Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
Transféré par
Rhanne Bolante0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
872 vues5 pagesThis document summarizes the side effects and nursing considerations for four antipsychotic medications - olanzapine, aripiprazole, chlorpromazine, and olanzapine. It lists common side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, hypotension, extrapyramidal symptoms, and tardive dyskinesia. Nurses should monitor patients for these side effects as well as signs of more severe reactions like neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Assessment includes monitoring vital signs, glucose levels, symptoms, and providing patient education about safety and side effect reporting.
Description originale:
Anti-Psychotic drugs with side effects
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document summarizes the side effects and nursing considerations for four antipsychotic medications - olanzapine, aripiprazole, chlorpromazine, and olanzapine. It lists common side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, hypotension, extrapyramidal symptoms, and tardive dyskinesia. Nurses should monitor patients for these side effects as well as signs of more severe reactions like neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Assessment includes monitoring vital signs, glucose levels, symptoms, and providing patient education about safety and side effect reporting.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
872 vues5 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
Transféré par
Rhanne BolanteThis document summarizes the side effects and nursing considerations for four antipsychotic medications - olanzapine, aripiprazole, chlorpromazine, and olanzapine. It lists common side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, hypotension, extrapyramidal symptoms, and tardive dyskinesia. Nurses should monitor patients for these side effects as well as signs of more severe reactions like neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Assessment includes monitoring vital signs, glucose levels, symptoms, and providing patient education about safety and side effect reporting.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 5
1.
Side effects and nursing implications of the following stabilizing agents:
1.3 Antipsychotics
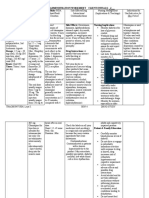
OLANZAPINE
(Zyprexa)
Side effects
CNS: Somnolence, dizziness, nervousness, headache, akathisia, personality disorders,
tardive dyskinesia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome
CV: Orthostatic hypotension, peripheral edema, tachycardia
GI: Constipation, abdominal pain
Respiratory: Cough, pharyngitis
Other: Fever, weight gain, joint pain
ASSESSMENT
History: Allergy to olanzapine, myeloproliferative disorders, severe CNS depression,
comatose states, history of seizure disorders, lactation; CV or cerebrovascular disease,
dehydration, Alzheimer's disease, prostate enlargement, narrow-angle glaucoma, history of
paralytic ileus or breast cancer, elderly or debilitated patients, pregnancy
Physical: T, weight; reflexes, orientation, intraocular pressure, ophthalmologic exam; P, BP,
orthostatic BP, ECG; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output, liver evaluation;
prostate palpation, normal urine output; CBC, urinalysis, liver and renal function tests
INTERVENTIONS
Do not dispense more than 1-wk supply at a time.
Peel back foil on blister pack of disintegrating tablets; do not push through foil; use dry hands
to remove tablet and place in mouth.
Monitor for the many possible drugdrug interactions before beginning therapy.
Monitor elderly patients for dehydration and institute remedial measures promptly; sedation
and decreased sensation of thirst related to CNS effects of drug can lead to dehydration.
Encourage patient to void before taking the drug to help decrease anticholinergic effects of
urinary retention.
Monitor for elevations of temperature and differentiate between infection and neuroleptic
malignant syndrome.
Monitor for orthostatic hypotension and provide appropriate safety measures as needed.
TEACHING POINTS
Take this drug exactly as prescribed; do not change dose without consulting your health care
provider.
Peel back foil on blister pack of disintegrating tablets; do not push through foil; use dry hands
to remove tablet, place entire tablet in mouth.
These side effects may occur: drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, seizures (avoid driving,
operating machinery, or performing tasks that require concentration); dizziness, faintness on
arising (change positions slowly, use caution); increased salivation (if bothersome, contact your
nurse or physician); constipation (consult with your nurse of physician for appropriate relief
measures); fast heart rate (rest and take your time if this occurs).
This drug cannot be taken during pregnancy. If you think you are pregnant or wish to become
pregnant, contact your nurse or physician.
Report lethargy, weakness, fever, sore throat, malaise, mouth ulcers, and flulike symptoms.
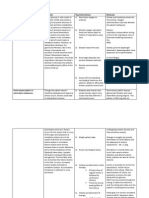
ARIRIPIPRAZOLE
(Abilify)
Side effects
CNS: headache, anxiety, insomnia, lightheadedness, somnolence, tremor, asthenia, tardive
dyskinesia, blurred vision, seizures (potentially life-threatening), akathisia
CV: orthostatic hypotension
Dermatologic: rash
GI: nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, esophageal dysmotility
Respiratory: rhinitis, cough
Other: fever, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, increased suicide risk
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
Assessment & Drug Effects
Monitor diabetics for loss of glycemic control.
Monitor cardiovascular status. Assess for and report orthostatic hypotension. Take BP
supine then in sitting position. Report systolic drop of >1520 mm Hg. Patients at
increased risk are those who are dehydrated, hypovolemic, or receiving concurrent
antihypertensive therapy.
Monitor body temperature in situations likely to elevate core temperature (e.g., exercising
strenuously, exposure to extreme heat, receiving drugs with anticholinergic activity, or
being subject to dehydration).
Monitor for and report signs of tardive dyskinesia.
Monitor for and immediately report S&S of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) that
include: hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, irregular pulse or blood
pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia. Withhold drug if NMS is
suspected.
Lab tests: Monitor periodically Hct & Hgb. Monitor periodically blood glucose. Monitor
for elevated CPK and myoglobinuria if NMS is suspected.
Patient & Family Education
Carefully monitor blood glucose levels if diabetic.
Do not drive or engage in other potentially hazardous activities until reaction to drug is
known.
Avoid situations where you are likely to become overheated or dehydrated.
Notify physician if you become pregnant or intend to become pregnant while taking this
drug.
Do not breast feed while taking this drug.
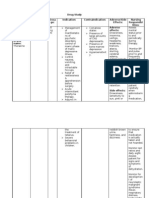
CHLORPROMAZINE
(Thorazine)
Side effects
CNS: Drowsiness, insomnia, vertigo, headache, weakness, tremors, ataxia, slurring,
cerebral edema, seizures, exacerbation of psychotic symptoms, extrapyramidal
syndromes, neuroleptic malignant syndrome
GI: Dry mouth, salivation, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, constipation, paralytic ileus,
incontinence
CV: Hypotension, otrhostatic hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, bradycardia,
cardiac arrest, CHF, cardiomegaly, refractory arrhythmias, pulmonary edema
Respiratory: Bronchospasm, laryngospasm, dyspnea, suppression of cough reflex and
potential aspiration
Hematologic: Eosinophilia, leukopenia, leukocytosis, anemia, aplastic anemia, hemolytic
anemia, thrombocytopenic or nonthrombocytopenic purpura, pancytopenia, elevated
serum cholesterol
GU: Urinary retention, polyuria, incontinence, priapism, ejaculation inhibition, male
impotence, urine discolored pink to red-brown
EENT: Nasal congestion, glaucoma, photophobia, blurred vision, miosis, mydriasis,
deposits in the cornea and lens, pigmentary retinopathy
Hypersensitivity: Jaundice, urticaria, angioneurotic edema, laryngeal edema,
photosensitivity, eczema, asthma, anaphylactoid reactions, exfoliative dermatitis, contact
dermatitis
Endocrine: Lactation, breast engorgement in females, galactorrhea, syndrome of
inappropriate ADH secretion, amenorrhea, menstrual irregularities, gynecomastia,
changes in libido, hyperglycemia, inhibition of ovulation, infertility, pseudopregnancy,
reduced urinary levels of gonadotropins, estrogens and progestins
Other: Fever, heat stroke, pallor, flushed facies, sweating, photosensitivity
Assessment & Drug Effects
Establish baseline BP (in standing and recumbent positions), and pulse, before initiating
treatment.
Monitor BP frequently. Hypotensive reactions, dizziness, and sedation are common
during early therapy, particularly in patients on high doses and in the older adult
receiving parenteral doses. Patients usually develop tolerance to these adverse effects;
however, lower doses or longer intervals between doses may be required.
Lab tests: Periodic CBC with differential, liver function tests, urinalysis, and blood
glucose.
Monitor cardiac status with baseline ECG in patients with preexisting cardiovascular
disease.
Be alert for signs of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (see Appendix G). Report
immediately.
Observe and record smoking since it increases metabolism of phenothiazines, resulting in
shortened half-life and more rapid clearance of drug. Higher dosage in smokers may be
required. Advise patient to stop or at least reduce smoking, if possible.
Monitor I&O ratio and pattern: Urinary retention due to mental depression and
compromised renal function may occur. If serum creatinine becomes elevated, therapy
should be discontinued.
Monitor for antiemetic effect of chlorpromazine, which may obscure signs of overdosage
of other drugs or other causes of nausea and vomiting.
Be alert to complaints of diminished visual acuity, reduced night vision, photophobia,
and a perceived brownish discoloration of objects. Patient may be more comfortable with
dark glasses.
Monitor diabetics or prediabetics on long-term, high-dose therapy for reduced glucose
tolerance and loss of diabetes control.
Ocular examinations, and EEG (in patients >50 y) are recommended before and
periodically during prolonged therapy.
Patient & Family Education
Take medication as prescribed and keep appointments for follow-up evaluation of dosage
regimen. Improvement may not be experienced until 7 or 8 wk into therapy.
Do not alter dosing regimen, and do not give the drug to another person.
May cause pink to red-brown discoloration of urine.
Wear protective clothing and sunscreen lotion with SPF above 12 when outdoors, even
on dark days. Photosensitivity associated with chlorpromazine therapy is a phototoxic
reaction. Severity of response depends on amount of exposure and drug dose. Exposed
skin areas have appearance of an exaggerated sunburn. If reaction occurs, report to
physician.
Practice meticulous oral hygiene. Oral candidiasis occurs frequently in patients receiving
phenothiazines.
Report extrapyramidal symptoms that occur most often in patients on high dosage, the
pediatric patient with severe dehydration and acute infection, the older adult, and women.
Avoid driving a car or undertaking activities requiring precision and mental alertness
until drug response is known.
Do not abruptly stop this drug. Abrupt withdrawal of drug or deliberate dose skipping,
especially after prolonged therapy with large doses, can cause onset of extrapyramidal
symptoms (see Appendix F) and severe GI disturbances. When drug is to be
discontinued, dosage must be tapered off gradually over a period of several weeks.
Do not breast feed while taking this drug.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Drugs Drugs Drugs STUDY GUIDEDocument13 pagesDrugs Drugs Drugs STUDY GUIDEAlexander Chamessian100% (1)
- Psychotropic MedicationsDocument87 pagesPsychotropic MedicationsDWAI McJohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Neurotransmitters in Schizophrenia A Comprehensive StudyDocument27 pagesRole of Neurotransmitters in Schizophrenia A Comprehensive StudyJosep Rio RambePas encore d'évaluation
- Lawrence J. Albers, MD: 2005 EditionDocument68 pagesLawrence J. Albers, MD: 2005 EditionAlex VimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychiatric Nursing Bullets Neurotransmission TheoryDocument4 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Bullets Neurotransmission TheoryDefensor Pison Gringgo100% (1)
- Drug ListDocument30 pagesDrug ListKristinePas encore d'évaluation
- Handy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For PsychosisDocument3 pagesHandy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For Psychosisrowanpurdy100% (2)
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureDocument31 pagesOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Review For FinalsDocument9 pagesPharmacology Review For FinalsJaya ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro CH 14 Study GuideDocument9 pagesNeuro CH 14 Study GuideMichael J MillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Antipsychotics Risks and BenefitsDocument38 pagesAntipsychotics Risks and BenefitsEllePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyRhanne Bolante100% (1)
- Psychiatric MedicationDocument22 pagesPsychiatric MedicationSofia Centro TaerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pagets DiseaseDocument2 pagesPagets DiseaseLov Raj LohaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Unit OutineDocument2 pagesGenetics Unit Outinejmunozbio@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotic Resistance Essay - Third DraftDocument5 pagesAntibiotic Resistance Essay - Third DraftKevin JohnsenPas encore d'évaluation
- Adrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseDocument8 pagesAdrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseyancefincePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug KenalogDocument1 pageDrug KenalogSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Psych DrugsDocument3 pagesCommon Psych Drugsrexinne noahPas encore d'évaluation
- Decision TreeDocument185 pagesDecision TreeNathan D. Croy50% (2)
- Asthma: A. Practice EssentialsDocument8 pagesAsthma: A. Practice EssentialsCandha NurcahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Depressants FinalDocument61 pagesAnti Depressants FinalAuthor Nauman Shad100% (1)
- 1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39Document94 pages1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39hamidPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Children-Cutting-Edge Controversy Insights and ResearchDocument176 pagesBipolar Children-Cutting-Edge Controversy Insights and Researchdariaevelin100% (1)
- Head, Mouth, Nose, Throat, Neck and Regional Lymph Nodes: Kristin Clephane, MSN, RN, CPNDocument44 pagesHead, Mouth, Nose, Throat, Neck and Regional Lymph Nodes: Kristin Clephane, MSN, RN, CPNMike100% (1)
- Olanzapine Drug StudyDocument1 pageOlanzapine Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia67% (3)
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument4 pagesAutoimmune DiseasesMahak JandwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyLeya ThaobunyuenPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of ParalysisDocument6 pagesTypes of ParalysisLoh Wei ChiehPas encore d'évaluation
- UPTODATE Management of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms of Dementia - UpToDateDocument32 pagesUPTODATE Management of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms of Dementia - UpToDateQwerty QwertyPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Features, Evaluation, and Diagnosis of Sepsis in Term and Late Preterm Infants PDFDocument27 pagesClinical Features, Evaluation, and Diagnosis of Sepsis in Term and Late Preterm Infants PDFJonathan WelchPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute PericarditisDocument14 pagesAcute PericarditisMila Ccasani100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyBarbara Detaro100% (2)
- Auxiliary Label Drugs: Abilify GeodonDocument18 pagesAuxiliary Label Drugs: Abilify GeodonXylex Dave Andres100% (1)
- Equivalencia AntipsicóticosDocument4 pagesEquivalencia AntipsicóticosLuis Felipe Varela Espinoza100% (1)
- Injection SOP 2011 (3rd Edition)Document70 pagesInjection SOP 2011 (3rd Edition)lynlgsxrPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan ProjectDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan ProjectMj WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Diagnosis For DKADocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis For DKARhanne Bolante88% (24)
- Nursing Diagnosis For DKADocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis For DKARhanne Bolante88% (24)
- DedicationDocument1 pageDedicationRhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Tylenol Overdose Case StudyDocument13 pagesTylenol Overdose Case Studyapi-544081136Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Assessment ToolDocument21 pagesPhysical Assessment ToolAmal LR100% (1)
- Editable Legal Letter Template For Money Owed WordDocument1 pageEditable Legal Letter Template For Money Owed Wordrevuri sunilPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohol DiabetesDocument3 pagesAlcohol DiabeteskoolshotPas encore d'évaluation
- Most Question That The "Psychiatrist" Would Ask?Document1 pageMost Question That The "Psychiatrist" Would Ask?Chayantorn NimmanwathanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Drug MonitoringAnnie SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Aripiprazole (Generic) ABILIFY (BRAND)Document3 pagesAripiprazole (Generic) ABILIFY (BRAND)missayayaya100% (1)
- Chlorpromazine: Brands If It WorksDocument6 pagesChlorpromazine: Brands If It WorksAnonymous cwlpSlReUYPas encore d'évaluation
- Psych Drugs List - To Be Filled inDocument3 pagesPsych Drugs List - To Be Filled inM Patel100% (1)
- The Detailed Neurologic Examination in Adults - UpToDate PDFDocument29 pagesThe Detailed Neurologic Examination in Adults - UpToDate PDFMiguel GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument2 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationdeabellarPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychotropic DrugsDocument60 pagesPsychotropic DrugsLaTasha Lindemann RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocument1 pageClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- Med CardsDocument4 pagesMed CardsSonia FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Report 3Document7 pagesCase Report 3Razan NasereddinePas encore d'évaluation
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument3 pagesHead To Toe Assessmentsandaman2225Pas encore d'évaluation
- List of Antidotes: No. Drugs AntidoteDocument3 pagesList of Antidotes: No. Drugs AntidotearjumandPas encore d'évaluation
- ABC Dictionary of Urinary SystemDocument26 pagesABC Dictionary of Urinary Systemaby_romero9750% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGracie S. VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- HESI Dosage Calculations QuizDocument2 pagesHESI Dosage Calculations QuizAna BiennePas encore d'évaluation
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmournePas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency DrugsDocument9 pagesEmergency DrugsaldwinngPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Brochure English FINAL 150109 PDFDocument9 pagesBipolar Brochure English FINAL 150109 PDFIka M. HendrajayaPas encore d'évaluation
- NANDA DX NI, NODocument165 pagesNANDA DX NI, NOKerry Brown100% (1)
- AnxietyDocument5 pagesAnxietyJohn HolmesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Side Effects of Common Psychiatric DrugsDocument40 pagesThe Side Effects of Common Psychiatric DrugsPhilip Jonkers100% (1)
- Issues in Nursing - Culture - Student (1) - 2Document3 pagesIssues in Nursing - Culture - Student (1) - 2Tiffany Glisch67% (6)
- Neurotransmitters in Schizophrenia: Dr. Adel El SheshaiDocument47 pagesNeurotransmitters in Schizophrenia: Dr. Adel El SheshaielvinegunawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concept - ATI Template Childhood InjuriesDocument1 pageBasic Concept - ATI Template Childhood InjuriesRafia HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Delirium, Dementia, PsychosisDocument2 pagesDelirium, Dementia, PsychosisLagente EstalocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Crash Cart PresentationDocument38 pagesCrash Cart PresentationElsubaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Care of Pediatric Client With Dermatologic DisorderDocument3 pagesCare of Pediatric Client With Dermatologic DisorderAraw GabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandHyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- I Got the Flu! What is Influenza? - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Diseases BooksD'EverandI Got the Flu! What is Influenza? - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Diseases BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease Signs & SymptomsDocument3 pagesDisease Signs & SymptomsRhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- DAP Week 2 Day 2Document2 pagesDAP Week 2 Day 2Rhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study TemplateDocument9 pagesCase Study Templatejadebesa6526Pas encore d'évaluation
- DAP Week 2 Day 2Document2 pagesDAP Week 2 Day 2Rhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia Still Responsible For One Fifth of Child DeathsDocument3 pagesPneumonia Still Responsible For One Fifth of Child DeathsRhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- DAP Week 2 Day 2Document2 pagesDAP Week 2 Day 2Rhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Labs (GC)Document24 pagesLabs (GC)Rhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Hazards of Oxygen: Bolante, Rhanne S. Con Iv-A01Document3 pagesHazards of Oxygen: Bolante, Rhanne S. Con Iv-A01Rhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Gordon - S 11 Functional Health PatternsDocument5 pagesGordon - S 11 Functional Health PatternsRhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs StudyDocument5 pagesDrugs StudyRhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Acknowledgement DoneDocument2 pagesAcknowledgement DoneRhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy Power Point PresentationDocument24 pagesLeprosy Power Point PresentationRhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- SoledadDocument6 pagesSoledadRhanne Bolante67% (3)
- Structures of Amino AcidsDocument8 pagesStructures of Amino AcidsRhanne BolantePas encore d'évaluation
- Psych Handout 1Document15 pagesPsych Handout 1in12kamal123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study-Grand Case PresDocument8 pagesDrug Study-Grand Case PresLorina Lynne ApelacioPas encore d'évaluation
- The Successful ConcurrentDocument5 pagesThe Successful ConcurrentShevamykolayovychshevchenko MilaniztyonlymilanelloPas encore d'évaluation
- tcrm0301 003Document11 pagestcrm0301 003paulPas encore d'évaluation
- Tom's Fourth Year Guide (2011-12)Document709 pagesTom's Fourth Year Guide (2011-12)jangyPas encore d'évaluation
- JAMA Psychiatry - : Original InvestigationDocument10 pagesJAMA Psychiatry - : Original InvestigationMesianissimoPas encore d'évaluation
- Template Aging Obat Jan 24Document654 pagesTemplate Aging Obat Jan 24fennyrahmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S2667382722000096 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S2667382722000096 MainAndrea SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- PosterDocument1 pagePosterAyar HeinPas encore d'évaluation
- Zyprexa: Generic Name: OlanzapineDocument3 pagesZyprexa: Generic Name: Olanzapinenasir khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurology MRCP Crib Sheet by Law and MedicineDocument53 pagesNeurology MRCP Crib Sheet by Law and MedicineMatin Ahmad Khan100% (1)
- Psychiatry and NeurologyDocument114 pagesPsychiatry and Neurologyjames.a.blairPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapid Cycling Bipolar Disorder in Adults - Treatment of Mania and Hypomania PDFDocument12 pagesRapid Cycling Bipolar Disorder in Adults - Treatment of Mania and Hypomania PDFdreamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Points of Psychotropic Drugs - 19!7!2021Document51 pagesPractical Points of Psychotropic Drugs - 19!7!2021HayaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Postpartum Psychosis: Madness, Mania, and Melancholia in MotherhoodDocument10 pagesPostpartum Psychosis: Madness, Mania, and Melancholia in MotherhoodAndreeaNicoletaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Written Output DidDocument29 pagesSample Written Output DidAyesha Tan100% (1)
- Rapid Tranquillisation-The Science and AdviceDocument13 pagesRapid Tranquillisation-The Science and AdviceDeanne Morris-DeveauxPas encore d'évaluation
- MMP Handy Chart October 2011 V2Document69 pagesMMP Handy Chart October 2011 V2Icha IchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To Bipolar Disorder: Jon Davine, MD, CCFP, FRCP (C)Document56 pagesApproach To Bipolar Disorder: Jon Davine, MD, CCFP, FRCP (C)safiraPas encore d'évaluation