Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
DRESSER Regulators Flowgrid
Transféré par
zalzizaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DRESSER Regulators Flowgrid
Transféré par
zalzizaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
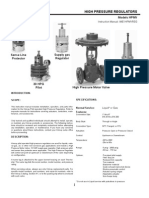
MOONEY
FLOWGRID
REGULATORS
The Flowgrid
Regulator is designed
for ease of maintenance
2 | Dresser
Mooney
Flowgrid
Regulator
The Mooney
Flowgrid
regulator was designed to fill the need for an easy-to-maintain valve that would be
used primarily with self-contained pilot systems for pressure or flow control of almost any gas or liquid.These
key design elements equate to increased productivity.
Extremely high accuracy of control, incredible responsiveness, wide rangeability, minimal parts and top entry
access to all components makes the Mooney Flowgrid regulator the regulator of choice. Our customers tell us
what they like most about the Mooney
Flowgrid regulator is....
Features
In-line maintenance with minimal parts
Rugged fabric-reinforced throttling element/diaphragm
provides wide-rangeability, stability and fast response in
severe service conditions
Elliptical main spring provides a high frequency
response, proportional action for stability, a consistent
low minimum differential and shut off force
Spring case has small volume to enhance speed of
response and stability
Over eighty-eight valve body options to fit any
application
you just set it and forget it.
Throttle plates offered in four standard capacities 100%,
50%, 75% and 35% or any custom capacity desired
Symmetrical throttle plate design inhibits debris from
accumulating under the seat and effecting shut-off
Drilled-hole throttle plates for reduced noise and extended
diaphragm life
Equal inlet/outlet pressure rating for all sizes assures easy
operation with no special start-up procedures
Dual-port valve design provides redundancy with dual pilots
and extra capacity with one pilot
Compact size for easy installation in any position
Mooney Flowgrid Regulator | 3
4 | Dresser
Pressure Relieving Valve
At no flow, when the outlet pressure is greater than the set
point of the Series 20
pilot regulator, the pilot is closed and
full inlet pressure loads the main valve spring case through the
pilot loading connection. In this condition, the main throttling
element is closed tightly against the throttling plate. The
pressure differential across the outlet half of the diaphragm
adds to the spring force to close the valve (Fig 1).
As demand for flow occurs in the downstream system,
the outlet pressure drops, causing the pilot to open and
start bleeding pressure out of the spring case faster than
it can enter through the restricting valve. Reducing the
loading pressure above the diaphragm allows inlet pressure
to progressively lift the diaphragm off the throttling plate,
opening the valve and satisfying the demand for the flow in
the downstream system (Fig 2).
When demand for flow ceases or is reduced, the downstream
pressure increases, causing the pilot regulator to close. Inlet
pressure continues to pass through the restriction until the
loading pressure equals the inlet pressure.
The spring force, plus the pressure differential across the
outlet half of the throttling plate closes the throttling element
against the throttling plate closing the main valve (Fig 1).
Adjustment of the variable restricting valve affects the
response rate, stability and sensitivity of the regulator. Smaller
restrictor openings result in higher gain (sensitivity) and slower
closing speeds. Larger openings result in lower gain (greater
proportional band), greater stability, and faster closing speed.
Back Pressure Valve
In a back pressure relief application (BPV) the valve functions
in the exact same way as previously described except that
the sense line for the control pilot is located upstream of the
regulator. The action of the pilot is the reverse of a pressure
reducing pilot such that the pilot opens when system pressure
increases above its set-point. The pilot will close when the
system pressure is less than its set-point (Fig 3).
Principle of Operation
PILOT LOADING
CONNECTION
PILOT SUPPLY
INLET OUTLET
PILOT OUTLET
CONNECTION
RESTRICTOR
PILOT SENSE
CONNECTION
PILOT SUPPLY
PILOT LOADING
CONNECTION
PILOT SENSE
CONNECTION
INLET OUTLET
PILOT OUTLET
CONNECTION
RESTRICTOR
PILOT SENSE
CONNECTION
PILOT LOADING
CONNECTION
PILOT SUPPLY
INLET OUTLET
PILOT OUTLET
CONNECTION
RESTRICTOR
Fig 1. Pressure Reducing Conguration Fully Closed.
Fig 2. Pressure Reducing Conguration Partially Open.
Fig 3. Back Pressure Valve
Applications
The Flowgrid
is ideal for pressure reducing (PRV), back pressure
or relief (BPV), flow-control, and multi-function control applications
where good regulation, simplicity, and ease of maintenance are of
prime importance.
The Flowgrid can handle gas and liquids that are relatively clean,
noncorrosive, and compatible with standard carbon steel/17-4ph
stainless steel/nitrile rubber construction. The normal temperature
range is -20F to 150F. Alternative materials for conditions outside
the normal temperature range are available.
The Flowgrid can easily be interfaced with conventional pneumatic,
electronic or microprocessor-based controllers for a variety of
pressure and flow control applications. These applications can
often result in lower overall costs and substantial energy savings.
Natural Gas Industry Applications
District Regulator
Monitor Regulator
Relief Valve (BPV)
Flow Control
Compressor Fuel Gas
Co-generation Fuel Supply
Industrial Applications
Boiler Fuel Gas
Oil
Water
Industrial Gasses (e.g., air, nitrogen, argon)
Bi-directional Pressure Control
Check Valve
Differential Control Pressure or Flow
Set-Point Control
The Jordan
1020 Actuator connected directly to any Series 20
pilot allows
remote control of any set point between 5 i.w.c. and 900 psig. The actuator
is available in a variety of electrical classications, voltages and input signals.
input signals.
Pneumatic Control Application
A pneumatic input signal to a Badger
Control Pilot mounted on
a Flowgrid
valve offers a variety of pressure, ow and remote
set point options.
Remote control of the Series 20
pilot set point is also possible
by pressure loading the spring case through the tapped vent
connection.
Mooney Flowgrid Regulator | 5
Standby Monitor System (Fig 4)
Under normal operating conditions, one of the Flowgrid
regulators operates as a worker while the other acts as a
monitor of the system. The upstream or downstream regulator can serve either function.
The monitor pilot is set at a slightly higher pressure than the worker (e.g., +5%). If the operating regulator should
fail, P2 will increase until it reaches the set point of the monitor pilot, allowing the monitor regulator to take over
protecting the downstream system P2 from being over pressured.
NOTE: On dead-end systems, a token relief downstream of the second stage regulator is recommended to
compensate for slight leaks due to wear or debris in the monitor regulator and/or operating regulator.
NOTE: Ref. Fig 4. Use alternative outlet to insure full capacity when the pressure drops across the regulator are
less than 60 psid. NOTE: System will shut off at upstream pilot setting.
Working Monitor System (Fig 5)
Under normal conditions, both Flowgrid
regulators are working to reduce pressure in a two-stage
sequence. If a problem occurs in the upstream regulator, the downstream regulator takes over the entire
pressure cut, maintaining P
3
at the same pressure. If the downstream regulator fails, P
3
will rise, causing
the monitor pilot on the upstream regulator to take over maintaining the pressure in the downstream
system P
3
at the set point of the monitor pilot.
NOTE: On dead-end systems, a token relief downstream of the second stage regulator is recommended
to compensate for slight leaks due to wear or debris in the monitor regulator.
NOTE: An additional benefit of this system is the lower noise level that results when the pressure is
reduced in two stages.
I
O
O L
RESTRICTOR
MONITOR REGULATOR
SERIES 20 PILOT
ALTERNATE OUTLET
If P1 - P2 < 60 psi
I
S
L
OPERATING REGULATOR
RESTRICTOR
S
FLOW
LEGEND
I = INLET
O= OUTLET
S= SENSE
L= LOADING
P2 P1
SERIES 20 PILOT
1ST STAGE PILOT
I
O
O
S
L
RESTRICTOR
1ST STAGE & MONITOR REGULATOR
2ND STAGE PILOT
I
S
L
MONITOR PILOT
2ND STAGE REGULATOR
RESTRICTOR
L
P3 P2 P1
S
O I
FLOW
LEGEND
I = INLET
O= OUTLET
S= SENSE
L= LOADING
6 | Dresser
Mooney Flowgrid Regulator | 7
Sizes 1- 12
Body Styles Single & Dual Port
Body Materials Steel, Ductile Iron*
End Connections Screwed, Socket Weld,
Flanged, Flangeless &
Buttweld
Outlet Pressures 5 i.w.c. - 900 psig
Maximum Operating Differential 800 psid,
1 1000 psid
Maximum Emergency
Differential
1,000 psid (unless limited
by body rating)
1 1500 psid
Cracking Differential 4 1 psid
Temperature Range -20F to 150F
Minimum/Maximum -40F to 175F
Flow Direction Bi-Directional
Specications
* Stainless steel available in some sizes. Factory quote required.
Spring Color Type 20
Pilot
Outlet Presure
Range
White 20L 5-15 i. w. c.
Brown 20L 10-40 i. w. c.
Yellow 20L 1-3 psig
Orange 20L 2-5 psig
Gray 20L 4-8 psig
Spring Color Type 20
Pilot
Outlet Presure
Range
Red 20 3-12 psig
Cadmium 20 10-40 psig
Blue 20 25-90 psig
Purple 20 60-200 psig
Black 20 100-260 psig
White/Green 20 200-450 psig
Black 20HP 200-520 psig
White/Green 20HP 400-900 psig
Pilot available in:
20L Aluminum & Bronze, 20 Brass and SST, 20H Brass and SST
Guidelines for Diaphragm Selection
Compound Temperature
Range
(Degrees F)
Maximum
Differential
1 Value
Maximum
Differential
All Others
Characteristics Recommended Applications
75 Duro
(standard)
-20 to 150 1000 psid 800 psid Best all around material 60 psid to Maximum Differential
60 Duro* -25 to 150 300 psid* 300 psid* Best shutoff at low differential
pressure
Low Differential (100 psid or less) or
low temperature
80 Duro
High ACN
-5 to 175 1000 psid 800 psid Higher abrasion and swelling
resistance
High Differential (400 psid or higher) or
abrasive conditions with distillates
80 Duro
Low ACN
-20 to 150 1000 psid 800 psid Higher abrasion resistance
and low temperature flexibility
High Differential (400 psid or higher) or
abrasive conditions at low temperatures
NOTE: Minimum temperature is dened as lowest temperature for normal valve operation. Valve will operate below this
temperature, but response times may increase and bubble-tight shutoff may be impaired. At extreme low temperatures
below -40 F), exure of the diaphragm may result in cracking of the material. This will require replacement of the diaphragm.
Maximum differentials listed are recommended for best diaphragm life. Exceeding these differentials will not result in
diaphragm damage, but may accelerate wear of the part.
* The 60 durometer diaphragm is standard on the Flowgrid
250 Valve which is a ductile iron and aluminum construction
with a maximum inlet and differential rating of 250 psi.
Valve Performance
Performance with Series 20L
and Series 20
Pilot
Mooney
Series 20L Pilot Pressure Reducing Mode Restrictor Set at 4
Pilot Spring Range Lockup Droop Maximum Capacity
1
Boost @ Constant Flow
White 5 i.w.c. - 15 i.w.c. 1.0. i.w.c. 0.5 i.w.c. 0.7 i.w.c.
Brown 10 i.w.c. - 40 i.w.c. 1.0 i.w.c. 2 i.w.c. 0.7 i.w.c.
Yellow 1-3 psig 0.2 psig 0.15 psig 0.25 psig
Orange 2-5 psig 0.35 psig 0.25 psig 0.25 psig
Gray 4-8 psig .5 psig 0.30 psig 0.25 psig
Mooney
Series 20 Pilot Pressure Reducing Mode Restrictor Set at 4 Back Pressure Mode Restrictor Set
at 4
Pilot Spring Range Lockup Droop
1
Maximum
Capacity
Boost at
2
Constant Flow
Buildup
Maximum
Capacity
Lockup
Red 3-12 psig 1.0 psig .30 .70 psig
4 4
Cadmium 10-40 psig 1.0 psig .30 .70 psig + .50 psig -1.0 psig
Blue 25-90 psig 2.0 psig .60 .70 psig + .50 psig -1.0 psig
Purple 60-200 psig 2.0 psig 1.30 .70 psig + 1.0 psig -1.0 psig
Black 100-260 psig 5.0 psig 2.00 .70 psig + 3.0 psig -1.5 psig
Green 200-450 psig 10.0 psig 4.00 .70 psig + 5.0 psig -2.0 psig
HP Black 200-520 psig 10.0 psig 4.00 1.50 psig + 5.0 psig
3
-3.0 psig
HP Green 400-900 psig 20.0 psig 8.00 1.50 psig +12.0 psig
3
-5.0 psig
1 Inlet pressure (P
1
) constant
2 Per 100 psi decrease in inlet pressure (P
1
)
3 SST/Delrin trim required
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
25% 50% 75% 100%
CAPACITY
D
I
F
F
E
R
E
N
T
I
A
L
P
S
I
D
A
I
B
H
F
E
G
J
D
C
Minimum Pressure Differential Versus Capacity
4 Minimum set point for the Flowgrid Valve and Pilot when used as a relief valve is 15 psig
or the minimum differential, whichever is greater.
A 1 75 Duro, STD Spring
B 1 60 Duro, Low Spring
C 2 LP 75 Duro, STD Spring
D 3 75 Duro. STD Spring
E 2 STD 75 Duro, STD Spring
F 4, 6 75 Duro, STD Spring
G 2 STD 60 Duro, Low Spring
H 4, 6 60 Duro, Low Spring
I 2 LP 60 Duro, Low Spring
J 3 60 Duro, Low Spring
Use the chart at left to determine the
amount of available capacity through
a Flowgrid
valve when the differen-
tial pressure across the regulator falls
below 30 psid.
For example: At 15 psid a 1 single
port valve with a standard main
spring and 75 durometer diaphragm
(A) can flow 50% of total calculated
capacity in this condition. With a
low differential main spring and 60
durometer diaphragm is installed
(B) the valve can flow 100% of its
calculated capacity.
8 | Dresser
Simplied Gas Sizing Equation
In the following term (P
1
-P
2
) /P
1
equals .64 or greater, then
sonic velocity is present in the valve and the simplified version
of the gas-sizing equation may be used.
Air: Q = P
1
Cg Natural Gas: Q = P
1
Cg 1.29
NOTE: Valve sizing and selection software is available for
download at: dresser.com/mooney
Liquid Sizing
Gas Velocity
To avoid generating additional noise in the outlet piping, it is
recommended that the body outlet velocity be limited to
approximately 0.5 of Mach. This equates to approximately
500 ft/sec for air and 700 ft/sec for natural gas. Swages
(reducers) should be used to further reduce the outlet piping
velocity to approximately 200 ft/sec or less to minimize
pressure loss. The formulas for velocity and pipe size are
as follows:
NOTE: To avoid the possibility of excessive noise, vibration,
and damage to the regulator and piping, the outlet velocity
should not exceed 70% of sonic velocity.
Air: 770 ft/sec Natural Gas: 1000 ft/sec
Universal Gas Sizing Equation
520
G T
SIN P
1
[ [
Cg = deg.
Q
3417
C
1
P
1
- P
2
P
1
Simplifies
1.29
Natural Gas at 60 F & 0.6 Sg
Simplifies
1.00
Critical Flow
Q Flow Rate (SCFH)
Cg Gas Sizing Coefcient
P
1
Inlet Pressure (psia)
P Pressure Drop Across Valve ( P = P
1
- P
2
) (psid)
P
2
Outlet Pressure (psia)
C1 Valve Recovery Coefcient (C
1
= Cg/C
v
)
Cv Liquid Sizing Coefcient
G Specic Gravity (0.6 for Natural Gas) (1.0 for Air)
T Gas Temperature (Rankine) (T - 460 + F)
P
A
G
Q = C
v
F
p
P
A
or
P
Allowable
P
A
P
1
- P
2
or
.8 (P
1
- P
v
) } whichever is less
Q Flow gpm (gallons per minute)
Cv Liquid Specic Gravity
Use the minimum inlet and maximum flow conditions for a
given application and solve the equation for Cg. For optimum
performance, select a regulator to operate in the 10-80%
range. A Dresser representative can help you select and
size a Flowgrid
regulator.
748 Q
d
2
P
2
V =
V Velocity in ft/sec
d Internal pipe diameter in inches
Q Flow in MSCFH
P
2
Outlet Pressure (psia)
Mooney Flowgrid Regulator | 9
520
G T
Cg P
1
SIN 3417
C
1
[ [
Q =
P
P
1
deg.
G Liquid Specic Gravity
P
1
Inlet Pressure (psia)
P
2
Outlet Pressure (psia)
Pv Vapor Pressure (psia)
F
P
Piping Swage Factor
Nominal
Size
inches
Stock No. End
Connections
Max
Pressure
(psig)
Nominal
Port Size
Cg C
v
C
1
Face to Face
inches
(metric)
Weight
(valve only)
1 FG11 & 12 NPT/SWE 1480 1 450 13.4 34 7.00 (178) 11 lbs.
1 FG 54** 150 CL FLG 285 1 450 13.4 34 7.25 (184) 14 lbs.
1 FG 55 ** 300 CL FLG 740 1 450 13.4 34 7.75 (197) 16 lbs.
1 FG 56** 600 CL FLG 1480 1 450 13.4 34 8.25 (210) 18 lbs.
1-1/4 FG 13 & 14 NPT/SWE 1480 1 450 13.4 34 7.00 (178) 11 lbs.
1-1/2 FG 47 &48 NPT/SWE 1480 1 480 13.4 36 7.00 (178) 11 lbs.
1 FG 24 NPT 250* 1 428 13.1 32 7.00 (178) 8 lbs.
1-1/4 FG 25 NPT 250* 1 432 13.6 31 7.00 (178) 8 lbs.
1-1/2 FG 26 NPT 250* 1 457 14 32 7.00 (178) 8 lbs
2 x 1 FG 29 & 50 NPT/SWE 1480 1 500 13.4 37 7.00 (178) 14 lbs.
2 x 1 FG 51 150 CL FLG 285 1 500 13.4 37 10.00 (254) 23 lbs.
2 x 1 FG 52 300 CL FLG 740 1 500 13.4 37 10.50 (267) 26 lbs.
2 x 1 FG 53 600 CL FLG 1480 1 500 13.4 37 11.25 (286) 30 lbs.
2 FG 1 & 2 NPT/SWE 1480 2 Std 1130 32 35 8.00 (203) 25 lbs.
2 FG 3 150 CL FLG 285 2 Std 1130 32 32 10.00 (254) 37 lbs.
2 FG 4 300 Cl FLG 740 2 Std 1130 32 35 10.50 (267) 39 lbs.
2 FG 5 600 CL FLG 1480 2 Std 1130 32 35 11.25 (286) 43 lbs.
2 FG 27 & 28 NPT/SWE 1480 2 LP 1420 40 35 8.00 (203) 25 lbs.
2 FG 29 150 CL FLG 285 2 LP 1420 40 35 10.00 (254) 34 lbs.
2 FG 30 300 CL FLG 740 2 LP 1420 40 35 10.50 (267) 37 lbs.
2 FG 31 600 CL FLG 1480 2 LP 1420 40 35 11.25 (286) 40 lbs.
2 FG 82 NPT 250* 2 LP 1600 46 35 8.00 (203) 17 lbs.
2 FG 83 150 CL FLG RF 250* 2 LP 1600 46 35 10.00 (254) 22 lbs.
2 FG 84 150 CL FLG FF 250* 2 LP 1600 46 35 10.00 (254) 22 lbs.
2 x 3 FG 119 150 CL FLG 285 3 1970 56 35 10.00 (254) 78 lbs.
2 x 3 FG 120 300 CL FLG 740 3 1970 56 35 10.50 (267) 82 lbs.
2 x 3 FG 121 600 CL FLG 1480 3 1970 56 35 11.25 (286) 88 lbs.
2 x 3 FG 117 NPT CL 600 1480 3 1970 56 35 8.00 (203) 68 lbs.
2 x 3 FG 118 SWE CL 600 1480 3 1970 56 35 8.00 (203) 68 lbs.
3 FG 16 150 CL FLG 285 3 3450 96 36 11.75 (298) 73 lbs.
3 FG 17 300 CL FLG 740 3 3450 96 36 12.50 (317) 85 lbs.
3 FG 18 600 CL FLG 1480 3 3450 96 36 13.25 (337) 94 lbs.
4 FG 39 150 CL FLG 285 4 6500 172 38 13.88 (352) 103 lbs.
4 FG 40 300 CL FLG 740 4 6500 172 38 14.50 (368) 117 lbs.
4 FG 41 600 CL FLG 1480 4 6500 172 38 15.50 (394) 143 lbs.
6 FG 44 150 CL FLG 285 6 12500 313 40 17.75 (451) 200 lbs.
6 FG 45 300 CL FLG 740 6 12500 313 40 18.62 (473) 240 lbs.
6 FG 46 600 CL FLG 1480 6 12500 313 40 20.00 (508) 330 lbs.
8 FG 72 150 CL FLG 285 8 20200 530 38 21.38 (543) 450 lbs.
8 FG 72 300 CL FLG 740 8 20200 530 38 22.38 (568) 500 lbs.
8 FG 80 600 CL FLG 1480 8 20200 530 38 24.00 (610) 650 lbs.
* Ductile Iron & Aluminum ** Special welded assembly
Single Port Designs
10 | Dresser
Nominal
Size
inches
Stock No. End
Connections
Max
Pressure
(psig)
Nominal
Port Size
Cg C
v
C
1
Face to Face
inches
(metric)
Weight
(valve only)
2 FG 8 150 CL FLG 285 2 Std 1960 56 35 10.00 (254) 52 lbs.
2 FG 9 300 CL FLG 740 2 Std 1960 56 35 10.50 (267) 55 lbs.
2 FG 10 600 CL FLG 1480 2 Std 1960 56 35 11.25 (286) 59 lbs.
2 FG 32 150 CL FLG 285 2 LP 2050 59 35 10.00 (254) 50 lbs.
2 FG 33 300 CL FLG 740 2 LP 2050 59 35 10.50 (267) 52 lbs.
2 FG 34 600 CL FLG 1480 2 LP 2050 59 35 11.25 (286) 54 lbs.
4 FG 21 150 CL FLG 285 3 6700 185 36 13.88 (352) 145 lbs.
4 FG 22 300 CL FLG 740 3 6700 185 36 14.50 (368) 160 lbs.
4 FG 23 600 CL FLG 1480 3 6700 185 36 15.50 (394) 194 lbs.
10 FG 57 150 CL FLG 285 6 22000 550 40 26.50 (673) 590 lbs.
10 FG 58 300 CL FLG 740 6 22000 550 40 27.88 (708) 670 lbs.
10 FG 59 600 CL FLG 1480 6 22000 550 40 29.60 (752) 900 lbs.
12 FG 74 150 CL FLG 285 8 40400 1060 38 29.00 (737) 1097 lbs.
12 FG 75 300 CL FLG 740 8 40400 1060 38 30.50 (775) 1195 lbs.
12 FG 81 600 CL FLG 1480 8 40400 1060 38 32.25 (819) 1383 lbs.
Dual Port Designs
Nominal
Size
inches
Stock No. End
Connections
Max
Pressure
(psig)
Nominal
Port Size
Cg C
v
C
1
Face to Face
inches
(metric)
Weight
(valve only)
2 FG 15 150 CL FLG 285 2 Std 1120 32 35 4.187 (106) 27 lbs.
2 FG 15 300 CL FLG 740 2 Std 1120 32 35 4.187 (106) 27 lbs.
2 FG 15 600 CL FLG 1480 2 Std 1120 32 35 4.187 (106) 27 lbs.
2 FG 35 150 CL FLG 285 2 LP 1300 37 35 4.187 (106) 27 lbs.
2 FG 35 300 CL FLG 740 2 LP 1300 37 35 4.187 (106) 27 lbs.
2 FG 35 600 CL FLG 1480 2 LP 1300 37 35 4.187 (106) 27 lbs.
4 x 3 FG 19 150 CL FLG 285 3 3400 95 36 5.81 (148) 92 lbs.
4 x 3 FG 20 300 CL FLG 740 3 3400 95 36 5.81 (148) 92 lbs.
6 x 4 FG 42 150 CL FLG 285 4 6400 172 37 8.00 (203) 115 lbs.
6 x 4 FG 43 300 CL FLG 740 4 6400 172 37 8.00 (203) 115 lbs.
Flangeless Port Designs
Nominal
Size
inches
Stock No. End
Connections
Max
Pressure
(psig)
Nominal
Port Size
Cg C
v
C
1
Face to Face
inches
(metric)
Weight
(valve only)
2 FG 100 150 CL FLG 285 2 LP 1420 40 35 3.03 (77) 29 lbs.
2 FG 101 300 CL FLG 740 2 LP 1420 40 35 3.03 (77) 29 lbs.
2 FG 102 600 CL FLG 1480 2 LP 1420 40 35 3.41 (87) 29 lbs.
3 FG 103 150 CL FLG 285 3 3240 95 36 3.72 (94) 60 lbs.
3 FG 104 300 CL FLG 740 3 3240 95 36 3.72 (94) 60 lbs.
4 FG 106 150 CL FLG 285 4 5800 168 35 4.50 (114) 85 lbs.
4 FG 107 300 CL FLG 740 4 5800 168 35 4.50 (114) 85 lbs.
Type-A Flangeless Port Designs*
* Same face-to-face dimensions as American Meter Axial
Flow Valves.
Mooney Flowgrid Regulator | 11
About Dresser, Inc.
Dresser, Inc. is a leader in providing highly engineered
infrastructure products for the global energy industry.
The company has leading positions in a broad portfolio
of products, including valves, actuators, meters,
switches, regulators, piping products, natural gas-
fueled engines, retail fuel dispensers and associated
retail point-of-sale systems, and air and gas handling
equipment. Leading brand names within the Dresser
portfolio include Dresser Wayne
retail fueling systems,
Waukesha
natural gas-fired engines, Masoneilan
control valves, Consolidated
pressure relief valves,
and Roots
blowers. It has manufacturing and cus-
tomer service facilities located strategically worldwide
and a sales presence in more than 100 countries.
About Dresser
Products
Dresser brand products are highly engineered, technically
superior and are designed to help global customers meet and
exceed requirements for mission critical energy applications.
The information presented in this brochure is for informational purposes only.
For actual design assistance please visit our website at www.dresser.com/mooneyregulators
or see your local representative.
www.dresser.com
Dresser, Inc.
2822 S. 1030 W.
Salt Lake City, Utah 84119
Phone: 801.487.2225 Fax: 801.487.2587
www.dresser.com/mooney
2010 Dresser, Inc.
FlowMax and Mooney are registered trademarks of Dresser, Inc.
Flowgrid Regulator
7.10
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Manual Regulators Man Slamshut 2-4inchDocument20 pagesManual Regulators Man Slamshut 2-4inchDelfin Rosanieto TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- HP Regulators v2Document9 pagesHP Regulators v2Danny SánchezPas encore d'évaluation
- High-pressure regulators for gas distributionDocument6 pagesHigh-pressure regulators for gas distributionManish SaraswatPas encore d'évaluation
- Gorter r100 enDocument6 pagesGorter r100 enManish SaraswatPas encore d'évaluation
- 399ADocument24 pages399ADana Mera100% (2)
- 4150K-4160K Controladores Fisher PDFDocument40 pages4150K-4160K Controladores Fisher PDFrichardPas encore d'évaluation
- Dresser-Rand GFC Databook - Gas Field Policies-4Document4 pagesDresser-Rand GFC Databook - Gas Field Policies-4kistaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Blowdown Valves and Safety Valves ExplainedDocument4 pagesBlowdown Valves and Safety Valves ExplainedAmanda MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Type 4100Z Wizard I Gauge Pressure ControllerDocument4 pagesType 4100Z Wizard I Gauge Pressure ControllerDatt NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- FloBoss™ S600+ Flow Computer Instruction Manual PDFDocument152 pagesFloBoss™ S600+ Flow Computer Instruction Manual PDFSibabrata ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ReportDocument36 pagesProject Reportvishi89Pas encore d'évaluation
- CVS pressure controllers instruction manualDocument12 pagesCVS pressure controllers instruction manualsalmo83:18Pas encore d'évaluation
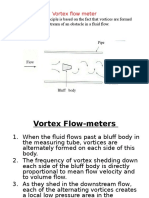
- VortexDocument8 pagesVortexNithya SubashPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisher l2 Liquid Level Controllers en 135074Document16 pagesFisher l2 Liquid Level Controllers en 135074GOKUL PRASADPas encore d'évaluation
- Deluge Valve Technical DataDocument16 pagesDeluge Valve Technical DataNata 1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1290 RegulatorsDocument3 pages1290 RegulatorsPitichai PakornrersiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Orbit ValveDocument12 pagesOrbit ValveanildhakePas encore d'évaluation
- Design Input - Pressure Reducing ValveDocument8 pagesDesign Input - Pressure Reducing ValvekausikrPas encore d'évaluation
- CARTRIDGE FILTER TECHNICAL MANUALDocument30 pagesCARTRIDGE FILTER TECHNICAL MANUALabessiPas encore d'évaluation
- PRV - CatalogueDocument6 pagesPRV - CatalogueSarbendu PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Sheet S7 - 2020 - ENG - Light - CavagnaDocument12 pagesData Sheet S7 - 2020 - ENG - Light - CavagnaWND PRTMPas encore d'évaluation
- HSV86 PDFDocument48 pagesHSV86 PDFMohamed El MaadawyPas encore d'évaluation
- SEVERN GLOCON CONTROL VALVE SPECIFICATION SHEETDocument6 pagesSEVERN GLOCON CONTROL VALVE SPECIFICATION SHEETAmit Surti0% (1)
- Automatic Linebreak Low Pressure Shutoff Control en 83906Document2 pagesAutomatic Linebreak Low Pressure Shutoff Control en 83906Carlos Alberto BalderramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Air or Gas Driven Injectors: Description ApplicationsDocument8 pagesAir or Gas Driven Injectors: Description ApplicationsEyo Etim0% (1)
- Separator NadobyDocument15 pagesSeparator NadobyVidyasenPas encore d'évaluation
- Atmospheric Relief Valve ManualDocument12 pagesAtmospheric Relief Valve ManualTarun ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Sizing PDFDocument36 pagesGas Sizing PDFChetan ChuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Valve Testing StandardsDocument2 pagesValve Testing StandardsPrashant Puri0% (1)
- F 0077 e 55Document6 pagesF 0077 e 55Bùi Cảnh TrungPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumatic LogicDocument27 pagesPneumatic LogicEliasPas encore d'évaluation
- Vortex Pilot Gas Heater Over Temperature ProtectionDocument17 pagesVortex Pilot Gas Heater Over Temperature ProtectionDon BettonPas encore d'évaluation
- LPG Air Mixing 2 A3Document1 pageLPG Air Mixing 2 A3ambientinstal instalPas encore d'évaluation
- Automation of Reciprocating Gas Engine Compressor Packages UsingDocument7 pagesAutomation of Reciprocating Gas Engine Compressor Packages UsingGnanaSekar0% (1)
- Valves: Relief and Safety ValvesDocument22 pagesValves: Relief and Safety ValvesهانيزايدPas encore d'évaluation
- Durco Plug Valve Dimensions PDFDocument28 pagesDurco Plug Valve Dimensions PDFjtai1983Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bv421 Pressure Reducing ValveDocument4 pagesBv421 Pressure Reducing ValveFAIYAZ AHMEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Canalta DCOF Product Manual LR PDFDocument13 pagesCanalta DCOF Product Manual LR PDFBelkhir GuerrachePas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical RegulatorDocument12 pagesMechanical Regulatorshashi chaugulePas encore d'évaluation
- Experimental Study and Modeling of Single - and Two-Phase Flow in Singular Geometries and Safety Relief ValvesDocument314 pagesExperimental Study and Modeling of Single - and Two-Phase Flow in Singular Geometries and Safety Relief ValvesMoisés SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Float Board Level GaugeDocument6 pagesFloat Board Level GaugeanaismariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyl Tel CutsheetDocument2 pagesCyl Tel CutsheetaLeXiNPas encore d'évaluation
- FLOW MEASUREMENT FUNDAMENTALSDocument38 pagesFLOW MEASUREMENT FUNDAMENTALSm.shehreyar.khan100% (1)
- TRG Control ValveDocument13 pagesTRG Control Valvemilton1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Installation and operation instructions iMTM-CT G40-G4000Document2 pagesInstallation and operation instructions iMTM-CT G40-G4000Luis Angel Cuevas Ortega0% (1)
- Natural Gas SolutionsDocument74 pagesNatural Gas SolutionsViorel Ciocoiu100% (1)
- LP Gas Regulators Equipment Application Guide Technical Section en 126594 PDFDocument152 pagesLP Gas Regulators Equipment Application Guide Technical Section en 126594 PDFIsaac FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Va18 Va19Document59 pagesVa18 Va19joymotiPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Valve Sizing and Selection GuideDocument5 pagesControl Valve Sizing and Selection Guideprassna_kamat15730% (1)
- Recent Advances Turbine BypassDocument4 pagesRecent Advances Turbine BypassretrogradesPas encore d'évaluation
- Deluge Valve - SD-DVH2Document16 pagesDeluge Valve - SD-DVH2Vijay Gaikwad0% (1)
- HNS Quick Start Guide - Rev.0 PDFDocument9 pagesHNS Quick Start Guide - Rev.0 PDFCarlos MagPas encore d'évaluation
- BS&W Models 4528EZ & 4728 Monitors FMCDocument14 pagesBS&W Models 4528EZ & 4728 Monitors FMCFernando MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Pressure Reducing ValvesDocument4 pagesRatio Pressure Reducing Valveskanem1Pas encore d'évaluation
- IR HL Heatless DryerDocument1 pageIR HL Heatless DryerYing Kei ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- CFD predictions on Liquid Pressure Recovery Factor (FL) for control valvesDocument9 pagesCFD predictions on Liquid Pressure Recovery Factor (FL) for control valvesAshok SureshPas encore d'évaluation
- 650 01 GB 0111 01Document12 pages650 01 GB 0111 01Phan HaiPas encore d'évaluation
- +FlowgridSlamShut Bro - 111Document8 pages+FlowgridSlamShut Bro - 111Carlos TarquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowgrid BrochureDocument12 pagesFlowgrid BrochureDante Cabrera GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Full Bore Emergency Unloading Valve Manual PDFDocument9 pagesSPM Full Bore Emergency Unloading Valve Manual PDFPablo SotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chamber-Diving DecompressionDocument1 pageChamber-Diving DecompressionzalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Recurring Fees: - (I) Registration (Ii) Service (Iii) Health (Iv) Library (V) Welfare (Vi) Recreation (Vii) ICTDocument1 pageRecurring Fees: - (I) Registration (Ii) Service (Iii) Health (Iv) Library (V) Welfare (Vi) Recreation (Vii) ICTzalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- V 113 N 08 P 643Document4 pagesV 113 N 08 P 643zalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- c2Document23 pagesc2zalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- UC Instrumen CatalogueDocument47 pagesUC Instrumen CatalogueOreolPas encore d'évaluation
- BS8666 2005 WMDocument1 pageBS8666 2005 WMzalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6Document5 pagesUnit 6alpmal_infoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pile Foundation Design & ConstructionDocument213 pagesPile Foundation Design & ConstructionGeorge Tsiamtsouris83% (6)
- What Is Ballasting and deDocument5 pagesWhat Is Ballasting and dezalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- MTH - Spec Cross-Ref Chartr1Document1 pageMTH - Spec Cross-Ref Chartr1RamuAlagappanPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Hydro TestDocument14 pagesRole of Hydro TestHazwan AizatPas encore d'évaluation
- "Refractory - Is It Working For You?": Cliff KnightDocument1 page"Refractory - Is It Working For You?": Cliff KnightzalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Export Import Practices Class Learning ObjectivesDocument32 pagesExport Import Practices Class Learning ObjectivesSheetal Ruth NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- c2Document23 pagesc2zalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- CyQmw - General Code of Practice For Medical SurveillanceDocument4 pagesCyQmw - General Code of Practice For Medical SurveillancezalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Surveillance ProceduresDocument20 pagesMedical Surveillance ProcedureszalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- V 113 N 08 P 643Document4 pagesV 113 N 08 P 643zalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- CF Vs CIDocument3 pagesCF Vs CIzalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- CFM Abb SmartpositionersDocument16 pagesCFM Abb SmartpositionerszalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6Document5 pagesUnit 6alpmal_infoPas encore d'évaluation
- Kir ChacDocument9 pagesKir ChaczalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- VDR Website Supplier InstructionsDocument1 pageVDR Website Supplier InstructionszalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Criteria For RCCDocument7 pagesDesign Criteria For RCCAtifkhan132Pas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Crane RuleDocument57 pagesConstruction Crane RulezalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rigger Training Stages 1 and 2 PDFDocument56 pagesRigger Training Stages 1 and 2 PDFzalziza100% (1)
- Neral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Seals, Gaskets, ValvesDocument37 pagesNeral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Seals, Gaskets, ValvesbrotaccristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Rigging TechniquesDocument184 pagesRigging TechniquesAAlmeidas86% (7)
- DOL Reversing StarterDocument2 pagesDOL Reversing StarterzalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Take-Off PDFDocument4 pagesMaterial Take-Off PDFRanilo SumalinogPas encore d'évaluation
- MRTA Vs MLTA - Which One Is The Best Housing Loan InsuranceDocument18 pagesMRTA Vs MLTA - Which One Is The Best Housing Loan InsurancezalzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: CNT CNT - 600 600Document2 pagesProduct Specifications Product Specifications: CNT CNT - 600 600Antonio CorreiaPas encore d'évaluation
- He165 (A4)Document4 pagesHe165 (A4)KennethWilfredoVegaOviedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ramgarh Gas Power Plant OverviewDocument31 pagesRamgarh Gas Power Plant Overviewswai singh100% (1)
- High Voltage Engineering Ref ManualDocument147 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering Ref Manualzeus009100% (1)
- Project Report of POL Terminals2 PDFDocument31 pagesProject Report of POL Terminals2 PDFRashmi RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Craftsman 320.29004Document28 pagesCraftsman 320.29004Pablo DPas encore d'évaluation
- DXXXX-QSOP - Well Control Procedure For Non - Routine OperationsDocument6 pagesDXXXX-QSOP - Well Control Procedure For Non - Routine Operationsharry mulyafitPas encore d'évaluation
- Trafo Las, Mesin Las, Kompressor Dan SandblastingDocument10 pagesTrafo Las, Mesin Las, Kompressor Dan SandblastingCv RONATAMA GUSLHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Generating Floor PDFDocument3 pagesPower Generating Floor PDFMeghjit MazumderPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 716554253262412976 PDFDocument5 pages1 716554253262412976 PDFAli YarahmadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Moving Iron InstrumentDocument16 pagesMoving Iron Instrumentmrsirjan802Pas encore d'évaluation
- Particulate Photocatalysts CRDocument67 pagesParticulate Photocatalysts CRYiou WangPas encore d'évaluation
- TOBUL OandMsheet052909v2Document5 pagesTOBUL OandMsheet052909v2Walter JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Spe 131758 Ms - GL and EspDocument11 pagesSpe 131758 Ms - GL and EspSamuel VmPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimized Skid Design For Compress Sor PackagesDocument5 pagesOptimized Skid Design For Compress Sor Packagessantosh kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel Engine Technical SpecificationsDocument3 pagesDiesel Engine Technical SpecificationsFahad MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- High Speed AerodynamicsDocument62 pagesHigh Speed AerodynamicsDavid Bond100% (2)
- Ecro RV: Technical ManualDocument21 pagesEcro RV: Technical ManualHyeong-Ho KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Plumbing Systems For BuildingsDocument62 pagesPlumbing Systems For BuildingsDileep Kumar100% (1)
- Equity Research Report On Bajaj Finserv LTD Authored By: Mohammad Reza PoyaDocument6 pagesEquity Research Report On Bajaj Finserv LTD Authored By: Mohammad Reza Poyashraddha anandPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Control Panel ArrangementDocument82 pagesHVAC Control Panel ArrangementMohamed Ali JPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychrometric Chart ReadingDocument10 pagesPsychrometric Chart ReadingEzakiman OtanimPas encore d'évaluation
- Monbat 12V200AhDocument1 pageMonbat 12V200AhMaria MuresanPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2 Financial Brick Case StudyDocument9 pagesGroup 2 Financial Brick Case StudyMDPas encore d'évaluation
- AHU data collection formDocument4 pagesAHU data collection formcajaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating monthly electricity consumptionDocument2 pagesCalculating monthly electricity consumptionStella KazanciPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Kobelco MARK 8 Mechatron Control SistemDocument45 pages08 Kobelco MARK 8 Mechatron Control SistemNadiel Aceto 46100% (1)
- Electronics MCQsDocument17 pagesElectronics MCQslovelyosmile253Pas encore d'évaluation
- HYpact Compact HybridDocument24 pagesHYpact Compact HybridMateo Alvez100% (1)
- Red Highlighted Red Highlighted: Refer Calculation Given Below (Note-8)Document5 pagesRed Highlighted Red Highlighted: Refer Calculation Given Below (Note-8)Víctor RojasPas encore d'évaluation