Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Scientific Watch 14102011
Transféré par
Franky Manoppo0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
9 vues4 pagesScientific and technique information are the product abundant archive quasi systematic ( bank data, documentations, technic documentation) and signals (based on bibliographic data, based on patent data) under electronic formation. By the scientific informations, people can know the scientific activity.
Description originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentScientific and technique information are the product abundant archive quasi systematic ( bank data, documentations, technic documentation) and signals (based on bibliographic data, based on patent data) under electronic formation. By the scientific informations, people can know the scientific activity.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
9 vues4 pagesScientific Watch 14102011
Transféré par
Franky ManoppoScientific and technique information are the product abundant archive quasi systematic ( bank data, documentations, technic documentation) and signals (based on bibliographic data, based on patent data) under electronic formation. By the scientific informations, people can know the scientific activity.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Scientific Watch (La Veille Scientifique)
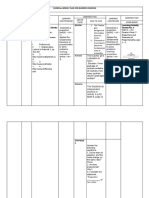
1. General Description of Scientific Information
1.1.1. Introduction
1.1.2. Flow of Scientific Information
1.1.3. Distribution of Information
1.1.4. Typology of the Source of Scientific Information
1.1.5. Sources of Scientifics
2. Concepts of the Scientific Watch
2.1. Introduction
2.2. Performance of wake-fullness of Scientific Watch
2.3. Prediction of Scientific Watch
2.4. Information and Indicators of the Scientific Watch
3. Description of the Scientific Watch
3.1 Supervision of Environment
a. Recherche of Information
b. Collection of Information
c. Diffusion of Information
3.2. Exploitation of Informations
a. Treatment of collection the Informations
b. Analysis and Validation of Treatment
c. Utilization of the Valid Information.
Scientific Watch
1. General Description of Scientific Information
1.1. Introduction
Information is a strategic matter which has a cost, sometimes high cost and
indispensable . ( Dou 95 ). A scientific writing is the production of thinking. The
activity of scientific publication is a confrontation perpetual between the peculiar
reflexion of the actors and the acquired knowledges through the lecture of the
eminent works of other actors ( Rost 96 ).
The scientific and technique information are the product abundant archive quasi
systematic ( bank data, documentations, technic documentation ), signals (based
on bibliographic data, based on patent data) and broadcasting ( CDROM, internet,
receiver) under electronic formation., By the scientific informations, people can
know the scientific activity.
1.2. The Flow of Scientific Information
The production acceleration is possible of return by the constantly drop of
technique cost as well as through the specialization which more and more push
the actors. This tendency , far away of weakness, only confirm in many years. The
difficulty will localize and standardize the good information. The Figure 1 shown
the growth of Scientific Informations.,
Number
PRICE 1950
Constant Growth
Diversity of Support
Diversity of Source
Law of Bradfort
Dispersion
Growth of Budget
Times / Years
Figure 1. Volume Growth of the Scientific Informations
1.3 Distribution of Information
Information can be included into 4 (four) group according to Hunt and Zartarian :
a. Type of Text Information (formal) (40%) is a structured information generally by
computer.
This information can make subject of various statistical treatment of information
which allow the global analysis to answer the question : Who make What, Where
and When ( Qui fait Quoi, Ou et Quand )
b. Type of Flux information (40%) is an information non structural come from outside
of the institution.
c. Information type expertise (10%), i.e. memory of a firm, knowledge of experts,( their
situation and location).
d. Information type fair and salons (10%)
1.4 Typology of the source of Scientific Information
Formal Information : books, catalogues, regulations, standards (norms), brevets, reports,
journal, norms, thesis, market revue, summary of congress, etc.
Informal information : various information stockiest in the individual dissertation of
experts, consultants, and research worker.
Exchange information from the manifestation of seminaries congress, professional
meeting, exposition, fair. (LEV, 2010)
1.5 Sources of Scientific Information
Traditional Publishing :
Journals, encyclopedic, summary of congress, these, reports of research, and pre-
publication
Other source of scientific information, patent, reports of Ambassador consulate, annual
reports of company / society.
Library
Producer of data bank
CD Room and Internet.
type TEXTE
type Floue
type expertise
type foires et salon
Figure 2. Distribution of Information.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Knowledge Management in Higher Education: Procedia Computer ScienceDocument6 pagesKnowledge Management in Higher Education: Procedia Computer ScienceFranky ManoppoPas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific Watch 14102011 (BHN Prof Umboh)Document17 pagesScientific Watch 14102011 (BHN Prof Umboh)Franky ManoppoPas encore d'évaluation
- Isdm21 DouDocument5 pagesIsdm21 DouFranky ManoppoPas encore d'évaluation
- Delphi Techno Forecast South KoreaDocument34 pagesDelphi Techno Forecast South KoreaFranky ManoppoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Toward A Rhetoric of Reason M. MeyerDocument10 pagesToward A Rhetoric of Reason M. MeyerMarcela RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Arbitrators Empanelled in IRC PDFDocument15 pagesList of Arbitrators Empanelled in IRC PDFMohit Nagar100% (1)
- Using Exams To Complete Your Excelsior College DegreeDocument44 pagesUsing Exams To Complete Your Excelsior College DegreesmartaleckPas encore d'évaluation
- Mogadishu University Prospectus 2012Document56 pagesMogadishu University Prospectus 2012Dr. Abdurahman M. Abdullahi ( baadiyow)100% (2)
- DIASS ModuleDocument22 pagesDIASS ModuleBernard LuisagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kulhawy (1991) Fiftreen+ Years of Model Foundation Testing in Large Chambers-185-195Document11 pagesKulhawy (1991) Fiftreen+ Years of Model Foundation Testing in Large Chambers-185-195Cesar Felipe Jimenez SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- 5, Socrates Sosyal Bilimler KitabıDocument103 pages5, Socrates Sosyal Bilimler KitabıVN MinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Table of Specification DiassDocument2 pagesTable of Specification DiassChris John GaraldaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Only Study Guide For PST103EDocument113 pagesThe Only Study Guide For PST103ECharmaine Verrall80% (5)
- SOCIOLOGY STRATEGY - Rank 63, Tanai Sultania, CSE - 2016 - INSIGHTS PDFDocument4 pagesSOCIOLOGY STRATEGY - Rank 63, Tanai Sultania, CSE - 2016 - INSIGHTS PDFmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- English Exam Normal Session-Spring 2019-2020: Name: Student NumberDocument7 pagesEnglish Exam Normal Session-Spring 2019-2020: Name: Student NumberYossef ARPas encore d'évaluation
- Glossary of Maharishi Effect TermsDocument2 pagesGlossary of Maharishi Effect TermsCarrissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rubrics Final Btech ProjectDocument6 pagesRubrics Final Btech ProjectAbhiram DonPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Statistical Approaches To Analysis of Small Clinical Trials - Small Clinical Trials - Issues and Challenges - The National Academies PressDocument47 pages3 Statistical Approaches To Analysis of Small Clinical Trials - Small Clinical Trials - Issues and Challenges - The National Academies PressSFDPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Timetable Full 13-14Document7 pagesExam Timetable Full 13-14Muhammad KaShifPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials of Marketing Research 5th Edition Zikmund Test BankDocument18 pagesEssentials of Marketing Research 5th Edition Zikmund Test Bankbrittanylamsfwkpbmzce100% (18)
- Activity 1.1 The Twin ParadoxDocument1 pageActivity 1.1 The Twin ParadoxBlessed May PastranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Media5258540449249166169Document4 pagesLocal Media5258540449249166169Rica Claire SerqueñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ostrom, Elinor 2011 'Background On The Institutional Analysis and Development Framework' Policy Studies Journal, Vol. 39, No. 1 (Feb. 15, Pp. 7 - 27)Document21 pagesOstrom, Elinor 2011 'Background On The Institutional Analysis and Development Framework' Policy Studies Journal, Vol. 39, No. 1 (Feb. 15, Pp. 7 - 27)voxpop88Pas encore d'évaluation
- DP EE - Interdisciplinary Approach-8-18Document11 pagesDP EE - Interdisciplinary Approach-8-18Android 18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Social PsychologyDocument95 pagesIntroduction To Social PsychologySagar SunuwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tok Devlin What Is MathematicsDocument4 pagesTok Devlin What Is MathematicsJessyHooPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 The Key Missing BasicDocument4 pages02 The Key Missing Basiclilli-pilliPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Science Experiment 2 (Assessment Rubrics)Document1 pageMaterial Science Experiment 2 (Assessment Rubrics)Aziful AimanPas encore d'évaluation
- RM Note Unit 2Document17 pagesRM Note Unit 2Kani MozhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesEvolution Lesson Planapi-252795781Pas encore d'évaluation
- STS-MAY-18-30m Module5Document4 pagesSTS-MAY-18-30m Module5Mariella MallariPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is ResearchDocument6 pagesWhat Is ResearchGlydenne Glaire Poncardas GayamPas encore d'évaluation
- A Systematic Review of Green Building Development in ChinaDocument29 pagesA Systematic Review of Green Building Development in Chinafaizsyam01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Raiseplus Weekly Plan For Blended Learning Name: Dante C. AtienzaDocument4 pagesRaiseplus Weekly Plan For Blended Learning Name: Dante C. AtienzaDante AtienzaPas encore d'évaluation