-833X
Article History:
Received 07
th
September, 2013
Received in revised form
15
th
October, 2013
Accepted 29
th
November, 2013
Published online 25
th
December, 2013
Key words:
Steroidogenesis, Neuroactive steroid,
3alpha-HSD, Aldo-keto reductase,
Labeo rohita.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
DYNAMICS OF NEUROSTEROIDS IN THE BRAIN: SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STEROIDOGENIC
HSD GENE EXPRESSION IN THE BRAIN OF AN INDIAN MAJOR
CARP LABEO ROHITA (HAM.)
Saravanan, N.,
1
Moses Inbaraj, R. and
2
Uma, T.
Department of Zoology, Madras Christian College, Tambaram, Chennai-
Department of Zoology, Pachaiyappas College for Women, Kanchipuram
ABSTRACT
Hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase (3-HSD) is a member of the aldo
enzyme is used in the synthesis of neuroactive steroids in steroidogenesis. The 3
version of 5-dihydroprogesterone (5-DHP) and 5-dihydrotestosterone (5
tetrahydroxyprogesterone (3,5-THPROG) and 3,5-tetrahydroxytestosterone (3
respectively. The progesterone metabolite of neuroactive steroid, 3
different regions of brain. In the present study, the gene expression of 3
was identified. The gene was observed by PCR amplification with a specific primer. The
showed has formed a basis for future investigations on the regulation and function of these enzymes in
the fishes.
is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits
unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
The steroids synthesised in the brain tissues or neural tissues
are generally called as neurosteroids. Pregnenolone (PREG)
and progesterone (PROG) can be synthesized in the nervous
A crucial biochemical reaction in vertebrates is the
progesterone conversion into neuroactive metabolites such as
DHP) and 3, 5-tetrahydro
THPROG), which regulate several
neurobiological processes, including stress, depression,
THPROG is a potent
amino butyric acid
(GABA), the main inhibitory neurotransmitter (Belelli and
Pinna, et al., 2006;
GABAergic neurons of the reticular
-RI and 3-HSD
and their nerve endings may secrete allopregnanolone and
release GABA in the proximity of postsynaptic GABA
A
receptors located on the dendrites and somata of glutamatergic
, 2004). Similar
considerations are also expected for allopregnanolone
y GABAergic neurons in the
caudate or putamen and also very likely by Purkinje cells that
modulate GABAA receptors expressed postsynaptically on cell
bodies or dendrites of deep cerebellar nuclei neurons (Agis-
keto reductase superfamily is
involved in the metabolism of endogenous substrate, such as
Department of Zoology, Madras
steroid hormones, prostaglandins, bile acids and
xenobiotics,such as drugs and environmental carcinogens
(Khanna et al., 1995). 3
chemical structure and low molecular weight of 318.49, easily
penetrates the blood-brain barrier to induce central nervous
system (CNS) effects, including anxiolytic and sedative
hypnotic properties (Gee et al.,
Functional analyses indicate that
myelin formation in both the CNS and the peripheral nervous
system (Baulieu and Schumacher 2000
2003) and promotes neuron survival.
advances in functional brain imag
neural circuits in cortico-limbic structures involved in the
modulation of fear responses, aggressiveness, anxiety, and
sexual behaviors that appear to be affected in mood disorders
(Carlson et al., 2006). These circuits include the amygdala,
hippocampus, and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC)
(Carlson et al., 2006; Nelson
the olfactory system has also been implicated
2005). 3-HSD gene expression has bee
other vertebrates like humans, rat, and cattle
1984; Qin et al., 1993; Lin et al.,
Recently it has been reported that both allopregnenolone and
isopregnenolone are also synthesized from PROG in CNS
tissues throughout the embryonic and early postnatal period of
development in the rat (Pomata
no evidence for the identification of 3
This is the first attempt to know the 3
of fish, particularly among the Indian carp.
Available online at http://www.journalcra.com
International Journal of Current Research
Vol. 5, Issue, 12, pp.4062-4065, December, 2013
INTERNATIONAL
z
DYNAMICS OF NEUROSTEROIDS IN THE BRAIN: SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STEROIDOGENIC
HSD GENE EXPRESSION IN THE BRAIN OF AN INDIAN MAJOR
-600 059, India
Department of Zoology, Pachaiyappas College for Women, Kanchipuram
HSD) is a member of the aldo-keto reductase family. The
enzyme is used in the synthesis of neuroactive steroids in steroidogenesis. The 3-HSD catalyzes the
dihydrotestosterone (5-DHT) into 3,5-
tetrahydroxytestosterone (3,5-THT)
respectively. The progesterone metabolite of neuroactive steroid, 3,5-THPROG is synthesized in
different regions of brain. In the present study, the gene expression of 3-HSD in the brain of Labeo
was identified. The gene was observed by PCR amplification with a specific primer. The result
re investigations on the regulation and function of these enzymes in
is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits
steroid hormones, prostaglandins, bile acids and
such as drugs and environmental carcinogens
,5-THPROG with a steroid
chemical structure and low molecular weight of 318.49, easily
brain barrier to induce central nervous
system (CNS) effects, including anxiolytic and sedative
et al., 1998; Brinton, 1994).
nctional analyses indicate that 3,5-THPROG induces
myelin formation in both the CNS and the peripheral nervous
Schumacher 2000; Schumacher et al.,
and promotes neuron survival. In humans, recent
advances in functional brain imaging have identified critical
limbic structures involved in the
modulation of fear responses, aggressiveness, anxiety, and
sexual behaviors that appear to be affected in mood disorders
. These circuits include the amygdala,
hippocampus, and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC)
Nelson and Trainor, 2007). In rodents,
the olfactory system has also been implicated (Mandiyan et al.,
HSD gene expression has been reported in some
other vertebrates like humans, rat, and cattle (Penning et al.,
et al., 1997).
Recently it has been reported that both allopregnenolone and
are also synthesized from PROG in CNS
tissues throughout the embryonic and early postnatal period of
Pomata et al., 2000). However, there is
no evidence for the identification of 3-HSD gene in fishes.
o know the 3-HSD enzyme in brain
of fish, particularly among the Indian carp. Labeo rohita
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL
OF CURRENT RESEARCH
(commonly called as Rohu) is an animal model for the present
research work and it is an economically important species
among the Indian major carps.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection
Fish samples of Labeo rohita were collected from the Lake
Sevilimedu located at Kanchipuram. Fishes were caught in
live condition and they were dissected to collect brain samples.
The brain tissues were fixed in a sterilized vials containing
RNAlater and they were stored at 4C until analysis.
Total RNA isolation
Total RNA was isolated by homogenizing the whole brain
sample (200mg) with 500l of TriReagent (Sigma) and 200l
of DEPC water. After homogenizing the sample, it was then
incubated at -20C for 5 minutes. 0.2ml of chloroform was
added and incubated at -20C for 5 minutes. It was then
centrifuged at 12,000rpm (4C) for 15 minutes. The
supernatant was collected in a fresh tube. RNA was
precipitated by adding equal volume of isopropanol and it was
stored at -20C for 45 minutes. The sample was centrifuged
again at 12,000 rpm (4C) for 15 minutes. Total RNA was
obtained as a pellet and 75% ethanol (7.5ml of Ethanol was
mixed with 2.5ml of DEPC water) was added. It was
centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes and air dried and
dissolved by adding 40l of DEPC water. This was frozen and
stored at -20C for half-an-hour. The sample was then tested
with the 1.2% agarose gel for its purity.
Synthesis of first strand cDNA
Total RNA was isolated from the brain of L. rohita. The
separated RNA has been reverse transcribed into cDNA using
RT-PCR method. A clean PCR tube was taken to this 1l of
the sample, 1 l of Oligo (dT)
18
primer, 9.5l of de-ionized
water was added and it was spinned gently for few seconds in a
micro centrifuge. This mixture was incubated at 70C for 5
minutes. After incubation, 4l of 5X reaction buffer, 0.5l of
Ribonuclease inhibitor (40l/dl), 2l of 10mM dNTP mix were
added. This was mixed gently, centrifuged and incubated at
42C for 5 minutes. After incubation, it was added with M-
MuLV reverse transcriptase (20U/l) to make it around 20 l
volumes. This was incubated finally at 42C for 60 min and
25C for 10 min.
The reaction was stopped by heating at 70C for 10 min and
chilled on ice. PCR products were then tested with agarose gel
electrophoresis.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
2l of cDNA was taken in a sterilized PCR tube with 1l of
3-HSD primers of sense and antisense. The following primers
were used at different reactions. Sense- 5CTGTGCCTGAGA
AGGTTGCT3, antisense-5CATGTGTCACAGATATCCAC
3, sense-5 GGAGGCCATGGAGAAGTGTA3, antisense
5CACCCATGTTTTGTCTCGTG3and sense- 5ACAAG
CGATGGATTCCATAT3 25l PCR master mix consists of
all basic components : Taq DNA Polymerase, dNTPs and
reaction buffer(1.5mM Magnesium chloride) were added. The
PCR amplification was used to check the expression of the
mRNAs of 3-HSD enzyme in the brain sample. The
temperature adopted in the amplification is as follows: 94C
for 2 minutes in 1 cycle, 94C for 1 minute, 56C for 1 minute
and 72C for 1 minute in 35cycles, the finally holding
temperature was 4C. The PCR products of gene specific
primer of 3-HSD along with 100bp DNA Ladder were then
subjected to 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis. After running
the gel, the image of specific bands were captured by using UV
trans illumination under the JH Bio geldoc system.
Sequencing
The PCR product was sequenced and the mRNA sequences of
3-HSD obtained for L. rohita were shown in the result. The
mRNA sequences of 3-HSD of L. rohita were multiple
aligned with vertebrate organisms to know the similarity,
relationship and evolutionary significance of L. rohita with
other organisms.
RESULTS
Total RNA was isolated from the entire male brain of L. rohita.
Two RNA bands as 28S and 18S were obtained and shown in
Fig.1A. The isolated RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA
using RT-PCR. The single strand cDNA was obtained and it
appeared as a smear. The PCR was made to run at specific
temperature to analyze the gene expression of 3-HSD by
adding the gene specific primer to the cDNA. The PCR
product shows a single band which is represented in Fig.1B
and Fig.1C. The PCR product and the 100bp DNA Ladder
4063 Saravanan, et al. Dynamics of neurosteroids in the brain: special reference to steroidogenic enzyme 3-hsd gene expression in the brain of an
indian major carp Labeo rohita (HAM.)
Fig.1. A. Shows the Two RNA bands as 28S and 18S were obtained from brain tissue of Labeo rohita, B and C. Shows the PCR products from cDNA
amplified along with specific primer of 3a-HSD, D. Shows the 100bp marker DNA and 431bp expression of 3a-HSD gene in the brain of Indian major
carp, Labeo rohita
were loaded in separate lanes in the gel. Single band at 431bp
was obtained and is shown in Fig.1D. The mRNA sequence of
3-HSD obtained for L. rohita are shown below. The obtained
mRNA sequence of 3HSD of L. rohita were multiple aligned
with different species of vertebrates to know the similarity of
L. rohita with other organisms. Relative score table and
multiple sequence alignment of complete mRNA sequence of
3-HSD of vertebrates along with the obtained sequence of
Labeo rohita showing the percentage of similarity shown in
Fig. 2.
The partial mRNA Sequences of 3-HSD of Labeo rohita
obtained from the present study
>gi|326325828|gb|JF683819.1| Labeo rohita 3-alpha hydroxy
steriod dehydrogenase (AKR1C) mRNA, complete sequence
GCGATGGTGCTGTGCTCTTGGATACCGTCATTTTTCAT
CGTCGCGAGCGTACTTAGGTGACCTGCCTGGCCACTT
GCATCTGCACGGCATTGCTTGGCTGGTCTGTCCAATA
TATTTGTGGGATTTTGAGAGTGAAGTAGCTCCTCTGTT
GGCTGCATTTGTAACTGCCATTCTGGCTGCAAATGAA
CCTGCTGGGAATGATTTCTAGTCTGCAAGTGCTGCGA
TCTAAGCTGCATGCGTTCATGTCTATTTGCATCGAAGC
TACGAGAGTGGTGTGGAACCATGTTTGGCAACAGCGT
TTCTGACATGATTCTACCAGGTAGAGGTGCCGTCCTT
CCGTTGTCTCGATCTAACCTTGGCCTACCTCTCCTGCC
GGTACTTACTCTACCTCGTTGAGAATGTATGGACAGT
GGATATCTGGTGACACATGA
DISCUSSION
Our results confirm the presence of 3-HSD in the brain of an
Indian Major Carp, L. rohita. Results from the present
experiment indicates the expression of the mRNAs of 3-HSD,
the enzyme involved in the conversion of 5-DHPROG into
3, 5-THPROG in the brain of L. rohita. Aldo-keto
reductases interconvert weak androgens, estrogens, progestin,
mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids to their more potent
counterparts by catalyzing the reduction and oxidation of keto-
and hydroxysteroids, respectively, thereby regulating a wide
range of physiological processes involved in development,
homeostasis and reproduction (Bauman et al., 2004). In this
manner, AKRs regulate the occupancy and transactivation of
several steroid receptors in target tissues leading to
transcription of hormone-responsive genes (Penning et al.,
2004). The products of AKR activity have been implicated in
prostate disease, breast cancer, obesity, poly cystic ovary
disease and delay in the onset of puberty in humans
(Stanbrough et al., 2006; Rittner et al., 1997; Nonneman et al.,
2006). They reported the AKR1C gene expression in different
tissues of pig. From the report it is noted that spleen, ovary,
lung, adrenal, kidney, and endometrial expressed all the five
genes. AKR1C2 and AKR1C4 were the most widely
expressed genes. AKR1C2 was expressed in all tissues except
pancreas and brain. Unlike human AKR1C4, pig AKR1C4
expression was not specific to the liver but was expressed in all
tissues and AKR1C2 was the only other AKR1C gene
expressed in brain. Because of their location in the swine
genome and their implication in reproductive physiology, this
gene cluster was characterized and evaluated for effects on
reproductive traits in swine. Results of the present experiment
confirm the presence of the gene AKR1C in the brain tissue of
L. rohita. The mRNA sequence obtained for L. rohita was
partial and it was multiple aligned with B. Taurus, M.
musculus, R. norvegicus, X. tropicalis and H. sapiens. The
phylogenetic analysis revealed that the tree was very well
bifurcated into two branches with H. sapiens at the top and L.
rohita at the bottom. H. sapiens and B. tarus arise from a same
point of origin whereas R. norvegicus and M. musculus have
arisen from a different branch which reveals that they share
quite conserved regions. L. rohita, S. scrofa and X. tropicalis
have risen from a common point which reveals that L. rohita is
more closely related to S. scrofa and distantly related to H.
sapiens. The present identified gene might be the AKR1C2
which is specific to brain of Indian major carp. The
identification of other genes AKR1C1, AKR1C3, AKR1C4
and AKR1C5 need to be studied in this carp to state whether
the 3-HSD expression is tissue specific. Further studies are
required to understand the expression of the enzyme in the
brain which will highlight the presence or absence of AKR1C2
or AKR1C1.
REFERENCES
Agis-Balboa RC, Pinna G, Zhubi A, Maloku E, Veldic M,
Costa E, Guidotti A. 2006. Characterization of brain
neurons that express enzymes mediating neurosteroid
biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103:1460214607.
4064 International Journal of Current Research, Vol. 5, Issue, 12, pp.4062-4065, December, 2013
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic tree of mRNA sequences of 3-HSD of different classes of vertebrates along with the obtained sequences from Labeo rohita
showing the relationship and evolutionary distance among the organisms when compared with each other
Baulieu EE, Schumacher M. 2000. Progesterone as a
neuroactive neurosteroid, with special reference to the
effect of progesterone on myelination. Hum Reprod, 15: 1-
13.
Bauman DR, Steckelbroeck S, Penning TM. 2004. The roles of
aldo-ketp reductases in steroid hormone action. Drug News
Perspective, 17: 563-578.
Belelli D, Herd MB. 2003. The contraceptive agent Provera
enhances GABA
A
receptor-mediated inhibitory
neurotransmission in the rat hippocampus: evidence for
endogenous neurosteroids? J Neurosci, 23:10013-10020
Belelli D, Lambert JJ. 2005. Neurosteroids: endogenous
regulators of the GABA
A
receptor. Nat Rev Neurosci,
6:565575.
Belyaeva OV, Chetyrkin SV, Clark AL, Kostereva NV,
SantaCruz KS, Chronwall BM, Kedishvili NY. 2007. Role
of Microsomal Retinol/Sterol Dehydrogenase-Like Short-
Chain Dehydrogenases/Reductases in the Oxidation and
Epimerization of 3-Hydroxysteroids in Human Tissues.
Endocrinology May, 148(5):2148-2156.
Brinton RD. 1994. The neurosteroid 3-hydroxy-5-pregnan-
20-one induces cytoarchitectural regression in cultured
fetal hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci, 14: 2763-2774.
Carlson PJ, Singh JB, Zarate CA Jr, Drevets WC, Manji HK.
2006. Neural circuitry and neuroplasticity in mood
disorders: insights for novel therapeutic targets. NeuroRx:
J Am Soc Exp NeuroTher, 3:22-41.
Gee KW, Bolger MB, Brinton RE, Coirini H, Mc Ewen BS.
1998. Steroid modulation of the chloride ionophore in rat
brain: structure-activity requirements, regional dependence
and mechanism of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 246:
803-812.
Khanna M, Qin KN, Wang RW, Cheng KC. 1995. Substrate
specificity, gene structure, and tissue-specific distribution
of multiple human 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases.
J Biol Chem, 270: 20162-20168.
Lin HK, Jez JM, Schlegel BB, Peehl DM, Pachter JA, Penning
TM. 1997. Expression and characterization of recombinant
type2 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD) from
human prostate: demonstration of bifunctional 3/17-
HSD activity and celluar distribution. Mol Endocrinol,
11: 1971-1984.
Mandiyan VS, Coats JK, Shah NM. 2005. Deficits in sexual
and aggressive behaviors in Cnga2 mutant mice. Nat
Neurosci, 8:16601662.
Nelson RJ, Trainor BC. 2007. Neural mechanisms of
aggression. Nature Rev Neurosci, 8:536-546.
Nonneman DJ, Wise TH, Ford JJ, Kuehn LA, Rohrer GA.
2006. Characterization of the aldo-keto reductase 1C gene
cluster on Pig chromosome 10: possible associations with
reproductive traits. BMC Veterinary Reasearch, 2: 1-11.
Penning TM, Jin Y, Steckelbroeck S, Lanisnik Rizner T,
Lewis M. 2004. Structure-functions of 3 alpha
hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: genes and proteins Mol
Cell Endocrinol, 215(1-2): 63-72.
Penning TM, Mukharji I, Barrows S, Talalay P. 1984.
Purification and properties of a 3-hydroxysteroid
dehydrogenase of rat liver cytosol and its inhibition by
anti-inflammatory drugs J Biochem, 222: 601-611.
Pinault D. 2004. The thalamic reticular nucleus: structure,
function and concept. Brain Res Rev, 46:1-31.
Pinna G, Costa E, Guidotti A. 2006. Fluoxetine and
norfluoxetine stereospecifically and selectively increase
brain neurosteroid content at doses that are inactive on 5-
HT reuptake. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 186:362-372
Pomata PE, Colman-Lerer AA, Baranao JL, Fiszman ML.
2000. In vivo evidences of early neurosteroid synthesis in
the developing rat central nervous system and placenta.
Brain Res Dev Brain Res, 120: 83-86.
Qin KN, New MI and Cheng KC. 1993. Molecular cloning of
multiple cDNAs encoding human enzymes structurally
related to 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol, 46: 673-679.
Rittner HL, Lee PD, Blum WF, Doerr HG, Steiss J, Kreuder J,
Rascher W, Kiess W. 1997. Developmental patterns of
serum 3alpha-androstanediol glucuronide. Journal of
Endocrinological Investigation, 20: 138-143.
Schumacher M, Weill-Engerer S, Liere P, Robert F, Franklin
RJ, Garcia-segura LM, Lambert JJ, Mayo W, Melcangi
RC, Parducz A, Suter U, Carelli C, Baulieu EE, Akwa Y.
2003. Steroid hormones and neurosteroids in normal and
pathological aging of the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol,
71: 3-29.
Stanbrough M, Bubley GJ, Ross K, Golub TR, Rubin MA,
Penning TM, Febbo PG, Balk SP. 2006. Increased
expression of genes converting adrenal androgens to
testosterone in androgen-independent prostate cancer.
Cancer Research, 66: 2815-2825.
*******
4065 Saravanan, et al. Dynamics of neurosteroids in the brain: special reference to steroidogenic enzyme 3-hsd gene expression in the brain of an
indian major carp Labeo rohita (HAM.)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Chapter 1 Life Span DevelopmentDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Life Span DevelopmentKayelita Wu100% (3)
- Induction Presentation Biology A Level and Gcse.204719226Document25 pagesInduction Presentation Biology A Level and Gcse.204719226Cut TirayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bruce Logan MFCDocument9 pagesBruce Logan MFCdavid_tomy_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Odisha PG Zoology SyllabusDocument35 pagesOdisha PG Zoology SyllabusThe IdyllicxPas encore d'évaluation
- Dalandan (Citrus Aurantium Linn.) Peelings and Calamansi (Citrofortunella Microcarpa) Extract As An Alternative Fire Ant KillerDocument6 pagesDalandan (Citrus Aurantium Linn.) Peelings and Calamansi (Citrofortunella Microcarpa) Extract As An Alternative Fire Ant KillerMaryknoll BernabePas encore d'évaluation
- G8 Q4 Bio ReviewedDocument5 pagesG8 Q4 Bio ReviewedSha RonPas encore d'évaluation
- Hubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan Dan Dukungan Keluarga Terhadap Kepatuhan Ibu Hamil Mengkonsumsi Tablet Zat BesiDocument13 pagesHubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan Dan Dukungan Keluarga Terhadap Kepatuhan Ibu Hamil Mengkonsumsi Tablet Zat Besinovilia eka sariPas encore d'évaluation
- Asgard Flag Above ElbrusDocument4 pagesAsgard Flag Above ElbrusAvaristanPas encore d'évaluation
- Curs Ginkgo BilobaDocument7 pagesCurs Ginkgo BilobaAnamaria RizacPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Primary Cataract: Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing S.Y. 2021-2022Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Primary Cataract: Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing S.Y. 2021-2022zoie ziazzettePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Human Anatomy Physiology With PathologyDocument41 pages1 Human Anatomy Physiology With PathologyEd dela PenaPas encore d'évaluation
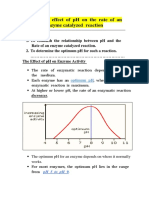
- Effect of PH On Enzyme ActivityDocument12 pagesEffect of PH On Enzyme ActivityAb AbPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue BrainDocument20 pagesBlue BrainAnkitaPatel009Pas encore d'évaluation
- AgeLOC R Squared Product and Science PresentationDocument27 pagesAgeLOC R Squared Product and Science PresentationSiaw Sing OngPas encore d'évaluation
- M.D. Sheets, M.L. Du Bois and J.G. WilliamsonDocument2 pagesM.D. Sheets, M.L. Du Bois and J.G. WilliamsonWinda AlpiniawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ of Diagnosis BacterialDocument11 pagesMCQ of Diagnosis Bacterialمحمد اللاميPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample-Anatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 9th 9EDocument30 pagesSample-Anatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 9th 9Erist0% (1)
- Activity No. 7.1 BloodDocument2 pagesActivity No. 7.1 BloodDree SermanPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Science ProjectDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Science ProjectRichard JebarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lucienne NeoMASS AAAC PlusDocument8 pagesLucienne NeoMASS AAAC PlusRanjith EswaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Matag Coconut 1. Matag CoconutDocument4 pagesMatag Coconut 1. Matag CoconutNek YakkPas encore d'évaluation
- Adhesive Systems in Restorative DentistryDocument6 pagesAdhesive Systems in Restorative DentistryStoian SimonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part-B Answer Any FIVE Questions. All Carry Equal Marks 5x4 20MDocument5 pagesPart-B Answer Any FIVE Questions. All Carry Equal Marks 5x4 20Mجمال عبداللهPas encore d'évaluation
- Is Basic Technique Used For The Examination of Movement and For Initiating Movement Into A Program of Therapeutic InterventionDocument9 pagesIs Basic Technique Used For The Examination of Movement and For Initiating Movement Into A Program of Therapeutic InterventionEric Carlos YumulPas encore d'évaluation
- UGK-Quotes With PhotosDocument77 pagesUGK-Quotes With PhotosRanganatha Gowda100% (1)
- Unit 3Document61 pagesUnit 3JessicaHaePas encore d'évaluation
- Hcin620 m6 Lab6 Hanifahmutesi-FinalprojectDocument5 pagesHcin620 m6 Lab6 Hanifahmutesi-Finalprojectapi-488096711Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vedantu Best Notes OrgDocument24 pagesVedantu Best Notes Orggaurav bhanotPas encore d'évaluation
- Imperata Cylindrica: Investigations On Some Aspects of Chemical Ecology of Cogongrass, (L.) BeauvDocument10 pagesImperata Cylindrica: Investigations On Some Aspects of Chemical Ecology of Cogongrass, (L.) BeauvDiroy ParulianPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 Cell Cycle - QuestionsDocument6 pagesLecture 3 Cell Cycle - Questions中华雅思王Pas encore d'évaluation