Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
2012 CBSE XIIScience 5 2 SET1 Sectionb
Transféré par
Min NimTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2012 CBSE XIIScience 5 2 SET1 Sectionb
Transféré par
Min NimDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Grade XII ALL INDIA SET 3
Chemistry (Theory)
[Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:70]
General Instructions:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each question are indicated against it.
(iii) Question number 1 to 8 are very short-answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
(iv) Question number 9 to 18 are short-answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
(v) Question number 19 to 27 are also short-answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
(vi) Question number 28 to 30 are long-answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
(vii) Use Log Tables, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
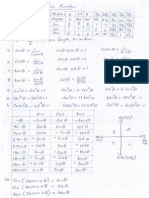
Q9. A reaction is of second order with respect to a reactant. How is its rate affected if the
concentration of the reactant is (i) doubled (ii) reduced to half? 2
Ans. Let the concentration of the reactant be [A] = a
Rate of reaction, R = k [A]
2
= ka
2
(i) If the concentration of the reactant is doubled, i.e. [A] = 2a, then the rate of the reaction
would be
( )
2
R 2 k a ' =
= 4ka
2
= 4 R
Therefore, the rate of the reaction would increase by 4 times.
(ii) If the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half, i.e. | |
1
A
2
a = , then the rate of the
reaction would be
2
2
1
R
2
1
4
1
4
k a
ka
R
| |
'' =
|
\ .
=
=
Therefore, the rate of the reaction would be reduced to
th
1
.
4
Grade XII ALL INDIA SET 3
Q10. Express the relation among cell constant, resistance of the solution in the cell and conductivity
of the solution. How is molar conductivity of a solution related to its conductivity?
OR
The molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm
2
mol
1
.
Calculate the conductivity of the conductivity of this solution. 2
Ans. (a) The conductivity ( k ) of the solution in a cell is the reciprocal of its resistivity.
1 l
R a
| |
=
|
\ .
k
The quantity
l
a
is cell constant.
l Distance between 2 electrodes
a Area of cross section
R Resistance
Also, conductivity,
Molar conductivity
Volumeof solution
= k
Thus, ^m = V k
OR
m
m
2 1
3
1
Conductivity
Molar Conductivity=
Concentration
=
Conductivity, =
138.9(Scm mol )1.5(mol/L)
=
1000(cm /L)
=0.208 Scm
k
c
k c
Q11. Explain the role of each of the following:
(i) NaCN in the extraction of silver
(ii) SiO
2
in the extraction of copper 2
Ans. (i) The roasted ore of gold is leached with a solution of sodium cyanide in the presence of
oxygen for many days. The role of NaCN in this process is to dissolve the gold to form an
aurocyanide complex, from which the metal is obtained by displacement.
| |
| |
2 2 2
2 2 4
4Au 8NaCN 2H O O 4Na Au(CN) 4KOH
2Na Au(CN) + Zn Na [Zn(CN) ] + 2 Au
+ + + +
Grade XII ALL INDIA SET 3
(ii) Copper matte contains Cu
2
S and FeS. In the blast furnace, copper matte is added with
powdered coke and silica. The oxidation of ore takes place in this process. As a result, cuprous
oxide and ferrous oxide are produced. The role of silica in this process is to remove the iron
oxide obtained as slag. FeO combines with silica (flux) to form iron silicate, FeSiO
3
(slag).
2 3
FeO SiO FeSiO
Flux Slag
A
+
Q12. Complete the following chemical reaction equations: 2
(i)
2
2 7
Cr O I H
+
+ +
(ii)
4 2
MnO NO H
+
+ +
Ans. (i)
2 + 3+
2 7 2 2
Cr O +14H +6I 2Cr +3I +7H O
(ii)
+ 2+
4 2 3 2
2MnO +5NO +6H 2Mn + 5NO +3H O
Q13. Explain the following facts giving appropriate reason in each case:
(i) NF
3
is an exothermic compound whereas NCl
3
is not.
(ii) All the bonds in SF
4
are not equivalent. 2
Ans. (i) The instability of NCl
3
is due to the weak NCl bond. This is due to the large difference in the
size of nitrogen and chlorine atoms. On the other hand, atoms of both nitrogen (75 pm) and
fluorine (72 pm) are small sized. Thus, bonding in NF
3
is quite strong and it is an exothermic
compound.
(ii) SF
4
has sp
3
d hydridisation and thus have trigonal bipyramid structure in which one axial
position is occupied by a lone pair of electrons. This results in two types of angles.
Equatorial bond angle
( )
F S F<120 LP-BPrepulsion>BPBPrepulsion
Axial bond angle F S F<90
Grade XII ALL INDIA SET 3
Q14. Explain the following behaviours:
(i) Alcohols are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular
masses.
(ii) Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol. 2
Ans. Alcohols undergo intermolecular H-bonding while hydrocarbons do not.
Hence, they are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
(ii)
The nitro-group is an electron-withdrawing group. The presence of this group in the ortho
position decreases the electron density in the OH bond. As a result, it is easier to lose a proton.
Also, the o-nitrophenoxide ion formed after the loss of protons is stabilized by resonance.
Hence, ortho nitrophenol is a stronger acid.
On the other hand, methoxy group is an electron-releasing group. Thus, it increases the electron
density in the OH bond and hence, the proton cannot be given out easily.
Grade XII ALL INDIA SET 3
For this reason, ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol.
Q15. Explain the mechanism of acid catalysed hydration of an alkene to form corresponding
alcohol. 2
Ans. Some reactive alkenes like 2 methyl propene undergo direct hydration in the presence of
mineral acids which act as catalysts. The addition of water to the double bond takes place in
accordance with Markonikoffs rule.
Q16. Complete the following chemical reaction equations: 2
(i)
6 5 2 3 2 2
C H N Cl+H PO H O +
(ii) ( )
6 5 2 2
C H NH +Br aq.
Ans. (i) C
6
H
5
N
2
Cl + H
3
PO
2
+ H
2
O C
6
H
6
+ N
2
+ H
3
PO
3
+ HCl
(ii)
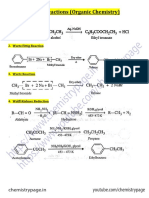
Q17. Describe the following giving the relevant chemical equation in each case: 2
(i) Carbylamine reaction
(ii) Hofmanns bromamide reaction.
Ans. (i) Carbylamine reaction
Carbylamine reaction is used as a test for the identification of primary amines. When aliphatic
and aromatic primary amines are heated with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide,
carbylamines (or isocyanides) are formed. These carbylamines have very unpleasant odours.
Secondary and tertiary amines do not respond to this test.
Grade XII ALL INDIA SET 3
( )
2 3 2
R NH CHCl 3KOH alc. R NC 3KCl 3H O
Primary Chloroform Potassium Carbylamine
amine hydroxide
A
+ + + +
For example,
( )
3 2 3 3 2
CH NH CHCl 3KOH alc. CH NC 3KCl 3H O
Methanamine Methyl carbylamine
or methyl isocyanide
A
+ + + +
Hoffmann bromamide reaction
When an amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic solution of sodium
hydroxide, a primary amine with one carbon atom less than the original amide is produced. This
degradation reaction is known as Hoffmann bromamide reaction. This reaction involves the
migration of an alkyl or aryl group from the carbonyl carbon atom of the amide to the nitrogen
atom.
For example,
Q18. Differentiate between disinfectants and antiseptics. Give one example of each group. 2
Ans. Antiseptics and disinfectants are effective against micro-organisms. However, antiseptics are
applied to the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers, and diseased skin surfaces, while
disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments, etc.
Disinfectants are harmful to the living tissues.
Iodine is an example of a strong antiseptic. Tincture of iodine (2 3 percent of solution of
iodine in alcohol water mixture) is applied to wounds. 1 percent solution of phenol is used as
a disinfectant.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- VB Physics Eng 12Document20 pagesVB Physics Eng 12abhishekprasad677Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- ShakespeareDocument4 pagesShakespeareMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- xyeuES 6Document34 pagesxyeuES 6Min NimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- WS 1 (N) ForceDocument1 pageWS 1 (N) ForceMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Multiple factors distinguish me as a strong candidate for CMU's Biological Sciences programDocument5 pagesMultiple factors distinguish me as a strong candidate for CMU's Biological Sciences programMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Electric Charge Physics Problems and SolutionsDocument2 pagesElectric Charge Physics Problems and SolutionsMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Previous Board QuestionsDocument41 pagesPrevious Board QuestionsMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- ELECTROSTATICS AND CURRENT ELECTRICITYDocument98 pagesELECTROSTATICS AND CURRENT ELECTRICITYShashank Rai0% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Goitre: Deficiency DiseasesDocument1 pageGoitre: Deficiency DiseasesMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 12 Lyp Physics 01Document60 pages2011 12 Lyp Physics 01abhishekprasad677Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- ELECTROSTATICS AND CURRENT ELECTRICITYDocument98 pagesELECTROSTATICS AND CURRENT ELECTRICITYShashank Rai0% (1)
- Electric Charge Physics Problems and SolutionsDocument2 pagesElectric Charge Physics Problems and SolutionsMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Phys102 Old Exams Chapter26Document4 pagesPhys102 Old Exams Chapter26Min NimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Phy 12 2003Document24 pagesPhy 12 2003Min NimPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Wave OpticsDocument9 pagesWave OpticsDhilipan RamachandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometryMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- 2011 12 Lyp Physics 01Document60 pages2011 12 Lyp Physics 01abhishekprasad677Pas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- Phy3 PDFDocument9 pagesPhy3 PDFOshin LambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Papers Class 12 PhysicsDocument53 pagesSample Papers Class 12 Physics0910ashuPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic DampingDocument57 pagesMagnetic DampingMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument4 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- PhotoDocument5 pagesPhotoMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- 13283cbse Important QuestionsDocument3 pages13283cbse Important QuestionsMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Wave OpticsDocument9 pagesWave OpticsDhilipan RamachandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatics and Current Electricity Concepts ExplainedDocument48 pagesElectrostatics and Current Electricity Concepts ExplainedMin NimPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics XII 2011 12Document226 pagesPhysics XII 2011 12Min NimPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsDocument33 pagesLecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- Dragonfly - Julia GoldingDocument210 pagesDragonfly - Julia GoldingMin Nim86% (7)
- Aldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesAldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidPRADEEP CPas encore d'évaluation
- BioreactorsDocument32 pagesBioreactorskhadeeja vjfndnPas encore d'évaluation
- ASPHALT METHOD STATEMENTDocument7 pagesASPHALT METHOD STATEMENTBasem Donia100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- SIP MeenakshDocument17 pagesSIP MeenakshRati GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio HGHDocument19 pagesBio HGHapi-240332064Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103L Santos Ronzel ANgelo M.Document3 pagesOrganic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103L Santos Ronzel ANgelo M.Akira SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Expwb3ans eDocument67 pagesExpwb3ans eOlivia LinPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalysis Norskov 05 15 02Document36 pagesCatalysis Norskov 05 15 02Rafael Ricardo Celin ManceraPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Plasticity: Rolf Mahnken, Andreas Schneidt, Thomas AntretterDocument22 pagesInternational Journal of Plasticity: Rolf Mahnken, Andreas Schneidt, Thomas AntretterKhouloud GharbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cosmetics 09 00063 v2Document44 pagesCosmetics 09 00063 v2maizhafiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 309-King Agar-110991 PDFDocument1 page309-King Agar-110991 PDFSneyder MurciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Agoo Montessori Learning Center and High School Inc.: Fruit Waste As Biodegradable PlasticDocument6 pagesAgoo Montessori Learning Center and High School Inc.: Fruit Waste As Biodegradable PlasticAlejandro De la GarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Best in the Long RunDocument23 pagesThe Best in the Long RunSheikh ZakirPas encore d'évaluation
- ESSO Shaft Sealing Systems SpecificationDocument13 pagesESSO Shaft Sealing Systems SpecificationFlorin Daniel AnghelPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of Elements Properties Use/S 1. ZinkDocument13 pagesName of Elements Properties Use/S 1. ZinkNora Alfaro BalsakiPas encore d'évaluation
- 20b. Global S CycleDocument15 pages20b. Global S CyclerossydaPas encore d'évaluation
- Square Duct Board Installation ManualDocument4 pagesSquare Duct Board Installation ManualApurv GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Based Evaluation of Industrial Grade Resins Duolite ARA-9366 and Duolite A-368Document8 pagesPerformance Based Evaluation of Industrial Grade Resins Duolite ARA-9366 and Duolite A-368misterno2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Name Reactions GuideDocument12 pagesOrganic Name Reactions GuidechinmayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Booher Chem Sketch Activity 1Document13 pagesBooher Chem Sketch Activity 1c_booher9561Pas encore d'évaluation
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Ephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Ephedrine HydrochlorideTyaga MahardikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical-Vocational and Livelihood: (Automotive Servicing NC I)Document35 pagesTechnical-Vocational and Livelihood: (Automotive Servicing NC I)Carina Tan100% (2)
- ERM99B ERP99B 3/16/07 Champion Gardner DenverDocument62 pagesERM99B ERP99B 3/16/07 Champion Gardner DenverManualstoHelpPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Properties of Food-1Document47 pagesChemical Properties of Food-1Mbabazi Jackson CalmaxPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Development of Stereolithography (SLA) 3D Printing in Additive Manufacturing For Biomedical IndustryDocument4 pagesA Review On Development of Stereolithography (SLA) 3D Printing in Additive Manufacturing For Biomedical IndustryFirdaus Mat SoibPas encore d'évaluation
- BOF1Document3 pagesBOF1Skartini DayPas encore d'évaluation
- Whirlpool Adp 533 WHDocument12 pagesWhirlpool Adp 533 WHGustavo ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Pinworm: Treatment & Education"TITLE"Adult Pinworm: Assessment & ManagementDocument3 pagesPediatric Pinworm: Treatment & Education"TITLE"Adult Pinworm: Assessment & ManagementSaul0% (1)
- Istory of Jellyfish Envenomation: 3.1.1. Class Cubozoa - Cubozoan JellyfishDocument16 pagesIstory of Jellyfish Envenomation: 3.1.1. Class Cubozoa - Cubozoan JellyfishRangsiyo BeabeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 13Document5 pagesLec 13Ghazy alshyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsD'EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeD'EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeD'EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeD'EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (14)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionD'EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsD'EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableD'EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (22)